Compare commits
531 Commits
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
6e1cd45a46 | ||
|
|
b86d130eb6 | ||
|
|
90afc72e64 | ||
|
|
042c697b6b | ||
|
|
02441ff031 | ||
|
|
210af1fd3d | ||
|
|
06eaa32bf0 | ||
|
|
4f88a5fddb | ||
|
|
eb6be1d725 | ||
|
|
1d99681fd4 | ||
|
|
618be44023 | ||
|
|
544afaff97 | ||
|
|
e6b3b994be | ||
|
|
67f148ff83 | ||
|
|
6c34600599 | ||
|
|
016a4b7491 | ||
|
|
be21b74ad5 | ||
|
|
0f152b4e97 | ||
|
|
0d165d1efa | ||
|
|
9d54215a3a | ||
|
|
8ab916baed | ||
|
|
c83c50b27d | ||
|
|
c2ad214a84 | ||
|
|
459f0e11e5 | ||
|
|
56e43ba204 | ||
|
|
10485cad5a | ||
|
|
53a7798e58 | ||
|
|
372ed58677 | ||
|
|
3f8bfd62b7 | ||
|
|
02a6fcad98 | ||
|
|
651ced68bf | ||
|
|
670b64360d | ||
|
|
1f53fef70a | ||
|
|
d1f067dc5b | ||
|
|
15241b53a8 | ||
|
|
38fd8a674b | ||
|
|
bd37d8d04f | ||
|
|
bc99ad0ad1 | ||
|
|
aea04ee32e | ||
|
|
869c7389e2 | ||
|
|
2738df3801 | ||
|
|
433d7862ea | ||
|
|
7625e1e386 | ||
|
|
53e773a2e1 | ||
|
|
c13b54ad0e | ||
|
|
71c2abb41d | ||
|
|
6205935323 | ||
|
|
5fd5b6e72d | ||
|
|
faf88cea0b | ||
|
|
025b38df40 | ||
|
|
ac60cba75f | ||
|
|
94ee932351 | ||
|
|
cf760d6802 | ||
|
|
c65fdc4bed | ||
|
|
0ac9b3ee5c | ||
|
|
f2bd2c44e2 | ||
|
|
f0beab1778 | ||
|
|
95f2dc065e | ||
|
|
4e8080f290 | ||
|
|
fbbed6fe81 | ||
|
|
2d5a5d0d9e | ||
|
|
d4ddf4e62a | ||
|
|
cb25dab986 | ||
|
|
7aa1628336 | ||
|
|
1dbd3d7aa7 | ||
|
|
24e73e01c7 | ||
|
|
e26f94018c | ||
|
|
1ce67887b9 | ||
|
|
8e0200607f | ||
|
|
bd407ca705 | ||
|
|
48b5ef1681 | ||
|
|
afad59dfbb | ||
|
|
0f9be1d2e7 | ||
|
|
48c2406495 | ||
|
|
9958d93120 | ||
|
|
b63512cd92 | ||
|
|
74c4d1c1db | ||
|
|
7ccd81f706 | ||
|
|
1da8d3f1e6 | ||
|
|
92016da962 | ||
|
|
9c3c9b6e78 | ||
|
|
687871e46a | ||
|
|
3c1803897f | ||
|
|
1c3289f115 | ||
|
|
35d41adc7b | ||
|
|
9a3dd91030 | ||
|
|
017eae63b1 | ||
|
|
8af4454251 | ||
|
|
adf252768c | ||
|
|
3705bdefd5 | ||
|
|
25e94d6344 | ||
|
|
26c345b766 | ||
|
|
9ce50b4684 | ||
|
|
66954c7ded | ||
|
|
e0c3519b94 | ||
|
|
d91b2b3ee8 | ||
|
|
1623b26855 | ||
|
|
9573130630 | ||
|
|
2e0a102565 | ||
|
|
636ce6b3f7 | ||
|
|
1fd1e8733a | ||
|
|
44b45caf65 | ||
|
|
e6da96fbb7 | ||
|
|
c425509d57 | ||
|
|
d8451f75a4 | ||
|
|
a448bd63bd | ||
|
|
27fb2b358c | ||
|
|
68723d5291 | ||
|
|
70bdade23b | ||
|
|
4f964939a1 | ||
|
|
55afb70b37 | ||
|
|
b307d38897 | ||
|
|
a085898309 | ||
|
|
3b40c557ce | ||
|
|
75a07f24bf | ||
|
|
7cea84b74c | ||
|
|
3a5158a784 | ||
|
|
bd581c5337 | ||
|
|
22982287ff | ||
|
|
a41a729682 | ||
|
|
174e7b1730 | ||
|
|
874d24181e | ||
|
|
5db99a27cf | ||
|
|
180b842a1e | ||
|
|
3f53deebc9 | ||
|
|
e5d7878856 | ||
|
|
3eca945bd1 | ||
|
|
ba9c9a3f78 | ||
|
|
a9673f145a | ||
|
|
aa28784f6b | ||
|
|
7b3319ddab | ||
|
|
6a20078259 | ||
|
|
d0ab909544 | ||
|
|
13da029dca | ||
|
|
91fe90e8e6 | ||
|
|
a0c8f93231 | ||
|
|
cad6a6e0c1 | ||
|
|
fd5ba77b83 | ||
|
|
cb1410426e | ||
|
|
7b31e52766 | ||
|
|
4151616681 | ||
|
|
462e24e864 | ||
|
|
9f9ed7a6bd | ||
|
|
b6ea9ea2ca | ||
|
|
b85b2e3942 | ||
|
|
08fc2a41ca | ||
|
|
8d3dcbcd1b | ||
|
|
861ed37c97 | ||
|
|
7a445402d4 | ||
|
|
04c8502cc7 | ||
|
|
c7c69586ae | ||
|
|
4e09feda9e | ||
|
|
73260971b5 | ||
|
|
b36bfff56e | ||
|
|
83d04df8a6 | ||
|
|
7bc78c5fd3 | ||
|
|
ae8fa3aacd | ||
|
|
08bc120771 | ||
|
|
a39efb029f | ||
|
|
58ca98285f | ||
|
|
3f5f81bbdc | ||
|
|
90236c8135 | ||
|
|
c200bc2240 | ||
|
|
e9861cd918 | ||
|
|
202fa11d50 | ||
|
|
4b6e09296c | ||
|
|
9bd0d6fa96 | ||
|
|
35510a5ea7 | ||
|
|
c1788a25c7 | ||
|
|
19c77e35bd | ||
|
|
cc4c13e4ae | ||
|
|
4f3764faa9 | ||
|
|
c27ad0dc26 | ||
|
|
6d0caf7522 | ||
|
|
06df32e84c | ||
|
|
28c089c029 | ||
|
|
44b26bb64c | ||
|
|
e04bae2286 | ||
|
|
23f5940e8b | ||
|
|
4915cf0561 | ||
|
|
a1c9eff041 | ||
|
|
57cb3f3089 | ||
|
|
bd6b3b07c5 | ||
|
|
3cf8b86dc1 | ||
|
|
55165f292a | ||
|
|
f3ddc7bdeb | ||
|
|
4356cc9588 | ||
|
|
cd9e87e60e | ||
|
|
4834d87dcd | ||
|
|
7781cc0936 | ||
|
|
23459d4a35 | ||
|
|
ab2b86fe2c | ||
|
|
90a5796b94 | ||
|
|
bb8a630fc3 | ||
|
|
f5a503afae | ||
|
|
49fba853c2 | ||
|
|
bac2f587b7 | ||
|
|
e1fd6785aa | ||
|
|
4e50f53459 | ||
|
|
933d4327fb | ||
|
|
c7902dd23a | ||
|
|
c5f5e63810 | ||
|
|
c3cc077fa9 | ||
|
|
c6f98c009f | ||
|
|
e4206772cb | ||
|
|
723ef07ccf | ||
|
|
8609beb9ab | ||
|
|
65536cbf63 | ||
|
|
0192eab557 | ||
|
|
3f9f4a0f8f | ||
|
|
380e3731a8 | ||
|
|
d6d99b86cb | ||
|
|
5592fa0f6f | ||
|
|
b65be5d496 | ||
|
|
6c7da43e51 | ||
|
|
dfec2d7644 | ||
|
|
8c3ef76139 | ||
|
|
7a504a721c | ||
|
|
dd963511d6 | ||
|
|
fdb6d43e10 | ||
|
|
a7c718e968 | ||
|
|
f4d753620b | ||
|
|
fadfe4c586 | ||
|
|
5fd83c5fa4 | ||
|
|
14daaf409f | ||
|
|
c7dc26b760 | ||
|
|
f5ccb3c35d | ||
|
|
4cea311e6e | ||
|
|
f8718072a0 | ||
|
|
3dbbecdd16 | ||
|
|
6d5530ec1c | ||
|
|
0761f11d1a | ||
|
|
f2e7ef7056 | ||
|
|
d5d9a20937 | ||
|
|
96f092179f | ||
|
|
8505b716af | ||
|
|
78272ac1f3 | ||
|
|
f1bee9a271 | ||
|
|
b20b2218cd | ||
|
|
b9cf69cd42 | ||
|
|
f803c77515 | ||
|
|
0c67022048 | ||
|
|
d8fe307d61 | ||
|
|
580cf8f4e2 | ||
|
|
af390af77c | ||
|
|
4642f63a1e | ||
|
|
203e10596f | ||
|
|
5a2278d09a | ||
|
|
47a8387a04 | ||
|
|
27ca0c9dca | ||
|
|
9418d78de6 | ||
|
|
4b74aef429 | ||
|
|
fc7d123347 | ||
|
|
53da56146e | ||
|
|
3799b9027e | ||
|
|
c70f3f1198 | ||
|
|
58dddc5e4f | ||
|
|
c90c4fb6c1 | ||
|
|
5b3df28f0c | ||
|
|
6c6bdb6233 | ||
|
|
f156f45193 | ||
|
|
f24d744a3b | ||
|
|
937b462cdd | ||
|
|
3025a368c6 | ||
|
|
c218e0d560 | ||
|
|
1ed5aa23e6 | ||
|
|
106d2171d8 | ||
|
|
c5817912d2 | ||
|
|
a7a92bc637 | ||
|
|
68d1fea961 | ||
|
|
8c6b2d5804 | ||
|
|
19c53b21c1 | ||
|
|
44d63cd555 | ||
|
|
55c4b5fb0b | ||
|
|
c32e800c23 | ||
|
|
73dbbeab55 | ||
|
|
417a3ab140 | ||
|
|
a3235ed8de | ||
|
|
38495fffa5 | ||
|
|
b77a43bcac | ||
|
|
483eb73b26 | ||
|
|
51a928d3f5 | ||
|
|
e71636e381 | ||
|
|
f7f17fcfd6 | ||
|
|
033bc2a6c9 | ||
|
|
28d3b9f783 | ||
|
|
0c55553328 | ||
|
|
b66056aa34 | ||
|
|
4f10b8b98d | ||
|
|
06eb421934 | ||
|
|
bf229ad5d8 | ||
|
|
d0319001be | ||
|
|
c4682af13d | ||
|
|
6ca3ce80e4 | ||
|
|
25e85c8522 | ||
|
|
6bf3ab3b7a | ||
|
|
f5ea5eef2a | ||
|
|
46a986cacf | ||
|
|
e620aeb46d | ||
|
|
d1e2e46b80 | ||
|
|
b1c4a8acd5 | ||
|
|
362e2cdc79 | ||
|
|
93e6a08acd | ||
|
|
3ec4342282 | ||
|
|
dc483478eb | ||
|
|
bdd251a05b | ||
|
|
195559ccba | ||
|
|
9a71672a95 | ||
|
|
7e48be1561 | ||
|
|
508f9ce954 | ||
|
|
afbdf2546f | ||
|
|
62df417807 | ||
|
|
09d2747a70 | ||
|
|
d3ea6f7514 | ||
|
|
02187636ea | ||
|
|
687065509b | ||
|
|
b30cca8e9e | ||
|
|
3906777065 | ||
|
|
d60a10fa59 | ||
|
|
54368e7b22 | ||
|
|
acc556e416 | ||
|
|
700585f99d | ||
|
|
4c2993f353 | ||
|
|
ea9277aab4 | ||
|
|
8d86fca027 | ||
|
|
fc0716a7dd | ||
|
|
1e593dc4d4 | ||
|
|
dcc1e1bcf8 | ||
|
|
06eb775c63 | ||
|
|
ab77c069d4 | ||
|
|
46fffc0e94 | ||
|
|
1c2cdb97e9 | ||
|
|
76b6fd5c18 | ||
|
|
a2fb716035 | ||
|
|
aa84ac8e3e | ||
|
|
4ed2bd1fea | ||
|
|
87b7a63ff2 | ||
|
|
06d0918c3d | ||
|
|
5b3adfe449 | ||
|
|
bdd794a0e6 | ||
|
|
f0df79aa91 | ||
|
|
c26f1760d4 | ||
|
|
e5fa4b0af6 | ||
|
|
a33c299fd7 | ||
|
|
6939621730 | ||
|
|
120ab08360 | ||
|
|
3f5521fdfb | ||
|
|
7244e4b612 | ||
|
|
d329745064 | ||
|
|
5f7fe926ab | ||
|
|
c8eea09664 | ||
|
|
5700d65188 | ||
|
|
46178a5347 | ||
|
|
bff5dbbf5d | ||
|
|
09cd7c47a1 | ||
|
|
e2fadcbc90 | ||
|
|
b3bb29afa8 | ||
|
|
c7db2ff858 | ||
|
|
2a7ef5504a | ||
|
|
27964c5ffd | ||
|
|
d262f6e929 | ||
|
|
d61f5e4b55 | ||
|
|
3ed112e8a9 | ||
|
|
9da626eb2c | ||
|
|
6f74c7327b | ||
|
|
360a2797c1 | ||
|
|
0552977cd6 | ||
|
|
bd407cc4ed | ||
|
|
83b1a117cc | ||
|
|
2a1ff213a0 | ||
|
|
62af6e0eeb | ||
|
|
15da01af5c | ||
|
|
d544bdf092 | ||
|
|
703ade7967 | ||
|
|
58f135ba2f | ||
|
|
713d374484 | ||
|
|
24e9ea28d3 | ||
|
|
cae53138b2 | ||
|
|
a49d45eaa9 | ||
|
|
3986f79029 | ||
|
|
7379fde5ee | ||
|
|
7b63bc5551 | ||
|
|
747ae8210f | ||
|
|
c651416e05 | ||
|
|
814f95e2bf | ||
|
|
d8716f94ae | ||
|
|
67f8cb3b4f | ||
|
|
5c2828bd13 | ||
|
|
b087246f26 | ||
|
|
219d299426 | ||
|
|
31da760729 | ||
|
|
fc89eb8f81 | ||
|
|
6fca1041e9 | ||
|
|
9db1f5641b | ||
|
|
c3beb56e63 | ||
|
|
325edd5f00 | ||
|
|
08322ef359 | ||
|
|
01b43e6e25 | ||
|
|
3cf92a156c | ||
|
|
f54d8d57a4 | ||
|
|
56ab106bbb | ||
|
|
e92b43b5c8 | ||
|
|
7c50025c47 | ||
|
|
adfbd27100 | ||
|
|
eada8bf7db | ||
|
|
440b7a8efa | ||
|
|
fcaff64646 | ||
|
|
d240421378 | ||
|
|
ca27317b65 | ||
|
|
ce02d3cb83 | ||
|
|
95475aaa9c | ||
|
|
7a8b054a12 | ||
|
|
7b2993682f | ||
|
|
73fad03b46 | ||
|
|
b0b88f9d5b | ||
|
|
49d33f9f70 | ||
|
|
1f27981045 | ||
|
|
f541d2c200 | ||
|
|
0e99b23ebc | ||
|
|
de341abe66 | ||
|
|
4a1648b04e | ||
|
|
5f13b53ea5 | ||
|
|
5189c93d85 | ||
|
|
e612989313 | ||
|
|
d675991a34 | ||
|
|
d03678dfbb | ||
|
|
6ff89284c5 | ||
|
|
7f673cf4e9 | ||
|
|
bac7230027 | ||
|
|
866af5bca6 | ||
|
|
f4be79be51 | ||
|
|
3797c04946 | ||
|
|
9a9bfd7f93 | ||
|
|
ada1ecdb00 | ||
|
|
3bbd38313b | ||
|
|
c1df0f6b84 | ||
|
|
0cd5485597 | ||
|
|
528ef7e079 | ||
|
|
8e3a7699a3 | ||
|
|
8998ccaffb | ||
|
|
2b7f201a44 | ||
|
|
192ebba2a2 | ||
|
|
8880c4cb03 | ||
|
|
6324be684f | ||
|
|
c705685394 | ||
|
|
945f401d8e | ||
|
|
f216d340ec | ||
|
|
a4558e7053 | ||
|
|
298f8478e2 | ||
|
|
b86d163470 | ||
|
|
9e2d37b89c | ||
|
|
97adadd9e1 | ||
|
|
26e3dffb37 | ||
|
|
aa7b4bd101 | ||
|
|
ffc4c716c0 | ||
|
|
ef7b6e8eaf | ||
|
|
596243f4a5 | ||
|
|
766bf1c5aa | ||
|
|
9e748dbca4 | ||
|
|
cefe6cf92c | ||
|
|
be3953499f | ||
|
|
546d233dec | ||
|
|
61dd36a945 | ||
|
|
27f9d55c3e | ||
|
|
906cc60f65 | ||
|
|
69afaf256f | ||
|
|
4ab349a2a8 | ||
|
|
9c258107b4 | ||
|
|
29a4f90bcd | ||
|
|
361fd00777 | ||
|
|
4c3cf31730 | ||
|
|
aad6b123f7 | ||
|
|
e40e87c662 | ||
|
|
84de980977 | ||
|
|
08484603ee | ||
|
|
ab6dd60997 | ||
|
|
c9ef7bd6dc | ||
|
|
88ece95a30 | ||
|
|
366c5db0bb | ||
|
|
46e3811f8d | ||
|
|
613e211d20 | ||
|
|
500f2b2ad4 | ||
|
|
5cf7718657 | ||
|
|
727b656c8d | ||
|
|
cc7102e9b8 | ||
|
|
5123915fe4 | ||
|
|
1b8bbd51d8 | ||
|
|
1e4f86db6d | ||
|
|
7391056daf | ||
|
|
6a274d18b4 | ||
|
|
62626b0175 | ||
|
|
c8df3ae57c | ||
|
|
6f7f9268f6 | ||
|
|
50653e205f | ||
|
|
50a280b17b | ||
|
|
c1da3b38a3 | ||
|
|
e68a68c97c | ||
|
|
907e613ff2 | ||
|
|
f0fc2fad2c | ||
|
|
ad471307e2 | ||
|
|
2bd775988f | ||
|
|
c59ddc8a24 | ||
|
|
378b39bbbc | ||
|
|
37e0306517 | ||
|
|
fad3a9e1dc | ||
|
|
b35b0a9a90 | ||
|
|
1426b6200a | ||
|
|
40e5f3764e | ||
|
|
e5c75807ce | ||
|
|
deff2b6678 | ||
|
|
7c572fdb3a | ||
|
|
ae970638cf | ||
|
|
deae92bba1 | ||
|
|
f806ba642a | ||
|
|
5a3cf863da | ||
|
|
dd6ab23b62 | ||
|
|
0449499188 | ||
|
|
4dc7b32861 | ||
|
|
08d849d5c5 | ||
|
|
714e68b5f0 | ||
|
|
3d4f59f35a | ||
|
|
3ce2920fef | ||
|
|
eda9b28338 | ||
|
|
7514ac6fb0 | ||
|
|
25fb4239cc | ||
|
|
65568065e0 | ||
|
|
95679ca5e6 | ||
|
|
84a300ef84 | ||
|
|
c6d28c8209 | ||
|
|
3984e9b8ac | ||
|
|
aa0bca7bb2 |
56
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.md
vendored
@@ -7,29 +7,48 @@ assignees: ''
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**Describe the bug**
|
||||
A clear and concise description of what the bug is.
|
||||
### Describe the bug
|
||||
|
||||
**To Reproduce**
|
||||
Steps to reproduce the behavior:
|
||||
1. Create a file with '...'
|
||||
2. Add a path operation function with '....'
|
||||
3. Open the browser and call it with a payload of '....'
|
||||
4. See error
|
||||
Write here a clear and concise description of what the bug is.
|
||||
|
||||
**Expected behavior**
|
||||
A clear and concise description of what you expected to happen.
|
||||
### To Reproduce
|
||||
|
||||
**Screenshots**
|
||||
If applicable, add screenshots to help explain your problem.
|
||||
Steps to reproduce the behavior with a minimum self-contained file.
|
||||
|
||||
**Environment:**
|
||||
- OS: [e.g. Linux / Windows / macOS]
|
||||
- FastAPI Version [e.g. 0.3.0], get it with:
|
||||
Replace each part with your own scenario:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a file with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
import fastapi
|
||||
print(fastapi.__version__)
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/")
|
||||
def read_root():
|
||||
return {"Hello": "World"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Open the browser and call the endpoint `/`.
|
||||
4. It returns a JSON with `{"Hello": "World"}`.
|
||||
5. But I expected it to return `{"Hello": "Sara"}`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Expected behavior
|
||||
|
||||
Add a clear and concise description of what you expected to happen.
|
||||
|
||||
### Screenshots
|
||||
|
||||
If applicable, add screenshots to help explain your problem.
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment
|
||||
|
||||
- OS: [e.g. Linux / Windows / macOS]
|
||||
- FastAPI Version [e.g. 0.3.0], get it with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "import fastapi; print(fastapi.__version__)"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Python version, get it with:
|
||||
@@ -38,5 +57,6 @@ print(fastapi.__version__)
|
||||
python --version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Additional context**
|
||||
### Additional context
|
||||
|
||||
Add any other context about the problem here.
|
||||
|
||||
20
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature_request.md
vendored
@@ -7,14 +7,20 @@ assignees: ''
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**Is your feature request related to a problem? Please describe.**
|
||||
A clear and concise description of what the problem is. Ex. I want to be able to [...] but I can't because [...]
|
||||
### Is your feature request related to a problem
|
||||
|
||||
**Describe the solution you'd like**
|
||||
A clear and concise description of what you want to happen.
|
||||
Is your feature request related to a problem?
|
||||
|
||||
**Describe alternatives you've considered**
|
||||
A clear and concise description of any alternative solutions or features you've considered.
|
||||
Add a clear and concise description of what the problem is. Ex. I want to be able to [...] but I can't because [...]
|
||||
|
||||
### The solution you would like
|
||||
|
||||
Add a clear and concise description of what you want to happen.
|
||||
|
||||
### Describe alternatives you've considered
|
||||
|
||||
Add a clear and concise description of any alternative solutions or features you've considered.
|
||||
|
||||
### Additional context
|
||||
|
||||
**Additional context**
|
||||
Add any other context or screenshots about the feature request here.
|
||||
|
||||
11
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/question.md
vendored
@@ -7,11 +7,18 @@ assignees: ''
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**Description**
|
||||
### First check
|
||||
|
||||
* [ ] I used the GitHub search to find a similar issue and didn't find it.
|
||||
* [ ] I searched the FastAPI documentation, with the integrated search.
|
||||
* [ ] I already searched in Google "How to X in FastAPI" and didn't find any information.
|
||||
|
||||
### Description
|
||||
|
||||
How can I [...]?
|
||||
|
||||
Is it possible to [...]?
|
||||
|
||||
**Additional context**
|
||||
### Additional context
|
||||
|
||||
Add any other context or screenshots about the feature request here.
|
||||
|
||||
29
.github/workflows/deploy-docs.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
name: Build and Deploy to Netlify
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
types: [opened, synchronize]
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-18.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.7"
|
||||
- name: Install Flit
|
||||
run: python3.7 -m pip install flit
|
||||
- name: Install docs extras
|
||||
run: python3.7 -m flit install --extras doc
|
||||
- name: Build Docs
|
||||
run: python3.7 ./scripts/docs.py build-all
|
||||
- name: Deploy to Netlify
|
||||
uses: nwtgck/actions-netlify@v1.0.3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
publish-dir: './site'
|
||||
production-branch: master
|
||||
github-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
NETLIFY_AUTH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NETLIFY_AUTH_TOKEN }}
|
||||
NETLIFY_SITE_ID: ${{ secrets.NETLIFY_SITE_ID }}
|
||||
19
.github/workflows/main.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
on:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 0 * * *"
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
issue-manager:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: tiangolo/issue-manager@master
|
||||
with:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
config: >
|
||||
{
|
||||
"answered": {
|
||||
"users": ["tiangolo", "dmontagu"],
|
||||
"delay": 864000,
|
||||
"message": "Assuming the original issue was solved, it will be automatically closed now. But feel free to add more comments or create new issues."
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
3
.gitignore
vendored
@@ -12,3 +12,6 @@ coverage.xml
|
||||
.netlify
|
||||
test.db
|
||||
log.txt
|
||||
Pipfile.lock
|
||||
env3.*
|
||||
docs_build
|
||||
|
||||
21
.travis.yml
@@ -1,14 +1,22 @@
|
||||
dist: xenial
|
||||
|
||||
language: python
|
||||
|
||||
cache: pip
|
||||
|
||||
python:
|
||||
- "3.6"
|
||||
- "3.7-dev"
|
||||
- "3.7"
|
||||
- "3.8"
|
||||
- "nightly"
|
||||
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
allow_failures:
|
||||
- python: "nightly"
|
||||
|
||||
install:
|
||||
- pip install flit
|
||||
- flit install
|
||||
- flit install --symlink
|
||||
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- bash scripts/test.sh
|
||||
@@ -17,7 +25,8 @@ after_script:
|
||||
- bash <(curl -s https://codecov.io/bash)
|
||||
|
||||
deploy:
|
||||
provider: script
|
||||
script: bash scripts/trigger-docker.sh
|
||||
on:
|
||||
branch: master
|
||||
provider: script
|
||||
script: bash scripts/deploy.sh
|
||||
on:
|
||||
tags: true
|
||||
python: "3.6"
|
||||
|
||||
1
CONTRIBUTING.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
Please read the [Development - Contributing](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/contributing/) guidelines in the documentation site.
|
||||
36
Pipfile
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[[source]]
|
||||
name = "pypi"
|
||||
url = "https://pypi.org/simple"
|
||||
verify_ssl = true
|
||||
|
||||
[dev-packages]
|
||||
mypy = "*"
|
||||
black = "*"
|
||||
jupyter = "*"
|
||||
better-exceptions = "*"
|
||||
pytest = "*"
|
||||
pytest-cov = "*"
|
||||
isort = "*"
|
||||
requests = "*"
|
||||
flit = "*"
|
||||
mkdocs = "*"
|
||||
mkdocs-material = "*"
|
||||
markdown-include = "*"
|
||||
autoflake = "*"
|
||||
email-validator = "*"
|
||||
ujson = "*"
|
||||
flake8 = "*"
|
||||
python-multipart = "*"
|
||||
sqlalchemy = "*"
|
||||
uvicorn = "*"
|
||||
|
||||
[packages]
|
||||
starlette = "==0.11.1"
|
||||
pydantic = "==0.21.0"
|
||||
databases = {extras = ["sqlite"],version = "*"}
|
||||
|
||||
[requires]
|
||||
python_version = "3.6"
|
||||
|
||||
[pipenv]
|
||||
allow_prereleases = true
|
||||
868
Pipfile.lock
generated
@@ -1,868 +0,0 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"_meta": {
|
||||
"hash": {
|
||||
"sha256": "24b3b7b88d3cbe671ddbe296e64c15f8558f0e5d5df977200119872a363aac13"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pipfile-spec": 6,
|
||||
"requires": {
|
||||
"python_version": "3.6"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sources": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "pypi",
|
||||
"url": "https://pypi.org/simple",
|
||||
"verify_ssl": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"default": {
|
||||
"aiocontextvars": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:1e0ff5837c8b01c36a1107acdd0baf7853ebdf6c9fc43e8e311f4be37ac2038a",
|
||||
"sha256:6ff7aee14f549d52f0446cbb84d0deddcd3fc677bcf8fbc2ce13f5756d2064dc"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"markers": "python_version < '3.7'",
|
||||
"version": "==0.2.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"aiosqlite": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:af4fed9e778756fa0ffffc7a8b14c4d7b1a57155dc5669f18e45107313f6019e"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.9.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"contextvars": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:2341042e1c03a271813e07dba29b6b60fa85c1005ea5ed1638a076cf50b4d625"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"markers": "python_version < '3.7'",
|
||||
"version": "==2.3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"databases": {
|
||||
"extras": [
|
||||
"sqlite"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:4a0f15669c390a04b439972426350c0ae921ddc08c42bd54f125eb2fb86ee728"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==0.2.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dataclasses": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:454a69d788c7fda44efd71e259be79577822f5e3f53f029a22d08004e951dc9f",
|
||||
"sha256:6988bd2b895eef432d562370bb707d540f32f7360ab13da45340101bc2307d84"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"markers": "python_version < '3.7'",
|
||||
"version": "==0.6"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"immutables": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:1e4f4513254ef11e0230a558ee0dcb4551b914993c330005d15338da595d3750",
|
||||
"sha256:228e38dc7a810ba4ff88909908ac47f840e5dc6c4c0da6b25009c626a9ae771c",
|
||||
"sha256:2ae88fbfe1d04f4e5859c924e97313edf70e72b4f19871bf329b96a67ede9ba0",
|
||||
"sha256:2d32b61c222cba1dd11f0faff67c7fb6204ef1982454e1b5b001d4b79966ef17",
|
||||
"sha256:35af186bfac5b62522fdf2cab11120d7b0547f405aa399b6a1e443cf5f5e318c",
|
||||
"sha256:63023fa0cceedc62e0d1535cd4ca7a1f6df3120a6d8e5c34e89037402a6fd809",
|
||||
"sha256:6bf5857f42a96331fd0929c357dc0b36a72f339f3b6acaf870b149c96b141f69",
|
||||
"sha256:7bb1590024a032c7a57f79faf8c8ff5e91340662550d2980e0177f67e66e9c9c",
|
||||
"sha256:7c090687d7e623d4eca22962635b5e1a1ee2d6f9a9aca2f3fb5a184a1ffef1f2",
|
||||
"sha256:bc36a0a8749881eebd753f696b081bd51145e4d77291d671d2e2f622e5b65d2f",
|
||||
"sha256:d9fc6a236018d99af6453ead945a6bb55f98d14b1801a2c229dd993edc753a00"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.6"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pydantic": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:93fa585402e7c8c01623ea8af6ca23363e8b4c6a020b7a2de9e99fa29d642d50",
|
||||
"sha256:eb441dd50779347a450494c437db3ecbb13c1f3854497df879662782af516c5c"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==0.21.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sqlalchemy": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:781fb7b9d194ed3fc596b8f0dd4623ff160e3e825dd8c15472376a438c19598b"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.3.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"starlette": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:9d48b35d1fc7521d59ae53c421297ab3878d3c7cd4b75266d77f6c73cccb78bb"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==0.11.1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"develop": {
|
||||
"appdirs": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:9e5896d1372858f8dd3344faf4e5014d21849c756c8d5701f78f8a103b372d92",
|
||||
"sha256:d8b24664561d0d34ddfaec54636d502d7cea6e29c3eaf68f3df6180863e2166e"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.4.3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"atomicwrites": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:03472c30eb2c5d1ba9227e4c2ca66ab8287fbfbbda3888aa93dc2e28fc6811b4",
|
||||
"sha256:75a9445bac02d8d058d5e1fe689654ba5a6556a1dfd8ce6ec55a0ed79866cfa6"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.3.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"attrs": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:69c0dbf2ed392de1cb5ec704444b08a5ef81680a61cb899dc08127123af36a79",
|
||||
"sha256:f0b870f674851ecbfbbbd364d6b5cbdff9dcedbc7f3f5e18a6891057f21fe399"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==19.1.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"autoflake": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:c103e63466f11db3617167a2c68ff6a0cda35b940222920631c6eeec6b67e807"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==1.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"backcall": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:38ecd85be2c1e78f77fd91700c76e14667dc21e2713b63876c0eb901196e01e4",
|
||||
"sha256:bbbf4b1e5cd2bdb08f915895b51081c041bac22394fdfcfdfbe9f14b77c08bf2"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.1.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"better-exceptions": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:bf79c87659bc849989d726bf0e4a2100edefe7eded112d201f54fe08467fdf63",
|
||||
"sha256:c196cad849de615abb9f6eb67ca1b83f33b938818f0e2fe8fa157b22aeb7b992"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==0.2.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"black": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:09a9dcb7c46ed496a9850b76e4e825d6049ecd38b611f1224857a79bd985a8cf",
|
||||
"sha256:68950ffd4d9169716bcb8719a56c07a2f4485354fec061cdd5910aa07369731c"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==19.3b0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"bleach": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:213336e49e102af26d9cde77dd2d0397afabc5a6bf2fed985dc35b5d1e285a16",
|
||||
"sha256:3fdf7f77adcf649c9911387df51254b813185e32b2c6619f690b593a617e19fa"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==3.1.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"certifi": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:59b7658e26ca9c7339e00f8f4636cdfe59d34fa37b9b04f6f9e9926b3cece1a5",
|
||||
"sha256:b26104d6835d1f5e49452a26eb2ff87fe7090b89dfcaee5ea2212697e1e1d7ae"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==2019.3.9"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"chardet": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:84ab92ed1c4d4f16916e05906b6b75a6c0fb5db821cc65e70cbd64a3e2a5eaae",
|
||||
"sha256:fc323ffcaeaed0e0a02bf4d117757b98aed530d9ed4531e3e15460124c106691"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==3.0.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"click": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:2335065e6395b9e67ca716de5f7526736bfa6ceead690adf616d925bdc622b13",
|
||||
"sha256:5b94b49521f6456670fdb30cd82a4eca9412788a93fa6dd6df72c94d5a8ff2d7"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==7.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"coverage": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:029c69deaeeeae1b15bc6c59f0ffa28aa8473721c614a23f2c2976dec245cd12",
|
||||
"sha256:02abbbebc6e9d5abe13cd28b5e963dedb6ffb51c146c916d17b18f141acd9947",
|
||||
"sha256:1bbfe5b82a3921d285e999c6d256c1e16b31c554c29da62d326f86c173d30337",
|
||||
"sha256:210c02f923df33a8d0e461c86fdcbbb17228ff4f6d92609fc06370a98d283c2d",
|
||||
"sha256:2d0807ba935f540d20b49d5bf1c0237b90ce81e133402feda906e540003f2f7a",
|
||||
"sha256:35d7a013874a7c927ce997350d314144ffc5465faf787bb4e46e6c4f381ef562",
|
||||
"sha256:3636f9d0dcb01aed4180ef2e57a4e34bb4cac3ecd203c2a23db8526d86ab2fb4",
|
||||
"sha256:42f4be770af2455a75e4640f033a82c62f3fb0d7a074123266e143269d7010ef",
|
||||
"sha256:48440b25ba6cda72d4c638f3a9efa827b5b87b489c96ab5f4ff597d976413156",
|
||||
"sha256:4dac8dfd1acf6a3ac657475dfdc66c621f291b1b7422a939cc33c13ac5356473",
|
||||
"sha256:4e8474771c69c2991d5eab65764289a7dd450bbea050bc0ebb42b678d8222b42",
|
||||
"sha256:551f10ddfeff56a1325e5a34eff304c5892aa981fd810babb98bfee77ee2fb17",
|
||||
"sha256:5b104982f1809c1577912519eb249f17d9d7e66304ad026666cb60a5ef73309c",
|
||||
"sha256:5c62aef73dfc87bfcca32cee149a1a7a602bc74bac72223236b0023543511c88",
|
||||
"sha256:633151f8d1ad9467b9f7e90854a7f46ed8f2919e8bc7d98d737833e8938fc081",
|
||||
"sha256:772207b9e2d5bf3f9d283b88915723e4e92d9a62c83f44ec92b9bd0cd685541b",
|
||||
"sha256:7d5e02f647cd727afc2659ec14d4d1cc0508c47e6cfb07aea33d7aa9ca94d288",
|
||||
"sha256:a9798a4111abb0f94584000ba2a2c74841f2cfe5f9254709756367aabbae0541",
|
||||
"sha256:b38ea741ab9e35bfa7015c93c93bbd6a1623428f97a67083fc8ebd366238b91f",
|
||||
"sha256:b6a5478c904236543c0347db8a05fac6fc0bd574c870e7970faa88e1d9890044",
|
||||
"sha256:c6248bfc1de36a3844685a2e10ba17c18119ba6252547f921062a323fb31bff1",
|
||||
"sha256:c705ab445936457359b1424ef25ccc0098b0491b26064677c39f1d14a539f056",
|
||||
"sha256:d95a363d663ceee647291131dbd213af258df24f41350246842481ec3709bd33",
|
||||
"sha256:e27265eb80cdc5dab55a40ef6f890e04ecc618649ad3da5265f128b141f93f78",
|
||||
"sha256:ebc276c9cb5d917bd2ae959f84ffc279acafa9c9b50b0fa436ebb70bbe2166ea",
|
||||
"sha256:f4d229866d030863d0fe3bf297d6d11e6133ca15bbb41ed2534a8b9a3d6bd061",
|
||||
"sha256:f95675bd88b51474d4fe5165f3266f419ce754ffadfb97f10323931fa9ac95e5",
|
||||
"sha256:f95bc54fb6d61b9f9ff09c4ae8ff6a3f5edc937cda3ca36fc937302a7c152bf1",
|
||||
"sha256:fd0f6be53de40683584e5331c341e65a679dbe5ec489a0697cec7c2ef1a48cda"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==5.0a4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"decorator": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:86156361c50488b84a3f148056ea716ca587df2f0de1d34750d35c21312725de",
|
||||
"sha256:f069f3a01830ca754ba5258fde2278454a0b5b79e0d7f5c13b3b97e57d4acff6"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==4.4.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"defusedxml": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:24d7f2f94f7f3cb6061acb215685e5125fbcdc40a857eff9de22518820b0a4f4",
|
||||
"sha256:702a91ade2968a82beb0db1e0766a6a273f33d4616a6ce8cde475d8e09853b20"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.5.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"dnspython": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:36c5e8e38d4369a08b6780b7f27d790a292b2b08eea01607865bf0936c558e01",
|
||||
"sha256:f69c21288a962f4da86e56c4905b49d11aba7938d3d740e80d9e366ee4f1632d"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.16.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"docutils": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:02aec4bd92ab067f6ff27a38a38a41173bf01bed8f89157768c1573f53e474a6",
|
||||
"sha256:51e64ef2ebfb29cae1faa133b3710143496eca21c530f3f71424d77687764274",
|
||||
"sha256:7a4bd47eaf6596e1295ecb11361139febe29b084a87bf005bf899f9a42edc3c6"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.14"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"email-validator": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:ddc4b5b59fa699bb10127adcf7ad4de78fde4ec539a072b104b8bb16da666ae5"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==1.0.3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"entrypoints": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:589f874b313739ad35be6e0cd7efde2a4e9b6fea91edcc34e58ecbb8dbe56d19",
|
||||
"sha256:c70dd71abe5a8c85e55e12c19bd91ccfeec11a6e99044204511f9ed547d48451"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"flake8": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:859996073f341f2670741b51ec1e67a01da142831aa1fdc6242dbf88dffbe661",
|
||||
"sha256:a796a115208f5c03b18f332f7c11729812c8c3ded6c46319c59b53efd3819da8"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==3.7.7"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"flit": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:1d93f7a833ed8a6e120ddc40db5c4763bc39bccc75c05081ec8285ece718aefb",
|
||||
"sha256:6f6f0fb83c51ffa3a150fa41b5ac118df9ea4a87c2c06dff4ebf9adbe7b52b36"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==1.3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"h11": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:acca6a44cb52a32ab442b1779adf0875c443c689e9e028f8d831a3769f9c5208",
|
||||
"sha256:f2b1ca39bfed357d1f19ac732913d5f9faa54a5062eca7d2ec3a916cfb7ae4c7"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.8.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"httptools": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:e00cbd7ba01ff748e494248183abc6e153f49181169d8a3d41bb49132ca01dfc"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.0.13"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"idna": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:c357b3f628cf53ae2c4c05627ecc484553142ca23264e593d327bcde5e9c3407",
|
||||
"sha256:ea8b7f6188e6fa117537c3df7da9fc686d485087abf6ac197f9c46432f7e4a3c"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==2.8"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ipykernel": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:0aeb7ec277ac42cc2b59ae3d08b10909b2ec161dc6908096210527162b53675d",
|
||||
"sha256:0fc0bf97920d454102168ec2008620066878848fcfca06c22b669696212e292f"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==5.1.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ipython": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:b038baa489c38f6d853a3cfc4c635b0cda66f2864d136fe8f40c1a6e334e2a6b",
|
||||
"sha256:f5102c1cd67e399ec8ea66bcebe6e3968ea25a8977e53f012963e5affeb1fe38"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"markers": "python_version >= '3.3'",
|
||||
"version": "==7.4.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ipython-genutils": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:72dd37233799e619666c9f639a9da83c34013a73e8bbc79a7a6348d93c61fab8",
|
||||
"sha256:eb2e116e75ecef9d4d228fdc66af54269afa26ab4463042e33785b887c628ba8"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.2.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ipywidgets": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:0f2b5cde9f272cb49d52f3f0889fdd1a7ae1e74f37b48dac35a83152780d2b7b",
|
||||
"sha256:a3e224f430163f767047ab9a042fc55adbcab0c24bbe6cf9f306c4f89fdf0ba3"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==7.4.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"isort": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:08f8e3f0f0b7249e9fad7e5c41e2113aba44969798a26452ee790c06f155d4ec",
|
||||
"sha256:4e9e9c4bd1acd66cf6c36973f29b031ec752cbfd991c69695e4e259f9a756927"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==4.3.16"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"jedi": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:2bb0603e3506f708e792c7f4ad8fc2a7a9d9c2d292a358fbbd58da531695595b",
|
||||
"sha256:2c6bcd9545c7d6440951b12b44d373479bf18123a401a52025cf98563fbd826c"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.13.3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"jinja2": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:74c935a1b8bb9a3947c50a54766a969d4846290e1e788ea44c1392163723c3bd",
|
||||
"sha256:f84be1bb0040caca4cea721fcbbbbd61f9be9464ca236387158b0feea01914a4"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==2.10"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"jsonschema": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:0c0a81564f181de3212efa2d17de1910f8732fa1b71c42266d983cd74304e20d",
|
||||
"sha256:a5f6559964a3851f59040d3b961de5e68e70971afb88ba519d27e6a039efff1a"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==3.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"jupyter": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:3e1f86076bbb7c8c207829390305a2b1fe836d471ed54be66a3b8c41e7f46cc7",
|
||||
"sha256:5b290f93b98ffbc21c0c7e749f054b3267782166d72fa5e3ed1ed4eaf34a2b78",
|
||||
"sha256:d9dc4b3318f310e34c82951ea5d6683f67bed7def4b259fafbfe4f1beb1d8e5f"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==1.0.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"jupyter-client": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:b5f9cb06105c1d2d30719db5ffb3ea67da60919fb68deaefa583deccd8813551",
|
||||
"sha256:c44411eb1463ed77548bc2d5ec0d744c9b81c4a542d9637c7a52824e2121b987"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==5.2.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"jupyter-console": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:308ce876354924fb6c540b41d5d6d08acfc946984bf0c97777c1ddcb42e0b2f5",
|
||||
"sha256:cc80a97a5c389cbd30252ffb5ce7cefd4b66bde98219edd16bf5cb6f84bb3568"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==6.0.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"jupyter-core": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:927d713ffa616ea11972534411544589976b2493fc7e09ad946e010aa7eb9970",
|
||||
"sha256:ba70754aa680300306c699790128f6fbd8c306ee5927976cbe48adacf240c0b7"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==4.4.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"livereload": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:29cadfabcedd12eed792e0131991235b9d4764d4474bed75cf525f57109ec0a2",
|
||||
"sha256:e632a6cd1d349155c1d7f13a65be873b38f43ef02961804a1bba8d817fa649a7"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==2.6.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"markdown": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:c00429bd503a47ec88d5e30a751e147dcb4c6889663cd3e2ba0afe858e009baa",
|
||||
"sha256:d02e0f9b04c500cde6637c11ad7c72671f359b87b9fe924b2383649d8841db7c"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==3.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"markdown-include": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:72a45461b589489a088753893bc95c5fa5909936186485f4ed55caa57d10250f"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==0.5.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"markupsafe": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:00bc623926325b26bb9605ae9eae8a215691f33cae5df11ca5424f06f2d1f473",
|
||||
"sha256:09027a7803a62ca78792ad89403b1b7a73a01c8cb65909cd876f7fcebd79b161",
|
||||
"sha256:09c4b7f37d6c648cb13f9230d847adf22f8171b1ccc4d5682398e77f40309235",
|
||||
"sha256:1027c282dad077d0bae18be6794e6b6b8c91d58ed8a8d89a89d59693b9131db5",
|
||||
"sha256:24982cc2533820871eba85ba648cd53d8623687ff11cbb805be4ff7b4c971aff",
|
||||
"sha256:29872e92839765e546828bb7754a68c418d927cd064fd4708fab9fe9c8bb116b",
|
||||
"sha256:43a55c2930bbc139570ac2452adf3d70cdbb3cfe5912c71cdce1c2c6bbd9c5d1",
|
||||
"sha256:46c99d2de99945ec5cb54f23c8cd5689f6d7177305ebff350a58ce5f8de1669e",
|
||||
"sha256:500d4957e52ddc3351cabf489e79c91c17f6e0899158447047588650b5e69183",
|
||||
"sha256:535f6fc4d397c1563d08b88e485c3496cf5784e927af890fb3c3aac7f933ec66",
|
||||
"sha256:62fe6c95e3ec8a7fad637b7f3d372c15ec1caa01ab47926cfdf7a75b40e0eac1",
|
||||
"sha256:6dd73240d2af64df90aa7c4e7481e23825ea70af4b4922f8ede5b9e35f78a3b1",
|
||||
"sha256:717ba8fe3ae9cc0006d7c451f0bb265ee07739daf76355d06366154ee68d221e",
|
||||
"sha256:79855e1c5b8da654cf486b830bd42c06e8780cea587384cf6545b7d9ac013a0b",
|
||||
"sha256:7c1699dfe0cf8ff607dbdcc1e9b9af1755371f92a68f706051cc8c37d447c905",
|
||||
"sha256:88e5fcfb52ee7b911e8bb6d6aa2fd21fbecc674eadd44118a9cc3863f938e735",
|
||||
"sha256:8defac2f2ccd6805ebf65f5eeb132adcf2ab57aa11fdf4c0dd5169a004710e7d",
|
||||
"sha256:98c7086708b163d425c67c7a91bad6e466bb99d797aa64f965e9d25c12111a5e",
|
||||
"sha256:9add70b36c5666a2ed02b43b335fe19002ee5235efd4b8a89bfcf9005bebac0d",
|
||||
"sha256:9bf40443012702a1d2070043cb6291650a0841ece432556f784f004937f0f32c",
|
||||
"sha256:ade5e387d2ad0d7ebf59146cc00c8044acbd863725f887353a10df825fc8ae21",
|
||||
"sha256:b00c1de48212e4cc9603895652c5c410df699856a2853135b3967591e4beebc2",
|
||||
"sha256:b1282f8c00509d99fef04d8ba936b156d419be841854fe901d8ae224c59f0be5",
|
||||
"sha256:b2051432115498d3562c084a49bba65d97cf251f5a331c64a12ee7e04dacc51b",
|
||||
"sha256:ba59edeaa2fc6114428f1637ffff42da1e311e29382d81b339c1817d37ec93c6",
|
||||
"sha256:c8716a48d94b06bb3b2524c2b77e055fb313aeb4ea620c8dd03a105574ba704f",
|
||||
"sha256:cd5df75523866410809ca100dc9681e301e3c27567cf498077e8551b6d20e42f",
|
||||
"sha256:e249096428b3ae81b08327a63a485ad0878de3fb939049038579ac0ef61e17e7"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.1.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"mccabe": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:ab8a6258860da4b6677da4bd2fe5dc2c659cff31b3ee4f7f5d64e79735b80d42",
|
||||
"sha256:dd8d182285a0fe56bace7f45b5e7d1a6ebcbf524e8f3bd87eb0f125271b8831f"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.6.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"mistune": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:59a3429db53c50b5c6bcc8a07f8848cb00d7dc8bdb431a4ab41920d201d4756e",
|
||||
"sha256:88a1051873018da288eee8538d476dffe1262495144b33ecb586c4ab266bb8d4"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.8.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"mkdocs": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:17d34329aad75d5de604b9ed4e31df3a4d235afefdc46ce7b1964fddb2e1e939",
|
||||
"sha256:8cc8b38325456b9e942c981a209eaeb1e9f3f77b493ad755bfef889b9c8d356a"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==1.0.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"mkdocs-material": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:0b394aa034b25a09a5874ae2a6ccc426fd81f5764e0991217b169e31cb0c1c0e",
|
||||
"sha256:f5bb80a2c16d045d380edb2c5b05636af1bb709cb859bfaa9d01063a11df803f"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==4.1.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"more-itertools": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:0125e8f60e9e031347105eb1682cef932f5e97d7b9a1a28d9bf00c22a5daef40",
|
||||
"sha256:590044e3942351a1bdb1de960b739ff4ce277960f2425ad4509446dbace8d9d1"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"markers": "python_version > '2.7'",
|
||||
"version": "==6.0.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"mypy": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:308c274eb8482fbf16006f549137ddc0d69e5a589465e37b99c4564414363ca7",
|
||||
"sha256:e80fd6af34614a0e898a57f14296d0dacb584648f0339c2e000ddbf0f4cc2f8d"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==0.670"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"mypy-extensions": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:37e0e956f41369209a3d5f34580150bcacfabaa57b33a15c0b25f4b5725e0812",
|
||||
"sha256:b16cabe759f55e3409a7d231ebd2841378fb0c27a5d1994719e340e4f429ac3e"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.4.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbconvert": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:302554a2e219bc0fc84f3edd3e79953f3767b46ab67626fdec16e38ba3f7efe4",
|
||||
"sha256:5de8fb2284422272a1d45abc77c07b888127550a6d602ce619592a2b08a474ff"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==5.4.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:b9a0dbdbd45bb034f4f8893cafd6f652ea08c8c1674ba83f2dc55d3955743b0b",
|
||||
"sha256:f7494ef0df60766b7cabe0a3651556345a963b74dbc16bc7c18479041170d402"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==4.4.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"notebook": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:18a98858c0331fb65a60f2ebb6439f8c0c4defd14ca363731b6cabc7f61624b4",
|
||||
"sha256:cc027a62be0f7756e0ef3d2d98458c4d7f4b3566449fb1a05891207f5bd9a1bf"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==5.7.6"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pandocfilters": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:b3dd70e169bb5449e6bc6ff96aea89c5eea8c5f6ab5e207fc2f521a2cf4a0da9"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.4.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"parso": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:4580328ae3f548b358f4901e38c0578229186835f0fa0846e47369796dd5bcc9",
|
||||
"sha256:68406ebd7eafe17f8e40e15a84b56848eccbf27d7c1feb89e93d8fca395706db"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.3.4"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pexpect": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:2a8e88259839571d1251d278476f3eec5db26deb73a70be5ed5dc5435e418aba",
|
||||
"sha256:3fbd41d4caf27fa4a377bfd16fef87271099463e6fa73e92a52f92dfee5d425b"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"markers": "sys_platform != 'win32'",
|
||||
"version": "==4.6.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pickleshare": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:87683d47965c1da65cdacaf31c8441d12b8044cdec9aca500cd78fc2c683afca",
|
||||
"sha256:9649af414d74d4df115d5d718f82acb59c9d418196b7b4290ed47a12ce62df56"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.7.5"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pluggy": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:19ecf9ce9db2fce065a7a0586e07cfb4ac8614fe96edf628a264b1c70116cf8f",
|
||||
"sha256:84d306a647cc805219916e62aab89caa97a33a1dd8c342e87a37f91073cd4746"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.9.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"prometheus-client": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:1b38b958750f66f208bcd9ab92a633c0c994d8859c831f7abc1f46724fcee490"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.6.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"prompt-toolkit": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:11adf3389a996a6d45cc277580d0d53e8a5afd281d0c9ec71b28e6f121463780",
|
||||
"sha256:2519ad1d8038fd5fc8e770362237ad0364d16a7650fb5724af6997ed5515e3c1",
|
||||
"sha256:977c6583ae813a37dc1c2e1b715892461fcbdaa57f6fc62f33a528c4886c8f55"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==2.0.9"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ptyprocess": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:923f299cc5ad920c68f2bc0bc98b75b9f838b93b599941a6b63ddbc2476394c0",
|
||||
"sha256:d7cc528d76e76342423ca640335bd3633420dc1366f258cb31d05e865ef5ca1f"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"markers": "os_name != 'nt'",
|
||||
"version": "==0.6.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"py": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:64f65755aee5b381cea27766a3a147c3f15b9b6b9ac88676de66ba2ae36793fa",
|
||||
"sha256:dc639b046a6e2cff5bbe40194ad65936d6ba360b52b3c3fe1d08a82dd50b5e53"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.8.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pycodestyle": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:95a2219d12372f05704562a14ec30bc76b05a5b297b21a5dfe3f6fac3491ae56",
|
||||
"sha256:e40a936c9a450ad81df37f549d676d127b1b66000a6c500caa2b085bc0ca976c"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==2.5.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pyflakes": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:17dbeb2e3f4d772725c777fabc446d5634d1038f234e77343108ce445ea69ce0",
|
||||
"sha256:d976835886f8c5b31d47970ed689944a0262b5f3afa00a5a7b4dc81e5449f8a2"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==2.1.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pygments": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:5ffada19f6203563680669ee7f53b64dabbeb100eb51b61996085e99c03b284a",
|
||||
"sha256:e8218dd399a61674745138520d0d4cf2621d7e032439341bc3f647bff125818d"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==2.3.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pymdown-extensions": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:25b0a7967fa697b5035e23340a48594e3e93acb10b06d74574218ace3347d1df",
|
||||
"sha256:6cf0cf36b5a03b291ace22dc2f320f4789ce56fbdb6635a3be5fadbf5d7694dd"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==6.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pyrsistent": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:3ca82748918eb65e2d89f222b702277099aca77e34843c5eb9d52451173970e2"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.14.11"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pytest": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:592eaa2c33fae68c7d75aacf042efc9f77b27c08a6224a4f59beab8d9a420523",
|
||||
"sha256:ad3ad5c450284819ecde191a654c09b0ec72257a2c711b9633d677c71c9850c4"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==4.3.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pytest-cov": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:0ab664b25c6aa9716cbf203b17ddb301932383046082c081b9848a0edf5add33",
|
||||
"sha256:230ef817450ab0699c6cc3c9c8f7a829c34674456f2ed8df1fe1d39780f7c87f"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==2.6.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"python-dateutil": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:7e6584c74aeed623791615e26efd690f29817a27c73085b78e4bad02493df2fb",
|
||||
"sha256:c89805f6f4d64db21ed966fda138f8a5ed7a4fdbc1a8ee329ce1b74e3c74da9e"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==2.8.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"python-multipart": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:f7bb5f611fc600d15fa47b3974c8aa16e93724513b49b5f95c81e6624c83fa43"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==0.0.5"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pytoml": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:ca2d0cb127c938b8b76a9a0d0f855cf930c1d50cc3a0af6d3595b566519a1013"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.1.20"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pyyaml": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:1adecc22f88d38052fb787d959f003811ca858b799590a5eaa70e63dca50308c",
|
||||
"sha256:436bc774ecf7c103814098159fbb84c2715d25980175292c648f2da143909f95",
|
||||
"sha256:460a5a4248763f6f37ea225d19d5c205677d8d525f6a83357ca622ed541830c2",
|
||||
"sha256:5a22a9c84653debfbf198d02fe592c176ea548cccce47553f35f466e15cf2fd4",
|
||||
"sha256:7a5d3f26b89d688db27822343dfa25c599627bc92093e788956372285c6298ad",
|
||||
"sha256:9372b04a02080752d9e6f990179a4ab840227c6e2ce15b95e1278456664cf2ba",
|
||||
"sha256:a5dcbebee834eaddf3fa7366316b880ff4062e4bcc9787b78c7fbb4a26ff2dd1",
|
||||
"sha256:aee5bab92a176e7cd034e57f46e9df9a9862a71f8f37cad167c6fc74c65f5b4e",
|
||||
"sha256:c51f642898c0bacd335fc119da60baae0824f2cde95b0330b56c0553439f0673",
|
||||
"sha256:c68ea4d3ba1705da1e0d85da6684ac657912679a649e8868bd850d2c299cce13",
|
||||
"sha256:e23d0cc5299223dcc37885dae624f382297717e459ea24053709675a976a3e19"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==5.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pyzmq": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:1651e52ed91f0736afd6d94ef9f3259b5534ce8beddb054f3d5ca989c4ef7c4f",
|
||||
"sha256:5ccb9b3d4cd20c000a9b75689d5add8cd3bce67fcbd0f8ae1b59345247d803af",
|
||||
"sha256:5e120c4cd3872e332fb35d255ad5998ebcee32ace4387b1b337416b6b90436c7",
|
||||
"sha256:5e2a3707c69a7281a9957f83718815fd74698cba31f6d69f9ed359921f662221",
|
||||
"sha256:63d51add9af8d0442dc90f916baf98fdc04e3b0a32afec4bfc83f8d85e72959f",
|
||||
"sha256:65c5a0bdc49e20f7d6b03a661f71e2fda7a99c51270cafe71598146d09810d0d",
|
||||
"sha256:66828fabe911aa545d919028441a585edb7c9c77969a5fea6722ef6e6ece38ab",
|
||||
"sha256:7d79427e82d9dad6e9b47c0b3e7ae5f9d489b1601e3a36ea629bb49501a4daf3",
|
||||
"sha256:824ee5d3078c4eae737ffc500fbf32f2b14e6ec89b26b435b7834febd70120cf",
|
||||
"sha256:89dc0a83cccec19ff3c62c091e43e66e0183d1e6b4658c16ee4e659518131494",
|
||||
"sha256:8b319805f6f7c907b101c864c3ca6cefc9db8ce0791356f180b1b644c7347e4c",
|
||||
"sha256:90facfb379ab47f94b19519c1ecc8ec8d10813b69d9c163117944948bdec5d15",
|
||||
"sha256:a0a178c7420021fc0730180a914a4b4b3092ce9696ceb8e72d0f60f8ce1655dd",
|
||||
"sha256:a7a89591ae315baccb8072f216614b3e59aed7385aef4393a6c741783d6ee9cf",
|
||||
"sha256:ba2578f0ae582452c02ed9fac2dc477b08e80ce05d2c0885becf5fff6651ccb0",
|
||||
"sha256:c69b0055c55702f5b0b6b354133e8325b9a56dbc80e1be2d240bead253fb9825",
|
||||
"sha256:ca434e1858fe222380221ddeb81e86f45522773344c9da63c311d17161df5e06",
|
||||
"sha256:d4b8ecfc3d92f114f04d5c40f60a65e5196198b827503341521dda12d8b14939",
|
||||
"sha256:d706025c47b09a54f005953ebe206f6d07a22516776faa4f509aaff681cc5468",
|
||||
"sha256:d8f27e958f8a2c0c8ffd4d8855c3ce8ac3fa1e105f0491ce31729aa2b3229740",
|
||||
"sha256:dbd264298f76b9060ce537008eb989317ca787c857e23cbd1b3ddf89f190a9b1",
|
||||
"sha256:e926d66f0df8fdbf03ba20583af0f215e475c667fb033d45fd031c66c63e34c9",
|
||||
"sha256:efc3bd48237f973a749f7312f68062f1b4ca5c2032a0673ca3ea8e46aa77187b",
|
||||
"sha256:f59bc782228777cbfe04555707a9c56d269c787ed25d6d28ed9d0fbb41cb1ad2",
|
||||
"sha256:f8da5322f4ff5f667a0d5a27e871b560c6637153c81e318b35cb012b2a98835c"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==18.0.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"qtconsole": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:1ac4a65e81a27b0838330a6d351c2f8435d4013d98a95373e8a41119b2968390",
|
||||
"sha256:bc1ba15f50c29ed50f1268ad823bb6543be263c18dd093b80495e9df63b003ac"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==4.4.3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"requests": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:502a824f31acdacb3a35b6690b5fbf0bc41d63a24a45c4004352b0242707598e",
|
||||
"sha256:7bf2a778576d825600030a110f3c0e3e8edc51dfaafe1c146e39a2027784957b"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==2.21.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"send2trash": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:60001cc07d707fe247c94f74ca6ac0d3255aabcb930529690897ca2a39db28b2",
|
||||
"sha256:f1691922577b6fa12821234aeb57599d887c4900b9ca537948d2dac34aea888b"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.5.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"six": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:3350809f0555b11f552448330d0b52d5f24c91a322ea4a15ef22629740f3761c",
|
||||
"sha256:d16a0141ec1a18405cd4ce8b4613101da75da0e9a7aec5bdd4fa804d0e0eba73"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.12.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sqlalchemy": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:781fb7b9d194ed3fc596b8f0dd4623ff160e3e825dd8c15472376a438c19598b"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.3.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"terminado": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:55abf9ade563b8f9be1f34e4233c7b7bde726059947a593322e8a553cc4c067a",
|
||||
"sha256:65011551baff97f5414c67018e908110693143cfbaeb16831b743fe7cad8b927"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.8.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"testpath": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:46c89ebb683f473ffe2aab0ed9f12581d4d078308a3cb3765d79c6b2317b0109",
|
||||
"sha256:b694b3d9288dbd81685c5d2e7140b81365d46c29f5db4bc659de5aa6b98780f8"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.4.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"toml": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:229f81c57791a41d65e399fc06bf0848bab550a9dfd5ed66df18ce5f05e73d5c",
|
||||
"sha256:235682dd292d5899d361a811df37e04a8828a5b1da3115886b73cf81ebc9100e"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.10.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"tornado": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:1174dcb84d08887b55defb2cda1986faeeea715fff189ef3dc44cce99f5fca6b",
|
||||
"sha256:2613fab506bd2aedb3722c8c64c17f8f74f4070afed6eea17f20b2115e445aec",
|
||||
"sha256:44b82bc1146a24e5b9853d04c142576b4e8fa7a92f2e30bc364a85d1f75c4de2",
|
||||
"sha256:457fcbee4df737d2defc181b9073758d73f54a6cfc1f280533ff48831b39f4a8",
|
||||
"sha256:49603e1a6e24104961497ad0c07c799aec1caac7400a6762b687e74c8206677d",
|
||||
"sha256:8c2f40b99a8153893793559919a355d7b74649a11e59f411b0b0a1793e160bc0",
|
||||
"sha256:e1d897889c3b5a829426b7d52828fb37b28bc181cd598624e65c8be40ee3f7fa"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==6.0.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"traitlets": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:9c4bd2d267b7153df9152698efb1050a5d84982d3384a37b2c1f7723ba3e7835",
|
||||
"sha256:c6cb5e6f57c5a9bdaa40fa71ce7b4af30298fbab9ece9815b5d995ab6217c7d9"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==4.3.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"typed-ast": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:035a54ede6ce1380599b2ce57844c6554666522e376bd111eb940fbc7c3dad23",
|
||||
"sha256:037c35f2741ce3a9ac0d55abfcd119133cbd821fffa4461397718287092d9d15",
|
||||
"sha256:049feae7e9f180b64efacbdc36b3af64a00393a47be22fa9cb6794e68d4e73d3",
|
||||
"sha256:19228f7940beafc1ba21a6e8e070e0b0bfd1457902a3a81709762b8b9039b88d",
|
||||
"sha256:2ea681e91e3550a30c2265d2916f40a5f5d89b59469a20f3bad7d07adee0f7a6",
|
||||
"sha256:3a6b0a78af298d82323660df5497bcea0f0a4a25a0b003afd0ce5af049bd1f60",
|
||||
"sha256:5385da8f3b801014504df0852bf83524599df890387a3c2b17b7caa3d78b1773",
|
||||
"sha256:606d8afa07eef77280c2bf84335e24390055b478392e1975f96286d99d0cb424",
|
||||
"sha256:69245b5b23bbf7fb242c9f8f08493e9ecd7711f063259aefffaeb90595d62287",
|
||||
"sha256:6f6d839ab09830d59b7fa8fb6917023d8cb5498ee1f1dbd82d37db78eb76bc99",
|
||||
"sha256:730888475f5ac0e37c1de4bd05eeb799fdb742697867f524dc8a4cd74bcecc23",
|
||||
"sha256:9819b5162ffc121b9e334923c685b0d0826154e41dfe70b2ede2ce29034c71d8",
|
||||
"sha256:9e60ef9426efab601dd9aa120e4ff560f4461cf8442e9c0a2b92548d52800699",
|
||||
"sha256:af5fbdde0690c7da68e841d7fc2632345d570768ea7406a9434446d7b33b0ee1",
|
||||
"sha256:b64efdbdf3bbb1377562c179f167f3bf301251411eb5ac77dec6b7d32bcda463",
|
||||
"sha256:bac5f444c118aeb456fac1b0b5d14c6a71ea2a42069b09c176f75e9bd4c186f6",
|
||||
"sha256:bda9068aafb73859491e13b99b682bd299c1b5fd50644d697533775828a28ee0",
|
||||
"sha256:d659517ca116e6750101a1326107d3479028c5191f0ecee3c7203c50f5b915b0",
|
||||
"sha256:eddd3fb1f3e0f82e5915a899285a39ee34ce18fd25d89582bc89fc9fb16cd2c6"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.3.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ujson": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:f66073e5506e91d204ab0c614a148d5aa938bdbf104751be66f8ad7a222f5f86"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==1.35"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"urllib3": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:61bf29cada3fc2fbefad4fdf059ea4bd1b4a86d2b6d15e1c7c0b582b9752fe39",
|
||||
"sha256:de9529817c93f27c8ccbfead6985011db27bd0ddfcdb2d86f3f663385c6a9c22"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==1.24.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uvicorn": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:d700b65169820fc260f39402b7f966c178691daaa40cb376cad99d7cd737f772"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"index": "pypi",
|
||||
"version": "==0.7.0b1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"uvloop": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:0fcd894f6fc3226a962ee7ad895c4f52e3f5c3c55098e21efb17c071849a0573",
|
||||
"sha256:2f31de1742c059c96cb76b91c5275b22b22b965c886ee1fced093fa27dde9e64",
|
||||
"sha256:459e4649fcd5ff719523de33964aa284898e55df62761e7773d088823ccbd3e0",
|
||||
"sha256:67867aafd6e0bc2c30a079603a85d83b94f23c5593b3cc08ec7e58ac18bf48e5",
|
||||
"sha256:8c200457e6847f28d8bb91c5e5039d301716f5f2fce25646f5fb3fd65eda4a26",
|
||||
"sha256:958906b9ca39eb158414fbb7d6b8ef1b7aee4db5c8e8e5d00fcbb69a1ce9dca7",
|
||||
"sha256:ac1dca3d8f3ef52806059e81042ee397ac939e5a86c8a3cea55d6b087db66115",
|
||||
"sha256:b284c22d8938866318e3b9d178142b8be316c52d16fcfe1560685a686718a021",
|
||||
"sha256:c48692bf4587ce281d641087658eca275a5ad3b63c78297bbded96570ae9ce8f",
|
||||
"sha256:fefc3b2b947c99737c348887db2c32e539160dcbeb7af9aa6b53db7a283538fe"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.12.2"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"wcwidth": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:3df37372226d6e63e1b1e1eda15c594bca98a22d33a23832a90998faa96bc65e",
|
||||
"sha256:f4ebe71925af7b40a864553f761ed559b43544f8f71746c2d756c7fe788ade7c"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.1.7"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"webencodings": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:a0af1213f3c2226497a97e2b3aa01a7e4bee4f403f95be16fc9acd2947514a78",
|
||||
"sha256:b36a1c245f2d304965eb4e0a82848379241dc04b865afcc4aab16748587e1923"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==0.5.1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"websockets": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:04b42a1b57096ffa5627d6a78ea1ff7fad3bc2c0331ffc17bc32a4024da7fea0",
|
||||
"sha256:08e3c3e0535befa4f0c4443824496c03ecc25062debbcf895874f8a0b4c97c9f",
|
||||
"sha256:10d89d4326045bf5e15e83e9867c85d686b612822e4d8f149cf4840aab5f46e0",
|
||||
"sha256:232fac8a1978fc1dead4b1c2fa27c7756750fb393eb4ac52f6bc87ba7242b2fa",
|
||||
"sha256:4bf4c8097440eff22bc78ec76fe2a865a6e658b6977a504679aaf08f02c121da",
|
||||
"sha256:51642ea3a00772d1e48fb0c492f0d3ae3b6474f34d20eca005a83f8c9c06c561",
|
||||
"sha256:55d86102282a636e195dad68aaaf85b81d0bef449d7e2ef2ff79ac450bb25d53",
|
||||
"sha256:564d2675682bd497b59907d2205031acbf7d3fadf8c763b689b9ede20300b215",
|
||||
"sha256:5d13bf5197a92149dc0badcc2b699267ff65a867029f465accfca8abab95f412",
|
||||
"sha256:5eda665f6789edb9b57b57a159b9c55482cbe5b046d7db458948370554b16439",
|
||||
"sha256:5edb2524d4032be4564c65dc4f9d01e79fe8fad5f966e5b552f4e5164fef0885",
|
||||
"sha256:79691794288bc51e2a3b8de2bc0272ca8355d0b8503077ea57c0716e840ebaef",
|
||||
"sha256:7fcc8681e9981b9b511cdee7c580d5b005f3bb86b65bde2188e04a29f1d63317",
|
||||
"sha256:8e447e05ec88b1b408a4c9cde85aa6f4b04f06aa874b9f0b8e8319faf51b1fee",
|
||||
"sha256:90ea6b3e7787620bb295a4ae050d2811c807d65b1486749414f78cfd6fb61489",
|
||||
"sha256:9e13239952694b8b831088431d15f771beace10edfcf9ef230cefea14f18508f",
|
||||
"sha256:d40f081187f7b54d7a99d8a5c782eaa4edc335a057aa54c85059272ed826dc09",
|
||||
"sha256:e1df1a58ed2468c7b7ce9a2f9752a32ad08eac2bcd56318625c3647c2cd2da6f",
|
||||
"sha256:e98d0cec437097f09c7834a11c69d79fe6241729b23f656cfc227e93294fc242",
|
||||
"sha256:f8d59627702d2ff27cb495ca1abdea8bd8d581de425c56e93bff6517134e0a9b",
|
||||
"sha256:fc30cdf2e949a2225b012a7911d1d031df3d23e99b7eda7dfc982dc4a860dae9"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==7.0"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"widgetsnbextension": {
|
||||
"hashes": [
|
||||
"sha256:14b2c65f9940c9a7d3b70adbe713dbd38b5ec69724eebaba034d1036cf3d4740",
|
||||
"sha256:fa618be8435447a017fd1bf2c7ae922d0428056cfc7449f7a8641edf76b48265"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"version": "==3.4.2"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
131
README.md
@@ -5,15 +5,18 @@
|
||||
<em>FastAPI framework, high performance, easy to learn, fast to code, ready for production</em>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://travis-ci.org/tiangolo/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://travis-ci.org/tiangolo/fastapi.svg?branch=master" alt="Build Status">
|
||||
<a href="https://travis-ci.com/tiangolo/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://travis-ci.com/tiangolo/fastapi.svg?branch=master" alt="Build Status">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://codecov.io/gh/tiangolo/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://codecov.io/gh/tiangolo/fastapi/branch/master/graph/badge.svg" alt="Coverage">
|
||||
<img src="https://img.shields.io/codecov/c/github/tiangolo/fastapi" alt="Coverage">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pypi.org/project/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://badge.fury.io/py/fastapi.svg" alt="Package version">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://badges.gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi.svg" alt="Join the chat at https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
@@ -36,10 +39,51 @@ The key features are:
|
||||
* **Easy**: Designed to be easy to use and learn. Less time reading docs.
|
||||
* **Short**: Minimize code duplication. Multiple features from each parameter declaration. Fewer bugs.
|
||||
* **Robust**: Get production-ready code. With automatic interactive documentation.
|
||||
* **Standards-based**: Based on (and fully compatible with) the open standards for APIs: <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification" target="_blank">OpenAPI</a> (previously known as Swagger) and <a href="http://json-schema.org/" target="_blank">JSON Schema</a>.
|
||||
* **Standards-based**: Based on (and fully compatible with) the open standards for APIs: <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI</a> (previously known as Swagger) and <a href="http://json-schema.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">JSON Schema</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
<small>* estimation based on tests on an internal development team, building production applications.</small>
|
||||
|
||||
## Opinions
|
||||
|
||||
"*[...] I'm using **FastAPI** a ton these days. [...] I'm actually planning to use it for all of my team's **ML services at Microsoft**. Some of them are getting integrated into the core **Windows** product and some **Office** products.*"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Kabir Khan - <strong>Microsoft</strong> <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/26" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*I’m over the moon excited about **FastAPI**. It’s so fun!*"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Brian Okken - <strong><a href="https://pythonbytes.fm/episodes/show/123/time-to-right-the-py-wrongs?time_in_sec=855" target="_blank">Python Bytes</a> podcast host</strong> <a href="https://twitter.com/brianokken/status/1112220079972728832" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*Honestly, what you've built looks super solid and polished. In many ways, it's what I wanted **Hug** to be - it's really inspiring to see someone build that.*"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Timothy Crosley - <strong><a href="http://www.hug.rest/" target="_blank">Hug</a> creator</strong> <a href="https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=19455465" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*If you're looking to learn one **modern framework** for building REST APIs, check out **FastAPI** [...] It's fast, easy to use and easy to learn [...]*"
|
||||
|
||||
"*We've switched over to **FastAPI** for our **APIs** [...] I think you'll like it [...]*"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Ines Montani - Matthew Honnibal - <strong><a href="https://explosion.ai" target="_blank">Explosion AI</a> founders - <a href="https://spacy.io" target="_blank">spaCy</a> creators</strong> <a href="https://twitter.com/_inesmontani/status/1144173225322143744" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a> - <a href="https://twitter.com/honnibal/status/1144031421859655680" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*We adopted the **FastAPI** library to spawn a **REST** server that can be queried to obtain **predictions**. [for Ludwig]*"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Piero Molino, Yaroslav Dudin, and Sai Sumanth Miryala - <strong>Uber</strong> <a href="https://eng.uber.com/ludwig-v0-2/" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## **Typer**, the FastAPI of CLIs
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com" target="_blank"><img src="https://typer.tiangolo.com/img/logo-margin/logo-margin-vector.svg" style="width: 20%;"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
If you are building a <abbr title="Command Line Interface">CLI</abbr> app to be used in the terminal instead of a web API, check out <a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">**Typer**</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
**Typer** is FastAPI's little sibling. And it's intended to be the **FastAPI of CLIs**. ⌨️ 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,22 +91,33 @@ Python 3.6+
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI stands on the shoulders of giants:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" target="_blank">Starlette</a> for the web parts.
|
||||
* <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/" target="_blank">Pydantic</a> for the data parts.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette</a> for the web parts.
|
||||
* <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic</a> for the data parts.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install fastapi
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will also need an ASGI server, for production such as <a href="http://www.uvicorn.org" target="_blank">uvicorn</a>.
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
You will also need an ASGI server, for production such as <a href="http://www.uvicorn.org" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uvicorn</a> or <a href="https://gitlab.com/pgjones/hypercorn" class="external-link" target="_blank">Hypercorn</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install uvicorn
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
### Create it
|
||||
@@ -84,6 +139,7 @@ def read_root():
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown="1">
|
||||
<summary>Or use <code>async def</code>...</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -106,7 +162,7 @@ async def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't know, check the _"In a hurry?"_ section about <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/async/#in-a-hurry" target="_blank">`async` and `await` in the docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
@@ -115,10 +171,20 @@ If you don't know, check the _"In a hurry?"_ section about <a href="https://fast
|
||||
|
||||
Run the server with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uvicorn main:app --reload
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --reload
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Started reloader process [28720]
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Started server process [28722]
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Waiting for application startup.
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Application startup complete.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown="1">
|
||||
<summary>About the command <code>uvicorn main:app --reload</code>...</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -132,7 +198,7 @@ The command `uvicorn main:app` refers to:
|
||||
|
||||
### Check it
|
||||
|
||||
Open your browser at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/5?q=somequery" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/5?q=somequery</a>.
|
||||
Open your browser at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/5?q=somequery" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/5?q=somequery</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the JSON response as:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -149,18 +215,17 @@ You already created an API that:
|
||||
|
||||
### Interactive API docs
|
||||
|
||||
Now go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
Now go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the automatic interactive API documentation (provided by <a href="https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui" target="_blank">Swagger UI</a>):
|
||||
You will see the automatic interactive API documentation (provided by <a href="https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui" class="external-link" target="_blank">Swagger UI</a>):
|
||||
|
||||
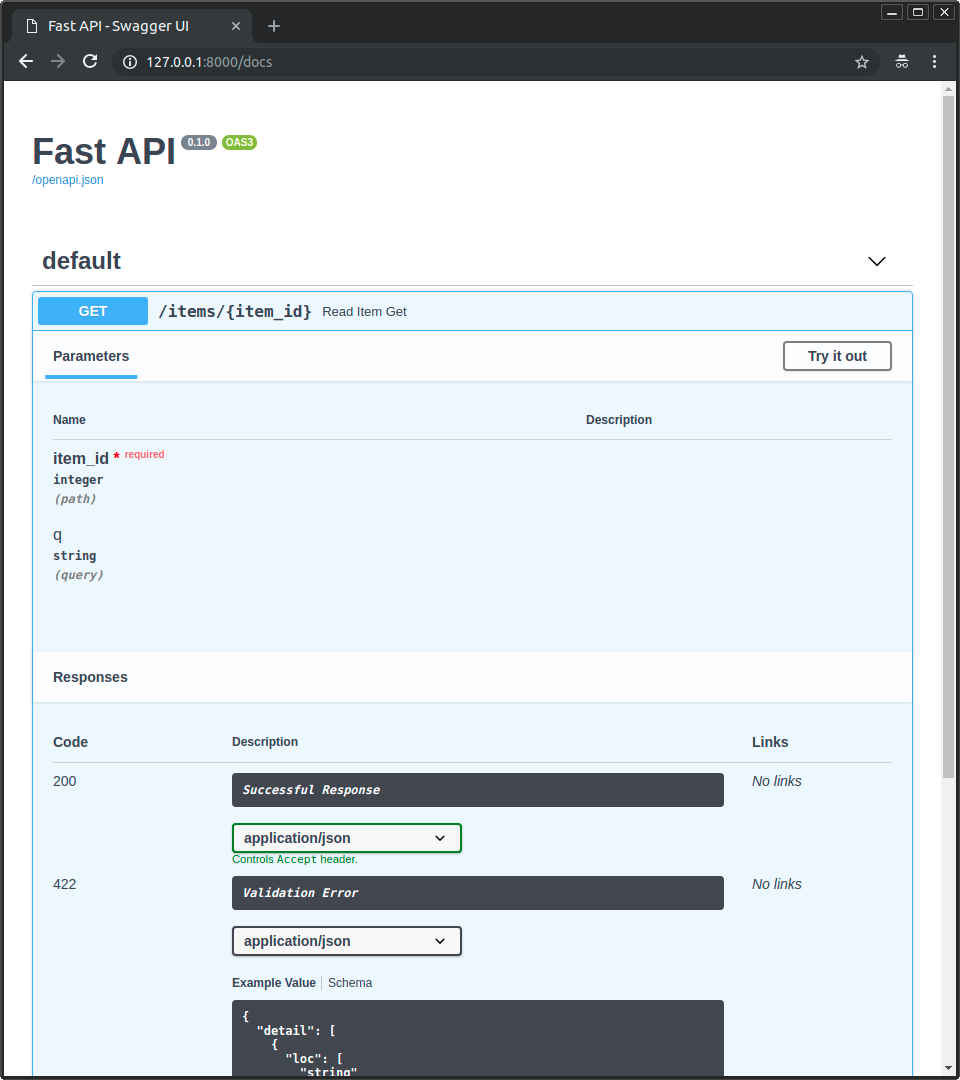
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Alternative API docs
|
||||
|
||||
And now, go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc</a>.
|
||||
And now, go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the alternative automatic documentation (provided by <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc" target="_blank">ReDoc</a>):
|
||||
You will see the alternative automatic documentation (provided by <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">ReDoc</a>):
|
||||
|
||||
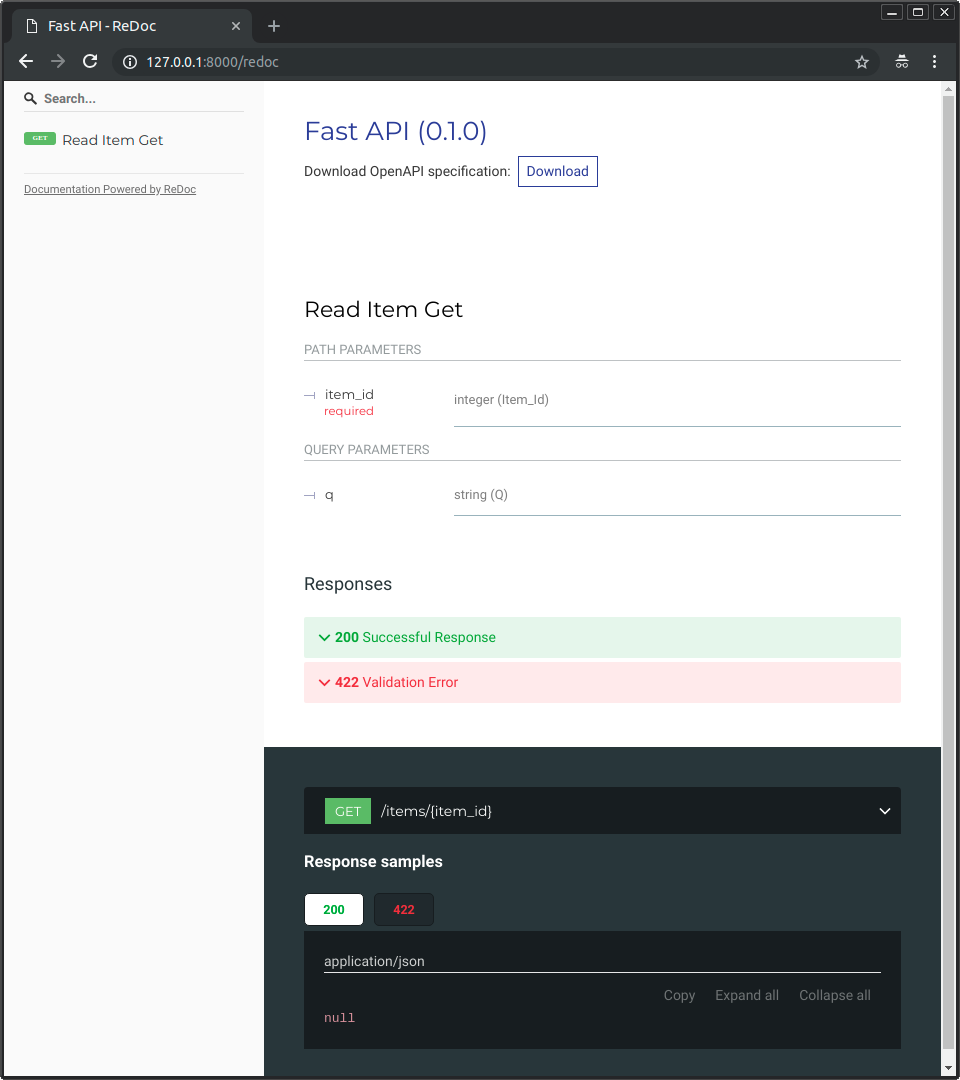
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -170,8 +235,7 @@ Now modify the file `main.py` to receive a body from a `PUT` request.
|
||||
|
||||
Declare the body using standard Python types, thanks to Pydantic.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 7 8 9 10 24"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 7 8 9 10 23 24 25"
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -195,7 +259,7 @@ def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
def create_item(item_id: int, item: Item):
|
||||
def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):
|
||||
return {"item_name": item.name, "item_id": item_id}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -203,7 +267,7 @@ The server should reload automatically (because you added `--reload` to the `uvi
|
||||
|
||||
### Interactive API docs upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
Now go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
Now go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* The interactive API documentation will be automatically updated, including the new body:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -217,16 +281,14 @@ Now go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:
|
||||
|
||||
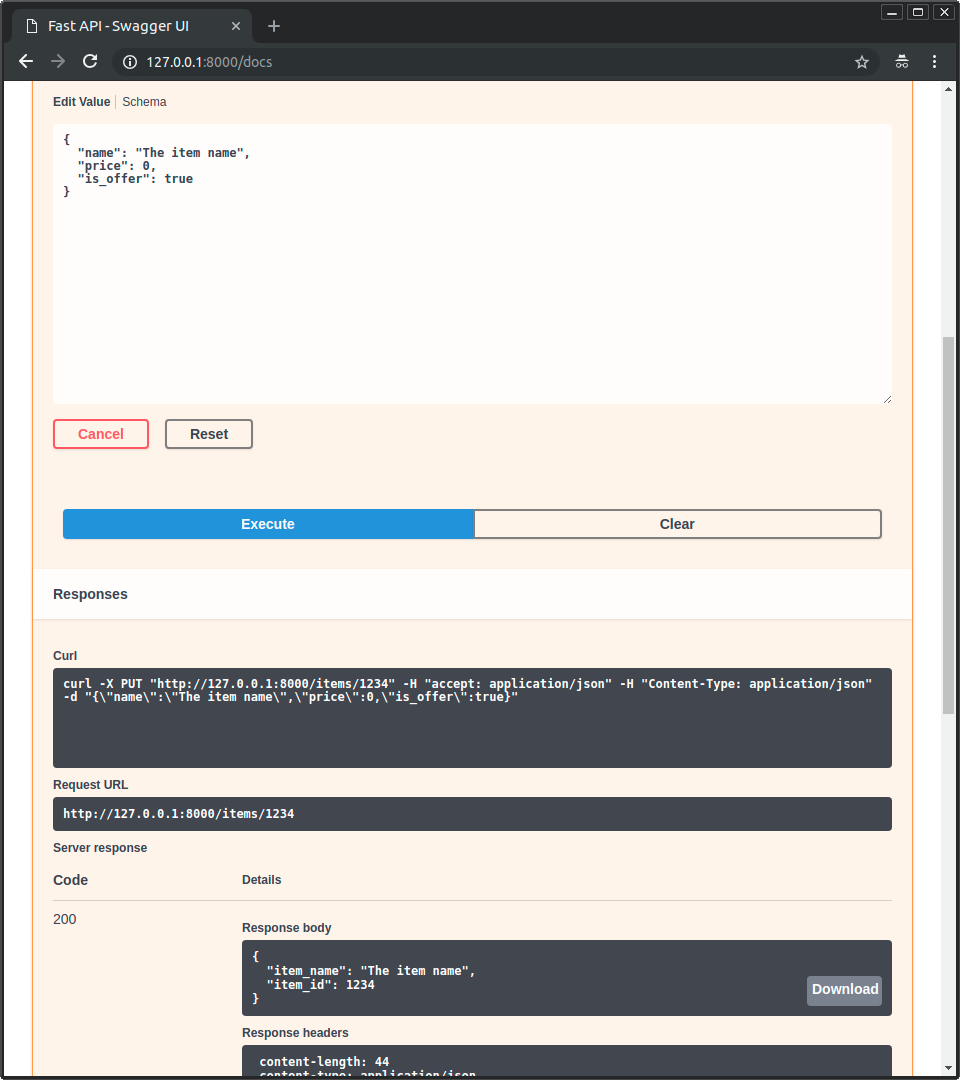
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Alternative API docs upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
And now, go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc</a>.
|
||||
And now, go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* The alternative documentation will also reflect the new query parameter and body:
|
||||
|
||||
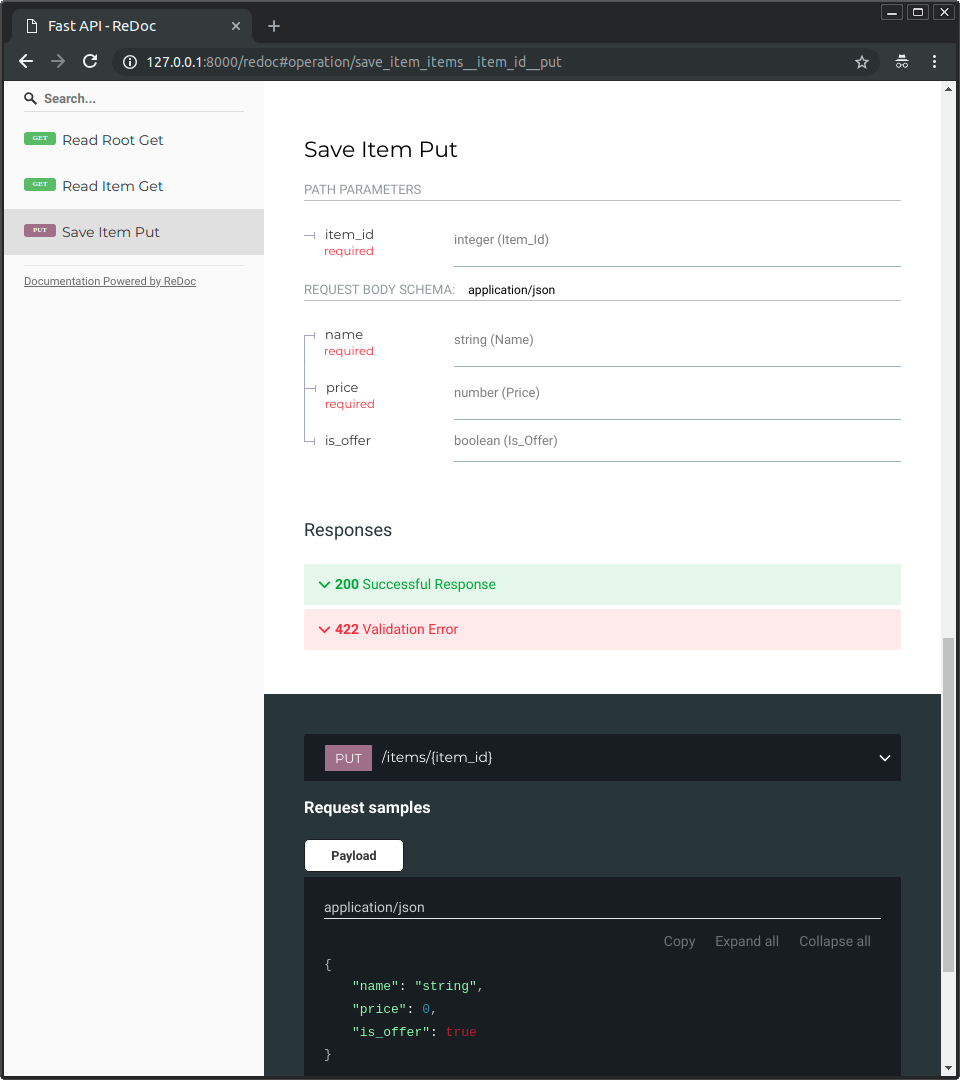
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Recap
|
||||
|
||||
In summary, you declare **once** the types of parameters, body, etc. as function parameters.
|
||||
@@ -287,7 +349,7 @@ Coming back to the previous code example, **FastAPI** will:
|
||||
* Without the `None` it would be required (as is the body in the case with `PUT`).
|
||||
* For `PUT` requests to `/items/{item_id}`, Read the body as JSON:
|
||||
* Check that it has a required attribute `name` that should be a `str`.
|
||||
* Check that is has a required attribute `price` that has to be a `float`.
|
||||
* Check that it has a required attribute `price` that has to be a `float`.
|
||||
* Check that it has an optional attribute `is_offer`, that should be a `bool`, if present.
|
||||
* All this would also work for deeply nested JSON objects.
|
||||
* Convert from and to JSON automatically.
|
||||
@@ -296,7 +358,6 @@ Coming back to the previous code example, **FastAPI** will:
|
||||
* Automatic client code generation systems, for many languages.
|
||||
* Provide 2 interactive documentation web interfaces directly.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
We just scratched the surface, but you already get the idea of how it all works.
|
||||
@@ -323,8 +384,7 @@ Try changing the line with:
|
||||
|
||||
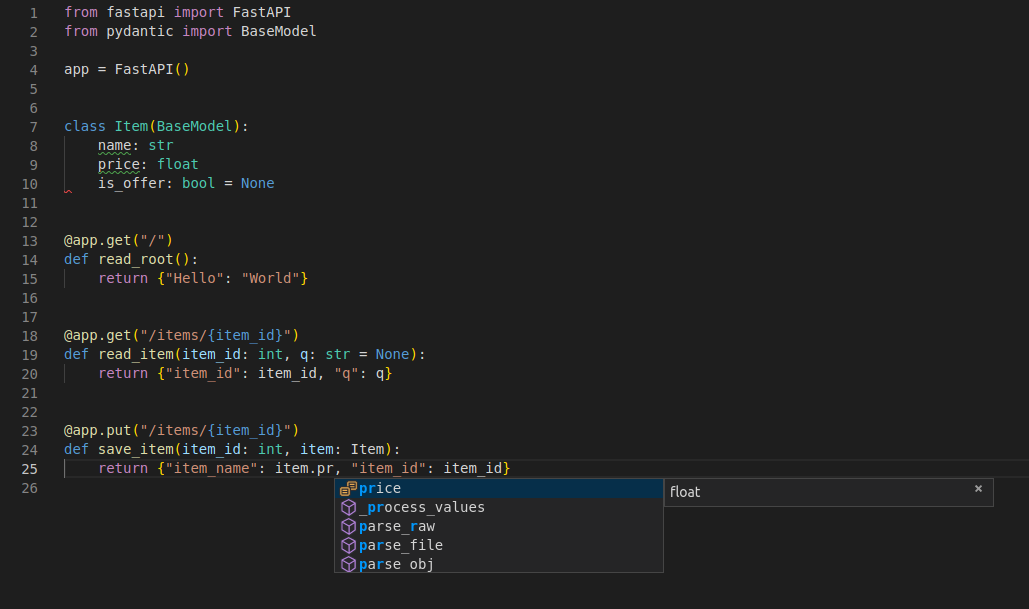
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For a more complete example including more features, see the <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/intro/">Tutorial - User Guide</a>.
|
||||
For a more complete example including more features, see the <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/">Tutorial - User Guide</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
**Spoiler alert**: the tutorial - user guide includes:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -341,12 +401,11 @@ For a more complete example including more features, see the <a href="https://fa
|
||||
* **Cookie Sessions**
|
||||
* ...and more.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Performance
|
||||
|
||||
Independent TechEmpower benchmarks show **FastAPI** applications running under Uvicorn as <a href="https://www.techempower.com/benchmarks/#section=test&runid=7464e520-0dc2-473d-bd34-dbdfd7e85911&hw=ph&test=query&l=zijzen-7" target="_blank">one of the fastest Python frameworks available</a>, only below Starlette and Uvicorn themselves (used internally by FastAPI). (*)
|
||||
Independent TechEmpower benchmarks show **FastAPI** applications running under Uvicorn as <a href="https://www.techempower.com/benchmarks/#section=test&runid=7464e520-0dc2-473d-bd34-dbdfd7e85911&hw=ph&test=query&l=zijzen-7" class="external-link" target="_blank">one of the fastest Python frameworks available</a>, only below Starlette and Uvicorn themselves (used internally by FastAPI). (*)
|
||||
|
||||
To understand more about it, see the section <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/benchmarks/" target="_blank">Benchmarks</a>.
|
||||
To understand more about it, see the section <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/benchmarks/" class="internal-link" target="_blank">Benchmarks</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Optional Dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -355,7 +414,6 @@ Used by Pydantic:
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/esnme/ultrajson" target="_blank"><code>ujson</code></a> - for faster JSON <abbr title="converting the string that comes from an HTTP request into Python data">"parsing"</abbr>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/JoshData/python-email-validator" target="_blank"><code>email_validator</code></a> - for email validation.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Used by Starlette:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="http://docs.python-requests.org" target="_blank"><code>requests</code></a> - Required if you want to use the `TestClient`.
|
||||
@@ -363,15 +421,16 @@ Used by Starlette:
|
||||
* <a href="http://jinja.pocoo.org" target="_blank"><code>jinja2</code></a> - Required if you want to use the default template configuration.
|
||||
* <a href="https://andrew-d.github.io/python-multipart/" target="_blank"><code>python-multipart</code></a> - Required if you want to support form <abbr title="converting the string that comes from an HTTP request into Python data">"parsing"</abbr>, with `request.form()`.
|
||||
* <a href="https://pythonhosted.org/itsdangerous/" target="_blank"><code>itsdangerous</code></a> - Required for `SessionMiddleware` support.
|
||||
* <a href="https://pyyaml.org/wiki/PyYAMLDocumentation" target="_blank"><code>pyyaml</code></a> - Required for `SchemaGenerator` support.
|
||||
* <a href="https://pyyaml.org/wiki/PyYAMLDocumentation" target="_blank"><code>pyyaml</code></a> - Required for Starlette's `SchemaGenerator` support (you probably don't need it with FastAPI).
|
||||
* <a href="https://graphene-python.org/" target="_blank"><code>graphene</code></a> - Required for `GraphQLApp` support.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/esnme/ultrajson" target="_blank"><code>ujson</code></a> - Required if you want to use `UJSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
Used by FastAPI / Starlette:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="http://www.uvicorn.org" target="_blank"><code>uvicorn</code></a> - for the server that loads and serves your application.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/ijl/orjson" target="_blank"><code>orjson</code></a> - Required if you want to use `ORJSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can install all of these with `pip3 install fastapi[all]`.
|
||||
You can install all of these with `pip install fastapi[all]`.
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,123 +0,0 @@
|
||||
First, you might want to see the basic ways to <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/help-fastapi/" target="_blank">help FastAPI and get help</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Developing
|
||||
|
||||
If you already cloned the repository and you know that you need to deep dive in the code, here are some guidelines to set up your environment.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Pipenv
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using <a href="https://pipenv.readthedocs.io/en/latest/" target="_blank">Pipenv</a>, you can create a virtual environment and install the packages with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pipenv install --dev
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can activate that virtual environment with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pipenv shell
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### No Pipenv
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not using Pipenv, you can create a virtual environment with your preferred tool, and install the packages listed in the file `Pipfile`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Flit
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** uses <a href="https://flit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html" target="_blank">Flit</a> to build, package and publish the project.
|
||||
|
||||
If you installed the development dependencies with one of the methods above, you already have the `flit` command.
|
||||
|
||||
To install your local version of FastAPI as a package in your local environment, run:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
flit install --symlink
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It will install your local FastAPI in your local environment.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using your local FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
If you create a Python file that imports and uses FastAPI, and run it with the Python from your local environment, it will use your local FastAPI source code.
|
||||
|
||||
And if you update that local FastAPI source code, as it is installed with `--symlink`, when you run that Python file again, it will use the fresh version of FastAPI you just edited.
|
||||
|
||||
That way, you don't have to "install" your local version to be able to test every change.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Format
|
||||
|
||||
There is a script that you can run that will format and clean all your code:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
bash scripts/lint.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It will also auto-sort all your imports.
|
||||
|
||||
For it to sort them correctly, you need to have FastAPI installed locally in your environment, with the command in the section above:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
flit install --symlink
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Docs
|
||||
|
||||
The documentation uses <a href="https://www.mkdocs.org/" target="_blank">MkDocs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
All the documentation is in Markdown format in the directory `./docs`.
|
||||
|
||||
Many of the tutorials have blocks of code.
|
||||
|
||||
In most of the cases, these blocks of code are actual complete applications that can be run as is.
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, those blocks of code are not written inside the Markdown, they are Python files in the `./docs/src/` directory.
|
||||
|
||||
And those Python files are included/injected in the documentation when generating the site.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Docs for tests
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the tests actually run against the example source files in the documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
This helps making sure that:
|
||||
|
||||
* The documentation is up to date.
|
||||
* The documentation examples can be run as is.
|
||||
* Most of the features are covered by the documentation, ensured by the coverage tests.
|
||||
|
||||
During local development, there is a script that builds the site and checks for any changes, live-reloading:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
bash scripts/docs-live.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It will serve the documentation on `http://0.0.0.0:8008`.
|
||||
|
||||
That way, you can edit the documentation/source files and see the changes live.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Apps and docs at the same time
|
||||
|
||||
And if you run the examples with, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uvicorn tutorial001:app --reload
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
as Uvicorn by default will use the port `8000`, the documentation on port `8008` won't clash.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Tests
|
||||
|
||||
There is a script that you can run locally to test all the code and generate coverage reports in HTML:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
bash scripts/test-cov-html.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command generates a directory `./htmlcov/`, if you open the file `./htmlcov/index.html` in your browser, you can explore interactively the regions of code that are covered by the tests, and notice if there is any region missing.
|
||||
@@ -1,254 +0,0 @@
|
||||
It is recommended to use <a href="https://www.docker.com/" target="_blank">**Docker**</a> for security, replicability, development simplicity, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
In this section you'll see instructions and links to guides to know how to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Make your **FastAPI** application a Docker image/container with maximum performance. In about **5 min**.
|
||||
* (Optionally) understand what you, as a developer, need to know about HTTPS.
|
||||
* Set up a Docker Swarm mode cluster with automatic HTTPS, even on a simple $5 USD/month server. In about **20 min**.
|
||||
* Generate and deploy a full **FastAPI** application, using your Docker Swarm cluster, with HTTPS, etc. In about **10 min**.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
You can also easily use **FastAPI** in a standard server directly too (without Docker).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Docker
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Docker, you can use the official Docker image:
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi-docker" target="_blank">tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi</a>
|
||||
|
||||
This image has an "auto-tuning" mechanism included, so that you can just add your code and get very high performance automatically. And without making sacrifices.
|
||||
|
||||
But you can still change and update all the configurations with environment variables or configuration files.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
To see all the configurations and options, go to the Docker image page: <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi-docker" target="_blank">tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a `Dockerfile`
|
||||
|
||||
* Go to your project directory.
|
||||
* Create a `Dockerfile` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Dockerfile
|
||||
FROM tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi:python3.7
|
||||
|
||||
COPY ./app /app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Bigger Applications
|
||||
|
||||
If you followed the section about creating <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/bigger-applications/" target="_blank">Bigger Applications with Multiple Files
|
||||
</a>, your `Dockerfile` might instead look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Dockerfile
|
||||
FROM tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi:python3.7
|
||||
|
||||
COPY ./app /app/app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Raspberry Pi and other architectures
|
||||
|
||||
If you are running Docker in a Raspberry Pi (that has an ARM processor) or any other architecture, you can create a `Dockerfile` from scratch, based on a Python base image (that is multi-architecture) and use Uvicorn alone.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, your `Dockerfile` could look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Dockerfile
|
||||
FROM python:3.7
|
||||
|
||||
RUN pip install fastapi uvicorn
|
||||
|
||||
EXPOSE 80
|
||||
|
||||
COPY ./app /app
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["uvicorn", "app.main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "80"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the **FastAPI** Code
|
||||
|
||||
* Create an `app` directory and enter in it.
|
||||
* Create a `main.py` file with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/")
|
||||
def read_root():
|
||||
return {"Hello": "World"}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* You should now have a directory structure like:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
├── app
|
||||
│ └── main.py
|
||||
└── Dockerfile
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Build the Docker image
|
||||
|
||||
* Go to the project directory (in where your `Dockerfile` is, containing your `app` directory).
|
||||
* Build your FastAPI image:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker build -t myimage .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Start the Docker container
|
||||
|
||||
* Run a container based on your image:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
docker run -d --name mycontainer -p 80:80 myimage
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have an optimized FastAPI server in a Docker container. Auto-tuned for your current server (and number of CPU cores).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Check it
|
||||
|
||||
You should be able to check it in your Docker container's URL, for example: <a href="http://192.168.99.100/items/5?q=somequery" target="_blank">http://192.168.99.100/items/5?q=somequery</a> or <a href="http://127.0.0.1/items/5?q=somequery" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1/items/5?q=somequery</a> (or equivalent, using your Docker host).
|
||||
|
||||
You will see something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{"item_id": 5, "q": "somequery"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Interactive API docs
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can go to <a href="http://192.168.99.100/docs" target="_blank">http://192.168.99.100/docs</a> or <a href="http://127.0.0.1/docs" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1/docs</a> (or equivalent, using your Docker host).
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the automatic interactive API documentation (provided by <a href="https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui" target="_blank">Swagger UI</a>):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Alternative API docs
|
||||
|
||||
And you can also go to <a href="http://192.168.99.100/redoc" target="_blank">http://192.168.99.100/redoc</a> or <a href="http://127.0.0.1/redoc" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1/redoc</a> (or equivalent, using your Docker host).
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the alternative automatic documentation (provided by <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc" target="_blank">ReDoc</a>):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## HTTPS
|
||||
|
||||
### About HTTPS
|
||||
|
||||
It is easy to assume that HTTPS is something that is just "enabled" or not.
|
||||
|
||||
But it is way more complex than that.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
If you are in a hurry or don't care, continue with the next section for step by step instructions to set everything up.
|
||||
|
||||
To learn the basics of HTTPS, from a consumer perspective, check <a href="https://howhttps.works/" target="_blank">https://howhttps.works/</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, from a developer's perspective, here are several things to have in mind while thinking about HTTPS:
|
||||
|
||||
* For HTTPS, the server needs to have "certificates" generated by a third party.
|
||||
* Those certificates are actually acquired from the third-party, not "generated".
|
||||
* Certificates have a lifetime.
|
||||
* They expire.
|
||||
* And then they need to be renewed, acquired again from the third party.
|
||||
* The encryption of the connection happens at the TCP level.
|
||||
* That's one layer below HTTP.
|
||||
* So, the certificate and encryption handling is done before HTTP.
|
||||
* TCP doesn't know about "domains". Only about IP addresses.
|
||||
* The information about the specific domain requested goes in the HTTP data.
|
||||
* The HTTPS certificates "certificate" a certain domain, but the protocol and encryption happen at the TCP level, before knowing which domain is being dealt with.
|
||||
* By default, that would mean that you can only have one HTTPS certificate per IP address.
|
||||
* No matter how big is your server and how small each application you have there might be. But...
|
||||
* There's an extension to the TLS protocol (the one handling the encryption at the TCP level, before HTTP) called <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Server_Name_Indication" target="_blank"><abbr title="Server Name Indication">SNI</abbr></a>.
|
||||
* This SNI extension allows one single server (with a single IP address) to have several HTTPS certificates and server multiple HTTPS domains/applications.
|
||||
* For this to work, a single component (program) running in the server, listening in the public IP address, must have all the HTTPS certificates in the server.
|
||||
* After having a secure connection, the communication protocol is the same HTTP.
|
||||
* It goes encrypted, but the encrypted contents are the same HTTP protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
It is a common practice to have one program/HTTP server running in the server (the machine, host, etc) and managing all the HTTPS parts, sending the decrypted HTTP requests to the actual HTTP application running in the same server (the **FastAPI** application, in this case), take the HTTP response from the application, encrypt it using the appropriate certificate and sending it back to the client using HTTPS. This server is ofter called a <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TLS_termination_proxy" target="_blank">TLS Termination Proxy</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Let's Encrypt
|
||||
|
||||
Up to some years ago, these HTTPS certificates were sold by trusted third-parties.
|
||||
|
||||
The process to acquire one of these certificates used to be cumbersome, require quite some paperwork and the certificates were quite expensive.
|
||||
|
||||
But then <a href="https://letsencrypt.org/" target="_blank">Let's Encrypt</a> was created.
|
||||
|
||||
It is a project from the Linux Foundation. It provides HTTPS certificates for free. In an automated way. These certificates use all the standard cryptographic security, and are short lived (about 3 months), so, the security is actually increased, by reducing their lifespan.
|
||||
|
||||
The domain's are securely verified and the certificates are generated automatically. This also allows automatizing the renewal of these certificates.
|
||||
|
||||
The idea is to automatize the acquisition and renewal of these certificates, so that you can have secure HTTPS, free, forever.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Traefik
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://traefik.io/" target="_blank">Traefik</a> is a high performance reverse proxy / load balancer. It can do the "TLS Termination Proxy" job (apart from other features).
|
||||
|
||||
It has integration with Let's Encrypt. So, it can handle all the HTTPS parts, including certificate acquisition and renewal.
|
||||
|
||||
It also has integrations with Docker. So, you can declare your domains in each application configurations and have it read those configurations, generate the HTTPS certificates and serve HTTPS to your application, all automatically. Without requiring any change in its configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
With this information and tools, continue with the next section to combine everything.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Docker Swarm mode cluster with Traefik and HTTPS
|
||||
|
||||
You can have a Docker Swarm mode cluster set up in minutes (about 20 min) with a main Traefik handling HTTPS (including certificate acquisition and renewal).
|
||||
|
||||
By using Docker Swarm mode, you can start with a "cluster" of a single machine (it can even be a $5 USD / month server) and then you can grow as much as you need adding more servers.
|
||||
|
||||
To set up a Docker Swarm Mode cluster with Traefik and HTTPS handling, follow this guide:
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://medium.com/@tiangolo/docker-swarm-mode-and-traefik-for-a-https-cluster-20328dba6232" target="_blank">Docker Swarm Mode and Traefik for an HTTPS cluster</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Deploy a FastAPI application
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to set everything up, would be using the <a href="/project-generation/" target="_blank">FastAPI project generator</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
It is designed to be integrated with this Docker Swarm cluster with Traefik and HTTPS described above.
|
||||
|
||||
You can generate a project in about 2 min.
|
||||
|
||||
The generated project has instructions to deploy it, doing it takes other 2 min.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Alternatively, deploy **FastAPI** without Docker
|
||||
|
||||
You can deploy **FastAPI** directly without Docker too.
|
||||
|
||||
You just need to install <a href="https://www.uvicorn.org/" target="_blank">Uvicorn</a> (or any other ASGI server).
|
||||
|
||||
And run your application the same way you have done in the tutorials, but without the `--reload` option, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uvicorn main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 80
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You might want to set up some tooling to make sure it is restarted automatically if it stops.
|
||||
|
||||
You might also want to install <a href="https://gunicorn.org/" target="_blank">Gunicorn</a> and <a href="https://www.uvicorn.org/#running-with-gunicorn" target="_blank">use it as a manager for Uvicorn</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
Making sure to fine-tune the number of workers, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
But if you are doing all that, you might just use the Docker image that does it automatically.
|
||||
240
docs/en/docs/advanced/additional-responses.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,240 @@
|
||||
# Additional Responses in OpenAPI
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
This is a rather advanced topic.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are starting with **FastAPI**, you might not need this.
|
||||
|
||||
You can declare additional responses, with additional status codes, media types, descriptions, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Those additional responses will be included in the OpenAPI schema, so they will also appear in the API docs.
|
||||
|
||||
But for those additional responses you have to make sure you return a `Response` like `JSONResponse` directly, with your status code and content.
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional Response with `model`
|
||||
|
||||
You can pass to your *path operation decorators* a parameter `responses`.
|
||||
|
||||
It receives a `dict`, the keys are status codes for each response, like `200`, and the values are other `dict`s with the information for each of them.
|
||||
|
||||
Each of those response `dict`s can have a key `model`, containing a Pydantic model, just like `response_model`.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** will take that model, generate its JSON Schema and include it in the correct place in OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to declare another response with a status code `404` and a Pydantic model `Message`, you can write:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="18 23"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/additional_responses/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
Have in mind that you have to return the `JSONResponse` directly.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
The `model` key is not part of OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** will take the Pydantic model from there, generate the `JSON Schema`, and put it in the correct place.
|
||||
|
||||
The correct place is:
|
||||
|
||||
* In the key `content`, that has as value another JSON object (`dict`) that contains:
|
||||
* A key with the media type, e.g. `application/json`, that contains as value another JSON object, that contains:
|
||||
* A key `schema`, that has as the value the JSON Schema from the model, here's the correct place.
|
||||
* **FastAPI** adds a reference here to the global JSON Schemas in another place in your OpenAPI instead of including it directly. This way, other applications and clients can use those JSON Schemas directly, provide better code generation tools, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
The generated responses in the OpenAPI for this *path operation* will be:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON hl_lines="3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12"
|
||||
{
|
||||
"responses": {
|
||||
"404": {
|
||||
"description": "Additional Response",
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"application/json": {
|
||||
"schema": {
|
||||
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/Message"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"200": {
|
||||
"description": "Successful Response",
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"application/json": {
|
||||
"schema": {
|
||||
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/Item"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"422": {
|
||||
"description": "Validation Error",
|
||||
"content": {
|
||||
"application/json": {
|
||||
"schema": {
|
||||
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/HTTPValidationError"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The schemas are referenced to another place inside the OpenAPI schema:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON hl_lines="4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16"
|
||||
{
|
||||
"components": {
|
||||
"schemas": {
|
||||
"Message": {
|
||||
"title": "Message",
|
||||
"required": [
|
||||
"message"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"type": "object",
|
||||
"properties": {
|
||||
"message": {
|
||||
"title": "Message",
|
||||
"type": "string"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"Item": {
|
||||
"title": "Item",
|
||||
"required": [
|
||||
"id",
|
||||
"value"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"type": "object",
|
||||
"properties": {
|
||||
"id": {
|
||||
"title": "Id",
|
||||
"type": "string"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"value": {
|
||||
"title": "Value",
|
||||
"type": "string"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"ValidationError": {
|
||||
"title": "ValidationError",
|
||||
"required": [
|
||||
"loc",
|
||||
"msg",
|
||||
"type"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"type": "object",
|
||||
"properties": {
|
||||
"loc": {
|
||||
"title": "Location",
|
||||
"type": "array",
|
||||
"items": {
|
||||
"type": "string"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"msg": {
|
||||
"title": "Message",
|
||||
"type": "string"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"type": {
|
||||
"title": "Error Type",
|
||||
"type": "string"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"HTTPValidationError": {
|
||||
"title": "HTTPValidationError",
|
||||
"type": "object",
|
||||
"properties": {
|
||||
"detail": {
|
||||
"title": "Detail",
|
||||
"type": "array",
|
||||
"items": {
|
||||
"$ref": "#/components/schemas/ValidationError"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional media types for the main response
|
||||
|
||||
You can use this same `responses` parameter to add different media types for the same main response.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can add an additional media type of `image/png`, declaring that your *path operation* can return a JSON object (with media type `application/json`) or a PNG image:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 28"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/additional_responses/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
Notice that you have to return the image using a `FileResponse` directly.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Unless you specify a different media type explicitly in your `responses` parameter, FastAPI will assume the response has the same media type as the main response class (default `application/json`).
|
||||
|
||||
But if you have specified a custom response class with `None` as its media type, FastAPI will use `application/json` for any additional response that has an associated model.
|
||||
|
||||
## Combining information
|
||||
|
||||
You can also combine response information from multiple places, including the `response_model`, `status_code`, and `responses` parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
You can declare a `response_model`, using the default status code `200` (or a custom one if you need), and then declare additional information for that same response in `responses`, directly in the OpenAPI schema.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** will keep the additional information from `responses`, and combine it with the JSON Schema from your model.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can declare a response with a status code `404` that uses a Pydantic model and has a custom `description`.
|
||||
|
||||
And a response with a status code `200` that uses your `response_model`, but includes a custom `example`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/additional_responses/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It will all be combined and included in your OpenAPI, and shown in the API docs:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/additional-responses/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
## Combine predefined responses and custom ones
|
||||
|
||||
You might want to have some predefined responses that apply to many *path operations*, but you want to combine them with custom responses needed by each *path operation*.
|
||||
|
||||
For those cases, you can use the Python technique of "unpacking" a `dict` with `**dict_to_unpack`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
old_dict = {
|
||||
"old key": "old value",
|
||||
"second old key": "second old value",
|
||||
}
|
||||
new_dict = {**old_dict, "new key": "new value"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, `new_dict` will contain all the key-value pairs from `old_dict` plus the new key-value pair:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
{
|
||||
"old key": "old value",
|
||||
"second old key": "second old value",
|
||||
"new key": "new value",
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can use that technique to re-use some predefined responses in your *path operations* and combine them with additional custom ones.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 12 13 14 15 24"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/additional_responses/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## More information about OpenAPI responses
|
||||
|
||||
To see what exactly you can include in the responses, you can check these sections in the OpenAPI specification:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/3.0.2.md#responsesObject" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI Responses Object</a>, it includes the `Response Object`.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/3.0.2.md#responseObject" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI Response Object</a>, you can include anything from this directly in each response inside your `responses` parameter. Including `description`, `headers`, `content` (inside of this is that you declare different media types and JSON Schemas), and `links`.
|
||||
37
docs/en/docs/advanced/additional-status-codes.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
# Additional Status Codes
|
||||
|
||||
By default, **FastAPI** will return the responses using a `JSONResponse`, putting the content you return from your *path operation* inside of that `JSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
It will use the default status code or the one you set in your *path operation*.
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional status codes
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to return additional status codes apart from the main one, you can do that by returning a `Response` directly, like a `JSONResponse`, and set the additional status code directly.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let's say that you want to have a *path operation* that allows to update items, and returns HTTP status codes of 200 "OK" when successful.
|
||||
|
||||
But you also want it to accept new items. And when the items didn't exist before, it creates them, and returns an HTTP status code of 201 "Created".
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve that, import `JSONResponse`, and return your content there directly, setting the `status_code` that you want:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 19"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/additional_status_codes/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
When you return a `Response` directly, like in the example above, it will be returned directly.
|
||||
|
||||
It won't be serialized with a model, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure it has the data you want it to have, and that the values are valid JSON (if you are using `JSONResponse`).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
You could also use `from starlette.responses import JSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** provides the same `starlette.responses` as `fastapi.responses` just as a convenience for you, the developer. But most of the available responses come directly from Starlette. The same with `status`.
|
||||
|
||||
## OpenAPI and API docs
|
||||
|
||||
If you return additional status codes and responses directly, they won't be included in the OpenAPI schema (the API docs), because FastAPI doesn't have a way to know beforehand what you are going to return.
|
||||
|
||||
But you can document that in your code, using: [Additional Responses](additional-responses.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
@@ -1,7 +1,4 @@
|
||||
!!! danger
|
||||
This is, more or less, an "advanced" chapter.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are just starting with **FastAPI** you might want to skip this chapter and come back to it later.
|
||||
# Advanced Dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
## Parameterized dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +19,7 @@ Not the class itself (which is already a callable), but an instance of that clas
|
||||
To do that, we declare a method `__call__`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10"
|
||||
{!./src/dependencies/tutorial006.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial011.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, this `__call__` is what **FastAPI** will use to check for additional parameters and sub-dependencies, and this is what will be called to pass a value to the parameter in your *path operation function* later.
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +29,7 @@ In this case, this `__call__` is what **FastAPI** will use to check for addition
|
||||
And now, we can use `__init__` to declare the parameters of the instance that we can use to "parameterize" the dependency:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
{!./src/dependencies/tutorial006.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial011.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, **FastAPI** won't ever touch or care about `__init__`, we will use it directly in our code.
|
||||
@@ -42,7 +39,7 @@ In this case, **FastAPI** won't ever touch or care about `__init__`, we will use
|
||||
We could create an instance of this class with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="16"
|
||||
{!./src/dependencies/tutorial006.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial011.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And that way we are able to "parameterize" our dependency, that now has `"bar"` inside of it, as the attribute `checker.fixed_content`.
|
||||
@@ -57,10 +54,10 @@ And when solving the dependency, **FastAPI** will call this `checker` like:
|
||||
checker(q="somequery")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...and pass whatever that returns as the value of the dependency in our path operation function as the parameter `fixed_content_included`:
|
||||
...and pass whatever that returns as the value of the dependency in our *path operation function* as the parameter `fixed_content_included`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="20"
|
||||
{!./src/dependencies/tutorial006.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial011.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
@@ -68,6 +65,6 @@ checker(q="somequery")
|
||||
|
||||
These examples are intentionally simple, but show how it all works.
|
||||
|
||||
In the chapters about security, you will be using utility functions that are implemented in this same way.
|
||||
In the chapters about security, there are utility functions that are implemented in this same way.
|
||||
|
||||
If you understood all this, you already know how those utility tools for security work underneath.
|
||||
@@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
|
||||
You can also use <a href="https://github.com/encode/databases" target="_blank">`encode/databases`</a> with **FastAPI** to connect to databases using `async` and `await`.
|
||||
# Async SQL (Relational) Databases
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use <a href="https://github.com/encode/databases" class="external-link" target="_blank">`encode/databases`</a> with **FastAPI** to connect to databases using `async` and `await`.
|
||||
|
||||
It is compatible with:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,9 +13,9 @@ In this example, we'll use **SQLite**, because it uses a single file and Python
|
||||
Later, for your production application, you might want to use a database server like **PostgreSQL**.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
You could adopt ideas from the previous section about <a href="/tutorial/sql-databases/" target="_blank">SQLAlchemy ORM</a>, like using utility functions to perform operations in the database, independent of your **FastAPI** code.
|
||||
You could adopt ideas from the section about SQLAlchemy ORM ([SQL (Relational) Databases](../tutorial/sql-databases.md){.internal-link target=_blank}), like using utility functions to perform operations in the database, independent of your **FastAPI** code.
|
||||
|
||||
This section doesn't apply those ideas, to be equivalent to the counterpart in <a href="https://www.starlette.io/database/" target="_blank">Starlette</a>.
|
||||
This section doesn't apply those ideas, to be equivalent to the counterpart in <a href="https://www.starlette.io/database/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Import and set up `SQLAlchemy`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +24,7 @@ Later, for your production application, you might want to use a database server
|
||||
* Create a table `notes` using the `metadata` object.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 14 16 17 18 19 20 21 22"
|
||||
{!./src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
@@ -37,11 +39,11 @@ Later, for your production application, you might want to use a database server
|
||||
* Create a `database` object.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 9 12"
|
||||
{!./src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
If you where connecting to a different database (e.g. PostgreSQL), you would need to change the `DATABASE_URL`.
|
||||
If you were connecting to a different database (e.g. PostgreSQL), you would need to change the `DATABASE_URL`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create the tables
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -53,7 +55,7 @@ Here, this section would run directly, right before starting your **FastAPI** ap
|
||||
* Create all the tables from the `metadata` object.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="25 26 27 28"
|
||||
{!./src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Create models
|
||||
@@ -64,7 +66,7 @@ Create Pydantic models for:
|
||||
* Notes to be returned (`Note`).
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="31 32 33 36 37 38 39"
|
||||
{!./src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By creating these Pydantic models, the input data will be validated, serialized (converted), and annotated (documented).
|
||||
@@ -77,7 +79,7 @@ So, you will be able to see it all in the interactive API docs.
|
||||
* Create event handlers to connect and disconnect from the database.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="42 45 46 47 50 51 52"
|
||||
{!./src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Read notes
|
||||
@@ -85,7 +87,7 @@ So, you will be able to see it all in the interactive API docs.
|
||||
Create the *path operation function* to read notes:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="55 56 57 58"
|
||||
{!./src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Note
|
||||
@@ -102,7 +104,7 @@ That documents (and validates, serializes, filters) the output data, as a `list`
|
||||
Create the *path operation function* to create notes:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="61 62 63 64 65"
|
||||
{!./src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/async_sql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Note
|
||||
@@ -149,7 +151,7 @@ So, the final result returned would be something like:
|
||||
|
||||
## Check it
|
||||
|
||||
You can copy this code as is, and see the docs at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
You can copy this code as is, and see the docs at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
There you can see all your API documented and interact with it:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -157,4 +159,4 @@ There you can see all your API documented and interact with it:
|
||||
|
||||
## More info
|
||||
|
||||
You can read more about <a href="https://github.com/encode/databases" target="_blank">`encode/databases` at its GitHub page</a>.
|
||||
You can read more about <a href="https://github.com/encode/databases" class="external-link" target="_blank">`encode/databases` at its GitHub page</a>.
|
||||
109
docs/en/docs/advanced/custom-request-and-route.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
# Custom Request and APIRoute class
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, you may want to override the logic used by the `Request` and `APIRoute` classes.
|
||||
|
||||
In particular, this may be a good alternative to logic in a middleware.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you want to read or manipulate the request body before it is processed by your application.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! danger
|
||||
This is an "advanced" feature.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are just starting with **FastAPI** you might want to skip this section.
|
||||
|
||||
## Use cases
|
||||
|
||||
Some use cases include:
|
||||
|
||||
* Converting non-JSON request bodies to JSON (e.g. <a href="https://msgpack.org/index.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`msgpack`</a>).
|
||||
* Decompressing gzip-compressed request bodies.
|
||||
* Automatically logging all request bodies.
|
||||
|
||||
## Handling custom request body encodings
|
||||
|
||||
Let's see how to make use of a custom `Request` subclass to decompress gzip requests.
|
||||
|
||||
And an `APIRoute` subclass to use that custom request class.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a custom `GzipRequest` class
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
This is a toy example to demonstrate how it works, if you need Gzip support, you can use the provided [`GzipMiddleware`](./middleware.md#gzipmiddleware){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
First, we create a `GzipRequest` class, which will overwrite the `Request.body()` method to decompress the body in the presence of an appropriate header.
|
||||
|
||||
If there's no `gzip` in the header, it will not try to decompress the body.
|
||||
|
||||
That way, the same route class can handle gzip compressed or uncompressed requests.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_request_and_route/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a custom `GzipRoute` class
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we create a custom subclass of `fastapi.routing.APIRoute` that will make use of the `GzipRequest`.
|
||||
|
||||
This time, it will overwrite the method `APIRoute.get_route_handler()`.
|
||||
|
||||
This method returns a function. And that function is what will receive a request and return a response.
|
||||
|
||||
Here we use it to create a `GzipRequest` from the original request.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_request_and_route/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
A `Request` has a `request.scope` attribute, that's just a Python `dict` containing the metadata related to the request.
|
||||
|
||||
A `Request` also has a `request.receive`, that's a function to "receive" the body of the request.
|
||||
|
||||
The `scope` `dict` and `receive` function are both part of the ASGI specification.
|
||||
|
||||
And those two things, `scope` and `receive`, are what is needed to create a new `Request` instance.
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about the `Request` check <a href="https://www.starlette.io/requests/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette's docs about Requests</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
The only thing the function returned by `GzipRequest.get_route_handler` does differently is convert the `Request` to a `GzipRequest`.
|
||||
|
||||
Doing this, our `GzipRequest` will take care of decompressing the data (if necessary) before passing it to our *path operations*.
|
||||
|
||||
After that, all of the processing logic is the same.
|
||||
|
||||
But because of our changes in `GzipRequest.body`, the request body will be automatically decompressed when it is loaded by **FastAPI** when needed.
|
||||
|
||||
## Accessing the request body in an exception handler
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
To solve this same problem, it's probably a lot easier to use the `body` in a custom handler for `RequestValidationError` ([Handling Errors](../tutorial/handling-errors.md#use-the-requestvalidationerror-body){.internal-link target=_blank}).
|
||||
|
||||
But this example is still valid and it shows how to interact with the internal components.
|
||||
|
||||
We can also use this same approach to access the request body in an exception handler.
|
||||
|
||||
All we need to do is handle the request inside a `try`/`except` block:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13 15"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_request_and_route/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If an exception occurs, the`Request` instance will still be in scope, so we can read and make use of the request body when handling the error:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="16 17 18"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_request_and_route/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom `APIRoute` class in a router
|
||||
|
||||
You can also set the `route_class` parameter of an `APIRouter`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="26"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_request_and_route/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, the *path operations* under the `router` will use the custom `TimedRoute` class, and will have an extra `X-Response-Time` header in the response with the time it took to generate the response:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_request_and_route/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
208
docs/en/docs/advanced/custom-response.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
|
||||
# Custom Response - HTML, Stream, File, others
|
||||
|
||||
By default, **FastAPI** will return the responses using `JSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can override it by returning a `Response` directly as seen in [Return a Response directly](response-directly.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
But if you return a `Response` directly, the data won't be automatically converted, and the documentation won't be automatically generated (for example, including the specific "media type", in the HTTP header `Content-Type` as part of the generated OpenAPI).
|
||||
|
||||
But you can also declare the `Response` that you want to be used, in the *path operation decorator*.
|
||||
|
||||
The contents that you return from your *path operation function* will be put inside of that `Response`.
|
||||
|
||||
And if that `Response` has a JSON media type (`application/json`), like is the case with the `JSONResponse` and `UJSONResponse`, the data you return will be automatically converted (and filtered) with any Pydantic `response_model` that you declared in the *path operation decorator*.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
If you use a response class with no media type, FastAPI will expect your response to have no content, so it will not document the response format in its generated OpenAPI docs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Use `ORJSONResponse`
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you are squeezing performance, you can install and use <a href="https://github.com/ijl/orjson" class="external-link" target="_blank">`orjson`</a> and set the response to be `ORJSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
Import the `Response` class (sub-class) you want to use and declare it in the *path operation decorator*.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 7"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial001b.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
The parameter `response_class` will also be used to define the "media type" of the response.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the HTTP header `Content-Type` will be set to `application/json`.
|
||||
|
||||
And it will be documented as such in OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The `ORJSONResponse` is currently only available in FastAPI, not in Starlette.
|
||||
|
||||
## HTML Response
|
||||
|
||||
To return a response with HTML directly from **FastAPI**, use `HTMLResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
* Import `HTMLResponse`.
|
||||
* Pass `HTMLResponse` as the parameter `content_type` of your *path operation*.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 7"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
The parameter `response_class` will also be used to define the "media type" of the response.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the HTTP header `Content-Type` will be set to `text/html`.
|
||||
|
||||
And it will be documented as such in OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
### Return a `Response`
|
||||
|
||||
As seen in [Return a Response directly](response-directly.md){.internal-link target=_blank}, you can also override the response directly in your *path operation*, by returning it.
|
||||
|
||||
The same example from above, returning an `HTMLResponse`, could look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 7 19"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
A `Response` returned directly by your *path operation function* won't be documented in OpenAPI (for example, the `Content-Type` won't be documented) and won't be visible in the automatic interactive docs.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Of course, the actual `Content-Type` header, status code, etc, will come from the `Response` object your returned.
|
||||
|
||||
### Document in OpenAPI and override `Response`
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to override the response from inside of the function but at the same time document the "media type" in OpenAPI, you can use the `response_class` parameter AND return a `Response` object.
|
||||
|
||||
The `response_class` will then be used only to document the OpenAPI *path operation*, but your `Response` will be used as is.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Return an `HTMLResponse` directly
|
||||
|
||||
For example, it could be something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7 23 21"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, the function `generate_html_response()` already generates and returns a `Response` instead of returning the HTML in a `str`.
|
||||
|
||||
By returning the result of calling `generate_html_response()`, you are already returning a `Response` that will override the default **FastAPI** behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
But as you passed the `HTMLResponse` in the `response_class` too, **FastAPI** will know how to document it in OpenAPI and the interactive docs as HTML with `text/html`:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/custom-response/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
## Available responses
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some of the available responses.
|
||||
|
||||
Have in mind that you can use `Response` to return anything else, or even create a custom sub-class.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
You could also use `from starlette.responses import HTMLResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** provides the same `starlette.responses` as `fastapi.responses` just as a convenience for you, the developer. But most of the available responses come directly from Starlette.
|
||||
|
||||
### `Response`
|
||||
|
||||
The main `Response` class, all the other responses inherit from it.
|
||||
|
||||
You can return it directly.
|
||||
|
||||
It accepts the following parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
* `content` - A `str` or `bytes`.
|
||||
* `status_code` - An `int` HTTP status code.
|
||||
* `headers` - A `dict` of strings.
|
||||
* `media_type` - A `str` giving the media type. E.g. `"text/html"`.
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI (actually Starlette) will automatically include a Content-Length header. It will also include a Content-Type header, based on the media_type and appending a charset for text types.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 18"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_directly/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### `HTMLResponse`
|
||||
|
||||
Takes some text or bytes and returns an HTML response, as you read above.
|
||||
|
||||
### `PlainTextResponse`
|
||||
|
||||
Takes some text or bytes and returns an plain text response.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 7 9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### `JSONResponse`
|
||||
|
||||
Takes some data and returns an `application/json` encoded response.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the default response used in **FastAPI**, as you read above.
|
||||
|
||||
### `ORJSONResponse`
|
||||
|
||||
A fast alternative JSON response using <a href="https://github.com/ijl/orjson" class="external-link" target="_blank">`orjson`</a>, as you read above.
|
||||
|
||||
### `UJSONResponse`
|
||||
|
||||
An alternative JSON response using <a href="https://github.com/ultrajson/ultrajson" class="external-link" target="_blank">`ujson`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
`ujson` is less careful than Python's built-in implementation in how it handles some edge-cases.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 7"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
It's possible that `ORJSONResponse` might be a faster alternative.
|
||||
|
||||
### `RedirectResponse`
|
||||
|
||||
Returns an HTTP redirect. Uses a 307 status code (Temporary Redirect) by default.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial006.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### `StreamingResponse`
|
||||
|
||||
Takes an async generator or a normal generator/iterator and streams the response body.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 14"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial007.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using `StreamingResponse` with file-like objects
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a file-like object (e.g. the object returned by `open()`), you can return it in a `StreamingResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
This includes many libraries to interact with cloud storage, video processing, and others.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 10 11"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial008.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Notice that here as we are using standard `open()` that doesn't support `async` and `await`, we declare the path operation with normal `def`.
|
||||
|
||||
### `FileResponse`
|
||||
|
||||
Asynchronously streams a file as the response.
|
||||
|
||||
Takes a different set of arguments to instantiate than the other response types:
|
||||
|
||||
* `path` - The filepath to the file to stream.
|
||||
* `headers` - Any custom headers to include, as a dictionary.
|
||||
* `media_type` - A string giving the media type. If unset, the filename or path will be used to infer a media type.
|
||||
* `filename` - If set, this will be included in the response `Content-Disposition`.
|
||||
|
||||
File responses will include appropriate `Content-Length`, `Last-Modified` and `ETag` headers.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 10"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial009.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional documentation
|
||||
|
||||
You can also declare the media type and many other details in OpenAPI using `responses`: [Additional Responses in OpenAPI](additional-responses.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
# Events: startup - shutdown
|
||||
|
||||
You can define event handlers (functions) that need to be executed before the application starts up, or when the application is shutting down.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +9,7 @@ These functions can be declared with `async def` or normal `def`.
|
||||
To add a function that should be run before the application starts, declare it with the event `"startup"`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8"
|
||||
{!./src/events/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/events/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the `startup` event handler function will initialize the items "database" (just a `dict`) with some values.
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +23,7 @@ And your application won't start receiving requests until all the `startup` even
|
||||
To add a function that should be run when the application is shutting down, declare it with the event `"shutdown"`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6"
|
||||
{!./src/events/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/events/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, the `shutdown` event handler function will write a text line `"Application shutdown"` to a file `log.txt`.
|
||||
@@ -32,12 +33,12 @@ Here, the `shutdown` event handler function will write a text line `"Application
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Notice that in this case we are using a standard Python `open()` function that interacts with a file.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
So, it involves I/O (input/output), that requires "waiting" for things to be written to disk.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
But `open()` doesn't use `async` and `await`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
So, we declare the event handler function with standard `def` instead of `async def`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
You can read more about these event handlers in <a href="https://www.starlette.io/events/" target="_blank">Starlette's Events' docs</a>.
|
||||
You can read more about these event handlers in <a href="https://www.starlette.io/events/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette's Events' docs</a>.
|
||||
251
docs/en/docs/advanced/extending-openapi.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
|
||||
# Extending OpenAPI
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
This is a rather advanced feature. You probably can skip it.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are just following the tutorial - user guide, you can probably skip this section.
|
||||
|
||||
If you already know that you need to modify the generated OpenAPI schema, continue reading.
|
||||
|
||||
There are some cases where you might need to modify the generated OpenAPI schema.
|
||||
|
||||
In this section you will see how.
|
||||
|
||||
## The normal process
|
||||
|
||||
The normal (default) process, is as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
A `FastAPI` application (instance) has an `.openapi()` method that is expected to return the OpenAPI schema.
|
||||
|
||||
As part of the application object creation, a *path operation* for `/openapi.json` (or for whatever you set your `openapi_url`) is registered.
|
||||
|
||||
It just returns a JSON response with the result of the application's `.openapi()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, what the method `.openapi()` does is check the property `.openapi_schema` to see if it has contents and return them.
|
||||
|
||||
If it doesn't, it generates them using the utility function at `fastapi.openapi.utils.get_openapi`.
|
||||
|
||||
And that function `get_openapi()` receives as parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
* `title`: The OpenAPI title, shown in the docs.
|
||||
* `version`: The version of your API, e.g. `2.5.0`.
|
||||
* `openapi_version`: The version of the OpenAPI specification used. By default, the latest: `3.0.2`.
|
||||
* `description`: The description of your API.
|
||||
* `routes`: A list of routes, these are each of the registered *path operations*. They are taken from `app.routes`.
|
||||
* `openapi_prefix`: The URL prefix to be used in your OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overriding the defaults
|
||||
|
||||
Using the information above, you can use the same utility function to generate the OpenAPI schema and override each part that you need.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let's add <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc/blob/master/docs/redoc-vendor-extensions.md#x-logo" class="external-link" target="_blank">ReDoc's OpenAPI extension to include a custom logo</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Normal **FastAPI**
|
||||
|
||||
First, write all your **FastAPI** application as normally:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 4 7 8 9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extending_openapi/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Generate the OpenAPI schema
|
||||
|
||||
Then, use the same utility function to generate the OpenAPI schema, inside a `custom_openapi()` function:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 15 16 17 18 19 20"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extending_openapi/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Modify the OpenAPI schema
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can add the ReDoc extension, adding a custom `x-logo` to the `info` "object" in the OpenAPI schema:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="21 22 23"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extending_openapi/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Cache the OpenAPI schema
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the property `.openapi_schema` as a "cache", to store your generated schema.
|
||||
|
||||
That way, your application won't have to generate the schema every time a user opens your API docs.
|
||||
|
||||
It will be generated only once, and then the same cached schema will be used for the next requests.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13 14 24 25"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extending_openapi/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Override the method
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can replace the `.openapi()` method with your new function.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="28"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extending_openapi/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Check it
|
||||
|
||||
Once you go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc</a> you will see that you are using your custom logo (in this example, **FastAPI**'s logo):
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/extending-openapi/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
## Self-hosting JavaScript and CSS for docs
|
||||
|
||||
The API docs use **Swagger UI** and **ReDoc**, and each of those need some JavaScript and CSS files.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, those files are served from a <abbr title="Content Delivery Network: A service, normally composed of several servers, that provides static files, like JavaScript and CSS. It's commonly used to serve those files from the server closer to the client, improving performance.">CDN</abbr>.
|
||||
|
||||
But it's possible to customize it, you can set a specific CDN, or serve the files yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
That's useful, for example, if you need your app to keep working even while offline, without open Internet access, or in a local network.
|
||||
|
||||
Here you'll see how to serve those files yourself, in the same FastAPI app, and configure the docs to use them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Project file structure
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say your project file structure looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
├── app
|
||||
│ ├── __init__.py
|
||||
│ ├── main.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now create a directory to store those static files.
|
||||
|
||||
Your new file structure could look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
├── app
|
||||
│ ├── __init__.py
|
||||
│ ├── main.py
|
||||
└── static/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Download the files
|
||||
|
||||
Download the static files needed for the docs and put them on that `static/` directory.
|
||||
|
||||
You can probably right-click each link and select an option similar to `Save link as...`.
|
||||
|
||||
**Swagger UI** uses the files:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/swagger-ui-dist@3/swagger-ui-bundle.js" class="external-link" target="_blank">`swagger-ui-bundle.js`</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/swagger-ui-dist@3/swagger-ui.css" class="external-link" target="_blank">`swagger-ui.css`</a>
|
||||
|
||||
And **ReDoc** uses the file:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/redoc@next/bundles/redoc.standalone.js" class="external-link" target="_blank">`redoc.standalone.js`</a>
|
||||
|
||||
After that, your file structure could look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
├── app
|
||||
│ ├── __init__.py
|
||||
│ ├── main.py
|
||||
└── static
|
||||
├── redoc.standalone.js
|
||||
├── swagger-ui-bundle.js
|
||||
└── swagger-ui.css
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Install `aiofiles`
|
||||
|
||||
Now you need to install `aiofiles`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install aiofiles
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
### Serve the static files
|
||||
|
||||
* Import `StaticFiles`.
|
||||
* "Mount" a `StaticFiles()` instance in a specific path.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7 11"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extending_openapi/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Test the static files
|
||||
|
||||
Start your application and go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/static/redoc.standalone.js" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/static/redoc.standalone.js</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You should see a very long JavaScript file for **ReDoc**.
|
||||
|
||||
It could start with something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```JavaScript
|
||||
/*!
|
||||
* ReDoc - OpenAPI/Swagger-generated API Reference Documentation
|
||||
* -------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
* Version: "2.0.0-rc.18"
|
||||
* Repo: https://github.com/Redocly/redoc
|
||||
*/
|
||||
!function(e,t){"object"==typeof exports&&"object"==typeof m
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That confirms that you are being able to serve static files from your app, and that you placed the static files for the docs in the correct place.
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can configure the app to use those static files for the docs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Disable the automatic docs
|
||||
|
||||
The first step is to disable the automatic docs, as those use the CDN by default.
|
||||
|
||||
To disable them, set their URLs to `None` when creating your `FastAPI` app:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extending_openapi/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Include the custom docs
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can create the *path operations* for the custom docs.
|
||||
|
||||
You can re-use FastAPI's internal functions to create the HTML pages for the docs, and pass them the needed arguments:
|
||||
|
||||
* `openapi_url`: the URL where the HTML page for the docs can get the OpenAPI schema for your API. You can use here the attribute `app.openapi_url`.
|
||||
* `title`: the title of your API.
|
||||
* `oauth2_redirect_url`: you can use `app.swagger_ui_oauth2_redirect_url` here to use the default.
|
||||
* `swagger_js_url`: the URL where the HTML for your Swagger UI docs can get the **JavaScript** file. This is the one that your own app is now serving.
|
||||
* `swagger_css_url`: the URL where the HTML for your Swagger UI docs can get the **CSS** file. This is the one that your own app is now serving.
|
||||
|
||||
And similarly for ReDoc...
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 3 4 5 6 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 25 26 27 30 31 32 33 34 35 36"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extending_openapi/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The *path operation* for `swagger_ui_redirect` is a helper for when you use OAuth2.
|
||||
|
||||
If you integrate your API with an OAuth2 provider, you will be able to authenticate and come back to the API docs with the acquired credentials. And interact with it using the real OAuth2 authentication.
|
||||
|
||||
Swagger UI will handle it behind the scenes for you, but it needs this "redirect" helper.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a *path operation* to test it
|
||||
|
||||
Now, to be able to test that everything works, create a *path operation*:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="39 40 41"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extending_openapi/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Test it
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you should be able to disconnect your WiFi, go to your docs at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>, and reload the page.
|
||||
|
||||
And even without Internet, you would be able to see the docs for your API and interact with it.
|
||||
@@ -1,16 +1,17 @@
|
||||
# GraphQL
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** has optional support for GraphQL (provided by Starlette directly), using the `graphene` library.
|
||||
|
||||
You can combine normal FastAPI path operations with GraphQL on the same application.
|
||||
You can combine normal FastAPI *path operations* with GraphQL on the same application.
|
||||
|
||||
## Import and use `graphene`
|
||||
|
||||
GraphQL is implemented with Graphene, you can check <a href="https://docs.graphene-python.org/en/latest/quickstart/" target="_blank">Graphene's docs</a> for more details.
|
||||
GraphQL is implemented with Graphene, you can check <a href="https://docs.graphene-python.org/en/latest/quickstart/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Graphene's docs</a> for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
Import `graphene` and define your GraphQL data:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 6 7 8 9 10"
|
||||
{!./src/graphql/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Add Starlette's `GraphQLApp`
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +19,7 @@ Import `graphene` and define your GraphQL data:
|
||||
Then import and add Starlette's `GraphQLApp`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 14"
|
||||
{!./src/graphql/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
@@ -26,13 +27,12 @@ Then import and add Starlette's `GraphQLApp`:
|
||||
|
||||
## Check it
|
||||
|
||||
Run it with Uvicorn and open your browser at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000</a>.
|
||||
Run it with Uvicorn and open your browser at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see GraphiQL web user interface:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/graphql/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## More details
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, including:
|
||||
@@ -41,4 +41,4 @@ For more details, including:
|
||||
* Adding background tasks
|
||||
* Using normal or async functions
|
||||
|
||||
check the official <a href="https://www.starlette.io/graphql/" target="_blank">Starlette GraphQL docs</a>.
|
||||
check the official <a href="https://www.starlette.io/graphql/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette GraphQL docs</a>.
|
||||
18
docs/en/docs/advanced/index.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
# Advanced User Guide - Intro
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional Features
|
||||
|
||||
The main [Tutorial - User Guide](../tutorial/){.internal-link target=_blank} should be enough to give you a tour through all the main features of **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
In the next sections you will see other options, configurations, and additional features.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The next sections are **not necessarily "advanced"**.
|
||||
|
||||
And it's possible that for your use case, the solution is in one of them.
|
||||
|
||||
## Read the Tutorial first
|
||||
|
||||
You could still use most of the features in **FastAPI** with the knowledge from the main [Tutorial - User Guide](../tutorial/){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
And the next sections assume you already read it, and assume that you know those main ideas.
|
||||
99
docs/en/docs/advanced/middleware.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
# Advanced Middleware
|
||||
|
||||
In the main tutorial you read how to add [Custom Middleware](../tutorial/middleware.md){.internal-link target=_blank} to your application.
|
||||
|
||||
And then you also read how to handle [CORS with the `CORSMiddleware`](../tutorial/cors.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
In this section we'll see how to use other middlewares.
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding ASGI middlewares
|
||||
|
||||
As **FastAPI** is based on Starlette and implements the <abbr title="Asynchronous Server Gateway Interface">ASGI</abbr> specification, you can use any ASGI middleware.
|
||||
|
||||
A middleware doesn't have to be made for FastAPI or Starlette to work, as long as it follows the ASGI spec.
|
||||
|
||||
In general, ASGI middlewares are classes that expect to receive an ASGI app as the first argument.
|
||||
|
||||
So, in the documentation for third-party ASGI middlewares they will probably tell you to do something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from unicorn import UnicornMiddleware
|
||||
|
||||
app = SomeASGIApp()
|
||||
|
||||
new_app = UnicornMiddleware(app, some_config="rainbow")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
But FastAPI (actually Starlette) provides a simpler way to do it that makes sure that the internal middlewares to handle server errors and custom exception handlers work properly.
|
||||
|
||||
For that, you use `app.add_middleware()` (as in the example for CORS).
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
from unicorn import UnicornMiddleware
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
app.add_middleware(UnicornMiddleware, some_config="rainbow")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`app.add_middleware()` receives a middleware class as the first argument and any additional arguments to be passed to the middleware.
|
||||
|
||||
## Integrated middlewares
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** includes several middlewares for common use cases, we'll see next how to use them.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
For the next examples, you could also use `from starlette.middleware.something import SomethingMiddleware`.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** provides several middlewares in `fastapi.middleware` just as a convenience for you, the developer. But most of the available middlewares come directly from Starlette.
|
||||
|
||||
## `HTTPSRedirectMiddleware`
|
||||
|
||||
Enforces that all incoming requests must either be `https` or `wss`.
|
||||
|
||||
Any incoming requests to `http` or `ws` will be redirected to the secure scheme instead.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 6"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/advanced_middleware/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## `TrustedHostMiddleware`
|
||||
|
||||
Enforces that all incoming requests have a correctly set `Host` header, in order to guard against HTTP Host Header attacks.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 6 7 8"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/advanced_middleware/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The following arguments are supported:
|
||||
|
||||
* `allowed_hosts` - A list of domain names that should be allowed as hostnames. Wildcard domains such as `*.example.com` are supported for matching subdomains to allow any hostname either use `allowed_hosts=["*"]` or omit the middleware.
|
||||
|
||||
If an incoming request does not validate correctly then a `400` response will be sent.
|
||||
|
||||
## `GZipMiddleware`
|
||||
|
||||
Handles GZip responses for any request that includes `"gzip"` in the `Accept-Encoding` header.
|
||||
|
||||
The middleware will handle both standard and streaming responses.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 6"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/advanced_middleware/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The following arguments are supported:
|
||||
|
||||
* `minimum_size` - Do not GZip responses that are smaller than this minimum size in bytes. Defaults to `500`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Other middlewares
|
||||
|
||||
There are many other ASGI middlewares.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://docs.sentry.io/platforms/python/asgi/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Sentry</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/encode/uvicorn/blob/master/uvicorn/middleware/proxy_headers.py" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uvicorn's `ProxyHeadersMiddleware`</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/florimondmanca/msgpack-asgi" class="external-link" target="_blank">MessagePack</a>
|
||||
|
||||
To see other available middlewares check <a href="https://www.starlette.io/middleware/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette's Middleware docs</a> and the <a href="https://github.com/florimondmanca/awesome-asgi" class="external-link" target="_blank">ASGI Awesome List</a>.
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,8 @@
|
||||
# NoSQL (Distributed / Big Data) Databases
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** can also be integrated with any <abbr title="Distributed database (Big Data), also 'Not Only SQL'">NoSQL</abbr>.
|
||||
|
||||
Here we'll see an example using **<a href="https://www.couchbase.com/" target="_blank">Couchbase</a>**, a <abbr title="Document here refers to a JSON object (a dict), with keys and values, and those values can also be other JSON objects, arrays (lists), numbers, strings, booleans, etc.">document</abbr> based NoSQL database.
|
||||
Here we'll see an example using **<a href="https://www.couchbase.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Couchbase</a>**, a <abbr title="Document here refers to a JSON object (a dict), with keys and values, and those values can also be other JSON objects, arrays (lists), numbers, strings, booleans, etc.">document</abbr> based NoSQL database.
|
||||
|
||||
You can adapt it to any other NoSQL database like:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,14 +13,14 @@ You can adapt it to any other NoSQL database like:
|
||||
* **ElasticSearch**, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
There is an official project generator with **FastAPI** and **Couchbase**, all based on **Docker**, including a frontend and more tools: <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-couchbase" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-couchbase</a>
|
||||
There is an official project generator with **FastAPI** and **Couchbase**, all based on **Docker**, including a frontend and more tools: <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-couchbase" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-couchbase</a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Import Couchbase components
|
||||
|
||||
For now, don't pay attention to the rest, only the imports:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6 7 8"
|
||||
{!./src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Define a constant to use as a "document type"
|
||||
@@ -28,7 +30,7 @@ We will use it later as a fixed field `type` in our documents.
|
||||
This is not required by Couchbase, but is a good practice that will help you afterwards.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10"
|
||||
{!./src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Add a function to get a `Bucket`
|
||||
@@ -53,7 +55,7 @@ This utility function will:
|
||||
* Return it.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22"
|
||||
{!./src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Create Pydantic models
|
||||
@@ -65,10 +67,10 @@ As **Couchbase** "documents" are actually just "JSON objects", we can model them
|
||||
First, let's create a `User` model:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="25 26 27 28 29"
|
||||
{!./src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We will use this model in our path operation function, so, we don't include in it the `hashed_password`.
|
||||
We will use this model in our *path operation function*, so, we don't include in it the `hashed_password`.
|
||||
|
||||
### `UserInDB` model
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -79,14 +81,13 @@ This will have the data that is actually stored in the database.
|
||||
We don't create it as a subclass of Pydantic's `BaseModel` but as a subclass of our own `User`, because it will have all the attributes in `User` plus a couple more:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="32 33 34"
|
||||
{!./src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
Notice that we have a `hashed_password` and a `type` field that will be stored in the database.
|
||||
|
||||
But it is not part of the general `User` model (the one we will return in the path operation).
|
||||
|
||||
But it is not part of the general `User` model (the one we will return in the *path operation*).
|
||||
|
||||
## Get the user
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -97,21 +98,21 @@ Now create a function that will:
|
||||
* Get the document with that ID.
|
||||
* Put the contents of the document in a `UserInDB` model.
|
||||
|
||||
By creating a function that is only dedicated to getting your user from a `username` (or any other parameter) independent of your path operation function, you can more easily re-use it in multiple parts and also add <abbr title="Automated test, written in code, that checks if another piece of code is working correctly.">unit tests</abbr> for it:
|
||||
By creating a function that is only dedicated to getting your user from a `username` (or any other parameter) independent of your *path operation function*, you can more easily re-use it in multiple parts and also add <abbr title="Automated test, written in code, that checks if another piece of code is working correctly.">unit tests</abbr> for it:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="37 38 39 40 41 42 43"
|
||||
{!./src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### f-strings
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not familiar with the `f"userprofile::{username}"`, it is a Python "<a href="https://docs.python.org/3/glossary.html#term-f-string" target="_blank">f-string</a>".
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not familiar with the `f"userprofile::{username}"`, it is a Python "<a href="https://docs.python.org/3/glossary.html#term-f-string" class="external-link" target="_blank">f-string</a>".
|
||||
|
||||
Any variable that is put inside of `{}` in an f-string will be expanded / injected in the string.
|
||||
|
||||
### `dict` unpacking
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not familiar with the `UserInDB(**result.value)`, <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/glossary.html#term-argument" target="_blank">it is using `dict` "unpacking"</a>.
|
||||
If you are not familiar with the `UserInDB(**result.value)`, <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/glossary.html#term-argument" class="external-link" target="_blank">it is using `dict` "unpacking"</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
It will take the `dict` at `result.value`, and take each of its keys and values and pass them as key-values to `UserInDB` as keyword arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -135,17 +136,17 @@ UserInDB(username="johndoe", hashed_password="some_hash")
|
||||
### Create the `FastAPI` app
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="47"
|
||||
{!./src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the path operation function
|
||||
### Create the *path operation function*
|
||||
|
||||
As our code is calling Couchbase and we are not using the <a href="https://docs.couchbase.com/python-sdk/2.5/async-programming.html#asyncio-python-3-5" target="_blank">experimental Python <code>await</code> support</a>, we should declare our function with normal `def` instead of `async def`.
|
||||
As our code is calling Couchbase and we are not using the <a href="https://docs.couchbase.com/python-sdk/2.5/async-programming.html#asyncio-python-3-5" class="external-link" target="_blank">experimental Python <code>await</code> support</a>, we should declare our function with normal `def` instead of `async def`.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, Couchbase recommends not using a single `Bucket` object in multiple "<abbr title="A sequence of code being executed by the program, while at the same time, or at intervals, there can be others being executed too.">thread</abbr>s", so, we can get just get the bucket directly and pass it to our utility functions:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="50 51 52 53 54"
|
||||
{!./src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Recap
|
||||
188
docs/en/docs/advanced/openapi-callbacks.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
|
||||
# OpenAPI Callbacks
|
||||
|
||||
You could create an API with a *path operation* that could trigger a request to an *external API* created by someone else (probably the same developer that would be *using* your API).
|
||||
|
||||
The process that happens when your API app calls the *external API* is named a "callback". Because the software that the external developer wrote sends a request to your API and then your API *calls back*, sending a request to an *external API* (that was probably created by the same developer).
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, you could want to document how that external API *should* look like. What *path operation* it should have, what body it should expect, what response it should return, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## An app with callbacks
|
||||
|
||||
Let's see all this with an example.
|
||||
|
||||
Imagine you develop an app that allows creating invoices.
|
||||
|
||||
These invoices will have an `id`, `title` (optional), `customer`, and `total`.
|
||||
|
||||
The user of your API (an external developer) will create an invoice in your API with a POST request.
|
||||
|
||||
Then your API will (let's imagine):
|
||||
|
||||
* Send the invoice to some customer of the external developer.
|
||||
* Collect the money.
|
||||
* Send a notification back to the API user (the external developer).
|
||||
* This will be done by sending a POST request (from *your API*) to some *external API* provided by that external developer (this is the "callback").
|
||||
|
||||
## The normal **FastAPI** app
|
||||
|
||||
Let's first see how the normal API app would look like before adding the callback.
|
||||
|
||||
It will have a *path operation* that will receive an `Invoice` body, and a query parameter `callback_url` that will contain the URL for the callback.
|
||||
|
||||
This part is pretty normal, most of the code is probably already familiar to you:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8 9 10 11 12 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/openapi_callbacks/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The `callback_url` query parameter uses a Pydantic <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/types/#urls" class="external-link" target="_blank">URL</a> type.
|
||||
|
||||
The only new thing is the `callbacks=messages_callback_router.routes` as an argument to the *path operation decorator*. We'll see what that is next.
|
||||
|
||||
## Documenting the callback
|
||||
|
||||
The actual callback code will depend heavily on your own API app.
|
||||
|
||||
And it will probably vary a lot from one app to the next.
|
||||
|
||||
It could be just one or two lines of code, like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
callback_url = "https://example.com/api/v1/invoices/events/"
|
||||
requests.post(callback_url, json={"description": "Invoice paid", "paid": True})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
But possibly the most important part of the callback is making sure that your API user (the external developer) implements the *external API* correctly, according to the data that *your API* is going to send in the request body of the callback, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
So, what we will do next is add the code to document how that *external API* should look like to receive the callback from *your API*.
|
||||
|
||||
That documentation will show up in the Swagger UI at `/docs` in your API, and it will let external developers know how to build the *external API*.
|
||||
|
||||
This example doesn't implement the callback itself (that could be just a line of code), only the documentation part.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The actual callback is just an HTTP request.
|
||||
|
||||
When implementing the callback yourself, you could use something like <a href="https://www.encode.io/httpx/" class="external-link" target="_blank">HTTPX</a> or <a href="https://requests.readthedocs.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Requests</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Write the callback documentation code
|
||||
|
||||
This code won't be executed in your app, we only need it to *document* how that *external API* should look like.
|
||||
|
||||
But, you already know how to easily create automatic documentation for an API with **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
So we are going to use that same knowledge to document how the *external API* should look like... by creating the *path operation(s)* that the external API should implement (the ones your API will call).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
When writing the code to document a callback, it might be useful to imagine that you are that *external developer*. And that you are currently implementing the *external API*, not *your API*.
|
||||
|
||||
Temporarily adopting this point of view (of the *external developer*) can help you feel like it's more obvious where to put the parameters, the Pydantic model for the body, for the response, etc. for that *external API*.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a callback `APIRouter`
|
||||
|
||||
First create a new `APIRouter` that will contain one or more callbacks.
|
||||
|
||||
This router will never be added to an actual `FastAPI` app (i.e. it will never be passed to `app.include_router(...)`).
|
||||
|
||||
Because of that, you need to declare what will be the `default_response_class`, and set it to `JSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! Note "Technical Details"
|
||||
The `response_class` is normally set by the `FastAPI` app during the call to `app.include_router(some_router)`.
|
||||
|
||||
But as we are never calling `app.include_router(some_router)`, we need to set the `default_response_class` during creation of the `APIRouter`.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 24"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/openapi_callbacks/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the callback *path operation*
|
||||
|
||||
To create the callback *path operation* use the same `APIRouter` you created above.
|
||||
|
||||
It should look just like a normal FastAPI *path operation*:
|
||||
|
||||
* It should probably have a declaration of the body it should receive, e.g. `body: InvoiceEvent`.
|
||||
* And it could also have a declaration of the response it should return, e.g. `response_model=InvoiceEventReceived`.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="15 16 17 20 21 27 28 29 30 31"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/openapi_callbacks/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are 2 main differences from a normal *path operation*:
|
||||
|
||||
* It doesn't need to have any actual code, because your app will never call this code. It's only used to document the *external API*. So, the function could just have `pass`.
|
||||
* The *path* can contain an <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/3.0.2.md#key-expression" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI 3 expression</a> (see more below) where it can use variables with parameters and parts of the original request sent to *your API*.
|
||||
|
||||
### The callback path expression
|
||||
|
||||
The callback *path* can have an <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/3.0.2.md#key-expression" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI 3 expression</a> that can contain parts of the original request sent to *your API*.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, it's the `str`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
"{$callback_url}/invoices/{$request.body.id}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
So, if your API user (the external developer) sends a request to *your API* to:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
https://yourapi.com/invoices/?callback_url=https://www.external.org/events
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
with a JSON body of:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{
|
||||
"id": "2expen51ve",
|
||||
"customer": "Mr. Richie Rich",
|
||||
"total": "9999"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then *your API* will process the invoice, and at some point later, send a callback request to the `callback_url` (the *external API*):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
https://www.external.org/events/invoices/2expen51ve
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
with a JSON body containing something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{
|
||||
"description": "Payment celebration",
|
||||
"paid": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and it would expect a response from that *external API* with a JSON body like:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{
|
||||
"ok": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Notice how the callback URL used contains the URL received as a query parameter in `callback_url` (`https://www.external.org/events`) and also the invoice `id` from inside of the JSON body (`2expen51ve`).
|
||||
|
||||
### Add the callback router
|
||||
|
||||
At this point you have the *callback path operation(s)* needed (the one(s) that the *external developer* should implement in the *external API*) in the callback router you created above.
|
||||
|
||||
Now use the parameter `callbacks` in *your API's path operation decorator* to pass the attribute `.routes` (that's actually just a `list` of routes/*path operations*) from that callback router:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="34"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/openapi_callbacks/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Notice that you are not passing the router itself (`invoices_callback_router`) to `callback=`, but the attribute `.routes`, as in `invoices_callback_router.routes`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Check the docs
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can start your app with Uvicorn and go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see your docs including a "Callback" section for your *path operation* that shows how the *external API* should look like:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/openapi-callbacks/image01.png">
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
# Path Operation Advanced Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
## OpenAPI operationId
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
If you are not an "expert" in OpenAPI, you probably don't need this.
|
||||
|
||||
You can set the OpenAPI `operationId` to be used in your *path operation* with the parameter `operation_id`.
|
||||
|
||||
You would have to make sure that it is unique for each operation.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Using the *path operation function* name as the operationId
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use your APIs' function names as `operationId`s, you can iterate over all of them and override each *path operation's* `operation_id` using their `APIRoute.name`.
|
||||
|
||||
You should do it after adding all your *path operations*.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 24"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
If you manually call `app.openapi()`, you should update the `operationId`s before that.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
If you do this, you have to make sure each one of your *path operation functions* has a unique name.
|
||||
|
||||
Even if they are in different modules (Python files).
|
||||
|
||||
## Exclude from OpenAPI
|
||||
|
||||
To exclude a *path operation* from the generated OpenAPI schema (and thus, from the automatic documentation systems), use the parameter `include_in_schema` and set it to `False`;
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced description from docstring
|
||||
|
||||
You can limit the lines used from the docstring of a *path operation function* for OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
Adding an `\f` (an escaped "form feed" character) causes **FastAPI** to truncate the output used for OpenAPI at this point.
|
||||
|
||||
It won't show up in the documentation, but other tools (such as Sphinx) will be able to use the rest.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
33
docs/en/docs/advanced/response-change-status-code.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
# Response - Change Status Code
|
||||
|
||||
You probably read before that you can set a default [Response Status Code](../tutorial/response-status-code.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
But in some cases you need to return a different status code than the default.
|
||||
|
||||
## Use case
|
||||
|
||||
For example, imagine that you want to return an HTTP status code of "OK" `200` by default.
|
||||
|
||||
But if the data didn't exist, you want to create it, and return an HTTP status code of "CREATED" `201`.
|
||||
|
||||
But you still want to be able to filter and convert the data you return with a `response_model`.
|
||||
|
||||
For those cases, you can use a `Response` parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
## Use a `Response` parameter
|
||||
|
||||
You can declare a parameter of type `Response` in your *path operation function* (as you can do for cookies and headers).
|
||||
|
||||
And then you can set the `status_code` in that *temporal* response object.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 9 12"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_change_status_code/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And then you can return any object you need, as you normally would (a `dict`, a database model, etc).
|
||||
|
||||
And if you declared a `response_model`, it will still be used to filter and convert the object you returned.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** will use that *temporal* response to extract the status code (also cookies and headers), and will put them in the final response that contains the value you returned, filtered by any `response_model`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also declare the `Response` parameter in dependencies, and set the status code in them. But have in mind that the last one to be set will win.
|
||||
49
docs/en/docs/advanced/response-cookies.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
# Response Cookies
|
||||
|
||||
## Use a `Response` parameter
|
||||
|
||||
You can declare a parameter of type `Response` in your *path operation function*.
|
||||
|
||||
And then you can set cookies in that *temporal* response object.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 8 9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_cookies/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And then you can return any object you need, as you normally would (a `dict`, a database model, etc).
|
||||
|
||||
And if you declared a `response_model`, it will still be used to filter and convert the object you returned.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** will use that *temporal* response to extract the cookies (also headers and status code), and will put them in the final response that contains the value you returned, filtered by any `response_model`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also declare the `Response` parameter in dependencies, and set cookies (and headers) in them.
|
||||
|
||||
## Return a `Response` directly
|
||||
|
||||
You can also create cookies when returning a `Response` directly in your code.
|
||||
|
||||
To do that, you can create a response as described in [Return a Response Directly](response-directly.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
Then set Cookies in it, and then return it:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10 11 12"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_cookies/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Have in mind that if you return a response directly instead of using the `Response` parameter, FastAPI will return it directly.
|
||||
|
||||
So, you will have to make sure your data is of the correct type. E.g. it is compatible with JSON, if you are returning a `JSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
And also that you are not sending any data that should have been filtered by a `response_model`.
|
||||
|
||||
### More info
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
You could also use `from starlette.responses import Response` or `from starlette.responses import JSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** provides the same `starlette.responses` as `fastapi.responses` just as a convenience for you, the developer. But most of the available responses come directly from Starlette.
|
||||
|
||||
And as the `Response` can be used frequently to set headers and cookies, **FastAPI** also provides it at `fastapi.Response`.
|
||||
|
||||
To see all the available parameters and options, check the <a href="https://www.starlette.io/responses/#set-cookie" class="external-link" target="_blank">documentation in Starlette</a>.
|
||||
63
docs/en/docs/advanced/response-directly.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
# Return a Response Directly
|
||||
|
||||
When you create a **FastAPI** *path operation* you can normally return any data from it: a `dict`, a `list`, a Pydantic model, a database model, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, **FastAPI** would automatically convert that return value to JSON using the `jsonable_encoder` explained in [JSON Compatible Encoder](../tutorial/encoder.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
Then, behind the scenes, it would put that JSON-compatible data (e.g. a `dict`) inside of a `JSONResponse` that would be used to send the response to the client.
|
||||
|
||||
But you can return a `JSONResponse` directly from your *path operations*.
|
||||
|
||||
It might be useful, for example, to return custom headers or cookies.
|
||||
|
||||
## Return a `Response`
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, you can return any `Response` or any sub-class of it.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
`JSONResponse` itself is a sub-class of `Response`.
|
||||
|
||||
And when you return a `Response`, **FastAPI** will pass it directly.
|
||||
|
||||
It won't do any data conversion with Pydantic models, it won't convert the contents to any type, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
This gives you a lot of flexibility. You can return any data type, override any data declaration or validation, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using the `jsonable_encoder` in a `Response`
|
||||
|
||||
Because **FastAPI** doesn't do any change to a `Response` you return, you have to make sure it's contents are ready for it.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you cannot put a Pydantic model in a `JSONResponse` without first converting it to a `dict` with all the data types (like `datetime`, `UUID`, etc) converted to JSON-compatible types.
|
||||
|
||||
For those cases, you can use the `jsonable_encoder` to convert your data before passing it to a response:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 6 20 21"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_directly/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
You could also use `from starlette.responses import JSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** provides the same `starlette.responses` as `fastapi.responses` just as a convenience for you, the developer. But most of the available responses come directly from Starlette.
|
||||
|
||||
## Returning a custom `Response`
|
||||
|
||||
The example above shows all the parts you need, but it's not very useful yet, as you could have just returned the `item` directly, and **FastAPI** would put it in a `JSONResponse` for you, converting it to a `dict`, etc. All that by default.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's see how you could use that to return a custom response.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say that you want to return an <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/XML" class="external-link" target="_blank">XML</a> response.
|
||||
|
||||
You could put your XML content in a string, put it in a `Response`, and return it:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 18"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_directly/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Notes
|
||||
|
||||
When you return a `Response` directly its data is not validated, converted (serialized), nor documented automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
But you can still document it as described in [Additional Responses in OpenAPI](additional-responses.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
You can see in later sections how to use/declare these custom `Response`s while still having automatic data conversion, documentation, etc.
|
||||
42
docs/en/docs/advanced/response-headers.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
# Response Headers
|
||||
|
||||
## Use a `Response` parameter
|
||||
|
||||
You can declare a parameter of type `Response` in your *path operation function* (as you can do for cookies).
|
||||
|
||||
And then you can set headers in that *temporal* response object.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 7 8"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_headers/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And then you can return any object you need, as you normally would (a `dict`, a database model, etc).
|
||||
|
||||
And if you declared a `response_model`, it will still be used to filter and convert the object you returned.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** will use that *temporal* response to extract the headers (also cookies and status code), and will put them in the final response that contains the value you returned, filtered by any `response_model`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also declare the `Response` parameter in dependencies, and set headers (and cookies) in them.
|
||||
|
||||
## Return a `Response` directly
|
||||
|
||||
You can also add headers when you return a `Response` directly.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a response as described in [Return a Response Directly](response-directly.md){.internal-link target=_blank} and pass the headers as an additional parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10 11 12"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_headers/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
You could also use `from starlette.responses import Response` or `from starlette.responses import JSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** provides the same `starlette.responses` as `fastapi.responses` just as a convenience for you, the developer. But most of the available responses come directly from Starlette.
|
||||
|
||||
And as the `Response` can be used frequently to set headers and cookies, **FastAPI** also provides it at `fastapi.Response`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom Headers
|
||||
|
||||
Have in mind that custom proprietary headers can be added <a href="https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers" class="external-link" target="_blank">using the 'X-' prefix</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
But if you have custom headers that you want a client in a browser to be able to see, you need to add them to your CORS configurations (read more in [CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)](../tutorial/cors.md){.internal-link target=_blank}), using the parameter `expose_headers` documented in <a href="https://www.starlette.io/middleware/#corsmiddleware" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette's CORS docs</a>.
|
||||
107
docs/en/docs/advanced/security/http-basic-auth.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
# HTTP Basic Auth
|
||||
|
||||
For the simplest cases, you can use HTTP Basic Auth.
|
||||
|
||||
In HTTP Basic Auth, the application expects a header that contains a username and a password.
|
||||
|
||||
If it doesn't receive it, it returns an HTTP 401 "Unauthorized" error.
|
||||
|
||||
And returns a header `WWW-Authenticate` with a value of `Basic`, and an optional `realm` parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
That tells the browser to show the integrated prompt for a username and password.
|
||||
|
||||
Then, when you type that username and password, the browser sends them in the header automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
## Simple HTTP Basic Auth
|
||||
|
||||
* Import `HTTPBasic` and `HTTPBasicCredentials`.
|
||||
* Create a "`security` scheme" using `HTTPBasic`.
|
||||
* Use that `security` with a dependency in your *path operation*.
|
||||
* It returns an object of type `HTTPBasicCredentials`:
|
||||
* It contains the `username` and `password` sent.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 6 10"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial006.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When you try to open the URL for the first time (or click the "Execute" button in the docs) the browser will ask you for your username and password:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/security/image12.png">
|
||||
|
||||
## Check the username
|
||||
|
||||
Here's a more complete example.
|
||||
|
||||
Use a dependency to check if the username and password are correct.
|
||||
|
||||
For this, use the Python standard module <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/secrets.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`secrets`</a> to check the username and password:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 11 12 13"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial007.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will ensure that `credentials.username` is `"stanleyjobson"`, and that `credentials.password` is `"swordfish"`. This would be similar to:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
if not (credentials.username == "stanleyjobson") or not (credentials.password == "swordfish"):
|
||||
# Return some error
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
But by using the `secrets.compare_digest()` it will be secure against a type of attacks called "timing attacks".
|
||||
|
||||
### Timing Attacks
|
||||
|
||||
But what's a "timing attack"?
|
||||
|
||||
Let's imagine an attacker is trying to guess the username and password.
|
||||
|
||||
And that attacker sends a request with a username `johndoe` and a password `love123`.
|
||||
|
||||
Then the Python code in your application would be equivalent to something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
if "johndoe" == "stanleyjobson" and "love123" == "swordfish":
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
But right at the moment Python compares the first `j` in `johndoe` to the first `s` in `stanleyjobson`, it will return `False`, because it already knows that those two strings are not the same, thinking that "there's no need to waste more computation comparing the rest of the letters". And your application will say "incorrect user or password".
|
||||
|
||||
But then the attacker tries with username `stanleyjobsox` and password `love123`.
|
||||
|
||||
And your application code does something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
if "stanleyjobsox" == "stanleyjobson" and "love123" == "swordfish":
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Python will have to compare the whole `stanleyjobso` in both `stanleyjobsox` and `stanleyjobson` before realizing that both strings are not the same. So it will take some extra microseconds to reply back "incorrect user or password".
|
||||
|
||||
#### The time to answer helps the attacker
|
||||
|
||||
At that point, by noticing that the server took some microseconds longer to send the "incorrect user or password" response, the attacker will know that she/he got _something_ right, some of the initial letters were right.
|
||||
|
||||
And then she/he can try again knowing that it's probably something more similar to `stanleyjobsox` than to `johndoe`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### A "professional" attack
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, the attacker would not try all this by hand, she/he would write a program to do it, possibly with thousands or millions of tests per second. And would get just one extra correct letter at a time.
|
||||
|
||||
But doing that, in some minutes or hours the attacker would have guessed the correct username and password, with the "help" of our application, just using the time taken to answer.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fix it with `secrets.compare_digest()`
|
||||
|
||||
But in our code we are actually using `secrets.compare_digest()`.
|
||||
|
||||
In short, it will take the same time to compare `stanleyjobsox` to `stanleyjobson` than it takes to compare `johndoe` to `stanleyjobson`. And the same for the password.
|
||||
|
||||
That way, using `secrets.compare_digest()` in your application code, it will be safe against this whole range of security attacks.
|
||||
|
||||
### Return the error
|
||||
|
||||
After detecting that the credentials are incorrect, return an `HTTPException` with a status code 401 (the same returned when no credentials are provided) and add the header `WWW-Authenticate` to make the browser show the login prompt again:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="15 16 17 18 19"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial007.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
16
docs/en/docs/advanced/security/index.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
# Advanced Security - Intro
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional Features
|
||||
|
||||
There are some extra features to handle security apart from the ones covered in the [Tutorial - User Guide: Security](../../tutorial/security/){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The next sections are **not necessarily "advanced"**.
|
||||
|
||||
And it's possible that for your use case, the solution is in one of them.
|
||||
|
||||
## Read the Tutorial first
|
||||
|
||||
The next sections assume you already read the main [Tutorial - User Guide: Security](../../tutorial/security/){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
They are all based on the same concepts, but allow some extra functionalities.
|
||||
269
docs/en/docs/advanced/security/oauth2-scopes.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,269 @@
|
||||
# OAuth2 scopes
|
||||
|
||||
You can use OAuth2 scopes directly with **FastAPI**, they are integrated to work seamlessly.
|
||||
|
||||
This would allow you to have a more fine-grained permission system, following the OAuth2 standard, integrated into your OpenAPI application (and the API docs).
|
||||
|
||||
OAuth2 with scopes is the mechanism used by many big authentication providers, like Facebook, Google, GitHub, Microsoft, Twitter, etc. They use it to provide specific permissions to users and applications.
|
||||
|
||||
Every time you "log in with" Facebook, Google, GitHub, Microsoft, Twitter, that application is using OAuth2 with scopes.
|
||||
|
||||
In this section you will see how to manage authentication and authorization with the same OAuth2 with scopes in your **FastAPI** application.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
This is a more or less advanced section. If you are just starting, you can skip it.
|
||||
|
||||
You don't necessarily need OAuth2 scopes, and you can handle authentication and authorization however you want.
|
||||
|
||||
But OAuth2 with scopes can be nicely integrated into your API (with OpenAPI) and your API docs.
|
||||
|
||||
Nevertheless, you still enforce those scopes, or any other security/authorization requirement, however you need, in your code.
|
||||
|
||||
In many cases, OAuth2 with scopes can be an overkill.
|
||||
|
||||
But if you know you need it, or you are curious, keep reading.
|
||||
|
||||
## OAuth2 scopes and OpenAPI
|
||||
|
||||
The OAuth2 specification defines "scopes" as a list of strings separated by spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
The content of each of these strings can have any format, but should not contain spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
These scopes represent "permissions".
|
||||
|
||||
In OpenAPI (e.g. the API docs), you can define "security schemes".
|
||||
|
||||
When one of these security schemes uses OAuth2, you can also declare and use scopes.
|
||||
|
||||
Each "scope" is just a string (without spaces).
|
||||
|
||||
They are normally used to declare specific security permissions, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
* `users:read` or `users:write` are common examples.
|
||||
* `instagram_basic` is used by Facebook / Instagram.
|
||||
* `https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive` is used by Google.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
In OAuth2 a "scope" is just a string that declares a specific permission required.
|
||||
|
||||
It doesn't matter if it has other characters like `:` or if it is a URL.
|
||||
|
||||
Those details are implementation specific.
|
||||
|
||||
For OAuth2 they are just strings.
|
||||
|
||||
## Global view
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's quickly see the parts that change from the examples in the main **Tutorial - User Guide** for [OAuth2 with Password (and hashing), Bearer with JWT tokens](../../tutorial/security/oauth2-jwt.md){.internal-link target=_blank}. Now using OAuth2 scopes:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 5 9 13 47 65 106 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 122 123 124 125 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 140 154"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's review those changes step by step.
|
||||
|
||||
## OAuth2 Security scheme
|
||||
|
||||
The first change is that now we are declaring the OAuth2 security scheme with two available scopes, `me` and `items`.
|
||||
|
||||
The `scopes` parameter receives a `dict` with each scope as a key and the description as the value:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="63 64 65 66"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Because we are now declaring those scopes, they will show up in the API docs when you log-in/authorize.
|
||||
|
||||
And you will be able to select which scopes you want to give access to: `me` and `items`.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the same mechanism used when you give permissions while logging in with Facebook, Google, GitHub, etc:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/security/image11.png">
|
||||
|
||||
## JWT token with scopes
|
||||
|
||||
Now, modify the token *path operation* to return the scopes requested.
|
||||
|
||||
We are still using the same `OAuth2PasswordRequestForm`. It includes a property `scopes` with a `list` of `str`, with each scope it received in the request.
|
||||
|
||||
And we return the scopes as part of the JWT token.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! danger
|
||||
For simplicity, here we are just adding the scopes received directly to the token.
|
||||
|
||||
But in your application, for security, you should make sure you only add the scopes that the user is actually able to have, or the ones you have predefined.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="155"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Declare scopes in *path operations* and dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
Now we declare that the *path operation* for `/users/me/items/` requires the scope `items`.
|
||||
|
||||
For this, we import and use `Security` from `fastapi`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use `Security` to declare dependencies (just like `Depends`), but `Security` also receives a parameter `scopes` with a list of scopes (strings).
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, we pass a dependency function `get_current_active_user` to `Security` (the same way we would do with `Depends`).
|
||||
|
||||
But we also pass a `list` of scopes, in this case with just one scope: `items` (it could have more).
|
||||
|
||||
And the dependency function `get_current_active_user` can also declare sub-dependencies, not only with `Depends` but also with `Security`. Declaring its own sub-dependency function (`get_current_user`), and more scope requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, it requires the scope `me` (it could require more than one scope).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
You don't necessarily need to add different scopes in different places.
|
||||
|
||||
We are doing it here to demonstrate how **FastAPI** handles scopes declared at different levels.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="5 140 167"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info "Technical Details"
|
||||
`Security` is actually a subclass of `Depends`, and it has just one extra parameter that we'll see later.
|
||||
|
||||
But by using `Security` instead of `Depends`, **FastAPI** will know that it can declare security scopes, use them internally, and document the API with OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
But when you import `Query`, `Path`, `Depends`, `Security` and others from `fastapi`, those are actually functions that return special classes.
|
||||
|
||||
## Use `SecurityScopes`
|
||||
|
||||
Now update the dependency `get_current_user`.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the one used by the dependencies above.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's were we are using the same OAuth2 scheme we created before, declaring it as a dependency: `oauth2_scheme`.
|
||||
|
||||
Because this dependency function doesn't have any scope requirements itself, we can use `Depends` with `oauth2_scheme`, we don't have to use `Security` when we don't need to specify security scopes.
|
||||
|
||||
We also declare a special parameter of type `SecurityScopes`, imported from `fastapi.security`.
|
||||
|
||||
This `SecurityScopes` class is similar to `Request` (`Request` was used to get the request object directly).
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 106"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Use the `scopes`
|
||||
|
||||
The parameter `security_scopes` will be of type `SecurityScopes`.
|
||||
|
||||
It will have a property `scopes` with a list containing all the scopes required by itself and all the dependencies that use this as a sub-dependency. That means, all the "dependants"... this might sound confusing, it is explained again later below.
|
||||
|
||||
The `security_scopes` object (of class `SecurityScopes`) also provides a `scope_str` attribute with a single string, containing those scopes separated by spaces (we are going to use it).
|
||||
|
||||
We create an `HTTPException` that we can re-use (`raise`) later at several points.
|
||||
|
||||
In this exception, we include the scopes required (if any) as a string separated by spaces (using `scope_str`). We put that string containing the scopes in in the `WWW-Authenticate` header (this is part of the spec).
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="106 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Verify the `username` and data shape
|
||||
|
||||
We verify that we get a `username`, and extract the scopes.
|
||||
|
||||
And then we validate that data with the Pydantic model (catching the `ValidationError` exception), and if we get an error reading the JWT token or validating the data with Pydantic, we raise the `HTTPException` we created before.
|
||||
|
||||
For that, we update the Pydantic model `TokenData` with a new property `scopes`.
|
||||
|
||||
By validating the data with Pydantic we can make sure that we have, for example, exactly a `list` of `str` with the scopes and a `str` with the `username`.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead of, for example, a `dict`, or something else, as it could break the application at some point later, making it a security risk.
|
||||
|
||||
We also verify that we have a user with that username, and if not, we raise that same exception we created before.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="47 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Verify the `scopes`
|
||||
|
||||
We now verify that all the scopes required, by this dependency and all the dependants (including *path operations*), are included in the scopes provided in the token received, otherwise raise an `HTTPException`.
|
||||
|
||||
For this, we use `security_scopes.scopes`, that contains a `list` with all these scopes as `str`.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="129 130 131 132 133 134 135"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Dependency tree and scopes
|
||||
|
||||
Let's review again this dependency tree and the scopes.
|
||||
|
||||
As the `get_current_active_user` dependency has as a sub-dependency on `get_current_user`, the scope `"me"` declared at `get_current_active_user` will be included in the list of required scopes in the `security_scopes.scopes` passed to `get_current_user`.
|
||||
|
||||
The *path operation* itself also declares a scope, `"items"`, so this will also be in the list of `security_scopes.scopes` passed to `get_current_user`.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how the hierarchy of dependencies and scopes looks like:
|
||||
|
||||
* The *path operation* `read_own_items` has:
|
||||
* Required scopes `["items"]` with the dependency:
|
||||
* `get_current_active_user`:
|
||||
* The dependency function `get_current_active_user` has:
|
||||
* Required scopes `["me"]` with the dependency:
|
||||
* `get_current_user`:
|
||||
* The dependency function `get_current_user` has:
|
||||
* No scopes required by itself.
|
||||
* A dependency using `oauth2_scheme`.
|
||||
* A `security_scopes` parameter of type `SecurityScopes`:
|
||||
* This `security_scopes` parameter has a property `scopes` with a `list` containing all these scopes declared above, so:
|
||||
* `security_scopes.scopes` will contain `["me", "items"]` for the *path operation* `read_own_items`.
|
||||
* `security_scopes.scopes` will contain `["me"]` for the *path operation* `read_users_me`, because it is declared in the dependency `get_current_active_user`.
|
||||
* `security_scopes.scopes` will contain `[]` (nothing) for the *path operation* `read_system_status`, because it didn't declare any `Security` with `scopes`, and its dependency, `get_current_user`, doesn't declare any `scope` either.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The important and "magic" thing here is that `get_current_user` will have a different list of `scopes` to check for each *path operation*.
|
||||
|
||||
All depending on the `scopes` declared in each *path operation* and each dependency in the dependency tree for that specific *path operation*.
|
||||
|
||||
## More details about `SecurityScopes`
|
||||
|
||||
You can use `SecurityScopes` at any point, and in multiple places, it doesn't have to be at the "root" dependency.
|
||||
|
||||
It will always have the security scopes declared in the current `Security` dependencies and all the dependants for **that specific** *path operation* and **that specific** dependency tree.
|
||||
|
||||
Because the `SecurityScopes` will have all the scopes declared by dependants, you can use it to verify that a token has the required scopes in a central dependency function, and then declare different scope requirements in different *path operations*.
|
||||
|
||||
They will be checked independently for each *path operation*.
|
||||
|
||||
## Check it
|
||||
|
||||
If you open the API docs, you can authenticate and specify which scopes you want to authorize.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/security/image11.png">
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't select any scope, you will be "authenticated", but when you try to access `/users/me/` or `/users/me/items/` you will get an error saying that you don't have enough permissions. You will still be able to access `/status/`.
|
||||
|
||||
And if you select the scope `me` but not the scope `items`, you will be able to access `/users/me/` but not `/users/me/items/`.
|
||||
|
||||
That's what would happen to a third party application that tried to access one of these *path operations* with a token provided by a user, depending on how many permissions the user gave the application.
|
||||
|
||||
## About third party integrations
|
||||
|
||||
In this example we are using the OAuth2 "password" flow.
|
||||
|
||||
This is appropriate when we are logging in to our own application, probably with our own frontend.
|
||||
|
||||
Because we can trust it to receive the `username` and `password`, as we control it.
|
||||
|
||||
But if you are building an OAuth2 application that others would connect to (i.e., if you are building an authentication provider equivalent to Facebook, Google, GitHub, etc.) you should use one of the other flows.
|
||||
|
||||
The most common is the implicit flow.
|
||||
|
||||
The most secure is the code flow, but is more complex to implement as it requires more steps. As it is more complex, many providers end up suggesting the implicit flow.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
It's common that each authentication provider names their flows in a different way, to make it part of their brand.
|
||||
|
||||
But in the end, they are implementing the same OAuth2 standard.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** includes utilities for all these OAuth2 authentication flows in `fastapi.security.oauth2`.
|
||||
|
||||
## `Security` in decorator `dependencies`
|
||||
|
||||
The same way you can define a `list` of `Depends` in the decorator's `dependencies` parameter (as explained in [Dependencies in path operation decorators](../../tutorial/dependencies/dependencies-in-path-operation-decorators.md){.internal-link target=_blank}), you could also use `Security` with `scopes` there.
|
||||
529
docs/en/docs/advanced/sql-databases-peewee.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,529 @@
|
||||
# SQL (Relational) Databases with Peewee
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
If you are just starting, the tutorial [SQL (Relational) Databases](../tutorial/sql-databases.md){.internal-link target=_blank} that uses SQLAlchemy should be enough.
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to skip this.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are starting a project from scratch, you are probably better off with SQLAlchemy ORM ([SQL (Relational) Databases](../tutorial/sql-databases.md){.internal-link target=_blank}), or any other async ORM.
|
||||
|
||||
If you already have a code base that uses <a href="http://docs.peewee-orm.com/en/latest/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Peewee ORM</a>, you can check here how to use it with **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning "Python 3.7+ required"
|
||||
You will need Python 3.7 or above to safely use Peewee with FastAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
## Peewee for async
|
||||
|
||||
Peewee was not designed for async frameworks, or with them in mind.
|
||||
|
||||
Peewee has some heavy assumptions about its defaults and about how it should be used.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are developing an application with an older non-async framework, and can work with all its defaults, **it can be a great tool**.
|
||||
|
||||
But if you need to change some of the defaults, support more than one predefined database, work with an async framework (like FastAPI), etc, you will need to add quite some complex extra code to override those defaults.
|
||||
|
||||
Nevertheless, it's possible to do it, and here you'll see exactly what code you have to add to be able to use Peewee with FastAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
You can read more about Peewee's stand about async in Python <a href="http://docs.peewee-orm.com/en/latest/peewee/database.html#async-with-gevent" class="external-link" target="_blank">in the docs</a>, <a href="https://github.com/coleifer/peewee/issues/263#issuecomment-517347032" class="external-link" target="_blank">an issue</a>, <a href="https://github.com/coleifer/peewee/pull/2072#issuecomment-563215132" class="external-link" target="_blank">a PR</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## The same app
|
||||
|
||||
We are going to create the same application as in the SQLAlchemy tutorial ([SQL (Relational) Databases](../tutorial/sql-databases.md){.internal-link target=_blank}).
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the code is actually the same.
|
||||
|
||||
So, we are going to focus only on the differences.
|
||||
|
||||
## File structure
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say you have a directory named `my_super_project` that contains a sub-directory called `sql_app` with a structure like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
└── sql_app
|
||||
├── __init__.py
|
||||
├── crud.py
|
||||
├── database.py
|
||||
├── main.py
|
||||
└── schemas.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is almost the same structure as we had for the SQLAlchemy tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's see what each file/module does.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create the Peewee parts
|
||||
|
||||
Let's refer to the file `sql_app/database.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
### The standard Peewee code
|
||||
|
||||
Let's first check all the normal Peewee code, create a Peewee database:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 5 22"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/database.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Have in mind that if you wanted to use a different database, like PostgreSQL, you couldn't just change the string. You would need to use a different Peewee database class.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Note
|
||||
|
||||
The argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
check_same_thread=False
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
is equivalent to the one in the SQLAlchemy tutorial:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
connect_args={"check_same_thread": False}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...it is needed only for `SQLite`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info "Technical Details"
|
||||
|
||||
Exactly the same technical details as in [SQL (Relational) Databases](../tutorial/sql-databases.md#note){.internal-link target=_blank} apply.
|
||||
|
||||
### Make Peewee async-compatible `PeeweeConnectionState`
|
||||
|
||||
The main issue with Peewee and FastAPI is that Peewee relies heavily on <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/threading.html#thread-local-data" class="external-link" target="_blank">Python's `threading.local`</a>, and it doesn't have a direct way to override it or let you handle connections/sessions directly (as is done in the SQLAlchemy tutorial).
|
||||
|
||||
And `threading.local` is not compatible with the new async features of modern Python.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
`threading.local` is used to have a "magic" variable that has a different value for each thread.
|
||||
|
||||
This was useful in older frameworks designed to have one single thread per request, no more, no less.
|
||||
|
||||
Using this, each request would have its own database connection/session, which is the actual final goal.
|
||||
|
||||
But FastAPI, using the new async features, could handle more than one request on the same thread. And at the same time, for a single request, it could run multiple things in different threads (in a threadpool), depending on if you use `async def` or normal `def`. This is what gives all the performance improvements to FastAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
But Python 3.7 and above provide a more advanced alternative to `threading.local`, that can also be used in the places where `threading.local` would be used, but is compatible with the new async features.
|
||||
|
||||
We are going to use that. It's called <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/contextvars.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`contextvars`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
We are going to override the internal parts of Peewee that use `threading.local` and replace them with `contextvars`, with the corresponding updates.
|
||||
|
||||
This might seem a bit complex (and it actually is), you don't really need to completely understand how it works to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
We will create a `PeeweeConnectionState`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/database.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This class inherits from a special internal class used by Peewee.
|
||||
|
||||
It has all the logic to make Peewee use `contextvars` instead of `threading.local`.
|
||||
|
||||
`contextvars` works a bit differently than `threading.local`. But the rest of Peewee's internal code assumes that this class works with `threading.local`.
|
||||
|
||||
So, we need to do some extra tricks to make it work as if it was just using `threading.local`. The `__init__`, `__setattr__`, and `__getattr__` implement all the required tricks for this to be used by Peewee without knowing that it is now compatible with FastAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
This will just make Peewee behave correctly when used with FastAPI. Not randomly opening or closing connections that are being used, creating errors, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
But it doesn't give Peewee async super-powers. You should still use normal `def` functions and not `async def`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use the custom `PeeweeConnectionState` class
|
||||
|
||||
Now, overwrite the `._state` internal attribute in the Peewee database `db` object using the new `PeeweeConnectionState`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="24"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/database.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Make sure you overwrite `db._state` *after* creating `db`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
You would do the same for any other Peewee database, including `PostgresqlDatabase`, `MySQLDatabase`, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create the database models
|
||||
|
||||
Let's now see the file `sql_app/models.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create Peewee models for our data
|
||||
|
||||
Now create the Peewee models (classes) for `User` and `Item`.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the same you would do if you followed the Peewee tutorial and updated the models to have the same data as in the SQLAlchemy tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Peewee also uses the term "**model**" to refer to these classes and instances that interact with the database.
|
||||
|
||||
But Pydantic also uses the term "**model**" to refer to something different, the data validation, conversion, and documentation classes and instances.
|
||||
|
||||
Import `db` from `database` (the file `database.py` from above) and use it here.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 15 16 17 18 19 20 21"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/models.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Peewee creates several magic attributes.
|
||||
|
||||
It will automatically add an `id` attribute as an integer to be the primary key.
|
||||
|
||||
It will chose the name of the tables based on the class names.
|
||||
|
||||
For the `Item`, it will create an attribute `owner_id` with the integer ID of the `User`. But we don't declare it anywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create the Pydantic models
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's check the file `sql_app/schemas.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
To avoid confusion between the Peewee *models* and the Pydantic *models*, we will have the file `models.py` with the Peewee models, and the file `schemas.py` with the Pydantic models.
|
||||
|
||||
These Pydantic models define more or less a "schema" (a valid data shape).
|
||||
|
||||
So this will help us avoiding confusion while using both.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the Pydantic *models* / schemas
|
||||
|
||||
Create all the same Pydantic models as in the SQLAlchemy tutorial:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="16 17 18 21 22 25 26 27 28 29 30 34 35 38 39 42 43 44 45 46 47 48"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/schemas.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Here we are creating the models with an `id`.
|
||||
|
||||
We didn't explicitly specify an `id` attribute in the Peewee models, but Peewee adds one automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
We are also adding the magic `owner_id` attribute to `Item`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a `PeeweeGetterDict` for the Pydantic *models* / schemas
|
||||
|
||||
When you access a relationship in a Peewee object, like in `some_user.items`, Peewee doesn't provide a `list` of `Item`.
|
||||
|
||||
It provides a special custom object of class `ModelSelect`.
|
||||
|
||||
It's possible to create a `list` of its items with `list(some_user.items)`.
|
||||
|
||||
But the object itself is not a `list`. And it's also not an actual Python <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/glossary.html#term-generator" class="external-link" target="_blank">generator</a>. Because of this, Pydantic doesn't know by default how to convert it to a `list` of Pydantic *models* / schemas.
|
||||
|
||||
But recent versions of Pydantic allow providing a custom class that inherits from `pydantic.utils.GetterDict`, to provide the functionality used when using the `orm_mode = True` to retrieve the values for ORM model attributes.
|
||||
|
||||
We are going to create a custom `PeeweeGetterDict` class and use it in all the same Pydantic *models* / schemas that use `orm_mode`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 8 9 10 11 12 13 31 49"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/schemas.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here we are checking if the attribute that is being accessed (e.g. `.items` in `some_user.items`) is an instance of `peewee.ModelSelect`.
|
||||
|
||||
And if that's the case, just return a `list` with it.
|
||||
|
||||
And then we use it in the Pydantic *models* / schemas that use `orm_mode = True`, with the configuration variable `getter_dict = PeeweeGetterDict`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
We only need to create one `PeeweeGetterDict` class, and we can use it in all the Pydantic *models* / schemas.
|
||||
|
||||
## CRUD utils
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's see the file `sql_app/crud.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create all the CRUD utils
|
||||
|
||||
Create all the same CRUD utils as in the SQLAlchemy tutorial, all the code is very similar:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 4 5 8 9 12 13 16 17 18 19 20 23 24 27 28 29 30"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/crud.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are some differences with the code for the SQLAlchemy tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
We don't pass a `db` attribute around. Instead we use the models directly. This is because the `db` object is a global object, that includes all the connection logic. That's why we had to do all the `contextvars` updates above.
|
||||
|
||||
Aso, when returning several objects, like in `get_users`, we directly call `list`, like in:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
list(models.User.select())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is for the same reason that we had to create a custom `PeeweeGetterDict`. But by returning something that is already a `list` instead of the `peewee.ModelSelect` the `response_model` in the *path operation* with `List[models.User]` (that we'll see later) will work correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
## Main **FastAPI** app
|
||||
|
||||
And now in the file `sql_app/main.py` let's integrate and use all the other parts we created before.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the database tables
|
||||
|
||||
In a very simplistic way create the database tables:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 10 11"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/main.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a dependency
|
||||
|
||||
Create a dependency that will connect the database right at the beginning of a request and disconnect it at the end:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="23 24 25 26 27 28 29"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/main.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here we have an empty `yield` because we are actually not using the database object directly.
|
||||
|
||||
It is connecting to the database and storing the connection data in an internal variable that is independent for each request (using the `contextvars` tricks from above).
|
||||
|
||||
Because the database connection is potentially I/O blocking, this dependency is created with a normal `def` function.
|
||||
|
||||
And then, in each *path operation function* that needs to access the database we add it as a dependency.
|
||||
|
||||
But we are not using the value given by this dependency (it actually doesn't give any value, as it has an empty `yield`). So, we don't add it to the *path operation function* but to the *path operation decorator* in the `dependencies` parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="32 40 47 59 65 72"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/main.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Context variable sub-dependency
|
||||
|
||||
For all the `contextvars` parts to work, we need to make sure we have an independent value in the `ContextVar` for each request that uses the database, and that value will be used as the database state (connection, transactions, etc) for the whole request.
|
||||
|
||||
For that, we need to create another `async` dependency `reset_db_state()` that is used as a sub-dependency in `get_db()`. It will set the value for the context variable (with just a default `dict`) that will be used as the database state for the whole request. And then the dependency `get_db()` will store in it the database state (connection, transactions, etc).
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="18 19 20"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/main.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the **next request**, as we will reset that context variable again in the `async` dependency `reset_db_state()` and then create a new connection in the `get_db()` dependency, that new request will have its own database state (connection, transactions, etc).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
As FastAPI is an async framework, one request could start being processed, and before finishing, another request could be received and start processing as well, and it all could be processed in the same thread.
|
||||
|
||||
But context variables are aware of these async features, so, a Peewee database state set in the `async` dependency `reset_db_state()` will keep its own data throughout the entire request.
|
||||
|
||||
And at the same time, the other concurrent request will have its own database state that will be independent for the whole request.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Peewee Proxy
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using a <a href="http://docs.peewee-orm.com/en/latest/peewee/database.html#dynamically-defining-a-database" class="external-link" target="_blank">Peewee Proxy</a>, the actual database is at `db.obj`.
|
||||
|
||||
So, you would reset it with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 4"
|
||||
async def reset_db_state():
|
||||
database.db.obj._state._state.set(db_state_default.copy())
|
||||
database.db.obj._state.reset()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Create your **FastAPI** *path operations*
|
||||
|
||||
Now, finally, here's the standard **FastAPI** *path operations* code.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="32 33 34 35 36 37 40 41 42 43 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 65 66 67 68 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/main.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### About `def` vs `async def`
|
||||
|
||||
The same as with SQLAlchemy, we are not doing something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
user = await models.User.select().first()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...but instead we are using:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
user = models.User.select().first()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
So, again, we should declare the *path operation functions* and the dependency without `async def`, just with a normal `def`, as:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2"
|
||||
# Something goes here
|
||||
def read_users(skip: int = 0, limit: int = 100):
|
||||
# Something goes here
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Testing Peewee with async
|
||||
|
||||
This example includes an extra *path operation* that simulates a long processing request with `time.sleep(sleep_time)`.
|
||||
|
||||
It will have the database connection open at the beginning and will just wait some seconds before replying back. And each new request will wait one second less.
|
||||
|
||||
This will easily let you test that your app with Peewee and FastAPI is behaving correctly with all the stuff about threads.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to check how Peewee would break your app if used without modification, go the the `sql_app/database.py` file and comment the line:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
# db._state = PeeweeConnectionState()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And in the file `sql_app/main.py` file, comment the body of the `async` dependency `reset_db_state()` and replace it with a `pass`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
async def reset_db_state():
|
||||
# database.db._state._state.set(db_state_default.copy())
|
||||
# database.db._state.reset()
|
||||
pass
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then run your app with Uvicorn:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn sql_app.main:app --reload
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Open your browser at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a> and create a couple of users.
|
||||
|
||||
Then open 10 tabs at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs#/default/read_slow_users_slowusers__get" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs#/default/read_slow_users_slowusers__get</a> at the same time.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the *path operation* "Get `/slowusers/`" in all of the tabs. Use the "Try it out" button and execute the request in each tab, one right after the other.
|
||||
|
||||
The tabs will wait for a bit and then some of them will show `Internal Server Error`.
|
||||
|
||||
### What happens
|
||||
|
||||
The first tab will make your app create a connection to the database and wait for some seconds before replying back and closing the database connection.
|
||||
|
||||
Then, for the request in the next tab, your app will wait for one second less, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
This means that it will end up finishing some of the last tabs' requests earlier than some of the previous ones.
|
||||
|
||||
Then one the last requests that wait less seconds will try to open a database connection, but as one of those previous requests for the other tabs will probably be handled in the same thread as the first one, it will have the same database connection that is already open, and Peewee will throw an error and you will see it in the terminal, and the response will have an `Internal Server Error`.
|
||||
|
||||
This will probably happen for more than one of those tabs.
|
||||
|
||||
If you had multiple clients talking to your app exactly at the same time, this is what could happen.
|
||||
|
||||
And as your app starts to handle more and more clients at the same time, the waiting time in a single request needs to be shorter and shorter to trigger the error.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fix Peewee with FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
Now go back to the file `sql_app/database.py`, and uncomment the line:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
db._state = PeeweeConnectionState()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And in the file `sql_app/main.py` file, uncomment the body of the `async` dependency `reset_db_state()`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
async def reset_db_state():
|
||||
database.db._state._state.set(db_state_default.copy())
|
||||
database.db._state.reset()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Terminate your running app and start it again.
|
||||
|
||||
Repeat the same process with the 10 tabs. This time all of them will wait and you will get all the results without errors.
|
||||
|
||||
...You fixed it!
|
||||
|
||||
## Review all the files
|
||||
|
||||
Remember you should have a directory named `my_super_project` (or however you want) that contains a sub-directory called `sql_app`.
|
||||
|
||||
`sql_app` should have the following files:
|
||||
|
||||
* `sql_app/__init__.py`: is an empty file.
|
||||
|
||||
* `sql_app/database.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/database.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* `sql_app/models.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/models.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* `sql_app/schemas.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/schemas.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* `sql_app/crud.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/crud.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* `sql_app/main.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases_peewee/sql_app/main.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Technical Details
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
These are very technical details that you probably don't need.
|
||||
|
||||
### The problem
|
||||
|
||||
Peewee uses <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/threading.html#thread-local-data" class="external-link" target="_blank">`threading.local`</a> by default to store it's database "state" data (connection, transactions, etc).
|
||||
|
||||
`threading.local` creates a value exclusive to the current thread, but an async framework would run all the code (e.g. for each request) in the same thread, and possibly not in order.
|
||||
|
||||
On top of that, an async framework could run some sync code in a threadpool (using `asyncio.run_in_executor`), but belonging to the same request.
|
||||
|
||||
This means that, with Peewee's current implementation, multiple tasks could be using the same `threading.local` variable and end up sharing the same connection and data (that they shouldn't), and at the same time, if they execute sync I/O-blocking code in a threadpool (as with normal `def` functions in FastAPI, in *path operations* and dependencies), that code won't have access to the database state variables, even while it's part of the same request and it should be able to get access to the same database state.
|
||||
|
||||
### Context variables
|
||||
|
||||
Python 3.7 has <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/contextvars.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`contextvars`</a> that can create a local variable very similar to `threading.local`, but also supporting these async features.
|
||||
|
||||
There are several things to have in mind.
|
||||
|
||||
The `ContextVar` has to be created at the top of the module, like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
some_var = ContextVar("some_var", default="default value")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To set a value used in the current "context" (e.g. for the current request) use:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
some_var.set("new value")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To get a value anywhere inside of the context (e.g. in any part handling the current request) use:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
some_var.get()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Set context variables in the `async` dependency `reset_db_state()`
|
||||
|
||||
If some part of the async code sets the value with `some_var.set("updated in function")` (e.g. like the `async` dependency), the rest of the code in it and the code that goes after (including code inside of `async` functions called with `await`) will see that new value.
|
||||
|
||||
So, in our case, if we set the Peewee state variable (with a default `dict`) in the `async` dependency, all the rest of the internal code in our app will see this value and will be able to reuse it for the whole request.
|
||||
|
||||
And the context variable would be set again for the next request, even if they are concurrent.
|
||||
|
||||
### Set database state in the dependency `get_db()`
|
||||
|
||||
As `get_db()` is a normal `def` function, **FastAPI** will make it run in a threadpool, with a *copy* of the "context", holding the same value for the context variable (the `dict` with the reset database state). Then it can add database state to that `dict`, like the connection, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
But if the value of the context variable (the default `dict`) was set in that normal `def` function, it would create a new value that would stay only in that thread of the threadpool, and the rest of the code (like the *path operation functions*) wouldn't have access to it. In `get_db()` we can only set values in the `dict`, but not the entire `dict` itself.
|
||||
|
||||
So, we need to have the `async` dependency `reset_db_state()` to set the `dict` in the context variable. That way, all the code has access to the same `dict` for the database state for a single request.
|
||||
|
||||
### Connect and disconnect in the dependency `get_db()`
|
||||
|
||||
Then the next question would be, why not just connect and disconnect the database in the `async` dependency itself, instead of in `get_db()`?
|
||||
|
||||
The `async` dependency has to be `async` for the context variable to be preserved for the rest of the request, but creating and closing the database connection is potentially blocking, so it could degrade performance if it was there.
|
||||
|
||||
So we also need the normal `def` dependency `get_db()`.
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
# Sub Applications - Behind a Proxy, Mounts
|
||||
|
||||
There are at least two situations where you could need to create your **FastAPI** application using some specific paths.
|
||||
|
||||
But then you need to set them up to be served with a path prefix.
|
||||
@@ -33,7 +35,6 @@ For these cases, you can declare an `openapi_prefix` parameter in your `FastAPI`
|
||||
|
||||
See the section below, about "mounting", for an example.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Mounting a **FastAPI** application
|
||||
|
||||
"Mounting" means adding a complete "independent" application in a specific path, that then takes care of handling all the sub-paths.
|
||||
@@ -42,22 +43,22 @@ You could want to do this if you have several "independent" applications that yo
|
||||
|
||||
### Top-level application
|
||||
|
||||
First, create the main, top-level, **FastAPI** application, and its path operations:
|
||||
First, create the main, top-level, **FastAPI** application, and its *path operations*:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 6 7 8"
|
||||
{!./src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Sub-application
|
||||
|
||||
Then, create your sub-application, and its path operations.
|
||||
Then, create your sub-application, and its *path operations*.
|
||||
|
||||
This sub-application is just another standard FastAPI application, but this is the one that will be "mounted".
|
||||
|
||||
When creating the sub-application, use the parameter `openapi_prefix`. In this case, with a prefix of `/subapi`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 14 15 16"
|
||||
{!./src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Mount the sub-application
|
||||
@@ -67,29 +68,33 @@ In your top-level application, `app`, mount the sub-application, `subapi`.
|
||||
Here you need to make sure you use the same path that you used for the `openapi_prefix`, in this case, `/subapi`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 19"
|
||||
{!./src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Check the automatic API docs
|
||||
|
||||
Now, run `uvicorn`, if your file is at `main.py`, it would be:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
uvicorn main:app --reload
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --reload
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And open the docs at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
And open the docs at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the automatic API docs for the main app, including only its own paths:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/sub-applications/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
And then, open the docs for the sub-application, at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/subapi/docs" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/subapi/docs</a>.
|
||||
And then, open the docs for the sub-application, at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/subapi/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/subapi/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the automatic API docs for the sub-application, including only its own sub-paths, with their correct prefix:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/sub-applications/image02.png">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If you try interacting with any of the two user interfaces, they will work, because the browser will be able to talk to the correct path (or sub-path).
|
||||
If you try interacting with any of the two user interfaces, they will work, because the browser will be able to talk to the correct path (or sub-path).
|
||||
86
docs/en/docs/advanced/templates.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
# Templates
|
||||
|
||||
You can use any template engine you want with **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
A common election is Jinja2, the same one used by Flask and other tools.
|
||||
|
||||
There are utilities to configure it easily that you can use directly in your **FastAPI** application (provided by Starlette).
|
||||
|
||||
## Install dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
Install `jinja2`:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install jinja2
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to also serve static files (as in this example), install `aiofiles`:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install aiofiles
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Using `Jinja2Templates`
|
||||
|
||||
* Import `Jinja2Templates`.
|
||||
* Create a `templates` object that you can re-use later.
|
||||
* Declare a `Request` parameter in the *path operation* that will return a template.
|
||||
* Use the `templates` you created to render and return a `TemplateResponse`, passing the `request` as one of the key-value pairs in the Jinja2 "context".
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 10 14 15"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/templates/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
Notice that you have to pass the `request` as part of the key-value pairs in the context for Jinja2. So, you also have to declare it in your *path operation*.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
You could also use `from starlette.templating import Jinja2Templates`.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** provides the same `starlette.templating` as `fastapi.templating` just as a convenience for you, the developer. But most of the available responses come directly from Starlette. The same with `Request` and `StaticFiles`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Writing templates
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can write a template at `templates/item.html` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```jinja hl_lines="7"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/templates/templates/item.html!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It will show the `id` taken from the "context" `dict` you passed:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
{"request": request, "id": id}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Templates and static files
|
||||
|
||||
And you can also use `url_for()` inside of the template, and use it, for example, with the `StaticFiles` you mounted.
|
||||
|
||||
```jinja hl_lines="4"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/templates/templates/item.html!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, it would link to a CSS file at `static/styles.css` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```CSS hl_lines="4"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/templates/static/styles.css!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And because you are using `StaticFiles`, that CSS file would be served automatically by your **FastAPI** application at the URL `/static/styles.css`.
|
||||
|
||||
## More details
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, including how to test templates, check <a href="https://www.starlette.io/templates/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette's docs on templates</a>.
|
||||
61
docs/en/docs/advanced/testing-dependencies.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
# Testing Dependencies with Overrides
|
||||
|
||||
## Overriding dependencies during testing
|
||||
|
||||
There are some scenarios where you might want to override a dependency during testing.
|
||||
|
||||
You don't want the original dependency to run (nor any of the sub-dependencies it might have).
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, you want to provide a different dependency that will be used only during tests (possibly only some specific tests), and will provide a value that can be used where the value of the original dependency was used.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use cases: external service
|
||||
|
||||
An example could be that you have an external authentication provider that you need to call.
|
||||
|
||||
You send it a token and it returns an authenticated user.
|
||||
|
||||
This provider might be charging you per request, and calling it might take some extra time than if you had a fixed mock user for tests.
|
||||
|
||||
You probably want to test the external provider once, but not necessarily call it for every test that runs.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, you can override the dependency that calls that provider, and use a custom dependency that returns a mock user, only for your tests.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use case: testing database
|
||||
|
||||
Other example could be that you are using a specific database only for testing.
|
||||
|
||||
Your normal dependency would return a database session.
|
||||
|
||||
But then, after each test, you could want to rollback all the operations or remove data.
|
||||
|
||||
Or you could want to alter the data before the tests run, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, you could use a dependency override to return your *custom* database session instead of the one that would be used normally.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use the `app.dependency_overrides` attribute
|
||||
|
||||
For these cases, your **FastAPI** application has an attribute `app.dependency_overrides`, it is a simple `dict`.
|
||||
|
||||
To override a dependency for testing, you put as a key the original dependency (a function), and as the value, your dependency override (another function).
|
||||
|
||||
And then **FastAPI** will call that override instead of the original dependency.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="24 25 28"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependency_testing/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
You can set a dependency override for a dependency used anywhere in your **FastAPI** application.
|
||||
|
||||
The original dependency could be used in a *path operation function*, a *path operation decorator* (when you don't use the return value), a `.include_router()` call, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI will still be able to override it.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can reset your overrides (remove them) by setting `app.dependency_overrides` to be an empty `dict`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
app.dependency_overrides = {}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
If you want to override a dependency only during some tests, you can set the override at the beginning of the test (inside the test function) and reset it at the end (at the end of the test function).
|
||||
7
docs/en/docs/advanced/testing-events.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
# Testing Events: startup - shutdown
|
||||
|
||||
When you need your event handlers (`startup` and `shutdown`) to run in your tests, you can use the `TestClient` with a `with` statement:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 10 11 12 20 21 22 23 24"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/app_testing/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
9
docs/en/docs/advanced/testing-websockets.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
# Testing WebSockets
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the same `TestClient` to test WebSockets.
|
||||
|
||||
For this, you use the `TestClient` in a `with` statement, connecting to the WebSocket:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="27 28 29 30 31"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/app_testing/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
# Using the Request Directly
|
||||
|
||||
Up to now, you have been declaring the parts of the request that you need with their types.
|
||||
|
||||
Taking data from:
|
||||
@@ -13,9 +15,9 @@ But there are situations where you might need to access the `Request` object dir
|
||||
|
||||
## Details about the `Request` object
|
||||
|
||||
As **FastAPI** is actually **Starlette** underneath, with a layer of several tools on top, you can use Starlette's <a href="https://www.starlette.io/requests/" target="_blank">`Request`</a> object directly when you need to.
|
||||
As **FastAPI** is actually **Starlette** underneath, with a layer of several tools on top, you can use Starlette's <a href="https://www.starlette.io/requests/" class="external-link" target="_blank">`Request`</a> object directly when you need to.
|
||||
|
||||
It would also mean that if you get data from the `Request` object directly (for example, read the body) it won't be validated, converted or annotated (with OpenAPI, for the automatic documentation) by FastAPI.
|
||||
It would also mean that if you get data from the `Request` object directly (for example, read the body) it won't be validated, converted or documented (with OpenAPI, for the automatic API user interface) by FastAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
Although any other parameter declared normally (for example, the body with a Pydantic model) would still be validated, converted, annotated, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -27,24 +29,14 @@ Let's imagine you want to get the client's IP address/host inside of your *path
|
||||
|
||||
For that you need to access the request directly.
|
||||
|
||||
### Import the `Request`
|
||||
|
||||
First, import the `Request` class from Starlette:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2"
|
||||
{!./src/using_request_directly/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 7 8"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/using_request_directly/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Declare the `Request` parameter
|
||||
|
||||
Then declare a *path operation function* parameter with the type being the `Request` class:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8"
|
||||
{!./src/using_request_directly/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
By declaring a *path operation function* parameter with the type being the `Request` **FastAPI** will know to pass the `Request` in that parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Note that in this case, we are declaring a path parameter besides the request parameter.
|
||||
Note that in this case, we are declaring a path parameter beside the request parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
So, the path parameter will be extracted, validated, converted to the specified type and annotated with OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -52,4 +44,9 @@ Then declare a *path operation function* parameter with the type being the `Requ
|
||||
|
||||
## `Request` documentation
|
||||
|
||||
You can read more details about the <a href="https://www.starlette.io/requests/" target="_blank">`Request` object in the official Starlette documentation site</a>.
|
||||
You can read more details about the <a href="https://www.starlette.io/requests/" class="external-link" target="_blank">`Request` object in the official Starlette documentation site</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
You could also use `from starlette.requests import Request`.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** provides it directly just as a convenience for you, the developer. But it comes directly from Starlette.
|
||||
117
docs/en/docs/advanced/websockets.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
|
||||
# WebSockets
|
||||
|
||||
You can use <a href="https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/WebSockets_API" class="external-link" target="_blank">WebSockets</a> with **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
## WebSockets client
|
||||
|
||||
### In production
|
||||
|
||||
In your production system, you probably have a frontend created with a modern framework like React, Vue.js or Angular.
|
||||
|
||||
And to communicate using WebSockets with your backend you would probably use your frontend's utilities.
|
||||
|
||||
Or you might have a native mobile application that communicates with your WebSocket backend directly, in native code.
|
||||
|
||||
Or you might have any other way to communicate with the WebSocket endpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
But for this example, we'll use a very simple HTML document with some JavaScript, all inside a long string.
|
||||
|
||||
This, of course, is not optimal and you wouldn't use it for production.
|
||||
|
||||
In production you would have one of the options above.
|
||||
|
||||
But it's the simplest way to focus on the server-side of WebSockets and have a working example:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 41 42 43"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/websockets/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a `websocket`
|
||||
|
||||
In your **FastAPI** application, create a `websocket`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 46 47"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/websockets/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
You could also use `from starlette.websockets import WebSocket`.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** provides the same `WebSocket` directly just as a convenience for you, the developer. But it comes directly from Starlette.
|
||||
|
||||
## Await for messages and send messages
|
||||
|
||||
In your WebSocket route you can `await` for messages and send messages.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="48 49 50 51 52"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/websockets/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can receive and send binary, text, and JSON data.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using `Depends` and others
|
||||
|
||||
In WebSocket endpoints you can import from `fastapi` and use:
|
||||
|
||||
* `Depends`
|
||||
* `Security`
|
||||
* `Cookie`
|
||||
* `Header`
|
||||
* `Path`
|
||||
* `Query`
|
||||
|
||||
They work the same way as for other FastAPI endpoints/*path operations*:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="53 54 55 56 57 58 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/websockets/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
In a WebSocket it doesn't really make sense to raise an `HTTPException`. So it's better to close the WebSocket connection directly.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use a closing code from the <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6455#section-7.4.1" class="external-link" target="_blank">valid codes defined in the specification</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
In the future, there will be a `WebSocketException` that you will be able to `raise` from anywhere, and add exception handlers for it. It depends on the <a href="https://github.com/encode/starlette/pull/527" class="external-link" target="_blank">PR #527</a> in Starlette.
|
||||
|
||||
## More info
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about the options, check Starlette's documentation for:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.starlette.io/websockets/" class="external-link" target="_blank">The `WebSocket` class</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.starlette.io/endpoints/#websocketendpoint" class="external-link" target="_blank">Class-based WebSocket handling</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Test it
|
||||
|
||||
If your file is named `main.py`, run your application with:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --reload
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Open your browser at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see a simple page like:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/websockets/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
You can type messages in the input box, and send them:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/websockets/image02.png">
|
||||
|
||||
And your **FastAPI** application with WebSockets will respond back:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/websockets/image03.png">
|
||||
|
||||
You can send (and receive) many messages:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/websockets/image04.png">
|
||||
|
||||
And all of them will use the same WebSocket connection.
|
||||
37
docs/en/docs/advanced/wsgi.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
# Including WSGI - Flask, Django, others
|
||||
|
||||
You can mount WSGI applications as you saw with [Sub Applications - Behind a Proxy, Mounts](./sub-applications-proxy.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
For that, you can use the `WSGIMiddleware` and use it to wrap your WSGI application, for example, Flask, Django, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using `WSGIMiddleware`
|
||||
|
||||
You need to import `WSGIMiddleware`.
|
||||
|
||||
Then wrap the WSGI (e.g. Flask) app with the middleware.
|
||||
|
||||
And then mount that under a path.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 3 22"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/wsgi/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Check it
|
||||
|
||||
Now, every request under the path `/v1/` will be handled by the Flask application.
|
||||
|
||||
And the rest will be handled by **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
If you run it with Uvicorn and go to <a href="http://localhost:8000/v1/" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://localhost:8000/v1/</a> you will see the response from Flask:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
Hello, World from Flask!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And if you go to <a href="http://localhost:8000/v2" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://localhost:8000/v2</a> you will see the response from FastAPI:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{
|
||||
"message": "Hello World"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
# Alternatives, Inspiration and Comparisons
|
||||
|
||||
What inspired **FastAPI**, how it compares to other alternatives and what it learned from them.
|
||||
|
||||
## Intro
|
||||
@@ -12,7 +14,7 @@ But at some point, there was no other option than creating something that provid
|
||||
|
||||
## Previous tools
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://www.djangoproject.com/" target="_blank">Django</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://www.djangoproject.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Django</a>
|
||||
|
||||
It's the most popular Python framework and is widely trusted. It is used to build systems like Instagram.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +22,7 @@ It's relatively tightly coupled with relational databases (like MySQL or Postgre
|
||||
|
||||
It was created to generate the HTML in the backend, not to create APIs used by a modern frontend (like React, Vue.js and Angular) or by other systems (like <abbr title="Internet of Things">IoT</abbr> devices) communicating with it.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://www.django-rest-framework.org/" target="_blank">Django REST Framework</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://www.django-rest-framework.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Django REST Framework</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Django REST framework was created to be a flexible toolkit for building Web APIs using Django underneath, to improve its API capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +37,7 @@ It was one of the first examples of **automatic API documentation**, and this wa
|
||||
!!! check "Inspired **FastAPI** to"
|
||||
Have an automatic API documentation web user interface.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="http://flask.pocoo.org/" target="_blank">Flask</a>
|
||||
### <a href="http://flask.pocoo.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Flask</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Flask is a "microframework", it doesn't include database integrations nor many of the things that come by default in Django.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -55,7 +57,7 @@ Given the simplicity of Flask, it seemed like a good match for building APIs. Th
|
||||
Have a simple and easy to use routing system.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="http://docs.python-requests.org" target="_blank">Requests</a>
|
||||
### <a href="http://docs.python-requests.org" class="external-link" target="_blank">Requests</a>
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** is not actually an alternative to **Requests**. Their scope is very different.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -79,7 +81,7 @@ The way you use it is very simple. For example, to do a `GET` request, you would
|
||||
response = requests.get("http://example.com/some/url")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The FastAPI counterpart API path operation could look like:
|
||||
The FastAPI counterpart API *path operation* could look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1"
|
||||
@app.get("/some/url")
|
||||
@@ -95,7 +97,7 @@ See the similarities in `requests.get(...)` and `@app.get(...)`.
|
||||
* Have sensible defaults, but powerful customizations.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://swagger.io/" target="_blank">Swagger</a> / <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/" target="_blank">OpenAPI</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://swagger.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Swagger</a> / <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI</a>
|
||||
|
||||
The main feature I wanted from Django REST Framework was the automatic API documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -112,8 +114,8 @@ That's why when talking about version 2.0 it's common to say "Swagger", and for
|
||||
|
||||
And integrate standards-based user interface tools:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui" target="_blank">Swagger UI</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc" target="_blank">ReDoc</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui" class="external-link" target="_blank">Swagger UI</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">ReDoc</a>
|
||||
|
||||
These two were chosen for being fairly popular and stable, but doing a quick search, you could find dozens of additional alternative user interfaces for OpenAPI (that you can use with **FastAPI**).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -121,7 +123,7 @@ That's why when talking about version 2.0 it's common to say "Swagger", and for
|
||||
|
||||
There are several Flask REST frameworks, but after investing the time and work into investigating them, I found that many are discontinued or abandoned, with several standing issues that made them unfit.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://marshmallow.readthedocs.io/en/3.0/" target="_blank">Marshmallow</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://marshmallow.readthedocs.io/en/3.0/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Marshmallow</a>
|
||||
|
||||
One of the main features needed by API systems is data "<abbr title="also called marshalling, conversion">serialization</abbr>" which is taking data from the code (Python) and converting it into something that can be sent through the network. For example, converting an object containing data from a database into a JSON object. Converting `datetime` objects into strings, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -136,23 +138,23 @@ But it was created before there existed Python type hints. So, to define every <
|
||||
!!! check "Inspired **FastAPI** to"
|
||||
Use code to define "schemas" that provide data types and validation, automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://webargs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/" target="_blank">Webargs</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://webargs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Webargs</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Another big feature required by APIs is <abbr title="reading and converting to Python data">parsing</abbr> data from incoming requests.
|
||||
|
||||
Webargs is a tool that was made to provide that on top of several frameworks, including Flask.
|
||||
|
||||
It uses Marshmallow underneath to do the data validation. And it was created by the same guys.
|
||||
It uses Marshmallow underneath to do the data validation. And it was created by the same developers.
|
||||
|
||||
It's a great tool and I have used it a lot too, before having **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Webargs was created by the same Marshmallow guys.
|
||||
Webargs was created by the same Marshmallow developers.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! check "Inspired **FastAPI** to"
|
||||
Have automatic validation of incoming request data.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://apispec.readthedocs.io/en/stable/" target="_blank">APISpec</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://apispec.readthedocs.io/en/stable/" class="external-link" target="_blank">APISpec</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Marshmallow and Webargs provide validation, parsing and serialization as plug-ins.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -171,13 +173,13 @@ But then, we have again the problem of having a micro-syntax, inside of a Python
|
||||
The editor can't help much with that. And if we modify parameters or Marshmallow schemas and forget to also modify that YAML docstring, the generated schema would be obsolete.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
APISpec was created by the same Marshmallow guys.
|
||||
APISpec was created by the same Marshmallow developers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
!!! check "Inspired **FastAPI** to"
|
||||
Support the open standard for APIs, OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://flask-apispec.readthedocs.io/en/latest/" target="_blank">Flask-apispec</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://flask-apispec.readthedocs.io/en/latest/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Flask-apispec</a>
|
||||
|
||||
It's a Flask plug-in, that ties together Webargs, Marshmallow and APISpec.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -191,19 +193,19 @@ This combination of Flask, Flask-apispec with Marshmallow and Webargs was my fav
|
||||
|
||||
Using it led to the creation of several Flask full-stack generators. These are the main stack I (and several external teams) have been using up to now:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-flask-couchbase" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-flask-couchbase</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-flask-couchdb" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-flask-couchdb</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-flask-couchbase" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-flask-couchbase</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-flask-couchdb" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-flask-couchdb</a>
|
||||
|
||||
And these same full-stack generators were the base of the <a href="/project-generation/" target="_blank">**FastAPI** project generator</a>.
|
||||
And these same full-stack generators were the base of the [**FastAPI** Project Generators](project-generation.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Flask-apispec was created by the same Marshmallow guys.
|
||||
Flask-apispec was created by the same Marshmallow developers.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! check "Inspired **FastAPI** to"
|
||||
Generate the OpenAPI schema automatically, from the same code that defines serialization and validation.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://nestjs.com/" target="_blank">NestJS</a> (and <a href="https://angular.io/" target="_blank">Angular</a>)
|
||||
### <a href="https://nestjs.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">NestJS</a> (and <a href="https://angular.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Angular</a>)
|
||||
|
||||
This isn't even Python, NestJS is a JavaScript (TypeScript) NodeJS framework inspired by Angular.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -222,21 +224,38 @@ It can't handle nested models very well. So, if the JSON body in the request is
|
||||
|
||||
Have a powerful dependency injection system. Find a way to minimize code repetition.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://sanic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/" target="_blank">Sanic</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://sanic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Sanic</a>
|
||||
|
||||
It was one of the first extremely fast Python frameworks based on `asyncio`. It was made to be very similar to Flask.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
It used <a href="https://github.com/MagicStack/uvloop" target="_blank">`uvloop`</a> instead of the default Python `asyncio` loop. That's what made it so fast.
|
||||
It used <a href="https://github.com/MagicStack/uvloop" class="external-link" target="_blank">`uvloop`</a> instead of the default Python `asyncio` loop. That's what made it so fast.
|
||||
|
||||
It <a href="https://github.com/huge-success/sanic/issues/761" target="_blank">still doesn't implement the ASGI spec for Python asynchronous web development</a>, but it clearly inspired Uvicorn and Starlette, that are currently faster than Sanic in open benchmarks.
|
||||
It clearly inspired Uvicorn and Starlette, that are currently faster than Sanic in open benchmarks.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! check "Inspired **FastAPI** to"
|
||||
Find a way to have a crazy performance.
|
||||
|
||||
That's why **FastAPI** is based on Starlette, as it is the fastest framework available (tested by third-party benchmarks).
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://moltenframework.com/" target="_blank">Molten</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://falconframework.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Falcon</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Falcon is another high performance Python framework, it is designed to be minimal, and work as the foundation of other frameworks like Hug.
|
||||
|
||||
It uses the previous standard for Python web frameworks (WSGI) which is synchronous, so it can't handle WebSockets and other use cases. Nevertheless, it also has a very good performance.
|
||||
|
||||
It is designed to have functions that receive two parameters, one "request" and one "response". Then you "read" parts from the request, and "write" parts to the response. Because of this design, it is not possible to declare request parameters and bodies with standard Python type hints as function parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
So, data validation, serialization, and documentation, have to be done in code, not automatically. Or they have to be implemented as a framework on top of Falcon, like Hug. This same distinction happens in other frameworks that are inspired by Falcon's design, of having one request object and one response object as parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! check "Inspired **FastAPI** to"
|
||||
Find ways to get great performance.
|
||||
|
||||
Along with Hug (as Hug is based on Falcon) inspired **FastAPI** to declare a `response` parameter in functions.
|
||||
|
||||
Although in FastAPI it's optional, and is used mainly to set headers, cookies, and alternative status codes.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://moltenframework.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Molten</a>
|
||||
|
||||
I discovered Molten in the first stages of building **FastAPI**. And it has quite similar ideas:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -257,11 +276,35 @@ Routes are declared in a single place, using functions declared in other places
|
||||
|
||||
This actually inspired updating parts of Pydantic, to support the same validation declaration style (all this functionality is now already available in Pydantic).
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://github.com/encode/apistar" target="_blank">APIStar</a> (<= 0.5)
|
||||
### <a href="http://www.hug.rest/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Hug</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Hug was one of the first frameworks to implement the declaration of API parameter types using Python type hints. This was a great idea that inspired other tools to do the same.
|
||||
|
||||
It used custom types in its declarations instead of standard Python types, but it was still a huge step forward.
|
||||
|
||||
It also was one of the first frameworks to generate a custom schema declaring the whole API in JSON.
|
||||
|
||||
It was not based on a standard like OpenAPI and JSON Schema. So it wouldn't be straightforward to integrate it with other tools, like Swagger UI. But again, it was a very innovative idea.
|
||||
|
||||
It has an interesting, uncommon feature: using the same framework, it's possible to create APIs and also CLIs.
|
||||
|
||||
As it is based on the previous standard for synchronous Python web frameworks (WSGI), it can't handle Websockets and other things, although it still has high performance too.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Hug was created by Timothy Crosley, the same creator of <a href="https://github.com/timothycrosley/isort" class="external-link" target="_blank">`isort`</a>, a great tool to automatically sort imports in Python files.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! check "Ideas inspired in **FastAPI**"
|
||||
Hug inspired parts of APIStar, and was one of the tools I found most promising, alongside APIStar.
|
||||
|
||||
Hug helped inspiring **FastAPI** to use Python type hints to declare parameters, and to generate a schema defining the API automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
Hug inspired **FastAPI** to declare a `response` parameter in functions to set headers and cookies.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://github.com/encode/apistar" class="external-link" target="_blank">APIStar</a> (<= 0.5)
|
||||
|
||||
Right before deciding to build **FastAPI** I found **APIStar** server. It had almost everything I was looking for and had a great design.
|
||||
|
||||
It was actually the first implementation of a framework using Python type hints to declare parameters and requests that I ever saw (before NestJS and Molten).
|
||||
It was one of the first implementations of a framework using Python type hints to declare parameters and requests that I ever saw (before NestJS and Molten). I found it more or less at the same time as Hug. But APIStar used the OpenAPI standard.
|
||||
|
||||
It had automatic data validation, data serialization and OpenAPI schema generation based on the same type hints in several places.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -301,7 +344,7 @@ Now APIStar is a set of tools to validate OpenAPI specifications, not a web fram
|
||||
|
||||
## Used by **FastAPI**
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/" target="_blank">Pydantic</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic is a library to define data validation, serialization and documentation (using JSON Schema) based on Python type hints.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -314,7 +357,7 @@ It is comparable to Marshmallow. Although it's faster than Marshmallow in benchm
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** then takes that JSON Schema data and puts it in OpenAPI, apart from all the other things it does.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" target="_blank">Starlette</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Starlette is a lightweight <abbr title="The new standard for building asynchronous Python web">ASGI</abbr> framework/toolkit, which is ideal for building high-performance asyncio services.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -354,7 +397,7 @@ That's one of the main things that **FastAPI** adds on top, all based on Python
|
||||
|
||||
So, anything that you can do with Starlette, you can do it directly with **FastAPI**, as it is basically Starlette on steroids.
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://www.uvicorn.org/" target="_blank">Uvicorn</a>
|
||||
### <a href="https://www.uvicorn.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uvicorn</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Uvicorn is a lightning-fast ASGI server, built on uvloop and httptools.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -367,8 +410,8 @@ It is the recommended server for Starlette and **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
You can combine it with Gunicorn, to have an asynchronous multi-process server.
|
||||
|
||||
Check more details in the <a href="/deployment/" target="_blank">Deployment</a> section.
|
||||
Check more details in the [Deployment](deployment.md){.internal-link target=_blank} section.
|
||||
|
||||
## Benchmarks and speed
|
||||
|
||||
To understand, compare, and see the difference between Uvicorn, Starlette and FastAPI, check the section about [Benchmarks](/benchmarks/).
|
||||
To understand, compare, and see the difference between Uvicorn, Starlette and FastAPI, check the section about [Benchmarks](benchmarks.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
@@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
|
||||
Details about the `async def` syntax for path operation functions and some background about asynchronous code, concurrency, and parallelism.
|
||||
# Concurrency and async / await
|
||||
|
||||
Details about the `async def` syntax for *path operation functions* and some background about asynchronous code, concurrency, and parallelism.
|
||||
|
||||
## In a hurry?
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,12 +8,11 @@ Details about the `async def` syntax for path operation functions and some backg
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using third party libraries that tell you to call them with `await`, like:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
results = await some_library()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, declare your path operation functions with `async def` like:
|
||||
Then, declare your *path operation functions* with `async def` like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2"
|
||||
@app.get('/')
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ async def read_results():
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using a third party library that communicates with something (a database, an API, the file system, etc) and doesn't have support for using `await`, (this is currently the case for most database libraries), then declare your path operation functions as normally, with just `def`, like:
|
||||
If you are using a third party library that communicates with something (a database, an API, the file system, etc) and doesn't have support for using `await`, (this is currently the case for most database libraries), then declare your *path operation functions* as normally, with just `def`, like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2"
|
||||
@app.get('/')
|
||||
@@ -45,13 +45,12 @@ If you just don't know, use normal `def`.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: you can mix `def` and `async def` in your path operation functions as much as you need and define each one using the best option for you. FastAPI will do the right thing with them.
|
||||
**Note**: you can mix `def` and `async def` in your *path operation functions* as much as you need and define each one using the best option for you. FastAPI will do the right thing with them.
|
||||
|
||||
Anyway, in any of the cases above, FastAPI will still work asynchronously and be extremely fast.
|
||||
|
||||
But by following the steps above, it will be able to do some performance optimizations.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Technical Details
|
||||
|
||||
Modern versions of Python have support for **"asynchronous code"** using something called **"coroutines"**, with **`async` and `await`** syntax.
|
||||
@@ -62,7 +61,6 @@ Let's see that phrase by parts in the sections below, below:
|
||||
* **`async` and `await`**
|
||||
* **Coroutines**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Asynchronous Code
|
||||
|
||||
Asynchronous code just means that the language has a way to tell the computer / program that at some point in the code, he will have to wait for *something else* to finish somewhere else. Let's say that *something else* is called "slow-file".
|
||||
@@ -92,7 +90,6 @@ Instead of that, by being an "asynchronous" system, once finished, the task can
|
||||
|
||||
For "synchronous" (contrary to "asynchronous") they commonly also use the term "sequential", because the computer / program follows all the steps in sequence before switching to a different task, even if those steps involve waiting.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Concurrency and Burgers
|
||||
|
||||
This idea of **asynchronous** code described above is also sometimes called **"concurrency"**. It is different from **"parallelism"**.
|
||||
@@ -103,7 +100,6 @@ But the details between *concurrency* and *parallelism* are quite different.
|
||||
|
||||
To see the difference, imagine the following story about burgers:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Concurrent Burgers
|
||||
|
||||
You go with your crush to get fast food, you stand in line while the cashier takes the orders from the people in front of you.
|
||||
@@ -144,14 +140,13 @@ So you wait for your crush to finish the story (finish the current work / task b
|
||||
|
||||
Then you go to the counter, to the initial task that is now finished, pick the burgers, say thanks and take them to the table. That finishes that step / task of interaction with the counter. That in turn, creates a new task, of "eating burgers", but the previous one of "getting burgers" is finished.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Parallel Burgers
|
||||
|
||||
You go with your crush to get parallel fast food.
|
||||
|
||||
You stand in line while several (let's say 8) cashiers take the orders from the people in front of you.
|
||||
|
||||
Everyone before you is waiting for their burgers to be ready before leaving the counter because each of the 8 cashiers goes himself and preparers the burger right away before getting the next order.
|
||||
Everyone before you is waiting for their burgers to be ready before leaving the counter because each of the 8 cashiers goes himself and prepares the burger right away before getting the next order.
|
||||
|
||||
Then it's finally your turn, you place your order of 2 very fancy burgers for your crush and you.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -195,7 +190,6 @@ And you have to wait in the line for a long time or you lose your turn.
|
||||
|
||||
You probably wouldn't want to take your crush with you to do errands at the bank.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Burger Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
In this scenario of "fast food burgers with your crush", as there is a lot of waiting, it makes a lot more sense to have a concurrent system.
|
||||
@@ -218,8 +212,7 @@ That kind of asynchronicity is what made NodeJS popular (even though NodeJS is n
|
||||
|
||||
And that's the same level of performance</a> you get with **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
And as you can have parallelism and asynchronicity at the same time, you get higher performance than most of the tested NodeJS frameworks and on par with Go, which is a compiled language closer to C <a href="https://www.techempower.com/benchmarks/#section=data-r17&hw=ph&test=query&l=zijmkf-1" target="_blank">(all thanks to Starlette)</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
And as you can have parallelism and asynchronicity at the same time, you get higher performance than most of the tested NodeJS frameworks and on par with Go, which is a compiled language closer to C <a href="https://www.techempower.com/benchmarks/#section=data-r17&hw=ph&test=query&l=zijmkf-1" class="external-link" target="_blank">(all thanks to Starlette)</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Is concurrency better than parallelism?
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -258,7 +251,6 @@ For example:
|
||||
* **Machine Learning**: it normally requires lots of "matrix" and "vector" multiplications. Think of a huge spreadsheet with numbers and multiplying all of them together at the same time.
|
||||
* **Deep Learning**: this is a sub-field of Machine Learning, so, the same applies. It's just that there is not a single spreadsheet of numbers to multiply, but a huge set of them, and in many cases, you use a special processor to build and / or use those models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Concurrency + Parallelism: Web + Machine Learning
|
||||
|
||||
With **FastAPI** you can take the advantage of concurrency that is very common for web development (the same main attractive of NodeJS).
|
||||
@@ -267,8 +259,7 @@ But you can also exploit the benefits of parallelism and multiprocessing (having
|
||||
|
||||
That, plus the simple fact that Python is the main language for **Data Science**, Machine Learning and especially Deep Learning, make FastAPI a very good match for Data Science / Machine Learning web APIs and applications (among many others).
|
||||
|
||||
To see how to achieve this parallelism in production see the section about [Deployment](deployment.md).
|
||||
|
||||
To see how to achieve this parallelism in production see the section about [Deployment](deployment.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
## `async` and `await`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -310,7 +301,7 @@ burgers = get_burgers(2)
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
So, if you are using a library that tells you that you can call it with `await`, you need to create the path operation functions that uses it with `async def`, like in:
|
||||
So, if you are using a library that tells you that you can call it with `await`, you need to create the *path operation functions* that uses it with `async def`, like in:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 3"
|
||||
@app.get('/burgers')
|
||||
@@ -327,10 +318,9 @@ But at the same time, functions defined with `async def` have to be "awaited". S
|
||||
|
||||
So, about the egg and the chicken, how do you call the first `async` function?
|
||||
|
||||
If you are working with **FastAPI** you don't have to worry about that, because that "first" function will be your path operation function, and FastAPI will know how to do the right thing.
|
||||
|
||||
But if you want to use `async` / `await` without FastAPI, <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/asyncio-task.html#coroutine" target="_blank">check the official Python docs</a>.
|
||||
If you are working with **FastAPI** you don't have to worry about that, because that "first" function will be your *path operation function*, and FastAPI will know how to do the right thing.
|
||||
|
||||
But if you want to use `async` / `await` without FastAPI, <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/asyncio-task.html#coroutine" class="external-link" target="_blank">check the official Python docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Other forms of asynchronous code
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -342,10 +332,9 @@ This same syntax (or almost identical) was also included recently in modern vers
|
||||
|
||||
But before that, handling asynchronous code was quite more complex and difficult.
|
||||
|
||||
In previous versions of Python, you could have used threads or <a href="http://www.gevent.org/" target="_blank">Gevent</a>. But the code is way more complex to understand, debug, and think about.
|
||||
|
||||
In previous versions of NodeJS / Browser JavaScript, you would have used "callbacks". Which lead to <a href="http://callbackhell.com/" target="_blank">callback hell</a>.
|
||||
In previous versions of Python, you could have used threads or <a href="http://www.gevent.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Gevent</a>. But the code is way more complex to understand, debug, and think about.
|
||||
|
||||
In previous versions of NodeJS / Browser JavaScript, you would have used "callbacks". Which lead to <a href="http://callbackhell.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">callback hell</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Coroutines
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -363,7 +352,6 @@ That should make more sense now.
|
||||
|
||||
All that is what powers FastAPI (through Starlette) and what makes it have such an impressive performance.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Very Technical Details
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
@@ -379,7 +367,7 @@ When you declare a *path operation function* with normal `def` instead of `async
|
||||
|
||||
If you are coming from another async framework that does not work in the way described above and you are used to define trivial compute-only *path operation functions* with plain `def` for a tiny performance gain (about 100 nanoseconds), please note that in **FastAPI** the effect would be quite opposite. In these cases, it's better to use `async def` unless your *path operation functions* use code that performs blocking <abbr title="Input/Output: disk reading or writing, network communications.">IO</abbr>.
|
||||
|
||||
Still, in both situations, chances are that **FastAPI** will <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/#performance" target="_blank">still be faster</a> than (or at least comparable to) your previous framework.
|
||||
Still, in both situations, chances are that **FastAPI** will [still be faster](/#performance){.internal-link target=_blank} than (or at least comparable to) your previous framework.
|
||||
|
||||
### Dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
|
||||
Independent TechEmpower benchmarks show **FastAPI** applications running under Uvicorn as <a href="https://www.techempower.com/benchmarks/#section=test&runid=a979de55-980d-4721-a46f-77298b3f3923&hw=ph&test=fortune&l=zijzen-7" target="_blank">one of the fastest Python frameworks available</a>, only below Starlette and Uvicorn themselves (used internally by FastAPI). (*)
|
||||
# Benchmarks
|
||||
|
||||
Independent TechEmpower benchmarks show **FastAPI** applications running under Uvicorn as <a href="https://www.techempower.com/benchmarks/#section=test&runid=7464e520-0dc2-473d-bd34-dbdfd7e85911&hw=ph&test=query&l=zijzen-7" class="external-link" target="_blank">one of the fastest Python frameworks available</a>, only below Starlette and Uvicorn themselves (used internally by FastAPI). (*)
|
||||
|
||||
But when checking benchmarks and comparisons you should have the following in mind.
|
||||
|
||||
485
docs/en/docs/contributing.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,485 @@
|
||||
# Development - Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
First, you might want to see the basic ways to [help FastAPI and get help](help-fastapi.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
## Developing
|
||||
|
||||
If you already cloned the repository and you know that you need to deep dive in the code, here are some guidelines to set up your environment.
|
||||
|
||||
### Virtual environment with `venv`
|
||||
|
||||
You can create a virtual environment in a directory using Python's `venv` module:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ python -m venv env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
That will create a directory `./env/` with the Python binaries and then you will be able to install packages for that isolated environment.
|
||||
|
||||
### Activate the environment
|
||||
|
||||
Activate the new environment with:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ source ./env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Or in Windows' PowerShell:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ .\env\Scripts\Activate.ps1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Or if you use Bash for Windows (e.g. <a href="https://gitforwindows.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Git Bash</a>):
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ source ./env/Scripts/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
To check it worked, use:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ which pip
|
||||
|
||||
some/directory/fastapi/env/bin/pip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
If it shows the `pip` binary at `env/bin/pip` then it worked. 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
Or in Windows PowerShell:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ Get-Command pip
|
||||
|
||||
some/directory/fastapi/env/bin/pip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Every time you install a new package with `pip` under that environment, activate the environment again.
|
||||
|
||||
This makes sure that if you use a terminal program installed by that package (like `flit`), you use the one from your local environment and not any other that could be installed globally.
|
||||
|
||||
### Flit
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** uses <a href="https://flit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">Flit</a> to build, package and publish the project.
|
||||
|
||||
After activating the environment as described above, install `flit`:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install flit
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Now re-activate the environment to make sure you are using the `flit` you just installed (and not a global one).
|
||||
|
||||
And now use `flit` to install the development dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ flit install --deps develop --symlink
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
If you are on Windows, use `--pth-file` instead of `--symlink`:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ flit install --deps develop --pth-file
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
It will install all the dependencies and your local FastAPI in your local environment.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Using your local FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
If you create a Python file that imports and uses FastAPI, and run it with the Python from your local environment, it will use your local FastAPI source code.
|
||||
|
||||
And if you update that local FastAPI source code, as it is installed with `--symlink` (or `--pth-file` on Windows), when you run that Python file again, it will use the fresh version of FastAPI you just edited.
|
||||
|
||||
That way, you don't have to "install" your local version to be able to test every change.
|
||||
|
||||
### Format
|
||||
|
||||
There is a script that you can run that will format and clean all your code:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ bash scripts/format.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
It will also auto-sort all your imports.
|
||||
|
||||
For it to sort them correctly, you need to have FastAPI installed locally in your environment, with the command in the section above using `--symlink` (or `--pth-file` on Windows).
|
||||
|
||||
### Format imports
|
||||
|
||||
There is another script that formats all the imports and makes sure you don't have unused imports:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ bash scripts/format-imports.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
As it runs one command after the other and modifies and reverts many files, it takes a bit longer to run, so it might be easier to use `scripts/format.sh` frequently and `scripts/format-imports.sh` only before committing.
|
||||
|
||||
## Docs
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure you set up your environment as described above, that will install all the requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
The documentation uses <a href="https://www.mkdocs.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">MkDocs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
And there are extra tools/scripts in place to handle translations in `./scripts/docs.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
You don't need to see the code in `./scripts/docs.py`, you just use it in the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
All the documentation is in Markdown format in the directory `./docs/en/`.
|
||||
|
||||
Many of the tutorials have blocks of code.
|
||||
|
||||
In most of the cases, these blocks of code are actual complete applications that can be run as is.
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, those blocks of code are not written inside the Markdown, they are Python files in the `./docs_src/` directory.
|
||||
|
||||
And those Python files are included/injected in the documentation when generating the site.
|
||||
|
||||
### Docs for tests
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the tests actually run against the example source files in the documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
This helps making sure that:
|
||||
|
||||
* The documentation is up to date.
|
||||
* The documentation examples can be run as is.
|
||||
* Most of the features are covered by the documentation, ensured by test coverage.
|
||||
|
||||
During local development, there is a script that builds the site and checks for any changes, live-reloading:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ python ./scripts/docs.py live
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">[INFO]</span> Serving on http://127.0.0.1:8008
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">[INFO]</span> Start watching changes
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">[INFO]</span> Start detecting changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
It will serve the documentation on `http://127.0.0.1:8008`.
|
||||
|
||||
That way, you can edit the documentation/source files and see the changes live.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Typer CLI (optional)
|
||||
|
||||
The instructions here show you how to use the script at `./scripts/docs.py` with the `python` program directly.
|
||||
|
||||
But you can also use <a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com/typer-cli/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Typer CLI</a>, and you will get autocompletion in your terminal for the commands after installing completion.
|
||||
|
||||
If you install Typer CLI, you can install completion with:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ typer --install-completion
|
||||
|
||||
zsh completion installed in /home/user/.bashrc.
|
||||
Completion will take effect once you restart the terminal.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
### Apps and docs at the same time
|
||||
|
||||
If you run the examples with, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn tutorial001:app --reload
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
as Uvicorn by default will use the port `8000`, the documentation on port `8008` won't clash.
|
||||
|
||||
### Translations
|
||||
|
||||
Help with translations is VERY MUCH appreciated! And it can't be done without the help from the community. 🌎 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the steps to help with translations.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tips and guidelines
|
||||
|
||||
* Add a single Pull Request per page translated. That will make it much easier for others to review it.
|
||||
|
||||
For the languages I don't speak, I'll wait for several others to review the translation before merging.
|
||||
|
||||
* You can also check if there are translations for your language and add a review to them, that will help me know that the translation is correct and I can merge it.
|
||||
|
||||
* Use the same Python examples and only translate the text in the docs. You don't have to change anything for this to work.
|
||||
|
||||
* Use the same images, file names, and links. You don't have to change anything for it to work.
|
||||
|
||||
* To check the 2-letter code for the language you want to translate you can use the table <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_ISO_639-1_codes" class="external-link" target="_blank">List of ISO 639-1 codes</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Existing language
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say you want to translate a page for a language that already has translations for some pages, like Spanish.
|
||||
|
||||
In the case of Spanish, the 2-letter code is `es`. So, the directory for Spanish translations is located at `docs/es/`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The main ("official") language is English, located at `docs/en/`.
|
||||
|
||||
Now run the live server for the docs in Spanish:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
// Use the command "live" and pass the language code as a CLI argument
|
||||
$ python ./scripts/docs.py live es
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">[INFO]</span> Serving on http://127.0.0.1:8008
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">[INFO]</span> Start watching changes
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">[INFO]</span> Start detecting changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8008" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8008</a> and see your changes live.
|
||||
|
||||
If you look at the FastAPI docs website, you will see that every language has all the pages. But some pages are not translated and have a notification about the missing translation.
|
||||
|
||||
But when you run it locally like this, you will only see the pages that are already translated.
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's say that you want to add a translation for the section [Features](features.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
* Copy the file at:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docs/en/docs/features.md
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Paste it in exactly the same location but for the language you want to translate, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docs/es/docs/features.md
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Notice that the only change in the path and file name is the language code, from `en` to `es`.
|
||||
|
||||
* Now open the MkDocs config file for English at:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docs/en/docs/mkdocs.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Find the place where that `docs/features.md` is located in the config file. Somewhere like:
|
||||
|
||||
```YAML hl_lines="8"
|
||||
site_name: FastAPI
|
||||
# More stuff
|
||||
nav:
|
||||
- FastAPI: index.md
|
||||
- Languages:
|
||||
- en: /
|
||||
- es: /es/
|
||||
- features.md
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Open the MkDocs config file for the language you are editing, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
docs/es/docs/mkdocs.yml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Add it there at the exact same location it was for English, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```YAML hl_lines="8"
|
||||
site_name: FastAPI
|
||||
# More stuff
|
||||
nav:
|
||||
- FastAPI: index.md
|
||||
- Languages:
|
||||
- en: /
|
||||
- es: /es/
|
||||
- features.md
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure that if there are other entries, the new entry with your translation is exactly in the same order as in the English version.
|
||||
|
||||
If you go to your browser you will see that now the docs show your new section. 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can translate it all and see how it looks as you save the file.
|
||||
|
||||
#### New Language
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say that you want to add translations for a language that is not yet translated, not even some pages.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say you want to add translations for Creole, and it's not yet there in the docs.
|
||||
|
||||
Checking the link from above, the code for "Creole" is `ht`.
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to run the script to generate a new translation directory:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
// Use the command new-lang, pass the language code as a CLI argument
|
||||
$ python ./scripts/docs.py new-lang ht
|
||||
|
||||
Successfully initialized: docs/ht
|
||||
Updating ht
|
||||
Updating en
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can check in your code editor the newly created directory `docs/ht/`.
|
||||
|
||||
Start by translating the main page, `docs/ht/index.md`.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can continue with the previous instructions, for an "Existing Language".
|
||||
|
||||
##### New Language not supported
|
||||
|
||||
If when running the live server script you get an error about the language not being supported, something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
raise TemplateNotFound(template)
|
||||
jinja2.exceptions.TemplateNotFound: partials/language/xx.html
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That means that the theme doesn't support that language (in this case, with a fake 2-letter code of `xx`).
|
||||
|
||||
But don't worry, you can set the theme language to English and then translate the content of the docs.
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to do that, edit the `mkdocs.yml` for your new language, it will have something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```YAML hl_lines="5"
|
||||
site_name: FastAPI
|
||||
# More stuff
|
||||
theme:
|
||||
# More stuff
|
||||
language: xx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Change that language from `xx` (from your language code) to `en`.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can start the live server again.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Preview the result
|
||||
|
||||
When you use the script at `./scripts/docs.py` with the `live` command it only shows the files and translations available for the current language.
|
||||
|
||||
But once you are done, you can test it all as it would look online.
|
||||
|
||||
To do that, first build all the docs:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
// Use the command "build-all", this will take a bit
|
||||
$ python ./scripts/docs.py build-all
|
||||
|
||||
Updating es
|
||||
Updating en
|
||||
Building docs for: en
|
||||
Building docs for: es
|
||||
Successfully built docs for: es
|
||||
Copying en index.md to README.md
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
That generates all the docs at `./docs_build/` for each language. This includes adding any files with missing translations, with a note saying that "this file doesn't have a translation yet". But you don't have to do anything with that directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Then it builds all those independent MkDocs sites for each language, combines them, and generates the final output at `./site/`.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can serve that with the command `serve`:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
// Use the command "serve" after running "build-all"
|
||||
$ python ./scripts/docs.py serve
|
||||
|
||||
Warning: this is a very simple server. For development, use mkdocs serve instead.
|
||||
This is here only to preview a site with translations already built.
|
||||
Make sure you run the build-all command first.
|
||||
Serving at: http://127.0.0.1:8008
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Tests
|
||||
|
||||
There is a script that you can run locally to test all the code and generate coverage reports in HTML:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ bash scripts/test-cov-html.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
This command generates a directory `./htmlcov/`, if you open the file `./htmlcov/index.html` in your browser, you can explore interactively the regions of code that are covered by the tests, and notice if there is any region missing.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tests in your editor
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use the integrated tests in your editor add `./docs_src` to your `PYTHONPATH` variable.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, in VS Code you can create a file `.env` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```env
|
||||
PYTHONPATH=./docs_src
|
||||
```
|
||||
13
docs/en/docs/css/custom.css
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
a.external-link::after {
|
||||
/* \00A0 is a non-breaking space
|
||||
to make the mark be on the same line as the link
|
||||
*/
|
||||
content: "\00A0[↪]";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a.internal-link::after {
|
||||
/* \00A0 is a non-breaking space
|
||||
to make the mark be on the same line as the link
|
||||
*/
|
||||
content: "\00A0↪";
|
||||
}
|
||||
108
docs/en/docs/css/termynal.css
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* termynal.js
|
||||
*
|
||||
* @author Ines Montani <ines@ines.io>
|
||||
* @version 0.0.1
|
||||
* @license MIT
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
:root {
|
||||
--color-bg: #252a33;
|
||||
--color-text: #eee;
|
||||
--color-text-subtle: #a2a2a2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-termynal] {
|
||||
width: 750px;
|
||||
max-width: 100%;
|
||||
background: var(--color-bg);
|
||||
color: var(--color-text);
|
||||
font-size: 18px;
|
||||
/* font-family: 'Fira Mono', Consolas, Menlo, Monaco, 'Courier New', Courier, monospace; */
|
||||
font-family: 'Roboto Mono', 'Fira Mono', Consolas, Menlo, Monaco, 'Courier New', Courier, monospace;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
padding: 75px 45px 35px;
|
||||
position: relative;
|
||||
-webkit-box-sizing: border-box;
|
||||
box-sizing: border-box;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-termynal]:before {
|
||||
content: '';
|
||||
position: absolute;
|
||||
top: 15px;
|
||||
left: 15px;
|
||||
display: inline-block;
|
||||
width: 15px;
|
||||
height: 15px;
|
||||
border-radius: 50%;
|
||||
/* A little hack to display the window buttons in one pseudo element. */
|
||||
background: #d9515d;
|
||||
-webkit-box-shadow: 25px 0 0 #f4c025, 50px 0 0 #3ec930;
|
||||
box-shadow: 25px 0 0 #f4c025, 50px 0 0 #3ec930;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-termynal]:after {
|
||||
content: 'bash';
|
||||
position: absolute;
|
||||
color: var(--color-text-subtle);
|
||||
top: 5px;
|
||||
left: 0;
|
||||
width: 100%;
|
||||
text-align: center;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a[data-terminal-control] {
|
||||
text-align: right;
|
||||
display: block;
|
||||
color: #aebbff;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-ty] {
|
||||
display: block;
|
||||
line-height: 2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-ty]:before {
|
||||
/* Set up defaults and ensure empty lines are displayed. */
|
||||
content: '';
|
||||
display: inline-block;
|
||||
vertical-align: middle;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-ty="input"]:before,
|
||||
[data-ty-prompt]:before {
|
||||
margin-right: 0.75em;
|
||||
color: var(--color-text-subtle);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-ty="input"]:before {
|
||||
content: '$';
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-ty][data-ty-prompt]:before {
|
||||
content: attr(data-ty-prompt);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
[data-ty-cursor]:after {
|
||||
content: attr(data-ty-cursor);
|
||||
font-family: monospace;
|
||||
margin-left: 0.5em;
|
||||
-webkit-animation: blink 1s infinite;
|
||||
animation: blink 1s infinite;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
/* Cursor animation */
|
||||
|
||||
@-webkit-keyframes blink {
|
||||
50% {
|
||||
opacity: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@keyframes blink {
|
||||
50% {
|
||||
opacity: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
388
docs/en/docs/deployment.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,388 @@
|
||||
# Deployment
|
||||
|
||||
Deploying a **FastAPI** application is relatively easy.
|
||||
|
||||
There are several ways to do it depending on your specific use case and the tools that you use.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see more about some of the ways to do it in the next sections.
|
||||
|
||||
## FastAPI versions
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** is already being used in production in many applications and systems. And the test coverage is kept at 100%. But its development is still moving quickly.
|
||||
|
||||
New features are added frequently, bugs are fixed regularly, and the code is still continuously improving.
|
||||
|
||||
That's why the current versions are still `0.x.x`, this reflects that each version could potentially have breaking changes. This follows the <a href="https://semver.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Semantic Versioning</a> conventions.
|
||||
|
||||
You can create production applications with **FastAPI** right now (and you have probably been doing it for some time), you just have to make sure that you use a version that works correctly with the rest of your code.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pin your `fastapi` version
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing you should do is to "pin" the version of **FastAPI** you are using to the specific latest version that you know works correctly for your application.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let's say you are using version `0.45.0` in your app.
|
||||
|
||||
If you use a `requirements.txt` file you could specify the version with:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
fastapi==0.45.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
that would mean that you would use exactly the version `0.45.0`.
|
||||
|
||||
Or you could also pin it with:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
fastapi>=0.45.0,<0.46.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
that would mean that you would use the versions `0.45.0` or above, but less than `0.46.0`, for example, a version `0.45.2` would still be accepted.
|
||||
|
||||
If you use any other tool to manage your installations, like Poetry, Pipenv, or others, they all have a way that you can use to define specific versions for your packages.
|
||||
|
||||
### Available versions
|
||||
|
||||
You can see the available versions (e.g. to check what is the current latest) in the [Release Notes](release-notes.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
### About versions
|
||||
|
||||
Following the Semantic Versioning conventions, any version below `1.0.0` could potentially add breaking changes.
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI also follows the convention that any "PATCH" version change is for bug fixes and non-breaking changes.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The "PATCH" is the last number, for example, in `0.2.3`, the PATCH version is `3`.
|
||||
|
||||
So, you should be able to pin to a version like:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
fastapi>=0.45.0,<0.46.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Breaking changes and new features are added in "MINOR" versions.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The "MINOR" is the number in the middle, for example, in `0.2.3`, the MINOR version is `2`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Upgrading the FastAPI versions
|
||||
|
||||
You should add tests for your app.
|
||||
|
||||
With **FastAPI** it's very easy (thanks to Starlette), check the docs: [Testing](tutorial/testing.md){.internal-link target=_blank}
|
||||
|
||||
After you have tests, then you can upgrade the **FastAPI** version to a more recent one, and make sure that all your code is working correctly by running your tests.
|
||||
|
||||
If everything is working, or after you make the necessary changes, and all your tests are passing, then you can pin your `fastapi` to that new recent version.
|
||||
|
||||
### About Starlette
|
||||
|
||||
You shouldn't pin the version of `starlette`.
|
||||
|
||||
Different versions of **FastAPI** will use a specific newer version of Starlette.
|
||||
|
||||
So, you can just let **FastAPI** use the correct Starlette version.
|
||||
|
||||
### About Pydantic
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic includes the tests for **FastAPI** with its own tests, so new versions of Pydantic (above `1.0.0`) are always compatible with FastAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
You can pin Pydantic to any version above `1.0.0` that works for you and below `2.0.0`.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
pydantic>=1.2.0,<2.0.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Docker
|
||||
|
||||
In this section you'll see instructions and links to guides to know how to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Make your **FastAPI** application a Docker image/container with maximum performance. In about **5 min**.
|
||||
* (Optionally) understand what you, as a developer, need to know about HTTPS.
|
||||
* Set up a Docker Swarm mode cluster with automatic HTTPS, even on a simple $5 USD/month server. In about **20 min**.
|
||||
* Generate and deploy a full **FastAPI** application, using your Docker Swarm cluster, with HTTPS, etc. In about **10 min**.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use <a href="https://www.docker.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">**Docker**</a> for deployment. It has several advantages like security, replicability, development simplicity, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Docker, you can use the official Docker image:
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi-docker" class="external-link" target="_blank">tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi</a>
|
||||
|
||||
This image has an "auto-tuning" mechanism included, so that you can just add your code and get very high performance automatically. And without making sacrifices.
|
||||
|
||||
But you can still change and update all the configurations with environment variables or configuration files.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
To see all the configurations and options, go to the Docker image page: <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi-docker" class="external-link" target="_blank">tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a `Dockerfile`
|
||||
|
||||
* Go to your project directory.
|
||||
* Create a `Dockerfile` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Dockerfile
|
||||
FROM tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi:python3.7
|
||||
|
||||
COPY ./app /app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Bigger Applications
|
||||
|
||||
If you followed the section about creating [Bigger Applications with Multiple Files](tutorial/bigger-applications.md){.internal-link target=_blank}, your `Dockerfile` might instead look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Dockerfile
|
||||
FROM tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi:python3.7
|
||||
|
||||
COPY ./app /app/app
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Raspberry Pi and other architectures
|
||||
|
||||
If you are running Docker in a Raspberry Pi (that has an ARM processor) or any other architecture, you can create a `Dockerfile` from scratch, based on a Python base image (that is multi-architecture) and use Uvicorn alone.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, your `Dockerfile` could look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Dockerfile
|
||||
FROM python:3.7
|
||||
|
||||
RUN pip install fastapi uvicorn
|
||||
|
||||
EXPOSE 80
|
||||
|
||||
COPY ./app /app
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["uvicorn", "app.main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "80"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the **FastAPI** Code
|
||||
|
||||
* Create an `app` directory and enter in it.
|
||||
* Create a `main.py` file with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/")
|
||||
def read_root():
|
||||
return {"Hello": "World"}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* You should now have a directory structure like:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
├── app
|
||||
│ └── main.py
|
||||
└── Dockerfile
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Build the Docker image
|
||||
|
||||
* Go to the project directory (in where your `Dockerfile` is, containing your `app` directory).
|
||||
* Build your FastAPI image:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ docker build -t myimage .
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
### Start the Docker container
|
||||
|
||||
* Run a container based on your image:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ docker run -d --name mycontainer -p 80:80 myimage
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have an optimized FastAPI server in a Docker container. Auto-tuned for your current server (and number of CPU cores).
|
||||
|
||||
### Check it
|
||||
|
||||
You should be able to check it in your Docker container's URL, for example: <a href="http://192.168.99.100/items/5?q=somequery" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://192.168.99.100/items/5?q=somequery</a> or <a href="http://127.0.0.1/items/5?q=somequery" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1/items/5?q=somequery</a> (or equivalent, using your Docker host).
|
||||
|
||||
You will see something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{"item_id": 5, "q": "somequery"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Interactive API docs
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can go to <a href="http://192.168.99.100/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://192.168.99.100/docs</a> or <a href="http://127.0.0.1/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1/docs</a> (or equivalent, using your Docker host).
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the automatic interactive API documentation (provided by <a href="https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui" class="external-link" target="_blank">Swagger UI</a>):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Alternative API docs
|
||||
|
||||
And you can also go to <a href="http://192.168.99.100/redoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://192.168.99.100/redoc</a> or <a href="http://127.0.0.1/redoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1/redoc</a> (or equivalent, using your Docker host).
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the alternative automatic documentation (provided by <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">ReDoc</a>):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## HTTPS
|
||||
|
||||
### About HTTPS
|
||||
|
||||
It is easy to assume that HTTPS is something that is just "enabled" or not.
|
||||
|
||||
But it is way more complex than that.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
If you are in a hurry or don't care, continue with the next section for step by step instructions to set everything up.
|
||||
|
||||
To learn the basics of HTTPS, from a consumer perspective, check <a href="https://howhttps.works/" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://howhttps.works/</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, from a developer's perspective, here are several things to have in mind while thinking about HTTPS:
|
||||
|
||||
* For HTTPS, the server needs to have "certificates" generated by a third party.
|
||||
* Those certificates are actually acquired from the third-party, not "generated".
|
||||
* Certificates have a lifetime.
|
||||
* They expire.
|
||||
* And then they need to be renewed, acquired again from the third party.
|
||||
* The encryption of the connection happens at the TCP level.
|
||||
* That's one layer below HTTP.
|
||||
* So, the certificate and encryption handling is done before HTTP.
|
||||
* TCP doesn't know about "domains". Only about IP addresses.
|
||||
* The information about the specific domain requested goes in the HTTP data.
|
||||
* The HTTPS certificates "certify" a certain domain, but the protocol and encryption happen at the TCP level, before knowing which domain is being dealt with.
|
||||
* By default, that would mean that you can only have one HTTPS certificate per IP address.
|
||||
* No matter how big your server is or how small each application you have on it might be.
|
||||
* There is a solution to this, however.
|
||||
* There's an extension to the TLS protocol (the one handling the encryption at the TCP level, before HTTP) called <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Server_Name_Indication" class="external-link" target="_blank"><abbr title="Server Name Indication">SNI</abbr></a>.
|
||||
* This SNI extension allows one single server (with a single IP address) to have several HTTPS certificates and serve multiple HTTPS domains/applications.
|
||||
* For this to work, a single component (program) running on the server, listening on the public IP address, must have all the HTTPS certificates in the server.
|
||||
* After obtaining a secure connection, the communication protocol is still HTTP.
|
||||
* The contents are encrypted, even though they are being sent with the HTTP protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
It is a common practice to have one program/HTTP server running on the server (the machine, host, etc.) and managing all the HTTPS parts : sending the decrypted HTTP requests to the actual HTTP application running in the same server (the **FastAPI** application, in this case), take the HTTP response from the application, encrypt it using the appropriate certificate and sending it back to the client using HTTPS. This server is often called a <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TLS_termination_proxy" class="external-link" target="_blank">TLS Termination Proxy</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Let's Encrypt
|
||||
|
||||
Before Let's Encrypt, these HTTPS certificates were sold by trusted third-parties.
|
||||
|
||||
The process to acquire one of these certificates used to be cumbersome, require quite some paperwork and the certificates were quite expensive.
|
||||
|
||||
But then <a href="https://letsencrypt.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Let's Encrypt</a> was created.
|
||||
|
||||
It is a project from the Linux Foundation. It provides HTTPS certificates for free. In an automated way. These certificates use all the standard cryptographic security, and are short lived (about 3 months), so the security is actually better because of their reduced lifespan.
|
||||
|
||||
The domains are securely verified and the certificates are generated automatically. This also allows automating the renewal of these certificates.
|
||||
|
||||
The idea is to automate the acquisition and renewal of these certificates, so that you can have secure HTTPS, for free, forever.
|
||||
|
||||
### Traefik
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://traefik.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Traefik</a> is a high performance reverse proxy / load balancer. It can do the "TLS Termination Proxy" job (apart from other features).
|
||||
|
||||
It has integration with Let's Encrypt. So, it can handle all the HTTPS parts, including certificate acquisition and renewal.
|
||||
|
||||
It also has integrations with Docker. So, you can declare your domains in each application configurations and have it read those configurations, generate the HTTPS certificates and serve HTTPS to your application automatically, without requiring any change in its configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
With this information and tools, continue with the next section to combine everything.
|
||||
|
||||
## Docker Swarm mode cluster with Traefik and HTTPS
|
||||
|
||||
You can have a Docker Swarm mode cluster set up in minutes (about 20 min) with a main Traefik handling HTTPS (including certificate acquisition and renewal).
|
||||
|
||||
By using Docker Swarm mode, you can start with a "cluster" of a single machine (it can even be a $5 USD / month server) and then you can grow as much as you need adding more servers.
|
||||
|
||||
To set up a Docker Swarm Mode cluster with Traefik and HTTPS handling, follow this guide:
|
||||
|
||||
### <a href="https://medium.com/@tiangolo/docker-swarm-mode-and-traefik-for-a-https-cluster-20328dba6232" class="external-link" target="_blank">Docker Swarm Mode and Traefik for an HTTPS cluster</a>
|
||||
|
||||
### Deploy a FastAPI application
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to set everything up, would be using the [**FastAPI** Project Generators](project-generation.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
It is designed to be integrated with this Docker Swarm cluster with Traefik and HTTPS described above.
|
||||
|
||||
You can generate a project in about 2 min.
|
||||
|
||||
The generated project has instructions to deploy it, doing it takes another 2 min.
|
||||
|
||||
## Alternatively, deploy **FastAPI** without Docker
|
||||
|
||||
You can deploy **FastAPI** directly without Docker too.
|
||||
|
||||
You just need to install an ASGI compatible server like:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.uvicorn.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uvicorn</a>, a lightning-fast ASGI server, built on uvloop and httptools.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install uvicorn
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://gitlab.com/pgjones/hypercorn" class="external-link" target="_blank">Hypercorn</a>, an ASGI server also compatible with HTTP/2.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install hypercorn
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
...or any other ASGI server.
|
||||
|
||||
And run your application the same way you have done in the tutorials, but without the `--reload` option, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 80
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:80 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
or with Hypercorn:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ hypercorn main:app --bind 0.0.0.0:80
|
||||
|
||||
Running on 0.0.0.0:8080 over http (CTRL + C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
You might want to set up some tooling to make sure it is restarted automatically if it stops.
|
||||
|
||||
You might also want to install <a href="https://gunicorn.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Gunicorn</a> and <a href="https://www.uvicorn.org/#running-with-gunicorn" class="external-link" target="_blank">use it as a manager for Uvicorn</a>, or use Hypercorn with multiple workers.
|
||||
|
||||
Making sure to fine-tune the number of workers, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
But if you are doing all that, you might just use the Docker image that does it automatically.
|
||||
123
docs/en/docs/external-links.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
||||
# External Links and Articles
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** has a great community constantly growing.
|
||||
|
||||
There are many posts, articles, tools, and projects, related to **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an incomplete list of some of them.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
If you have an article, project, tool, or anything related to **FastAPI** that is not yet listed here, create a <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/edit/master/docs/external-links.md" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pull Request adding it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Articles
|
||||
|
||||
### English
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@williamhayes/fastapi-starlette-debug-vs-prod-5f7561db3a59" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI/Starlette debug vs prod</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@williamhayes" class="external-link" target="_blank">William Hayes</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/data-rebels/fastapi-google-as-an-external-authentication-provider-3a527672cf33" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI — Google as an external authentication provider</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@nils_29588" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nils de Bruin</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/data-rebels/fastapi-how-to-add-basic-and-cookie-authentication-a45c85ef47d3" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI — How to add basic and cookie authentication</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@nils_29588" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nils de Bruin</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://dev.to/errietta/introduction-to-the-fastapi-python-framework-2n10" class="external-link" target="_blank">Introduction to the fastapi python framework</a> by <a href="https://dev.to/errietta" class="external-link" target="_blank">Errieta Kostala</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="http://nickc1.github.io/api,/scikit-learn/2019/01/10/scikit-fastapi.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI and Scikit-Learn: Easily Deploy Models</a> by <a href="http://nickc1.github.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nick Cortale</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/data-rebels/fastapi-authentication-revisited-enabling-api-key-authentication-122dc5975680" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI authentication revisited: Enabling API key authentication</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@nils_29588" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nils de Bruin</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://blog.bartab.fr/fastapi-logging-on-the-fly/" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI, a simple use case on logging</a> by <a href="https://blog.bartab.fr/" class="external-link" target="_blank">@euri10</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@nico.axtmann95/deploying-a-scikit-learn-model-with-onnx-und-fastapi-1af398268915" class="external-link" target="_blank">Deploying a scikit-learn model with ONNX and FastAPI</a> by <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/nico-axtmann" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nico Axtmann</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://geekflare.com/python-asynchronous-web-frameworks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Top 5 Asynchronous Web Frameworks for Python</a> by <a href="https://geekflare.com/author/ankush/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Ankush Thakur</a> on <a href="https://geekflare.com" class="external-link" target="_blank">GeekFlare</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@gntrm/jwt-authentication-with-fastapi-and-aws-cognito-1333f7f2729e" class="external-link" target="_blank">JWT Authentication with FastAPI and AWS Cognito</a> by <a href="https://twitter.com/gntrm" class="external-link" target="_blank">Johannes Gontrum</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-deploy-a-machine-learning-model-dc51200fe8cf" class="external-link" target="_blank">How to Deploy a Machine Learning Model</a> by <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/mgrootendorst/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Maarten Grootendorst</a> on <a href="https://towardsdatascience.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Towards Data Science</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* [Uber: Ludwig v0.2 Adds New Features and Other Improvements to its Deep Learning Toolbox [including a FastAPI server]](https://eng.uber.com/ludwig-v0-2/){.external-link target=_blank} on <a href="https://eng.uber.com" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uber Engineering</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://gitlab.com/euri10/fastapi_cheatsheet" class="external-link" target="_blank">A FastAPI and Swagger UI visual cheatsheet</a> by <a href="https://gitlab.com/euri10" class="external-link" target="_blank">@euri10</a>
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@mike.p.moritz/using-docker-compose-to-deploy-a-lightweight-python-rest-api-with-a-job-queue-37e6072a209b" class="external-link" target="_blank">Using Docker Compose to deploy a lightweight Python REST API with a job queue</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@mike.p.moritz" class="external-link" target="_blank">Mike Moritz</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://robwagner.dev/tortoise-fastapi-setup/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Setting up Tortoise ORM with FastAPI</a> by <a href="https://robwagner.dev/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Rob Wagner</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://dev.to/dbanty/why-i-m-leaving-flask-3ki6" class="external-link" target="_blank">Why I'm Leaving Flask</a> by <a href="https://dev.to/dbanty" class="external-link" target="_blank">Dylan Anthony</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/python-data/how-to-deploy-tensorflow-2-0-models-as-an-api-service-with-fastapi-docker-128b177e81f3" class="external-link" target="_blank">How To Deploy Tensorflow 2.0 Models As An API Service With FastAPI & Docker</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@bbrenyah" class="external-link" target="_blank">Bernard Brenyah</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://testdriven.io/blog/fastapi-crud/" class="external-link" target="_blank">TestDriven.io: Developing and Testing an Asynchronous API with FastAPI and Pytest</a> by <a href="https://testdriven.io/authors/herman/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Michael Herman</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://towardsdatascience.com/deploying-iris-classifications-with-fastapi-and-docker-7c9b83fdec3a" class="external-link" target="_blank">Towards Data Science: Deploying Iris Classifications with FastAPI and Docker</a> by <a href="https://towardsdatascience.com/@mandygu" class="external-link" target="_blank">Mandy Gu</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/deploy-machine-learning-models-with-keras-fastapi-redis-and-docker-4940df614ece" class="external-link" target="_blank">Deploy Machine Learning Models with Keras, FastAPI, Redis and Docker</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@shane.soh" class="external-link" target="_blank">Shane Soh</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@arthur393/another-boilerplate-to-fastapi-azure-pipeline-ci-pytest-3c8d9a4be0bb" class="external-link" target="_blank">Another Boilerplate to FastAPI: Azure Pipeline CI + Pytest</a> by <a href="https://twitter.com/arthurheinrique" class="external-link" target="_blank">Arthur Henrique</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://iwpnd.pw/articles/2020-01/deploy-fastapi-to-aws-lambda" class="external-link" target="_blank">How to continuously deploy a FastAPI to AWS Lambda with AWS SAM</a> by <a href="https://iwpnd.pw" class="external-link" target="_blank">Benjamin Ramser</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.tutlinks.com/create-and-deploy-fastapi-app-to-heroku/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Create and Deploy FastAPI app to Heroku without using Docker</a> by <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/navule/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Navule Pavan Kumar Rao</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://iwpnd.pw/articles/2020-03/apache-kafka-fastapi-geostream" class="external-link" target="_blank">Apache Kafka producer and consumer with FastAPI and aiokafka</a> by <a href="https://iwpnd.pw" class="external-link" target="_blank">Benjamin Ramser</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Japanese
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/mtitg/items/47770e9a562dd150631d" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI|DB接続してCRUDするPython製APIサーバーを構築</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/mtitg" class="external-link" target="_blank">@mtitg</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/ryoryomaru/items/59958ed385b3571d50de" class="external-link" target="_blank">python製の最新APIフレームワーク FastAPI を触ってみた</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/ryoryomaru" class="external-link" target="_blank">@ryoryomaru</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku/items/0e1f5dbbe62efc612a78" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPIでCORSを回避</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku" class="external-link" target="_blank">@angel_katayoku</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku/items/4fbc1a4e2b33fa2237d2" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPIをMySQLと接続してDockerで管理してみる</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku" class="external-link" target="_blank">@angel_katayoku</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku/items/8a458a8952f50b73f420" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPIでPOSTされたJSONのレスポンスbodyを受け取る</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku" class="external-link" target="_blank">@angel_katayoku</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/hikarut/items/b178af2e2440c67c6ac4" class="external-link" target="_blank">フロントエンド開発者向けのDockerによるPython開発環境構築</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/hikarut" class="external-link" target="_blank">Hikaru Takahashi</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-environment" class="external-link" target="_blank">【第1回】FastAPIチュートリアル: ToDoアプリを作ってみよう【環境構築編】</a> by <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun" class="external-link" target="_blank">ライトコードメディア編集部</a>
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-model-building" class="external-link" target="_blank">【第2回】FastAPIチュートリアル: ToDoアプリを作ってみよう【モデル構築編】</a> by <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun" class="external-link" target="_blank">ライトコードメディア編集部</a>
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-authentication-user-registration" class="external-link" target="_blank">【第3回】FastAPIチュートリアル: toDoアプリを作ってみよう【認証・ユーザ登録編】</a> by <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun" class="external-link" target="_blank">ライトコードメディア編集部</a>
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-admin-page-improvement" class="external-link" target="_blank">【第4回】FastAPIチュートリアル: toDoアプリを作ってみよう【管理者ページ改良編】</a> by <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun" class="external-link" target="_blank">ライトコードメディア編集部</a>
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/bee2/items/0ad260ab9835a2087dae" class="external-link" target="_blank">PythonのWeb frameworkのパフォーマンス比較 (Django, Flask, responder, FastAPI, japronto)</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/bee2" class="external-link" target="_blank">@bee2</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/bee2/items/75d9c0d7ba20e7a4a0e9" class="external-link" target="_blank">[FastAPI] Python製のASGI Web フレームワーク FastAPIに入門する</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/bee2" class="external-link" target="_blank">@bee2</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Chinese
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1431448" class="external-link" target="_blank">使用FastAPI框架快速构建高性能的api服务</a> by <a href="https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/user/5471722" class="external-link" target="_blank">逍遥散人</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://wxq0309.github.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI框架中文文档</a> by <a href="https://wxq0309.github.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">何大仙</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Vietnamese
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://fullstackstation.com/fastapi-trien-khai-bang-docker/" class="external-link" target="_blank">FASTAPI: TRIỂN KHAI BẰNG DOCKER</a> by <a href="https://fullstackstation.com/author/figonking/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nguyễn Nhân</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Russian
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://habr.com/ru/post/454440/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Мелкая питонячая радость #2: Starlette - Солидная примочка – FastAPI</a> by <a href="https://habr.com/ru/users/57uff3r/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Andrey Korchak</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://habr.com/ru/post/478620/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Почему Вы должны попробовать FastAPI?</a> by <a href="https://github.com/prostomarkeloff" class="external-link" target="_blank">prostomarkeloff</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### German
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://blog.codecentric.de/2019/08/inbetriebnahme-eines-scikit-learn-modells-mit-onnx-und-fastapi/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Inbetriebnahme eines scikit-learn-Modells mit ONNX und FastAPI</a> by <a href="https://twitter.com/_nicoax" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nico Axtmann</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Podcasts
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://pythonbytes.fm/episodes/show/123/time-to-right-the-py-wrongs?time_in_sec=855" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI on PythonBytes</a> by <a href="https://pythonbytes.fm/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Python Bytes FM</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Talks
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3DLwPcrE5mA" class="external-link" target="_blank">PyCon UK 2019: FastAPI from the ground up</a> by <a href="https://twitter.com/chriswithers13" class="external-link" target="_blank">Chris Withers</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Projects
|
||||
|
||||
Latest GitHub projects with the topic `fastapi`:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="github-topic-projects">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
# Features
|
||||
|
||||
## FastAPI features
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,8 +6,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### Based on open standards
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification" target="_blank"><strong>OpenAPI</strong></a> for API creation, including declarations of <abbr title="also known as: endpoints, routes">path</abbr> <abbr title="also known as HTTP methods, as POST, GET, PUT, DELETE">operations</abbr>, parameters, body requests, security, etc.
|
||||
* Automatic data model documentation with <a href="http://json-schema.org/" target="_blank"><strong>JSON Schema</strong></a> (as OpenAPI itself is based on JSON Schema).
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>OpenAPI</strong></a> for API creation, including declarations of <abbr title="also known as: endpoints, routes">path</abbr> <abbr title="also known as HTTP methods, as POST, GET, PUT, DELETE">operations</abbr>, parameters, body requests, security, etc.
|
||||
* Automatic data model documentation with <a href="http://json-schema.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>JSON Schema</strong></a> (as OpenAPI itself is based on JSON Schema).
|
||||
* Designed around these standards, after a meticulous study. Instead of an afterthought layer on top.
|
||||
* This also allows using automatic **client code generation** in many languages.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,20 +15,19 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Interactive API documentation and exploration web user interfaces. As the framework is based on OpenAPI, there are multiple options, 2 included by default.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui" target="_blank"><strong>Swagger UI</strong></a>, with interactive exploration, call and test your API directly from the browser.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>Swagger UI</strong></a>, with interactive exploration, call and test your API directly from the browser.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
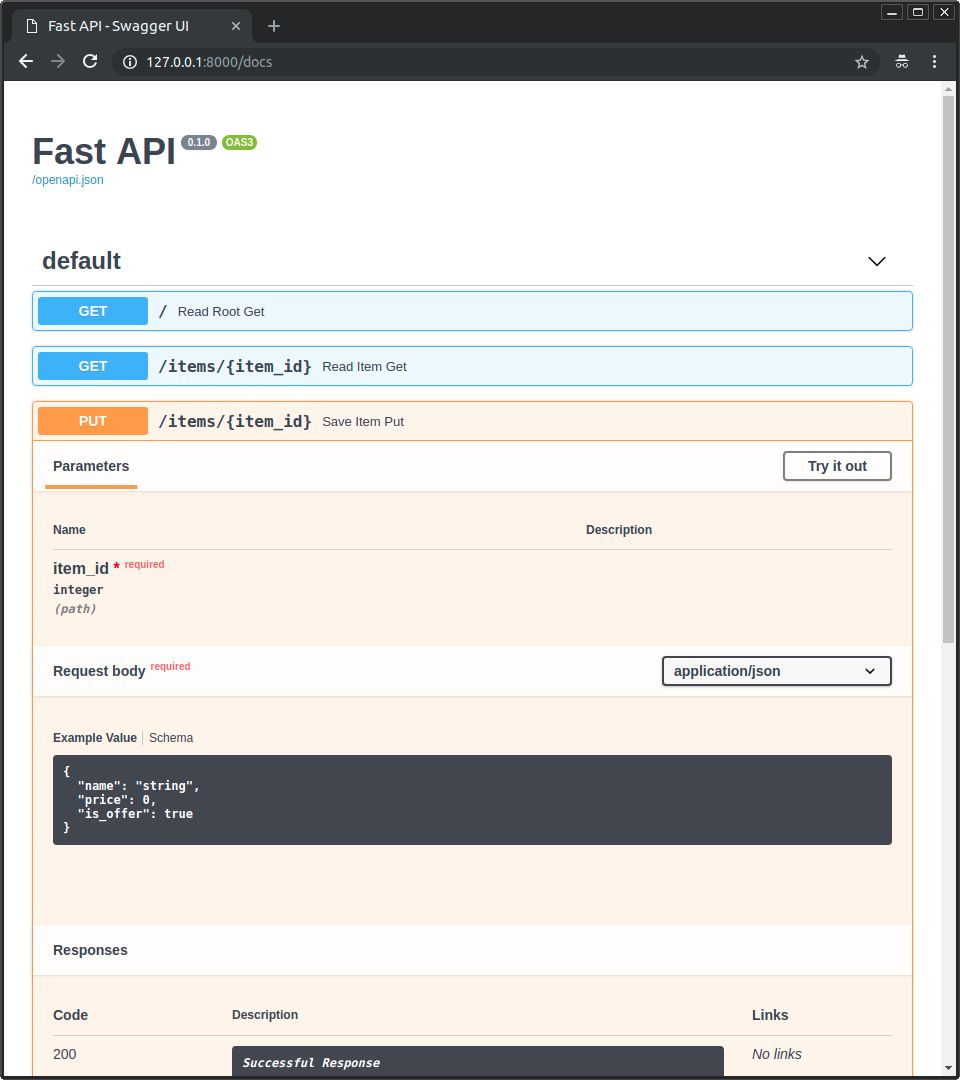
|
||||
|
||||
* Alternative API documentation with <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc" target="_blank"><strong>ReDoc</strong></a>.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
* Alternative API documentation with <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>ReDoc</strong></a>.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Just Modern Python
|
||||
|
||||
It's all based on standard **Python 3.6 type** declarations (thanks to Pydantic). No new syntax to learn. Just standard modern Python.
|
||||
|
||||
If you need a 2 minute refresher of how to use Python types (even if you don't use FastAPI), check the tutorial section: [Python types](python-types.md).
|
||||
If you need a 2 minute refresher of how to use Python types (even if you don't use FastAPI), check the short tutorial: [Python Types](python-types.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
You write standard Python with types:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ from datetime import date
|
||||
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
# Declare a variable as an str
|
||||
# Declare a variable as a str
|
||||
# and get editor support inside the function
|
||||
def main(user_id: str):
|
||||
return user_id
|
||||
@@ -66,14 +66,14 @@ my_second_user: User = User(**second_user_data)
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
`**second_user_data` means:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Pass the keys and values of the `second_user_data` dict directly as key-value arguments, equivalent to: `User(id=4, name="Mary", joined="2018-11-30")`
|
||||
|
||||
### Editor support
|
||||
|
||||
All the framework was designed to be easy and intuitive to use, all the decisions where tested on multiple editors even before starting development, to ensure the best development experience.
|
||||
|
||||
In the last Python developer survey it was clear <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/research/python-developers-survey-2017/#tools-and-features" target="_blank">that the most used feature is "autocompletion"</a>.
|
||||
In the last Python developer survey it was clear <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/research/python-developers-survey-2017/#tools-and-features" class="external-link" target="_blank">that the most used feature is "autocompletion"</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
The whole **FastAPI** framework is based to satisfy that. Autocompletion works everywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -81,13 +81,13 @@ You will rarely need to come back to the docs.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how your editor might help you:
|
||||
|
||||
* in <a href="https://code.visualstudio.com/" target="_blank">Visual Studio Code</a>:
|
||||
* in <a href="https://code.visualstudio.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Visual Studio Code</a>:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* in <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/" target="_blank">PyCharm</a>:
|
||||
* in <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/" class="external-link" target="_blank">PyCharm</a>:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
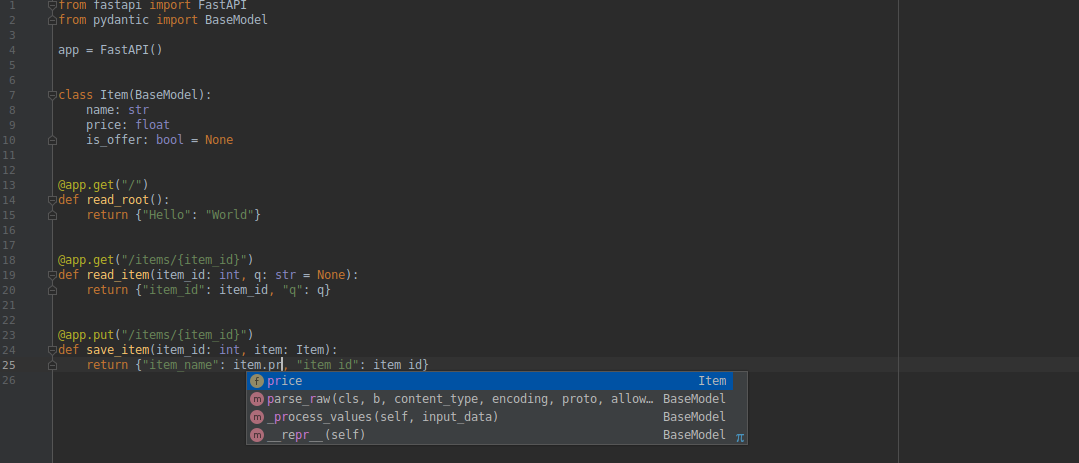
|
||||
|
||||
You will get completion in code you might even consider impossible before. As for example, the `price` key inside a JSON body (that could have been nested) that comes from a request.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -122,13 +122,13 @@ Security and authentication integrated. Without any compromise with databases or
|
||||
All the security schemes defined in OpenAPI, including:
|
||||
|
||||
* HTTP Basic.
|
||||
* **OAuth2** (also with **JWT tokens**). Check the [tutorial on OAuth2 with JWT](tutorial/security/oauth2-jwt.md).
|
||||
* **OAuth2** (also with **JWT tokens**). Check the tutorial on [OAuth2 with JWT](tutorial/security/oauth2-jwt.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
* API keys in:
|
||||
* Headers.
|
||||
* Query parameters.
|
||||
* Cookies, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Plus all the security features from Starlette (including **session cookies**).
|
||||
Plus all the security features from Starlette (including **session cookies**).
|
||||
|
||||
All built as reusable tools and components that are easy to integrate with your systems, data stores, relational and NoSQL databases, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -137,19 +137,17 @@ All built as reusable tools and components that are easy to integrate with your
|
||||
FastAPI includes an extremely easy to use, but extremely powerful <abbr title='also known as "components", "resources", "services", "providers"'><strong>Dependency Injection</strong></abbr> system.
|
||||
|
||||
* Even dependencies can have dependencies, creating a hierarchy or **"graph" of dependencies**.
|
||||
* All **automatically handled** by the framework.
|
||||
* All **automatically handled** by the framework.
|
||||
* All the dependencies can require data from requests and **augment the path operation** constraints and automatic documentation.
|
||||
* **Automatic validation** even for path operation parameters defined in dependencies.
|
||||
* **Automatic validation** even for *path operation* parameters defined in dependencies.
|
||||
* Support for complex user authentication systems, **database connections**, etc.
|
||||
* **No compromise** with databases, frontends, etc. But easy integration with all of them.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Unlimited "plug-ins"
|
||||
|
||||
Or in other way, no need for them, import and use the code you need.
|
||||
|
||||
Any integration is designed to be so simple to use (with dependencies) that you can create a "plug-in" for your application in 2 lines of code using the same structure and syntax used for your path operations.
|
||||
Or in other way, no need for them, import and use the code you need.
|
||||
|
||||
Any integration is designed to be so simple to use (with dependencies) that you can create a "plug-in" for your application in 2 lines of code using the same structure and syntax used for your *path operations*.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tested
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -159,13 +157,13 @@ Any integration is designed to be so simple to use (with dependencies) that you
|
||||
|
||||
## Starlette features
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** is fully compatible with (and based on) <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" target="_blank"><strong>Starlette</strong></a>. So, any additional Starlette code you have, will also work.
|
||||
**FastAPI** is fully compatible with (and based on) <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>Starlette</strong></a>. So, any additional Starlette code you have, will also work.
|
||||
|
||||
`FastAPI` is actually a sub-class of `Starlette`. So, if you already know or use Starlette, most of the functionality will work the same way.
|
||||
|
||||
With **FastAPI** you get all of **Starlette**'s features (as FastAPI is just Starlette on steroids):
|
||||
|
||||
* Seriously impressive performance. It is <a href="https://github.com/encode/starlette#performance" target="_blank">one of the fastest Python frameworks available, on par with **NodeJS** and **Go**</a>.
|
||||
* Seriously impressive performance. It is <a href="https://github.com/encode/starlette#performance" class="external-link" target="_blank">one of the fastest Python frameworks available, on par with **NodeJS** and **Go**</a>.
|
||||
* **WebSocket** support.
|
||||
* **GraphQL** support.
|
||||
* In-process background tasks.
|
||||
@@ -178,7 +176,7 @@ With **FastAPI** you get all of **Starlette**'s features (as FastAPI is just Sta
|
||||
|
||||
## Pydantic features
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** is fully compatible with (and based on) <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io" target="_blank"><strong>Pydantic</strong></a>. So, any additional Pydantic code you have, will also work.
|
||||
**FastAPI** is fully compatible with (and based on) <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>Pydantic</strong></a>. So, any additional Pydantic code you have, will also work.
|
||||
|
||||
Including external libraries also based on Pydantic, as <abbr title="Object-Relational Mapper">ORM</abbr>s, <abbr title="Object-Document Mapper">ODM</abbr>s for databases.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -188,13 +186,13 @@ The same applies the other way around, in many cases you can just pass the objec
|
||||
|
||||
With **FastAPI** you get all of **Pydantic**'s features (as FastAPI is based on Pydantic for all the data handling):
|
||||
|
||||
* **No brainfuck**:
|
||||
* **No brainfuck**:
|
||||
* No new schema definition micro-language to learn.
|
||||
* If you know Python types you know how to use Pydantic.
|
||||
* Plays nicely with your **<abbr title="Integrated Development Environment, similar to a code editor">IDE</abbr>/<abbr title="A program that checks for code errors">linter</abbr>/brain**:
|
||||
* Because pydantic data structures are just instances of classes you define; auto-completion, linting, mypy and your intuition should all work properly with your validated data.
|
||||
* **Fast**:
|
||||
* in <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/#benchmarks-tag" target="_blank">benchmarks</a> Pydantic is faster than all other tested libraries.
|
||||
* in <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/#benchmarks-tag" class="external-link" target="_blank">benchmarks</a> Pydantic is faster than all other tested libraries.
|
||||
* Validate **complex structures**:
|
||||
* Use of hierarchical Pydantic models, Python `typing`’s `List` and `Dict`, etc.
|
||||
* And validators allow complex data schemas to be clearly and easily defined, checked and documented as JSON Schema.
|
||||
106
docs/en/docs/help-fastapi.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
||||
# Help FastAPI - Get Help
|
||||
|
||||
Do you like **FastAPI**?
|
||||
|
||||
Would you like to help FastAPI, other users, and the author?
|
||||
|
||||
Or would you like to get help with **FastAPI**?
|
||||
|
||||
There are very simple ways to help (several involve just one or two clicks).
|
||||
|
||||
And there are several ways to get help too.
|
||||
|
||||
## Star **FastAPI** in GitHub
|
||||
|
||||
You can "star" FastAPI in GitHub (clicking the star button at the top right): <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
By adding a star, other users will be able to find it more easily and see that it has been already useful for others.
|
||||
|
||||
## Watch the GitHub repository for releases
|
||||
|
||||
You can "watch" FastAPI in GitHub (clicking the "watch" button at the top right): <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
There you can select "Releases only".
|
||||
|
||||
Doing it, you will receive notifications (in your email) whenever there's a new release (a new version) of **FastAPI** with bug fixes and new features.
|
||||
|
||||
## Join the chat
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://badges.gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi.svg" alt="Join the chat at https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Join the chat on Gitter: <a href="https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
There you can ask quick questions, help others, share ideas, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Connect with the author
|
||||
|
||||
You can connect with <a href="https://tiangolo.com" class="external-link" target="_blank">me (Sebastián Ramírez / `tiangolo`)</a>, the author.
|
||||
|
||||
You can:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">Follow me on **GitHub**</a>.
|
||||
* See other Open Source projects I have created that could help you.
|
||||
* Follow me to see when I create a new Open Source project.
|
||||
* <a href="https://twitter.com/tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">Follow me on **Twitter**</a>.
|
||||
* Tell me how you use FastAPI (I love to hear that).
|
||||
* Ask questions.
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/tiangolo/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Connect with me on **Linkedin**</a>.
|
||||
* Talk to me.
|
||||
* Endorse me or recommend me :)
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">Read what I write (or follow me) on **Medium**</a>.
|
||||
* Read other ideas, articles and tools I have created.
|
||||
* Follow me to see when I publish something new.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tweet about **FastAPI**
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://twitter.com/compose/tweet?text=I'm loving FastAPI because... https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi cc @tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">Tweet about **FastAPI**</a> and let me and others know why you like it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Let me know how are you using **FastAPI**
|
||||
|
||||
I love to hear about how **FastAPI** is being used, what have you liked in it, in which project/company are you using it, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
You can let me know:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://twitter.com/compose/tweet?text=Hey @tiangolo, I'm using FastAPI at..." class="external-link" target="_blank">On **Twitter**</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/tiangolo/" class="external-link" target="_blank">On **Linkedin**</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">On **Medium**</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Vote for FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/vinta/awesome-python/pull/1209" class="external-link" target="_blank">Vote to include **FastAPI** in `awesome-python`</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.slant.co/options/34241/~fastapi-review" class="external-link" target="_blank">Vote for **FastAPI** in Slant</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Help others with issues in GitHub
|
||||
|
||||
You can see <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/issues" class="external-link" target="_blank">existing issues</a> and try and help others.
|
||||
|
||||
## Watch the GitHub repository
|
||||
|
||||
You can "watch" FastAPI in GitHub (clicking the "watch" button at the top right): <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
If you select "Watching" instead of "Releases only", you will receive notifications when someone creates a new issue.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can try and help them solving those issues.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create issues
|
||||
|
||||
You can <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/issues/new/choose" class="external-link" target="_blank">create a new issue</a> in the GitHub repository, for example to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Report a bug/issue.
|
||||
* Suggest a new feature.
|
||||
* Ask a question.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a Pull Request
|
||||
|
||||
You can <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">create a Pull Request</a>, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
* To fix a typo you found on the documentation.
|
||||
* To propose new documentation sections.
|
||||
* To fix an existing issue/bug.
|
||||
* To add a new feature.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks!
|
||||
@@ -1,10 +1,11 @@
|
||||
Some time ago, <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/issues/3#issuecomment-454956920" target="_blank">a **FastAPI** user asked</a>:
|
||||
# History, Design and Future
|
||||
|
||||
Some time ago, <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/issues/3#issuecomment-454956920" class="external-link" target="_blank">a **FastAPI** user asked</a>:
|
||||
|
||||
> What’s the history of this project? It seems to have come from nowhere to awesome in a few weeks [...]
|
||||
|
||||
Here's a little bit of that history.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Alternatives
|
||||
|
||||
I have been creating APIs with complex requirements for several years (Machine Learning, distributed systems, asynchronous jobs, NoSQL databases, etc), leading several teams of developers.
|
||||
@@ -13,7 +14,7 @@ As part of that, I needed to investigate, test and use many alternatives.
|
||||
|
||||
The history of **FastAPI** is in great part the history of its predecessors.
|
||||
|
||||
As said in the section <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/alternatives/" target="_blank">Alternatives</a>:
|
||||
As said in the section [Alternatives](alternatives.md){.internal-link target=_blank}:
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote markdown="1">
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -27,7 +28,6 @@ But at some point, there was no other option than creating something that provid
|
||||
|
||||
</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Investigation
|
||||
|
||||
By using all the previous alternatives I had the chance to learn from all of them, take ideas, and combine them in the best way I could find for myself and the teams of developers I have worked with.
|
||||
@@ -38,14 +38,13 @@ Also, the best approach was to use already existing standards.
|
||||
|
||||
So, before even starting to code **FastAPI**, I spent several months studying the specs for OpenAPI, JSON Schema, OAuth2, etc. Understanding their relationship, overlap, and differences.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Design
|
||||
|
||||
Then I spent some time designing the developer "API" I wanted to have as a user (as a developer using FastAPI).
|
||||
|
||||
I tested several ideas in the most popular Python editors: PyCharm, VS Code, Jedi based editors.
|
||||
|
||||
By the last <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/research/python-developers-survey-2018/#development-tools" target="_blank">Python Developer Survey</a>, that covers about 80% of the users.
|
||||
By the last <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/research/python-developers-survey-2018/#development-tools" class="external-link" target="_blank">Python Developer Survey</a>, that covers about 80% of the users.
|
||||
|
||||
It means that **FastAPI** was specifically tested with the editors used by 80% of the Python developers. And as most of the other editors tend to work similarly, all its benefits should work for virtually all editors.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -53,21 +52,18 @@ That way I could find the best ways to reduce code duplication as much as possib
|
||||
|
||||
All in a way that provided the best development experience for all the developers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
After testing several alternatives, I decided that I was going to use <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/" target="_blank">**Pydantic**</a> for its advantages.
|
||||
After testing several alternatives, I decided that I was going to use <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">**Pydantic**</a> for its advantages.
|
||||
|
||||
Then I contributed to it, to make it fully compliant with JSON Schema, to support different ways to define constraint declarations, and to improve editor support (type checks, autocompletion) based on the tests in several editors.
|
||||
|
||||
During the development, I also contributed to <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" target="_blank">**Starlette**</a>, the other key requirement.
|
||||
|
||||
During the development, I also contributed to <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">**Starlette**</a>, the other key requirement.
|
||||
|
||||
## Development
|
||||
|
||||
By the time I started creating **FastAPI** itself, most of the pieces were already in place, the design was defined, the requirements and tools were ready, and the knowledge about the standards and specifications was clear and fresh.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Future
|
||||
|
||||
By this point, it's already clear that **FastAPI** with its ideas is being useful for many people.
|
||||
@@ -80,4 +76,4 @@ But still, there are many improvements and features to come.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** has a great future ahead.
|
||||
|
||||
And <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/help-fastapi/" target="_blank">your help</a> is greatly appreciated.
|
||||
And [your help](help-fastapi.md){.internal-link target=_blank} is greatly appreciated.
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 412 B After Width: | Height: | Size: 412 B |
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/github-social-preview.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 57 KiB |
98
docs/en/docs/img/github-social-preview.svg
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="no"?>
|
||||
<svg
|
||||
xmlns:dc="http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/"
|
||||
xmlns:cc="http://creativecommons.org/ns#"
|
||||
xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
|
||||
xmlns:svg="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
|
||||
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
|
||||
xmlns:sodipodi="http://sodipodi.sourceforge.net/DTD/sodipodi-0.dtd"
|
||||
xmlns:inkscape="http://www.inkscape.org/namespaces/inkscape"
|
||||
id="svg8"
|
||||
version="1.1"
|
||||
viewBox="0 0 338.66665 169.33332"
|
||||
height="169.33333mm"
|
||||
width="338.66666mm"
|
||||
sodipodi:docname="github-social-preview.svg"
|
||||
inkscape:version="0.92.3 (2405546, 2018-03-11)"
|
||||
inkscape:export-filename="/home/user/code/fastapi/docs/img/github-social-preview.png"
|
||||
inkscape:export-xdpi="96"
|
||||
inkscape:export-ydpi="96">
|
||||
<sodipodi:namedview
|
||||
pagecolor="#ffffff"
|
||||
bordercolor="#666666"
|
||||
borderopacity="1"
|
||||
objecttolerance="10"
|
||||
gridtolerance="10"
|
||||
guidetolerance="10"
|
||||
inkscape:pageopacity="0"
|
||||
inkscape:pageshadow="2"
|
||||
inkscape:window-width="1920"
|
||||
inkscape:window-height="1025"
|
||||
id="namedview9"
|
||||
showgrid="false"
|
||||
inkscape:zoom="0.52249777"
|
||||
inkscape:cx="565.37328"
|
||||
inkscape:cy="403.61034"
|
||||
inkscape:window-x="0"
|
||||
inkscape:window-y="27"
|
||||
inkscape:window-maximized="1"
|
||||
inkscape:current-layer="svg8" />
|
||||
<defs
|
||||
id="defs2" />
|
||||
<metadata
|
||||
id="metadata5">
|
||||
<rdf:RDF>
|
||||
<cc:Work
|
||||
rdf:about="">
|
||||
<dc:format>image/svg+xml</dc:format>
|
||||
<dc:type
|
||||
rdf:resource="http://purl.org/dc/dcmitype/StillImage" />
|
||||
<dc:title></dc:title>
|
||||
</cc:Work>
|
||||
</rdf:RDF>
|
||||
</metadata>
|
||||
<rect
|
||||
style="opacity:0.98000004;fill:#ffffff;fill-opacity:1;stroke-width:0.26458332"
|
||||
id="rect853"
|
||||
width="338.66666"
|
||||
height="169.33333"
|
||||
x="-1.0833333e-05"
|
||||
y="0.71613133"
|
||||
inkscape:export-xdpi="96"
|
||||
inkscape:export-ydpi="96" />
|
||||
<g
|
||||
transform="matrix(0.73259569,0,0,0.73259569,64.842852,-4.5763945)"
|
||||
id="layer1">
|
||||
<path
|
||||
style="opacity:0.98000004;fill:#009688;fill-opacity:1;stroke-width:3.20526505"
|
||||
id="path817"
|
||||
d="m 1.4365174,55.50154 c -17.6610514,0 -31.9886064,14.327532 -31.9886064,31.988554 0,17.661036 14.327555,31.988586 31.9886064,31.988586 17.6609756,0 31.9885196,-14.32755 31.9885196,-31.988586 0,-17.661022 -14.327544,-31.988554 -31.9885196,-31.988554 z m -1.66678692,57.63069 V 93.067264 H -11.384533 L 4.6417437,61.847974 V 81.912929 H 15.379405 Z"
|
||||
inkscape:connector-curvature="0" />
|
||||
<text
|
||||
id="text979"
|
||||
y="114.91215"
|
||||
x="52.115433"
|
||||
style="font-style:normal;font-weight:normal;font-size:79.71511078px;line-height:1.25;font-family:sans-serif;letter-spacing:0px;word-spacing:0px;fill:#009688;fill-opacity:1;stroke:none;stroke-width:1.99287772"
|
||||
xml:space="preserve"><tspan
|
||||
style="font-style:normal;font-variant:normal;font-weight:normal;font-stretch:normal;font-family:Ubuntu;-inkscape-font-specification:Ubuntu;fill:#009688;fill-opacity:1;stroke-width:1.99287772"
|
||||
y="114.91215"
|
||||
x="52.115433"
|
||||
id="tspan977">FastAPI</tspan></text>
|
||||
</g>
|
||||
<text
|
||||
xml:space="preserve"
|
||||
style="font-style:normal;font-weight:normal;font-size:10.58333302px;line-height:1.25;font-family:sans-serif;letter-spacing:0px;word-spacing:0px;fill:#000000;fill-opacity:1;stroke:none;stroke-width:0.26458332"
|
||||
x="169.60979"
|
||||
y="119.20409"
|
||||
id="text851"><tspan
|
||||
sodipodi:role="line"
|
||||
id="tspan849"
|
||||
x="169.60979"
|
||||
y="119.20409"
|
||||
style="font-style:italic;font-variant:normal;font-weight:normal;font-stretch:normal;font-family:Roboto;-inkscape-font-specification:'Roboto Italic';text-align:center;text-anchor:middle;stroke-width:0.26458332">High performance, easy to learn,</tspan><tspan
|
||||
sodipodi:role="line"
|
||||
x="169.60979"
|
||||
y="132.53661"
|
||||
style="font-style:italic;font-variant:normal;font-weight:normal;font-stretch:normal;font-family:Roboto;-inkscape-font-specification:'Roboto Italic';text-align:center;text-anchor:middle;stroke-width:0.26458332"
|
||||
id="tspan855">fast to code, ready for production</tspan></text>
|
||||
</svg>
|
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 4.1 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 4.4 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 4.4 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 5.1 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 5.1 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 1.3 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 1.3 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 72 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 72 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 67 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 67 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 73 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 73 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 66 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 66 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 70 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 70 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 77 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 77 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 7.8 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 7.8 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 17 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 17 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 2.0 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 2.0 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 21 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 21 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 7.7 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 7.7 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 1.9 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 1.9 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 50 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 50 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 17 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 17 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 47 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 47 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 42 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 42 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 42 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 42 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 29 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 29 KiB |
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/tutorial/additional-responses/image01.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 80 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 37 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 37 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 69 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 69 KiB |
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/tutorial/bigger-applications/image01.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 76 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 77 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 77 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 40 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 40 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 54 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 54 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 79 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 79 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 64 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 64 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 39 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 39 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 52 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 52 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 54 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 54 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 170 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 170 KiB |
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/tutorial/debugging/image02.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 97 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 78 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 78 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 65 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 65 KiB |
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/tutorial/extending-openapi/image01.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 63 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 93 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 93 KiB |
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/tutorial/openapi-callbacks/image01.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 97 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 41 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 41 KiB |