## Motivation In the model picker, non-runnable models were not clearly separated between two different cases: - model exceeds currently available RAM but can fit in total cluster capacity - model exceeds total cluster capacity That made it harder to distinguish "not runnable right now" from "too large for this cluster." ## Changes - Added a tri-state fit status in dashboard model-picker flow: - `fits_now` - `fits_cluster_capacity` - `too_large` - Updated dashboard logic to compute both available cluster RAM and total cluster RAM. - Passed fit status through picker components. - Updated model size color mapping: - `fits_now` -> white/gray - `fits_cluster_capacity` -> orange - `too_large` -> red - Updated group ordering for non-runnable models: - orange groups (`fits_cluster_capacity`) are listed above red groups (`too_large`). ## Why It Works Launch safety is unchanged: selection is still gated by existing placement feasibility (`canModelFit`), so models that cannot run now remain disabled. The new fit status is used for visual distinction and ordering only: - runnable now - fits cluster capacity but not free RAM now - too large for cluster capacity ## Before Non-runnable models were not clearly distinguished by temporary capacity vs hard capacity limit. ## After Model picker clearly separates states by both color and order: - Runnable now (white/gray) - Fits cluster capacity but not free RAM now (orange, disabled) - Exceeds cluster capacity (red, disabled) ## Test Plan ### Manual testing - Open model picker with live cluster memory telemetry. - Verify white/gray models are selectable. - Verify orange models are disabled and appear above red models. - Verify red models are disabled and appear below orange models. ### Automated checks - `npm --prefix dashboard run build` passes. - `uv run basedpyright` passes. - `uv run ruff check` passes. - `npm --prefix dashboard run check` reports existing pre-change Svelte diagnostics (same known SVG title/a11y items). - `uv run pytest` in this local environment exits during collection due existing `tests/start_distributed_test.py` `SystemExit` usage. - No Python code was changed. --------- Co-authored-by: Alex Cheema <41707476+AlexCheema@users.noreply.github.com>
exo connects all your devices into an AI cluster. Not only does exo enable running models larger than would fit on a single device, but with day-0 support for RDMA over Thunderbolt, makes models run faster as you add more devices.
Features
- Automatic Device Discovery: Devices running exo automatically discover each other - no manual configuration.
- RDMA over Thunderbolt: exo ships with day-0 support for RDMA over Thunderbolt 5, enabling 99% reduction in latency between devices.
- Topology-Aware Auto Parallel: exo figures out the best way to split your model across all available devices based on a realtime view of your device topology. It takes into account device resources and network latency/bandwidth between each link.
- Tensor Parallelism: exo supports sharding models, for up to 1.8x speedup on 2 devices and 3.2x speedup on 4 devices.
- MLX Support: exo uses MLX as an inference backend and MLX distributed for distributed communication.
Dashboard
exo includes a built-in dashboard for managing your cluster and chatting with models.
4 × 512GB M3 Ultra Mac Studio running DeepSeek v3.1 (8-bit) and Kimi-K2-Thinking (4-bit)
Benchmarks
Qwen3-235B (8-bit) on 4 × M3 Ultra Mac Studio with Tensor Parallel RDMA
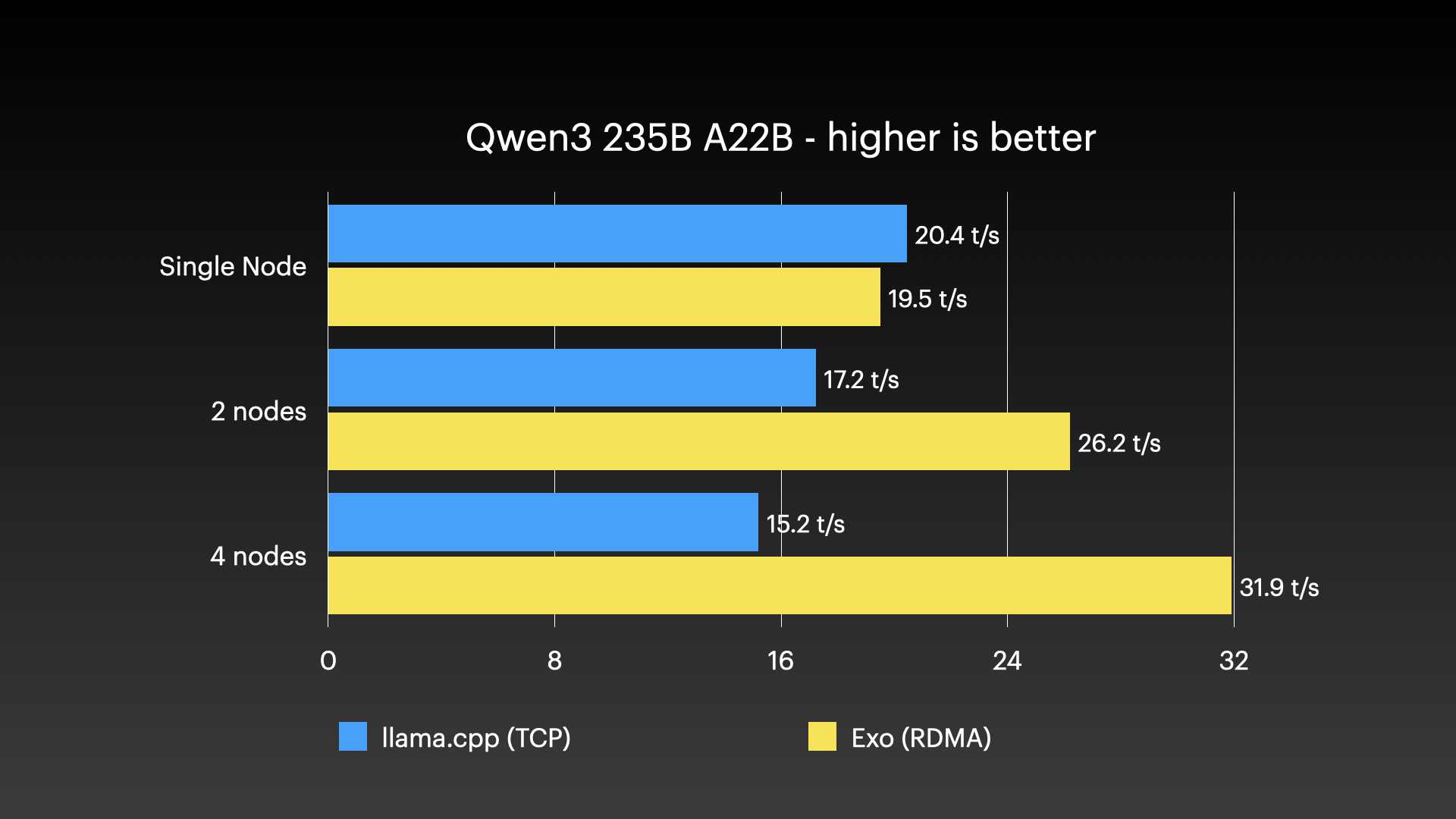
Source: Jeff Geerling: 15 TB VRAM on Mac Studio – RDMA over Thunderbolt 5
DeepSeek v3.1 671B (8-bit) on 4 × M3 Ultra Mac Studio with Tensor Parallel RDMA
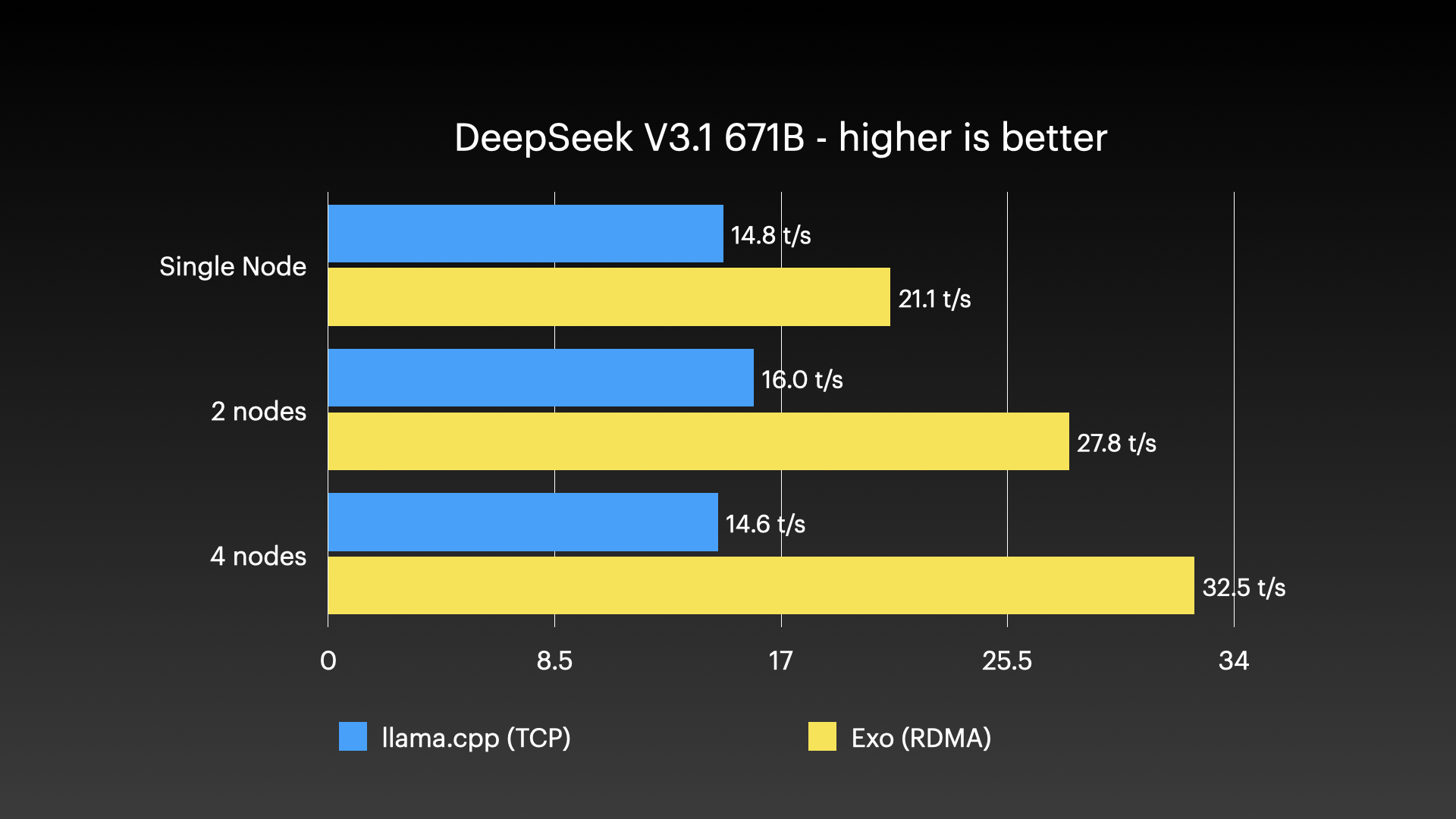
Source: Jeff Geerling: 15 TB VRAM on Mac Studio – RDMA over Thunderbolt 5
Kimi K2 Thinking (native 4-bit) on 4 × M3 Ultra Mac Studio with Tensor Parallel RDMA
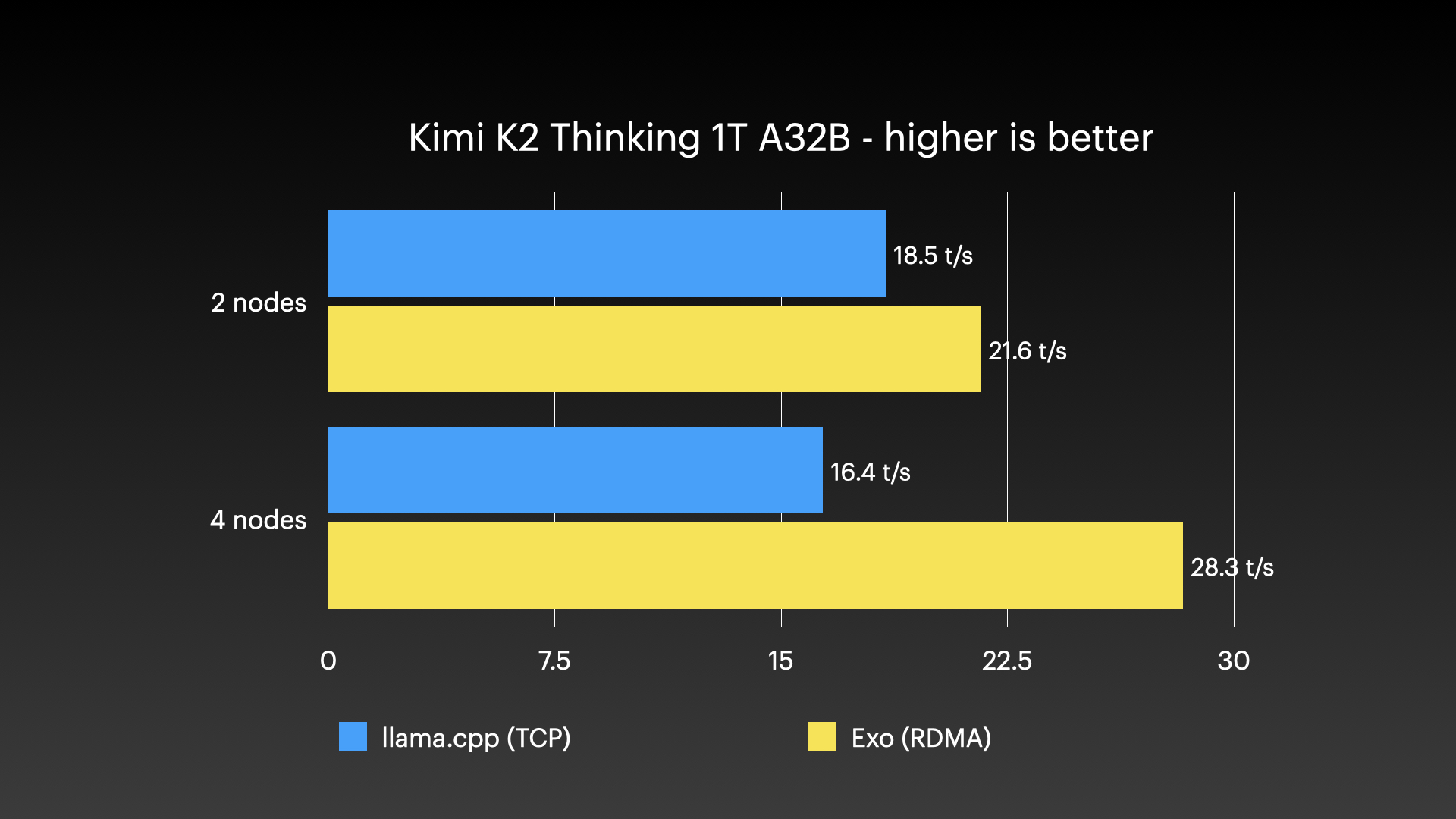
Source: Jeff Geerling: 15 TB VRAM on Mac Studio – RDMA over Thunderbolt 5
Quick Start
Devices running exo automatically discover each other, without needing any manual configuration. Each device provides an API and a dashboard for interacting with your cluster (runs at http://localhost:52415).
There are two ways to run exo:
Run from Source (macOS)
Prerequisites:
-
brew (for simple package management on macOS)
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)" -
uv (for Python dependency management)
-
macmon (for hardware monitoring on Apple Silicon)
-
node (for building the dashboard)
brew install uv macmon node -
rust (to build Rust bindings, nightly for now)
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh rustup toolchain install nightly
Clone the repo, build the dashboard, and run exo:
# Clone exo
git clone https://github.com/exo-explore/exo
# Build dashboard
cd exo/dashboard && npm install && npm run build && cd ..
# Run exo
uv run exo
This starts the exo dashboard and API at http://localhost:52415/
Please view the section on RDMA to enable this feature on MacOS >=26.2!
Run from Source (Linux)
Prerequisites:
- uv (for Python dependency management)
- node (for building the dashboard) - version 18 or higher
- rust (to build Rust bindings, nightly for now)
Installation methods:
Option 1: Using system package manager (Ubuntu/Debian example):
# Install Node.js and npm
sudo apt update
sudo apt install nodejs npm
# Install uv
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
# Install Rust (using rustup)
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
rustup toolchain install nightly
Option 2: Using Homebrew on Linux (if preferred):
# Install Homebrew on Linux
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
# Install dependencies
brew install uv node
# Install Rust (using rustup)
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
rustup toolchain install nightly
Note: The macmon package is macOS-only and not required for Linux.
Clone the repo, build the dashboard, and run exo:
# Clone exo
git clone https://github.com/exo-explore/exo
# Build dashboard
cd exo/dashboard && npm install && npm run build && cd ..
# Run exo
uv run exo
This starts the exo dashboard and API at http://localhost:52415/
Important note for Linux users: Currently, exo runs on CPU on Linux. GPU support for Linux platforms is under development. If you'd like to see support for your specific Linux hardware, please search for existing feature requests or create a new one.
Configuration Options:
-
--no-worker: Run exo without the worker component. Useful for coordinator-only nodes that handle networking and orchestration but don't execute inference tasks. This is helpful for machines without sufficient GPU resources but with good network connectivity.uv run exo --no-worker
File Locations (Linux):
exo follows the XDG Base Directory Specification on Linux:
- Configuration files:
~/.config/exo/(or$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/exo/) - Data files:
~/.local/share/exo/(or$XDG_DATA_HOME/exo/) - Cache files:
~/.cache/exo/(or$XDG_CACHE_HOME/exo/)
You can override these locations by setting the corresponding XDG environment variables.
macOS App
exo ships a macOS app that runs in the background on your Mac.
The macOS app requires macOS Tahoe 26.2 or later.
Download the latest build here: EXO-latest.dmg.
The app will ask for permission to modify system settings and install a new Network profile. Improvements to this are being worked on.
Custom Namespace for Cluster Isolation:
The macOS app includes a custom namespace feature that allows you to isolate your exo cluster from others on the same network. This is configured through the EXO_LIBP2P_NAMESPACE setting:
-
Use cases:
- Running multiple separate exo clusters on the same network
- Isolating development/testing clusters from production clusters
- Preventing accidental cluster joining
-
Configuration: Access this setting in the app's Advanced settings (or set the
EXO_LIBP2P_NAMESPACEenvironment variable when running from source)
The namespace is logged on startup for debugging purposes.
Uninstalling the macOS App
The recommended way to uninstall is through the app itself: click the menu bar icon → Advanced → Uninstall. This cleanly removes all system components.
If you've already deleted the app, you can run the standalone uninstaller script:
sudo ./app/EXO/uninstall-exo.sh
This removes:
- Network setup LaunchDaemon
- Network configuration script
- Log files
- The "exo" network location
Note: You'll need to manually remove EXO from Login Items in System Settings → General → Login Items.
Enabling RDMA on macOS
RDMA is a new capability added to macOS 26.2. It works on any Mac with Thunderbolt 5 (M4 Pro Mac Mini, M4 Max Mac Studio, M4 Max MacBook Pro, M3 Ultra Mac Studio).
Please refer to the caveats for immediate troubleshooting.
To enable RDMA on macOS, follow these steps:
- Shut down your Mac.
- Hold down the power button for 10 seconds until the boot menu appears.
- Select "Options" to enter Recovery mode.
- When the Recovery UI appears, open the Terminal from the Utilities menu.
- In the Terminal, type:
and press Enter.
rdma_ctl enable - Reboot your Mac.
After that, RDMA will be enabled in macOS and exo will take care of the rest.
Important Caveats
- Devices that wish to be part of an RDMA cluster must be connected to all other devices in the cluster.
- The cables must support TB5.
- On a Mac Studio, you cannot use the Thunderbolt 5 port next to the Ethernet port.
- If running from source, please use the script found at
tmp/set_rdma_network_config.sh, which will disable Thunderbolt Bridge and set dhcp on each RDMA port. - RDMA ports may be unable to discover each other on different versions of MacOS. Please ensure that OS versions match exactly (even beta version numbers) on all devices.
Using the API
If you prefer to interact with exo via the API, here is an example creating an instance of a small model (mlx-community/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit), sending a chat completions request and deleting the instance.
1. Preview instance placements
The /instance/previews endpoint will preview all valid placements for your model.
curl "http://localhost:52415/instance/previews?model_id=llama-3.2-1b"
Sample response:
{
"previews": [
{
"model_id": "mlx-community/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit",
"sharding": "Pipeline",
"instance_meta": "MlxRing",
"instance": {...},
"memory_delta_by_node": {"local": 729808896},
"error": null
}
// ...possibly more placements...
]
}
This will return all valid placements for this model. Pick a placement that you like.
To pick the first one, pipe into jq:
curl "http://localhost:52415/instance/previews?model_id=llama-3.2-1b" | jq -c '.previews[] | select(.error == null) | .instance' | head -n1
2. Create a model instance
Send a POST to /instance with your desired placement in the instance field (the full payload must match types as in CreateInstanceParams), which you can copy from step 1:
curl -X POST http://localhost:52415/instance \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"instance": {...}
}'
Sample response:
{
"message": "Command received.",
"command_id": "e9d1a8ab-...."
}
3. Send a chat completion
Now, make a POST to /v1/chat/completions (the same format as OpenAI's API):
curl -N -X POST http://localhost:52415/v1/chat/completions \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"model": "mlx-community/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "What is Llama 3.2 1B?"}
],
"stream": true
}'
4. Delete the instance
When you're done, delete the instance by its ID (find it via /state or /instance endpoints):
curl -X DELETE http://localhost:52415/instance/YOUR_INSTANCE_ID
Other useful API endpoints:*
- List all models:
curl http://localhost:52415/models - Inspect instance IDs and deployment state:
curl http://localhost:52415/state
For further details, see:
- API basic documentation in docs/api.md.
- API types and endpoints in src/exo/master/api.py.
Benchmarking
The exo-bench tool measures model prefill and token generation speed across different placement configurations. This helps you optimize model performance and validate improvements.
Prerequisites:
- Nodes should be running with
uv run exobefore benchmarking - The tool uses the
/bench/chat/completionsendpoint
Basic usage:
uv run bench/exo_bench.py \
--model Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit \
--pp 128,256,512 \
--tg 128,256
Key parameters:
--model: Model to benchmark (short ID or HuggingFace ID)--pp: Prompt size hints (comma-separated integers)--tg: Generation lengths (comma-separated integers)--max-nodes: Limit placements to N nodes (default: 4)--instance-meta: Filter byring,jaccl, orboth(default: both)--sharding: Filter bypipeline,tensor, orboth(default: both)--repeat: Number of repetitions per configuration (default: 1)--warmup: Warmup runs per placement (default: 0)--json-out: Output file for results (default: bench/results.json)
Example with filters:
uv run bench/exo_bench.py \
--model Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct-4bit \
--pp 128,512 \
--tg 128 \
--max-nodes 2 \
--sharding tensor \
--repeat 3 \
--json-out my-results.json
The tool outputs performance metrics including prompt tokens per second (prompt_tps), generation tokens per second (generation_tps), and peak memory usage for each configuration.
Hardware Accelerator Support
On macOS, exo uses the GPU. On Linux, exo currently runs on CPU. We are working on extending hardware accelerator support. If you'd like support for a new hardware platform, please search for an existing feature request and add a thumbs up so we know what hardware is important to the community.
Contributing
See CONTRIBUTING.md for guidelines on how to contribute to exo.




