mirror of
https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi.git
synced 2025-12-27 00:01:03 -05:00
Compare commits
21 Commits
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
cd90c78391 | ||
|
|
93f4dfd88b | ||
|
|
535b5daa31 | ||
|
|
6b53786f62 | ||
|
|
d98f4eb56e | ||
|
|
8cefc4b7cc | ||
|
|
3063ada72f | ||
|
|
5eb8d6ed8a | ||
|
|
7c751a2e1c | ||
|
|
55b556a7d1 | ||
|
|
a4d04c9b7e | ||
|
|
23caa2709b | ||
|
|
c264467efe | ||
|
|
2b212ddd76 | ||
|
|
7203e860b3 | ||
|
|
e55f223b46 | ||
|
|
a329baaa54 | ||
|
|
a7a0aee984 | ||
|
|
6539b80d9f | ||
|
|
e1bd9f3e33 | ||
|
|
b9b2793bda |
2
.github/workflows/build-docs.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/build-docs.yml
vendored
@@ -60,8 +60,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
pyproject.toml
|
||||
- name: Install docs extras
|
||||
run: uv pip install -r requirements-docs.txt
|
||||
- name: Verify Docs
|
||||
run: python ./scripts/docs.py verify-docs
|
||||
- name: Export Language Codes
|
||||
id: show-langs
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
|
||||
11
.github/workflows/pre-commit.yml
vendored
11
.github/workflows/pre-commit.yml
vendored
@@ -7,7 +7,8 @@ on:
|
||||
- synchronize
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
IS_FORK: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.repo.full_name != github.repository }}
|
||||
# Forks and Dependabot don't have access to secrets
|
||||
HAS_SECRETS: ${{ secrets.PRE_COMMIT != '' }}
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
pre-commit:
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +20,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: echo "$GITHUB_CONTEXT"
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v5
|
||||
name: Checkout PR for own repo
|
||||
if: env.IS_FORK == 'false'
|
||||
if: env.HAS_SECRETS == 'true'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# To be able to commit it needs to fetch the head of the branch, not the
|
||||
# merge commit
|
||||
@@ -31,7 +32,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
# pre-commit lite ci needs the default checkout configs to work
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v5
|
||||
name: Checkout PR for fork
|
||||
if: env.IS_FORK == 'true'
|
||||
if: env.HAS_SECRETS == 'false'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# To be able to commit it needs the head branch of the PR, the remote one
|
||||
ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}
|
||||
@@ -56,7 +57,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: uvx prek run --from-ref origin/${GITHUB_BASE_REF} --to-ref HEAD --show-diff-on-failure
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
- name: Commit and push changes
|
||||
if: env.IS_FORK == 'false'
|
||||
if: env.HAS_SECRETS == 'true'
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git config user.name "github-actions[bot]"
|
||||
git config user.email "github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
|
||||
@@ -68,7 +69,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
git push
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- uses: pre-commit-ci/lite-action@v1.1.0
|
||||
if: env.IS_FORK == 'true'
|
||||
if: env.HAS_SECRETS == 'false'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
msg: 🎨 Auto format
|
||||
- name: Error out on pre-commit errors
|
||||
|
||||
32
.github/workflows/test.yml
vendored
32
.github/workflows/test.yml
vendored
@@ -16,29 +16,6 @@ env:
|
||||
UV_SYSTEM_PYTHON: 1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
lint:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Dump GitHub context
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GITHUB_CONTEXT: ${{ toJson(github) }}
|
||||
run: echo "$GITHUB_CONTEXT"
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v6
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v6
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.11"
|
||||
- name: Setup uv
|
||||
uses: astral-sh/setup-uv@v7
|
||||
with:
|
||||
cache-dependency-glob: |
|
||||
requirements**.txt
|
||||
pyproject.toml
|
||||
- name: Install Dependencies
|
||||
run: uv pip install -r requirements-tests.txt
|
||||
- name: Lint
|
||||
run: bash scripts/lint.sh
|
||||
|
||||
test:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
@@ -54,10 +31,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- os: windows-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.12"
|
||||
coverage: coverage
|
||||
# Ubuntu with 3.13 needs coverage for CodSpeed benchmarks
|
||||
- os: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.13"
|
||||
coverage: coverage
|
||||
# Ubuntu with 3.13 needs coverage for CodSpeed benchmarks
|
||||
- os: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.13"
|
||||
coverage: coverage
|
||||
codspeed: codspeed
|
||||
- os: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.14"
|
||||
coverage: coverage
|
||||
@@ -85,12 +66,13 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: uv pip install -r requirements-tests.txt
|
||||
- run: mkdir coverage
|
||||
- name: Test
|
||||
if: matrix.codspeed != 'codspeed'
|
||||
run: bash scripts/test.sh
|
||||
env:
|
||||
COVERAGE_FILE: coverage/.coverage.${{ runner.os }}-py${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
CONTEXT: ${{ runner.os }}-py${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
- name: CodSpeed benchmarks
|
||||
if: matrix.os == 'ubuntu-latest' && matrix.python-version == '3.13'
|
||||
if: matrix.codspeed == 'codspeed'
|
||||
uses: CodSpeedHQ/action@v4
|
||||
env:
|
||||
COVERAGE_FILE: coverage/.coverage.${{ runner.os }}-py${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,19 +12,48 @@ repos:
|
||||
- --unsafe
|
||||
- id: end-of-file-fixer
|
||||
- id: trailing-whitespace
|
||||
- repo: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-pre-commit
|
||||
rev: v0.14.3
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: ruff
|
||||
args:
|
||||
- --fix
|
||||
- id: ruff-format
|
||||
|
||||
- repo: local
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: local-script
|
||||
- id: local-ruff-check
|
||||
name: ruff check
|
||||
entry: uv run ruff check --force-exclude --fix --exit-non-zero-on-fix
|
||||
require_serial: true
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
name: local script
|
||||
types: [python]
|
||||
|
||||
- id: local-ruff-format
|
||||
name: ruff format
|
||||
entry: uv run ruff format --force-exclude --exit-non-zero-on-format
|
||||
require_serial: true
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
types: [python]
|
||||
|
||||
- id: add-permalinks-pages
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
name: add-permalinks-pages
|
||||
entry: uv run ./scripts/docs.py add-permalinks-pages
|
||||
args:
|
||||
- --update-existing
|
||||
files: ^docs/en/docs/.*\.md$
|
||||
|
||||
- id: generate-readme
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
name: generate README.md from index.md
|
||||
entry: uv run ./scripts/docs.py generate-readme
|
||||
files: ^docs/en/docs/index\.md|docs/en/data/sponsors\.yml|scripts/docs\.py$
|
||||
pass_filenames: false
|
||||
|
||||
- id: update-languages
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
name: update languages
|
||||
entry: uv run ./scripts/docs.py update-languages
|
||||
files: ^docs/.*|scripts/docs\.py$
|
||||
pass_filenames: false
|
||||
|
||||
- id: ensure-non-translated
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
name: ensure non-translated files are not modified
|
||||
entry: uv run ./scripts/docs.py ensure-non-translated
|
||||
files: ^docs/(?!en/).*|^scripts/docs\.py$
|
||||
pass_filenames: false
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -120,6 +120,12 @@ The key features are:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## FastAPI mini documentary
|
||||
|
||||
There's a <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI mini documentary</a> released at the end of 2025, you can watch it online:
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" target="_blank"><img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/fastapi-documentary.jpg" alt="FastAPI Mini Documentary"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## **Typer**, the FastAPI of CLIs
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com" target="_blank"><img src="https://typer.tiangolo.com/img/logo-margin/logo-margin-vector.svg" style="width: 20%;"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI basiert auf **Pydantic**, und ich habe Ihnen gezeigt, wie Sie Pydantic-M
|
||||
|
||||
Aber FastAPI unterstützt auf die gleiche Weise auch die Verwendung von <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a>:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Das ist dank **Pydantic** ebenfalls möglich, da es <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses` intern unterstützt</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Wenn Sie jedoch eine Menge Datenklassen herumliegen haben, ist dies ein guter Tr
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können `dataclasses` auch im Parameter `response_model` verwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Die Datenklasse wird automatisch in eine Pydantic-Datenklasse konvertiert.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ In einigen Fällen müssen Sie möglicherweise immer noch Pydantics Version von
|
||||
|
||||
In diesem Fall können Sie einfach die Standard-`dataclasses` durch `pydantic.dataclasses` ersetzen, was einen direkten Ersatz darstellt:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
1. Wir importieren `field` weiterhin von Standard-`dataclasses`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ Sie können die verwendeten Zeilen aus dem Docstring einer *Pfadoperation-Funkti
|
||||
|
||||
Das Hinzufügen eines `\f` (ein maskiertes „Form Feed“-Zeichen) führt dazu, dass **FastAPI** die für OpenAPI verwendete Ausgabe an dieser Stelle abschneidet.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie wird nicht in der Dokumentation angezeigt, aber andere Tools (z. B. Sphinx) können den Rest verwenden.
|
||||
Sie wird nicht in der Dokumentation angezeigt, aber andere Tools (wie z. B. Sphinx) können den Rest verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial004_py310.py hl[17:27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -153,48 +153,16 @@ Und Sie könnten dies auch tun, wenn der Datentyp im Request nicht JSON ist.
|
||||
|
||||
In der folgenden Anwendung verwenden wir beispielsweise weder die integrierte Funktionalität von FastAPI zum Extrahieren des JSON-Schemas aus Pydantic-Modellen noch die automatische Validierung für JSON. Tatsächlich deklarieren wir den Request-Content-Type als YAML und nicht als JSON:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_py39.py hl[15:20, 22] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_pv1_py39.py hl[15:20, 22] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic Version 1 hieß die Methode zum Abrufen des JSON-Schemas für ein Modell `Item.schema()`, in Pydantic Version 2 heißt die Methode `Item.model_json_schema()`.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Obwohl wir nicht die standardmäßig integrierte Funktionalität verwenden, verwenden wir dennoch ein Pydantic-Modell, um das JSON-Schema für die Daten, die wir in YAML empfangen möchten, manuell zu generieren.
|
||||
|
||||
Dann verwenden wir den Request direkt und extrahieren den Body als `bytes`. Das bedeutet, dass FastAPI nicht einmal versucht, den Request-Payload als JSON zu parsen.
|
||||
Dann verwenden wir den Request direkt und extrahieren den Body als `bytes`. Das bedeutet, dass FastAPI nicht einmal versucht, die Request-Payload als JSON zu parsen.
|
||||
|
||||
Und dann parsen wir in unserem Code diesen YAML-Inhalt direkt und verwenden dann wieder dasselbe Pydantic-Modell, um den YAML-Inhalt zu validieren:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_py39.py hl[24:31] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_pv1_py39.py hl[24:31] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic Version 1 war die Methode zum Parsen und Validieren eines Objekts `Item.parse_obj()`, in Pydantic Version 2 heißt die Methode `Item.model_validate()`.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip | Tipp
|
||||
|
||||
Hier verwenden wir dasselbe Pydantic-Modell wieder.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -60,24 +60,8 @@ Auf die gleiche Weise wie bei Pydantic-Modellen deklarieren Sie Klassenattribute
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können dieselben Validierungs-Funktionen und -Tools verwenden, die Sie für Pydantic-Modelle verwenden, z. B. verschiedene Datentypen und zusätzliche Validierungen mit `Field()`.
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/tutorial001_py39.py hl[2,5:8,11] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 würden Sie `BaseSettings` direkt von `pydantic` statt von `pydantic_settings` importieren.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/tutorial001_pv1_py39.py hl[2,5:8,11] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip | Tipp
|
||||
|
||||
Für ein schnelles Copy-and-paste verwenden Sie nicht dieses Beispiel, sondern das letzte unten.
|
||||
@@ -215,8 +199,6 @@ APP_NAME="ChimichangApp"
|
||||
|
||||
Und dann aktualisieren Sie Ihre `config.py` mit:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/app03_an_py39/config.py hl[9] *}
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip | Tipp
|
||||
@@ -225,26 +207,6 @@ Das Attribut `model_config` wird nur für die Pydantic-Konfiguration verwendet.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/app03_an_py39/config_pv1.py hl[9:10] *}
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip | Tipp
|
||||
|
||||
Die Klasse `Config` wird nur für die Pydantic-Konfiguration verwendet. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/1.10/usage/model_config/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic Model Config</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic Version 1 erfolgte die Konfiguration in einer internen Klasse `Config`, in Pydantic Version 2 erfolgt sie in einem Attribut `model_config`. Dieses Attribut akzeptiert ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr>. Um automatische Codevervollständigung und Inline-Fehlerberichte zu erhalten, können Sie `SettingsConfigDict` importieren und verwenden, um dieses `dict` zu definieren.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Hier definieren wir die Konfiguration `env_file` innerhalb Ihrer Pydantic-`Settings`-Klasse und setzen den Wert auf den Dateinamen mit der dotenv-Datei, die wir verwenden möchten.
|
||||
|
||||
### Die `Settings` nur einmal laden mittels `lru_cache` { #creating-the-settings-only-once-with-lru-cache }
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Abhängig von Ihrem Anwendungsfall könnten Sie eine andere Bibliothek vorziehen
|
||||
|
||||
Hier ist eine kleine Vorschau, wie Sie Strawberry mit FastAPI integrieren können:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql_/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen zu Strawberry finden Sie in der <a href="https://strawberry.rocks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Strawberry-Dokumentation</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,21 +2,23 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie eine ältere FastAPI-App haben, nutzen Sie möglicherweise Pydantic Version 1.
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI unterstützt seit Version 0.100.0 sowohl Pydantic v1 als auch v2.
|
||||
FastAPI Version 0.100.0 unterstützte sowohl Pydantic v1 als auch v2. Es verwendete, was auch immer Sie installiert hatten.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie Pydantic v2 installiert hatten, wurde dieses verwendet. Wenn stattdessen Pydantic v1 installiert war, wurde jenes verwendet.
|
||||
FastAPI Version 0.119.0 führte eine teilweise Unterstützung für Pydantic v1 innerhalb von Pydantic v2 (als `pydantic.v1`) ein, um die Migration zu v2 zu erleichtern.
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic v1 ist jetzt deprecatet und die Unterstützung dafür wird in den nächsten Versionen von FastAPI entfernt, Sie sollten also zu **Pydantic v2 migrieren**. Auf diese Weise erhalten Sie die neuesten Features, Verbesserungen und Fixes.
|
||||
FastAPI 0.126.0 entfernte die Unterstützung für Pydantic v1, während `pydantic.v1` noch eine Weile unterstützt wurde.
|
||||
|
||||
/// warning | Achtung
|
||||
|
||||
Außerdem hat das Pydantic-Team die Unterstützung für Pydantic v1 in den neuesten Python-Versionen eingestellt, beginnend mit **Python 3.14**.
|
||||
Das Pydantic-Team hat die Unterstützung für Pydantic v1 in den neuesten Python-Versionen eingestellt, beginnend mit **Python 3.14**.
|
||||
|
||||
Dies schließt `pydantic.v1` ein, das unter Python 3.14 und höher nicht mehr unterstützt wird.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie die neuesten Features von Python nutzen möchten, müssen Sie sicherstellen, dass Sie Pydantic v2 verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie eine ältere FastAPI-App mit Pydantic v1 haben, zeige ich Ihnen hier, wie Sie sie zu Pydantic v2 migrieren, und die **neuen Features in FastAPI 0.119.0**, die Ihnen bei einer schrittweisen Migration helfen.
|
||||
Wenn Sie eine ältere FastAPI-App mit Pydantic v1 haben, zeige ich Ihnen hier, wie Sie sie zu Pydantic v2 migrieren, und die **Features in FastAPI 0.119.0**, die Ihnen bei einer schrittweisen Migration helfen.
|
||||
|
||||
## Offizieller Leitfaden { #official-guide }
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +46,7 @@ Danach können Sie die Tests ausführen und prüfen, ob alles funktioniert. Fall
|
||||
|
||||
## Pydantic v1 in v2 { #pydantic-v1-in-v2 }
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic v2 enthält alles aus Pydantic v1 als Untermodul `pydantic.v1`.
|
||||
Pydantic v2 enthält alles aus Pydantic v1 als Untermodul `pydantic.v1`. Dies wird aber in Versionen oberhalb von Python 3.13 nicht mehr unterstützt.
|
||||
|
||||
Das bedeutet, Sie können die neueste Version von Pydantic v2 installieren und die alten Pydantic‑v1‑Komponenten aus diesem Untermodul importieren und verwenden, als hätten Sie das alte Pydantic v1 installiert.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# Separate OpenAPI-Schemas für Eingabe und Ausgabe oder nicht { #separate-openapi-schemas-for-input-and-output-or-not }
|
||||
|
||||
Bei Verwendung von **Pydantic v2** ist die generierte OpenAPI etwas genauer und **korrekter** als zuvor. 😎
|
||||
Seit der Veröffentlichung von **Pydantic v2** ist die generierte OpenAPI etwas genauer und **korrekter** als zuvor. 😎
|
||||
|
||||
Tatsächlich gibt es in einigen Fällen sogar **zwei JSON-Schemas** in OpenAPI für dasselbe Pydantic-Modell, für Eingabe und Ausgabe, je nachdem, ob sie **Defaultwerte** haben.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -100,5 +100,3 @@ Und jetzt wird es ein einziges Schema für die Eingabe und Ausgabe des Modells g
|
||||
<div class="screenshot">
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/separate-openapi-schemas/image05.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Dies ist das gleiche Verhalten wie in Pydantic v1. 🤓
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -117,6 +117,12 @@ Seine Schlüssel-Merkmale sind:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## FastAPI Mini-Dokumentarfilm { #fastapi-mini-documentary }
|
||||
|
||||
Es gibt einen <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI-Mini-Dokumentarfilm</a>, veröffentlicht Ende 2025, Sie können ihn online ansehen:
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" target="_blank"><img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/fastapi-documentary.jpg" alt="FastAPI Mini-Dokumentarfilm"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## **Typer**, das FastAPI der CLIs { #typer-the-fastapi-of-clis }
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com" target="_blank"><img src="https://typer.tiangolo.com/img/logo-margin/logo-margin-vector.svg" style="width: 20%;"></a>
|
||||
@@ -233,7 +239,7 @@ INFO: Application startup complete.
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown="1">
|
||||
<summary>Was der Befehl <code>fastapi dev main.py</code> macht ...</summary>
|
||||
<summary>Über den Befehl <code>fastapi dev main.py</code> ...</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
Der Befehl `fastapi dev` liest Ihre `main.py`-Datei, erkennt die **FastAPI**-App darin und startet einen Server mit <a href="https://www.uvicorn.dev" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uvicorn</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -276,7 +282,7 @@ Sie sehen die alternative automatische Dokumentation (bereitgestellt von <a href
|
||||
|
||||
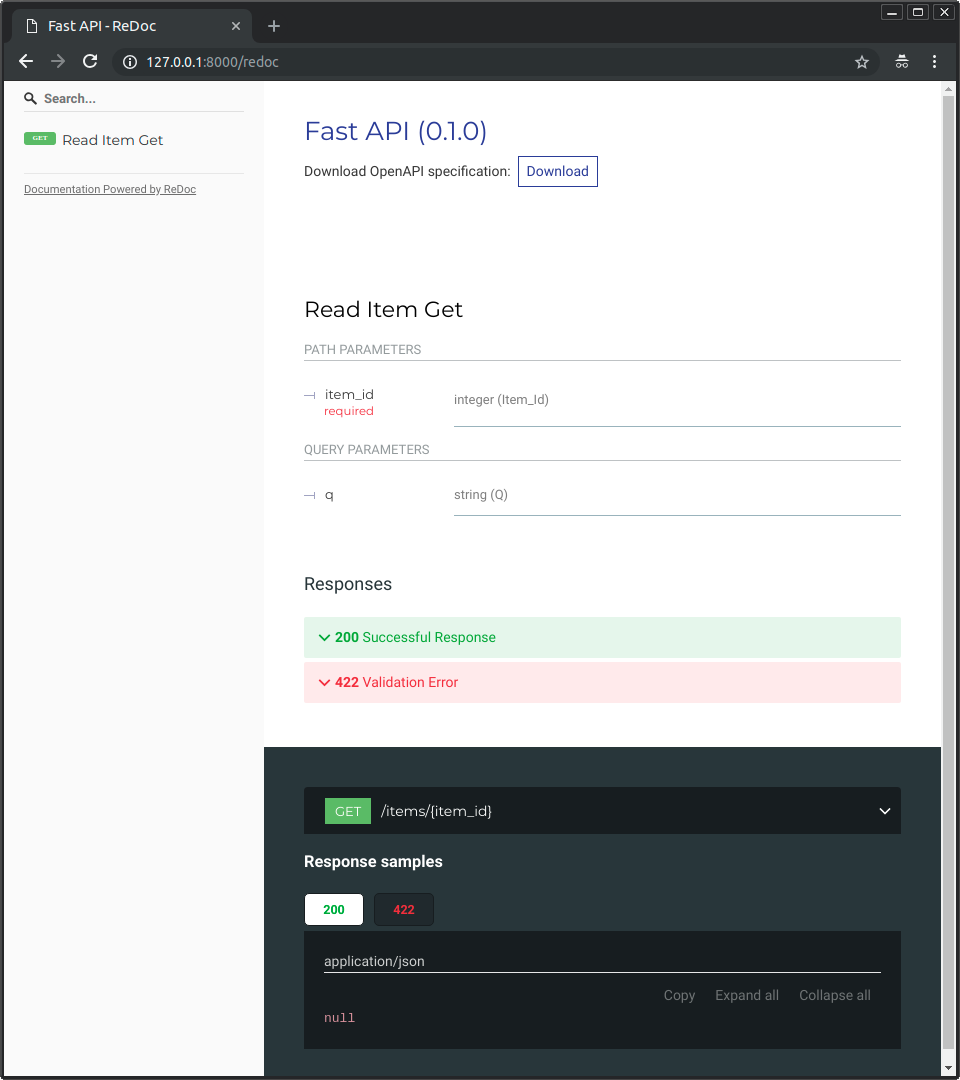
|
||||
|
||||
## Beispiel Aktualisierung { #example-upgrade }
|
||||
## Beispielaktualisierung { #example-upgrade }
|
||||
|
||||
Ändern Sie jetzt die Datei `main.py`, um den <abbr title="Body – Körper, Inhalt: Der eigentliche Inhalt einer Nachricht, nicht die Metadaten">Body</abbr> eines `PUT`-Requests zu empfangen.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -326,7 +332,7 @@ Gehen Sie jetzt auf <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" t
|
||||
|
||||
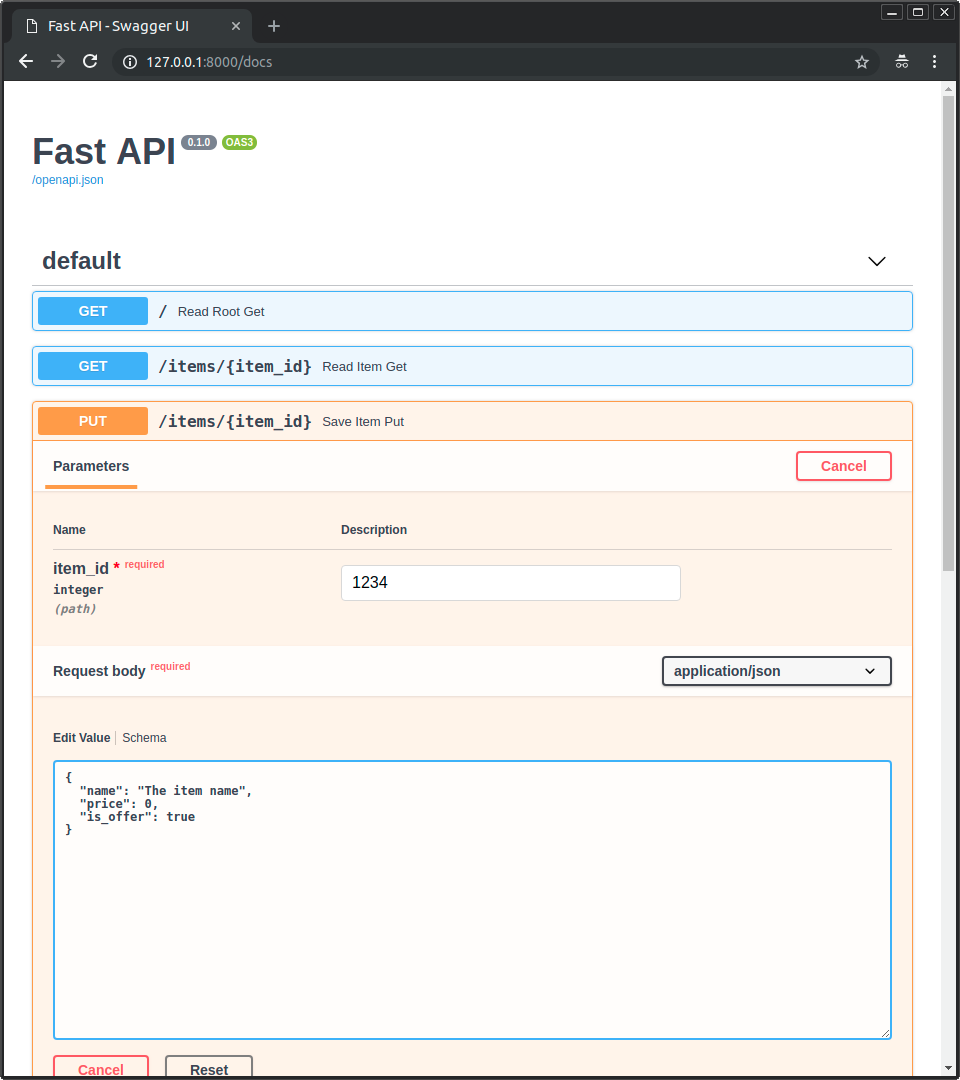
|
||||
|
||||
* Klicken Sie dann auf den Button „Execute“, die Benutzeroberfläche wird mit Ihrer API kommunizieren, sendet die Parameter, holt die Ergebnisse und zeigt sie auf dem Bildschirm an:
|
||||
* Klicken Sie dann auf den Button „Execute“, die Benutzeroberfläche wird mit Ihrer API kommunizieren, die Parameter senden, die Ergebnisse erhalten und sie auf dem Bildschirm anzeigen:
|
||||
|
||||
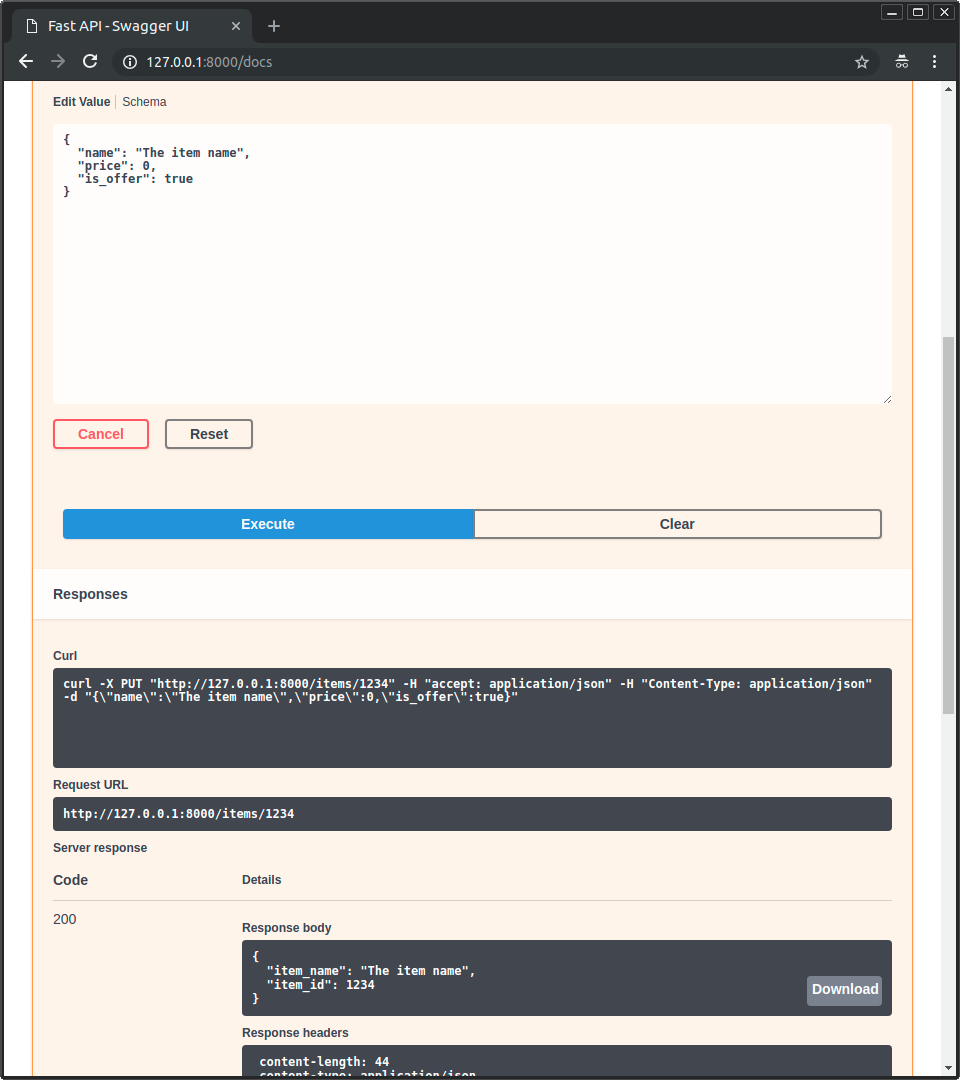
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -439,7 +445,7 @@ Für ein vollständigeres Beispiel, mit weiteren Funktionen, siehe das <a href="
|
||||
|
||||
* Deklaration von **Parametern** von anderen verschiedenen Stellen wie: **Header**, **Cookies**, **Formularfelder** und **Dateien**.
|
||||
* Wie man **Validierungs-Constraints** wie `maximum_length` oder `regex` setzt.
|
||||
* Ein sehr leistungsfähiges und einfach zu bedienendes System für **<abbr title="Dependency Injection – Einbringen von Abhängigkeiten: Auch bekannt als Komponenten, Ressourcen, Provider, Services, Injectables">Dependency Injection</abbr>**.
|
||||
* Ein sehr leistungsfähiges und einfach zu bedienendes System für **<abbr title="auch bekannt als Komponenten, Ressourcen, Provider, Services, Injectables">Dependency Injection</abbr>**.
|
||||
* Sicherheit und Authentifizierung, einschließlich Unterstützung für **OAuth2** mit **JWT-Tokens** und **HTTP Basic** Authentifizierung.
|
||||
* Fortgeschrittenere (aber ebenso einfache) Techniken zur Deklaration **tief verschachtelter JSON-Modelle** (dank Pydantic).
|
||||
* **GraphQL**-Integration mit <a href="https://strawberry.rocks" class="external-link" target="_blank">Strawberry</a> und anderen Bibliotheken.
|
||||
@@ -452,7 +458,7 @@ Für ein vollständigeres Beispiel, mit weiteren Funktionen, siehe das <a href="
|
||||
|
||||
### Ihre App deployen (optional) { #deploy-your-app-optional }
|
||||
|
||||
Optional können Sie Ihre FastAPI-App in die <a href="https://fastapicloud.com" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI Cloud</a> deployen, treten Sie der Warteliste bei, falls noch nicht geschehen. 🚀
|
||||
Optional können Sie Ihre FastAPI-App in die <a href="https://fastapicloud.com" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI Cloud</a> deployen, gehen Sie und treten Sie der Warteliste bei, falls noch nicht geschehen. 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie bereits ein **FastAPI Cloud**-Konto haben (wir haben Sie von der Warteliste eingeladen 😉), können Sie Ihre Anwendung mit einem einzigen Befehl deployen.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -494,7 +500,7 @@ Es vereinfacht den Prozess des **Erstellens**, **Deployens** und **Zugreifens**
|
||||
|
||||
Es bringt die gleiche **Developer-Experience** beim Erstellen von Apps mit FastAPI auch zum **Deployment** in der Cloud. 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI Cloud ist der Hauptsponsor und Finanzierer der „FastAPI and friends“ Open-Source-Projekte. ✨
|
||||
FastAPI Cloud ist der Hauptsponsor und Finanzierer der *FastAPI and friends* Open-Source-Projekte. ✨
|
||||
|
||||
#### Bei anderen Cloudanbietern deployen { #deploy-to-other-cloud-providers }
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -50,14 +50,6 @@ Wenn Sie Teil-Aktualisierungen entgegennehmen, ist der `exclude_unset`-Parameter
|
||||
|
||||
Wie in `item.model_dump(exclude_unset=True)`.
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 hieß diese Methode `.dict()`, in Pydantic v2 wurde sie <abbr title="veraltet, obsolet: Es soll nicht mehr verwendet werden">deprecatet</abbr> (aber immer noch unterstützt) und in `.model_dump()` umbenannt.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Beispiele hier verwenden `.dict()` für die Kompatibilität mit Pydantic v1, Sie sollten jedoch stattdessen `.model_dump()` verwenden, wenn Sie Pydantic v2 verwenden können.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Das wird ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr> erstellen, mit nur den Daten, die gesetzt wurden, als das `item`-Modell erstellt wurde, Defaultwerte ausgeschlossen.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können das verwenden, um ein `dict` zu erstellen, das nur die (im <abbr title="Request – Anfrage: Daten, die der Client zum Server sendet">Request</abbr>) gesendeten Daten enthält, ohne Defaultwerte:
|
||||
@@ -68,14 +60,6 @@ Sie können das verwenden, um ein `dict` zu erstellen, das nur die (im <abbr tit
|
||||
|
||||
Jetzt können Sie eine Kopie des existierenden Modells mittels `.model_copy()` erstellen, wobei Sie dem `update`-Parameter ein `dict` mit den zu ändernden Daten übergeben.
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 hieß diese Methode `.copy()`, in Pydantic v2 wurde sie <abbr title="veraltet, obsolet: Es soll nicht mehr verwendet werden">deprecatet</abbr> (aber immer noch unterstützt) und in `.model_copy()` umbenannt.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Beispiele hier verwenden `.copy()` für die Kompatibilität mit Pydantic v1, Sie sollten jedoch stattdessen `.model_copy()` verwenden, wenn Sie Pydantic v2 verwenden können.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Wie in `stored_item_model.model_copy(update=update_data)`:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/body_updates/tutorial002_py310.py hl[33] *}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -127,14 +127,6 @@ Innerhalb der Funktion können Sie alle Attribute des Modellobjekts direkt verwe
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/body/tutorial002_py310.py *}
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 hieß die Methode `.dict()`, sie wurde in Pydantic v2 deprecatet (aber weiterhin unterstützt) und in `.model_dump()` umbenannt.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Beispiele hier verwenden `.dict()` zur Kompatibilität mit Pydantic v1, aber Sie sollten stattdessen `.model_dump()` verwenden, wenn Sie Pydantic v2 nutzen können.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
## Requestbody- + Pfad-Parameter { #request-body-path-parameters }
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können Pfad-Parameter und den Requestbody gleichzeitig deklarieren.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,21 +22,13 @@ Hier ist eine allgemeine Idee, wie die Modelle mit ihren Passwortfeldern aussehe
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial001_py310.py hl[7,9,14,20,22,27:28,31:33,38:39] *}
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
### Über `**user_in.model_dump()` { #about-user-in-model-dump }
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 hieß die Methode `.dict()`, in Pydantic v2 wurde sie <abbr title="veraltet, obsolet: Es soll nicht mehr verwendet werden">deprecatet</abbr> (aber weiterhin unterstützt) und in `.model_dump()` umbenannt.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Beispiele hier verwenden `.dict()` für die Kompatibilität mit Pydantic v1, aber Sie sollten `.model_dump()` verwenden, wenn Sie Pydantic v2 verwenden können.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
### Über `**user_in.dict()` { #about-user-in-dict }
|
||||
|
||||
#### Die `.dict()`-Methode von Pydantic { #pydantics-dict }
|
||||
#### Pydantics `.model_dump()` { #pydantics-model-dump }
|
||||
|
||||
`user_in` ist ein Pydantic-Modell der Klasse `UserIn`.
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic-Modelle haben eine `.dict()`-Methode, die ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr> mit den Daten des Modells zurückgibt.
|
||||
Pydantic-Modelle haben eine `.model_dump()`-Methode, die ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr> mit den Daten des Modells zurückgibt.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn wir also ein Pydantic-Objekt `user_in` erstellen, etwa so:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,7 +39,7 @@ user_in = UserIn(username="john", password="secret", email="john.doe@example.com
|
||||
und dann aufrufen:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.dict()
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.model_dump()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
haben wir jetzt ein `dict` mit den Daten in der Variablen `user_dict` (es ist ein `dict` statt eines Pydantic-Modellobjekts).
|
||||
@@ -103,20 +95,20 @@ UserInDB(
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ein Pydantic-Modell aus dem Inhalt eines anderen { #a-pydantic-model-from-the-contents-of-another }
|
||||
|
||||
Da wir im obigen Beispiel `user_dict` von `user_in.dict()` bekommen haben, wäre dieser Code:
|
||||
Da wir im obigen Beispiel `user_dict` von `user_in.model_dump()` bekommen haben, wäre dieser Code:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.dict()
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.model_dump()
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_dict)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gleichwertig zu:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.dict())
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.model_dump())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
... weil `user_in.dict()` ein `dict` ist, und dann lassen wir Python es „entpacken“, indem wir es an `UserInDB` mit vorangestelltem `**` übergeben.
|
||||
... weil `user_in.model_dump()` ein `dict` ist, und dann lassen wir Python es „entpacken“, indem wir es an `UserInDB` mit vorangestelltem `**` übergeben.
|
||||
|
||||
Auf diese Weise erhalten wir ein Pydantic-Modell aus den Daten eines anderen Pydantic-Modells.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -125,7 +117,7 @@ Auf diese Weise erhalten wir ein Pydantic-Modell aus den Daten eines anderen Pyd
|
||||
Und dann fügen wir das zusätzliche Schlüsselwort-Argument `hashed_password=hashed_password` hinzu, wie in:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.dict(), hashed_password=hashed_password)
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.model_dump(), hashed_password=hashed_password)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
... was so ist wie:
|
||||
@@ -180,7 +172,6 @@ Wenn Sie eine <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/types/#unions"
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,14:15,18:20,33] *}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### `Union` in Python 3.10 { #union-in-python-3-10 }
|
||||
|
||||
In diesem Beispiel übergeben wir `Union[PlaneItem, CarItem]` als Wert des Arguments `response_model`.
|
||||
@@ -203,7 +194,6 @@ Dafür verwenden Sie Pythons Standard-`typing.List` (oder nur `list` in Python 3
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial004_py39.py hl[18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Response mit beliebigem `dict` { #response-with-arbitrary-dict }
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können auch eine Response deklarieren, die ein beliebiges `dict` zurückgibt, indem Sie nur die Typen der Schlüssel und Werte ohne ein Pydantic-Modell deklarieren.
|
||||
@@ -214,7 +204,6 @@ In diesem Fall können Sie `typing.Dict` verwenden (oder nur `dict` in Python 3.
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial005_py39.py hl[6] *}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Zusammenfassung { #recap }
|
||||
|
||||
Verwenden Sie gerne mehrere Pydantic-Modelle und vererben Sie je nach Bedarf.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -205,20 +205,6 @@ Wenn Sie sich mit all diesen **„regulärer Ausdruck“**-Ideen verloren fühle
|
||||
|
||||
Aber nun wissen Sie, dass Sie sie in **FastAPI** immer dann verwenden können, wenn Sie sie brauchen.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pydantic v1 `regex` statt `pattern` { #pydantic-v1-regex-instead-of-pattern }
|
||||
|
||||
Vor Pydantic Version 2 und FastAPI 0.100.0, hieß der Parameter `regex` statt `pattern`, aber das ist jetzt obsolet.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie könnten immer noch Code sehen, der den alten Namen verwendet:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial004_regex_an_py310.py hl[11] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
Beachten Sie aber, dass das obsolet ist und auf den neuen Parameter `pattern` aktualisiert werden sollte. 🤓
|
||||
|
||||
## Defaultwerte { #default-values }
|
||||
|
||||
Natürlich können Sie Defaultwerte verwenden, die nicht `None` sind.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -252,20 +252,6 @@ Wenn Sie also den Artikel mit der ID `foo` bei der *Pfadoperation* anfragen, wir
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 hieß diese Methode `.dict()`, in Pydantic v2 wurde sie <abbr title="veraltet, obsolet: Es soll nicht mehr verwendet werden">deprecatet</abbr> (aber immer noch unterstützt) und in `.model_dump()` umbenannt.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Beispiele hier verwenden `.dict()` für die Kompatibilität mit Pydantic v1, Sie sollten jedoch stattdessen `.model_dump()` verwenden, wenn Sie Pydantic v2 verwenden können.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI verwendet `.dict()` von Pydantic Modellen, <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/1.10/usage/exporting_models/#modeldict" class="external-link" target="_blank">mit dessen `exclude_unset`-Parameter</a>, um das zu erreichen.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können auch:
|
||||
|
||||
* `response_model_exclude_defaults=True`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,36 +8,14 @@ Hier sind mehrere Möglichkeiten, das zu tun.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können `examples` („Beispiele“) für ein Pydantic-Modell deklarieren, welche dem generierten JSON-Schema hinzugefügt werden.
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/schema_extra_example/tutorial001_py310.py hl[13:24] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/schema_extra_example/tutorial001_pv1_py310.py hl[13:23] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
Diese zusätzlichen Informationen werden unverändert zum für dieses Modell ausgegebenen **JSON-Schema** hinzugefügt und in der API-Dokumentation verwendet.
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic Version 2 würden Sie das Attribut `model_config` verwenden, das ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr> akzeptiert, wie beschrieben in <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/api/config/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic-Dokumentation: Configuration</a>.
|
||||
Sie können das Attribut `model_config` verwenden, das ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr> akzeptiert, wie beschrieben in <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/api/config/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic-Dokumentation: Configuration</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können `json_schema_extra` setzen, mit einem `dict`, das alle zusätzlichen Daten enthält, die im generierten JSON-Schema angezeigt werden sollen, einschließlich `examples`.
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic Version 1 würden Sie eine interne Klasse `Config` und `schema_extra` verwenden, wie beschrieben in <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/1.10/usage/schema/#schema-customization" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic-Dokumentation: Schema customization</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können `schema_extra` setzen, mit einem `dict`, das alle zusätzlichen Daten enthält, die im generierten JSON-Schema angezeigt werden sollen, einschließlich `examples`.
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip | Tipp
|
||||
|
||||
Mit derselben Technik können Sie das JSON-Schema erweitern und Ihre eigenen benutzerdefinierten Zusatzinformationen hinzufügen.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -251,6 +251,7 @@ Below is a list of English terms and their preferred German translations, separa
|
||||
* «the button»: «der Button»
|
||||
* «the cloud provider»: «der Cloudanbieter»
|
||||
* «the CLI»: «Das CLI»
|
||||
* «the coverage»: «Die Testabdeckung»
|
||||
* «the command line interface»: «Das Kommandozeileninterface»
|
||||
* «the default value»: «der Defaultwert»
|
||||
* «the default value»: NOT «der Standardwert»
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI is built on top of **Pydantic**, and I have been showing you how to use
|
||||
|
||||
But FastAPI also supports using <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a> the same way:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
This is still supported thanks to **Pydantic**, as it has <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">internal support for `dataclasses`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ But if you have a bunch of dataclasses laying around, this is a nice trick to us
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use `dataclasses` in the `response_model` parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
The dataclass will be automatically converted to a Pydantic dataclass.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ In some cases, you might still have to use Pydantic's version of `dataclasses`.
|
||||
|
||||
In that case, you can simply swap the standard `dataclasses` with `pydantic.dataclasses`, which is a drop-in replacement:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
1. We still import `field` from standard `dataclasses`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Depending on your use case, you might prefer to use a different library, but if
|
||||
|
||||
Here's a small preview of how you could integrate Strawberry with FastAPI:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql_/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about Strawberry in the <a href="https://strawberry.rocks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Strawberry documentation</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/fastapi-documentary.jpg
Normal file
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/fastapi-documentary.jpg
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 187 KiB |
@@ -117,6 +117,12 @@ The key features are:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## FastAPI mini documentary { #fastapi-mini-documentary }
|
||||
|
||||
There's a <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI mini documentary</a> released at the end of 2025, you can watch it online:
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" target="_blank"><img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/fastapi-documentary.jpg" alt="FastAPI Mini Documentary"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## **Typer**, the FastAPI of CLIs { #typer-the-fastapi-of-clis }
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com" target="_blank"><img src="https://typer.tiangolo.com/img/logo-margin/logo-margin-vector.svg" style="width: 20%;"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,6 +7,30 @@ hide:
|
||||
|
||||
## Latest Changes
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.127.1
|
||||
|
||||
### Refactors
|
||||
|
||||
* 🔊 Add a custom `FastAPIDeprecationWarning`. PR [#14605](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14605) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
### Docs
|
||||
|
||||
* 📝 Add documentary to website. PR [#14600](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14600) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
### Translations
|
||||
|
||||
* 🌐 Update translations for de (update-outdated). PR [#14602](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14602) by [@nilslindemann](https://github.com/nilslindemann).
|
||||
* 🌐 Update translations for de (update-outdated). PR [#14581](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14581) by [@nilslindemann](https://github.com/nilslindemann).
|
||||
|
||||
### Internal
|
||||
|
||||
* 🔧 Update pre-commit to use local Ruff instead of hook. PR [#14604](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14604) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* ✅ Add missing tests for code examples. PR [#14569](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14569) by [@YuriiMotov](https://github.com/YuriiMotov).
|
||||
* 👷 Remove `lint` job from `test` CI workflow. PR [#14593](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14593) by [@YuriiMotov](https://github.com/YuriiMotov).
|
||||
* 👷 Update secrets check. PR [#14592](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14592) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 👷 Run CodSpeed tests in parallel to other tests to speed up CI. PR [#14586](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14586) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 🔨 Update scripts and pre-commit to autofix files. PR [#14585](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14585) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.127.0
|
||||
|
||||
### Breaking Changes
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI está construido sobre **Pydantic**, y te he estado mostrando cómo usar
|
||||
|
||||
Pero FastAPI también soporta el uso de <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a> de la misma manera:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Esto sigue siendo soportado gracias a **Pydantic**, ya que tiene <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">soporte interno para `dataclasses`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Pero si tienes un montón de dataclasses por ahí, este es un buen truco para us
|
||||
|
||||
También puedes usar `dataclasses` en el parámetro `response_model`:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
El dataclass será automáticamente convertido a un dataclass de Pydantic.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ En algunos casos, todavía podrías tener que usar la versión de `dataclasses`
|
||||
|
||||
En ese caso, simplemente puedes intercambiar los `dataclasses` estándar con `pydantic.dataclasses`, que es un reemplazo directo:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
1. Todavía importamos `field` de los `dataclasses` estándar.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Dependiendo de tu caso de uso, podrías preferir usar un paquete diferente, pero
|
||||
|
||||
Aquí tienes una pequeña vista previa de cómo podrías integrar Strawberry con FastAPI:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql_/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Puedes aprender más sobre Strawberry en la <a href="https://strawberry.rocks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">documentación de Strawberry</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI é construído em cima do **Pydantic**, e eu tenho mostrado como usar mo
|
||||
|
||||
Mas o FastAPI também suporta o uso de <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a> da mesma forma:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Isso ainda é suportado graças ao **Pydantic**, pois ele tem <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">suporte interno para `dataclasses`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Mas se você tem um monte de dataclasses por aí, este é um truque legal para u
|
||||
|
||||
Você também pode usar `dataclasses` no parâmetro `response_model`:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
A dataclass será automaticamente convertida para uma dataclass Pydantic.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ Em alguns casos, você ainda pode ter que usar a versão do Pydantic das `datacl
|
||||
|
||||
Nesse caso, você pode simplesmente trocar as `dataclasses` padrão por `pydantic.dataclasses`, que é um substituto direto:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
1. Ainda importamos `field` das `dataclasses` padrão.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Dependendo do seu caso de uso, você pode preferir usar uma biblioteca diferente
|
||||
|
||||
Aqui está uma pequena prévia de como você poderia integrar Strawberry com FastAPI:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql_/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Você pode aprender mais sobre Strawberry na <a href="https://strawberry.rocks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">documentação do Strawberry</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI построен поверх **Pydantic**, и я показывал в
|
||||
|
||||
Но FastAPI также поддерживает использование <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a> тем же способом:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Это по-прежнему поддерживается благодаря **Pydantic**, так как в нём есть <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">встроенная поддержка `dataclasses`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ FastAPI построен поверх **Pydantic**, и я показывал в
|
||||
|
||||
Вы также можете использовать `dataclasses` в параметре `response_model`:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Этот dataclass будет автоматически преобразован в Pydantic dataclass.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ FastAPI построен поверх **Pydantic**, и я показывал в
|
||||
|
||||
В таком случае вы можете просто заменить стандартные `dataclasses` на `pydantic.dataclasses`, которая является полностью совместимой заменой (drop-in replacement):
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
1. Мы по-прежнему импортируем `field` из стандартных `dataclasses`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Вот небольшой пример того, как можно интегрировать Strawberry с FastAPI:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql_/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Подробнее о Strawberry можно узнать в <a href="https://strawberry.rocks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">документации Strawberry</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI 基于 **Pydantic** 构建,前文已经介绍过如何使用 Pydantic
|
||||
|
||||
但 FastAPI 还可以使用数据类(<a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a>):
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001.py hl[1,7:12,19:20] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001.py hl[1,7:12,19:20] *}
|
||||
|
||||
这还是借助于 **Pydantic** 及其<a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">内置的 `dataclasses`</a>。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ FastAPI 基于 **Pydantic** 构建,前文已经介绍过如何使用 Pydantic
|
||||
|
||||
在 `response_model` 参数中使用 `dataclasses`:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002.py hl[1,7:13,19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002.py hl[1,7:13,19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
本例把数据类自动转换为 Pydantic 数据类。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ API 文档中也会显示相关概图:
|
||||
本例把标准的 `dataclasses` 直接替换为 `pydantic.dataclasses`:
|
||||
|
||||
```{ .python .annotate hl_lines="1 5 8-11 14-17 23-25 28" }
|
||||
{!../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
{!../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. 本例依然要从标准的 `dataclasses` 中导入 `field`;
|
||||
|
||||
0
docs_src/additional_responses/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/additional_responses/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/additional_status_codes/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/additional_status_codes/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/advanced_middleware/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/advanced_middleware/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/background_tasks/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/background_tasks/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/behind_a_proxy/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/behind_a_proxy/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_fields/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_fields/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_multiple_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_multiple_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_nested_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_nested_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_updates/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_updates/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/conditional_openapi/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/conditional_openapi/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/configure_swagger_ui/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/configure_swagger_ui/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/cookie_param_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/cookie_param_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/cookie_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/cookie_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/cors/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/cors/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_docs_ui/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_docs_ui/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_request_and_route/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_request_and_route/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_response/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_response/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dataclasses_/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dataclasses_/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/debugging/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/debugging/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dependencies/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dependencies/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dependency_testing/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dependency_testing/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/encoder/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/encoder/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/events/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/events/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extending_openapi/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extending_openapi/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extra_data_types/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extra_data_types/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extra_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extra_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/first_steps/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/first_steps/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/generate_clients/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/generate_clients/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/graphql_/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/graphql_/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/handling_errors/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/handling_errors/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/header_param_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/header_param_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/header_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/header_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/metadata/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/metadata/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/middleware/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/middleware/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/openapi_callbacks/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/openapi_callbacks/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/openapi_webhooks/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/openapi_webhooks/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/path_operation_configuration/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/path_operation_configuration/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/path_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/path_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/pydantic_v1_in_v2/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/pydantic_v1_in_v2/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/python_types/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/python_types/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/query_param_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/query_param_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/query_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/query_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/query_params_str_validations/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/query_params_str_validations/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/request_files/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/request_files/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/request_form_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/request_form_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/request_forms/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/request_forms/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/request_forms_and_files/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/request_forms_and_files/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_change_status_code/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_change_status_code/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_cookies/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_cookies/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_directly/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_directly/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_headers/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_headers/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_model/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_model/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_status_code/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/response_status_code/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/schema_extra_example/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/schema_extra_example/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/security/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/security/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/separate_openapi_schemas/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/separate_openapi_schemas/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/settings/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/settings/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/static_files/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/static_files/__init__.py
Normal file
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user