## Motivation <!-- Why is this change needed? What problem does it solve? --> <!-- If it fixes an open issue, please link to the issue here --> ## Changes <!-- Describe what you changed in detail --> ## Why It Works <!-- Explain why your approach solves the problem --> ## Test Plan ### Manual Testing <!-- Hardware: (e.g., MacBook Pro M1 Max 32GB, Mac Mini M2 16GB, connected via Thunderbolt 4) --> <!-- What you did: --> <!-- - --> ### Automated Testing <!-- Describe changes to automated tests, or how existing tests cover this change --> <!-- - -->
9.8 KiB
exo connects all your devices into an AI cluster. Not only does exo enable running models larger than would fit on a single device, but with day-0 support for RDMA over Thunderbolt, makes models run faster as you add more devices.
Features
- Automatic Device Discovery: Devices running exo automatically discover each other - no manual configuration.
- RDMA over Thunderbolt: exo ships with day-0 support for RDMA over Thunderbolt 5, enabling 99% reduction in latency between devices.
- Topology-Aware Auto Parallel: exo figures out the best way to split your model across all available devices based on a realtime view of your device topology. It takes into account device resources and network latency/bandwidth between each link.
- Tensor Parallelism: exo supports sharding models, for up to 1.8x speedup on 2 devices and 3.2x speedup on 4 devices.
- MLX Support: exo uses MLX as an inference backend and MLX distributed for distributed communication.
Benchmarks
Qwen3-235B (8-bit) on 4 × M3 Ultra Mac Studio with Tensor Parallel RDMA
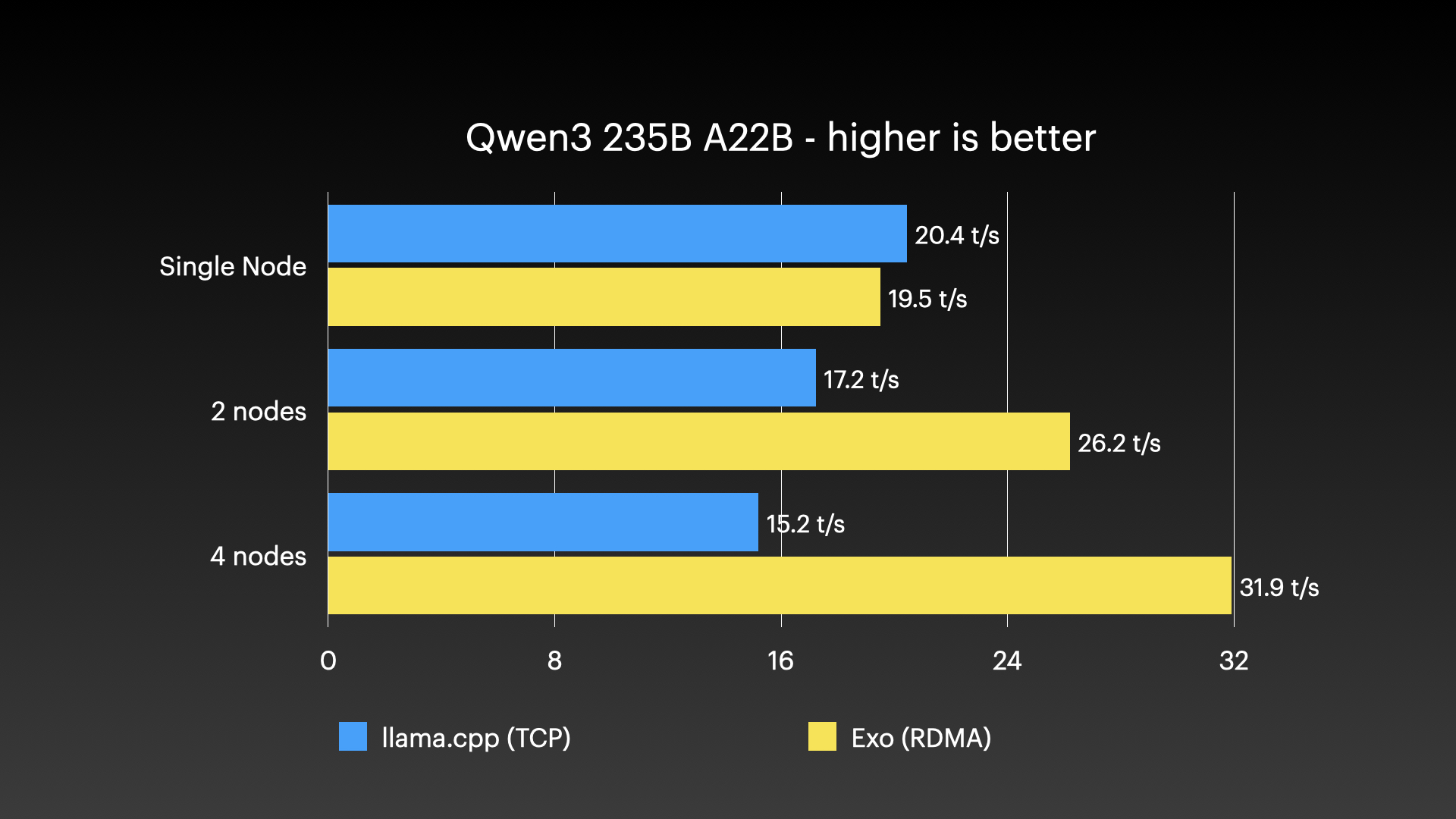
Source: Jeff Geerling: 15 TB VRAM on Mac Studio – RDMA over Thunderbolt 5
DeepSeek v3.1 671B (8-bit) on 4 × M3 Ultra Mac Studio with Tensor Parallel RDMA
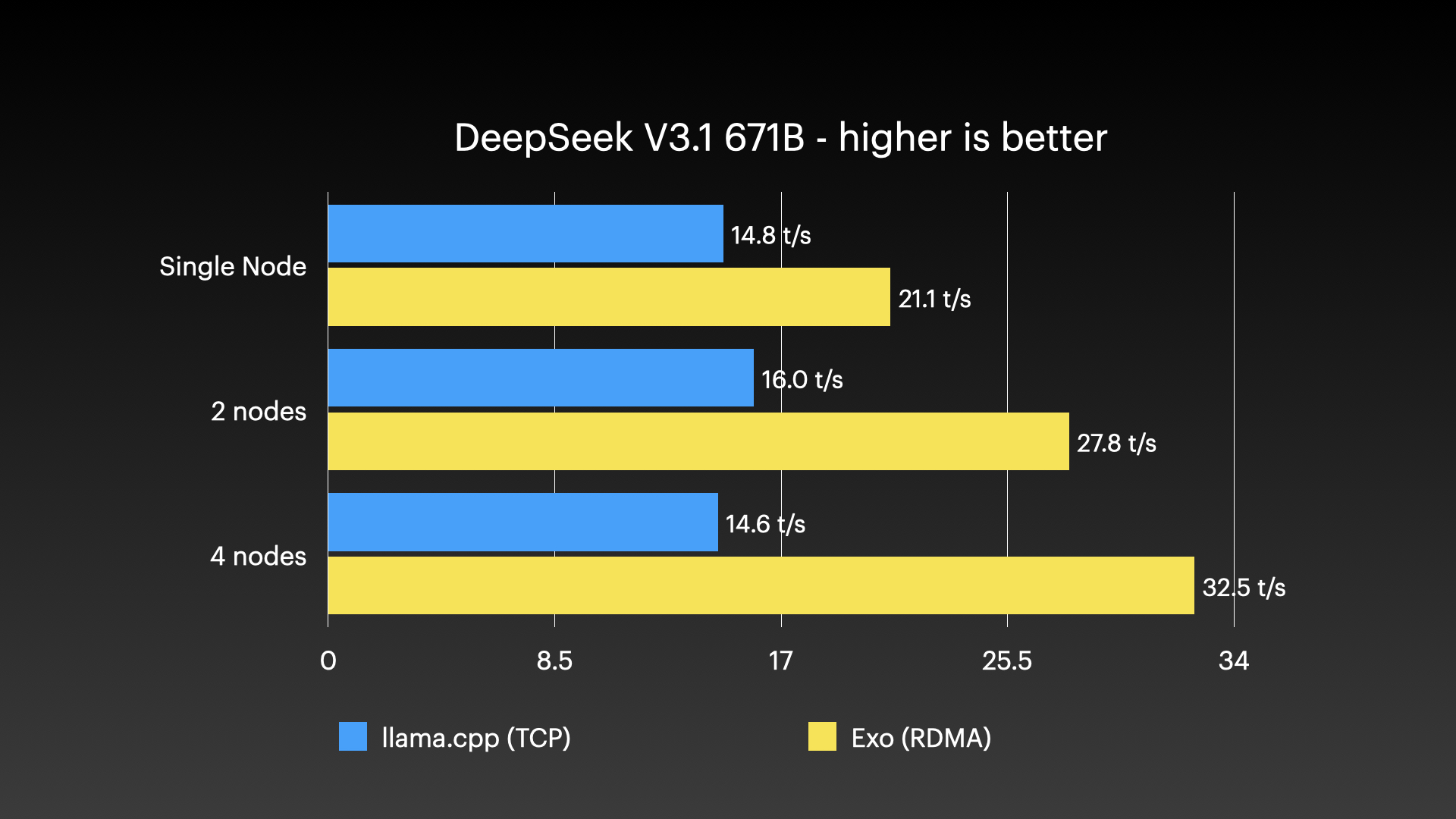
Source: Jeff Geerling: 15 TB VRAM on Mac Studio – RDMA over Thunderbolt 5
Kimi K2 Thinking (native 4-bit) on 4 × M3 Ultra Mac Studio with Tensor Parallel RDMA

Source: Jeff Geerling: 15 TB VRAM on Mac Studio – RDMA over Thunderbolt 5
Quick Start
Devices running exo automatically discover each other, without needing any manual configuration. Each device provides an API and a dashboard for interacting with your cluster (runs at http://localhost:52415).
There are two ways to run exo:
Run from Source (Mac & Linux)
Clone the repo, build the dashboard, and run exo:
# Clone exo
git clone https://github.com/exo-explore/exo
# Build dashboard
cd exo/dashboard && npm install && npm run build && cd ..
# Run exo
uv run exo
This starts the exo dashboard and API at http://localhost:52415/
macOS App
exo ships a macOS app that runs in the background on your Mac.

The macOS app requires macOS Tahoe 26.2 or later.
Download the latest build here: EXO-latest.dmg.
The app will ask for permission to modify system settings and install a new Network profile. Improvements to this are being worked on.
Using the API
If you prefer to interact with exo via the API, here is a complete example using curl and a real, small model (mlx-community/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit). All API endpoints and request shapes match src/exo/master/api.py and src/exo/shared/types/api.py.
1. Preview instance placements
Obtain valid deployment placements for your model. This helps you choose a valid configuration:
curl "http://localhost:52415/instance/previews?model_id=mlx-community/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit"
Sample response:
{
"previews": [
{
"model_id": "mlx-community/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit",
"sharding": "Pipeline",
"instance_meta": "MlxRing",
"instance": {...},
"memory_delta_by_node": {"local": 734003200},
"error": null
}
// ...possibly more placements...
]
}
This will return all valid placements for this model. Pick a placement that you like.
2. Create a model instance
Send a POST to /instance with your placement in the instance field (the full payload must match types as in CreateInstanceParams):
curl -X POST http://localhost:52415/instance \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"instance": {
"model_id": "mlx-community/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit",
"instance_meta": "MlxRing",
"sharding": "Pipeline",
"min_nodes": 1
}
}'
Sample response:
{
"message": "Command received.",
"command_id": "e9d1a8ab-...."
}
3. Issue a chat completion
Now, make a POST to /v1/chat/completions (the same format as OpenAI's API):
curl -N -X POST http://localhost:52415/v1/chat/completions \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"model": "mlx-community/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "What is Llama 3.2 1B?"}
]
}'
You will receive a streamed or non-streamed JSON reply.
4. Delete the instance
When you're done, delete the instance by its ID (find it via /state or /instance endpoints):
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:52415/instance/YOUR_INSTANCE_ID
Tip:
- List all models:
curl http://localhost:52415/models - Inspect instance IDs and deployment state:
curl http://localhost:52415/state
For further details, see API types and endpoints in src/exo/master/api.py.
Using the API
If you prefer to interact with exo via the API, here is an example creating an instance of a small model (mlx-community/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit), sending a chat completions request and deleting the instance.
1. Preview instance placements
The /instance/previews endpoint will preview all valid placements for your model.
curl "http://localhost:52415/instance/previews?model_id=llama-3.2-1b"
Sample response:
{
"previews": [
{
"model_id": "mlx-community/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit",
"sharding": "Pipeline",
"instance_meta": "MlxRing",
"instance": {...},
"memory_delta_by_node": {"local": 729808896},
"error": null
}
// ...possibly more placements...
]
}
This will return all valid placements for this model. Pick a placement that you like.
To pick the first one, pipe into jq:
curl "http://localhost:52415/instance/previews?model_id=llama-3.2-1b" | jq -c '.previews[] | select(.error == null) | .instance' | head -n1
2. Create a model instance
Send a POST to /instance with your desired placement in the instance field (the full payload must match types as in CreateInstanceParams), which you can copy from step 1:
curl -X POST http://localhost:52415/instance \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"instance": {...}
}'
Sample response:
{
"message": "Command received.",
"command_id": "e9d1a8ab-...."
}
3. Send a chat completion
Now, make a POST to /v1/chat/completions (the same format as OpenAI's API):
curl -N -X POST http://localhost:52415/v1/chat/completions \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"model": "mlx-community/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "What is Llama 3.2 1B?"}
],
"stream": true
}'
4. Delete the instance
When you're done, delete the instance by its ID (find it via /state or /instance endpoints):
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:52415/instance/YOUR_INSTANCE_ID
Other useful API endpoints:*
- List all models:
curl http://localhost:52415/models - Inspect instance IDs and deployment state:
curl http://localhost:52415/state
For further details, see API types and endpoints in src/exo/master/api.py.
Hardware Accelerator Support
On macOS, exo uses the GPU. On Linux, exo currently runs on CPU. We are working on extending hardware accelerator support. If you'd like support for a new hardware platform, please search for an existing feature request and add a thumbs up so we know what hardware is important to the community.
Contributing
See CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines on how to contribute to exo.



