Compare commits
276 Commits
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
f64c448329 | ||
|
|
df6cbc5ec6 | ||
|
|
0f0af751e4 | ||
|
|
6c9dca55bc | ||
|
|
d71e807401 | ||
|
|
7df9ddfe4e | ||
|
|
4170659359 | ||
|
|
2940a7fdfa | ||
|
|
dadd6650ed | ||
|
|
c5a21354af | ||
|
|
8bafe2a482 | ||
|
|
42f1716b48 | ||
|
|
6ab2841dbb | ||
|
|
0f54657377 | ||
|
|
79e5b36551 | ||
|
|
074868d77e | ||
|
|
3dd16a9458 | ||
|
|
62c23ab5fa | ||
|
|
11c05beece | ||
|
|
7b3ef43127 | ||
|
|
e0080e5f75 | ||
|
|
e1ba54bd12 | ||
|
|
7032dfb4f1 | ||
|
|
14e7f7c1f4 | ||
|
|
9ed6f1e419 | ||
|
|
b268c39758 | ||
|
|
4dd386b807 | ||
|
|
b7251f1654 | ||
|
|
780d3e65ad | ||
|
|
cc8cac200f | ||
|
|
e7be5c8ac5 | ||
|
|
8f52864899 | ||
|
|
47a630721a | ||
|
|
10ae6de111 | ||
|
|
2b47f3e56b | ||
|
|
d60dd1b60e | ||
|
|
2822f7ca64 | ||
|
|
ff6afeaf78 | ||
|
|
74852d406c | ||
|
|
921642dc7b | ||
|
|
5c01d44ee9 | ||
|
|
135704dcc8 | ||
|
|
88793bb6c2 | ||
|
|
70a51b3aff | ||
|
|
340a582be7 | ||
|
|
5f66b5466f | ||
|
|
d2169ee567 | ||
|
|
a5c03ba1b7 | ||
|
|
e4ea6426dc | ||
|
|
8bf7cd1dc6 | ||
|
|
92feb3ade7 | ||
|
|
d0e739d8f2 | ||
|
|
4efa6bd75e | ||
|
|
600f15faa0 | ||
|
|
250fa519f9 | ||
|
|
3c6dafcc8e | ||
|
|
8447000eee | ||
|
|
fe453f80ed | ||
|
|
3ff504f03f | ||
|
|
eea9ab6106 | ||
|
|
e9e07c41bb | ||
|
|
17a5e18f46 | ||
|
|
9148bd8b6f | ||
|
|
39766d0f96 | ||
|
|
2d9bca56b2 | ||
|
|
f158d95ce9 | ||
|
|
7a4164ef60 | ||
|
|
f3730a79af | ||
|
|
42eff23a79 | ||
|
|
25bc33350d | ||
|
|
b84d082005 | ||
|
|
1f01ce9615 | ||
|
|
352c5f5ecc | ||
|
|
e5594e860f | ||
|
|
50926faead | ||
|
|
a303afc0e5 | ||
|
|
12607e85e3 | ||
|
|
38fd363e89 | ||
|
|
7f62cfd231 | ||
|
|
c5168bd036 | ||
|
|
be472c5215 | ||
|
|
adac38ecea | ||
|
|
c8b634226e | ||
|
|
ca4cf7cc70 | ||
|
|
b87072bc12 | ||
|
|
04e2bfafbc | ||
|
|
181a32236a | ||
|
|
1f54a8e0a1 | ||
|
|
d63475bb7d | ||
|
|
5a3c5f1523 | ||
|
|
12bc9285f7 | ||
|
|
31df2ea940 | ||
|
|
50b90dd6a4 | ||
|
|
7dd881334d | ||
|
|
530fc8ff3f | ||
|
|
ef460b4d23 | ||
|
|
b591de2ace | ||
|
|
34c857b7cb | ||
|
|
c78bc0c82d | ||
|
|
194446e51a | ||
|
|
777e2151e6 | ||
|
|
5ce5bdba0b | ||
|
|
e4300769ac | ||
|
|
c6dd627bdd | ||
|
|
6576f724bb | ||
|
|
91a6736d0e | ||
|
|
8fb755703d | ||
|
|
748bedd37c | ||
|
|
bf58788f29 | ||
|
|
5f78ba4a31 | ||
|
|
db9f827263 | ||
|
|
dd9e94cf21 | ||
|
|
e482d74241 | ||
|
|
bd2acbcabb | ||
|
|
f913d469a8 | ||
|
|
66cb266641 | ||
|
|
74954894c5 | ||
|
|
ceedfccde0 | ||
|
|
2ee0eedf23 | ||
|
|
c0f3019764 | ||
|
|
dd6d0cb23c | ||
|
|
fe15620df3 | ||
|
|
6af857f206 | ||
|
|
7ce756f9dd | ||
|
|
c0b1fddb31 | ||
|
|
9aea85a84e | ||
|
|
fddd1c12de | ||
|
|
b13a4baf32 | ||
|
|
5ffa18f10f | ||
|
|
828915baf5 | ||
|
|
a071ddf3cd | ||
|
|
3651b8a30f | ||
|
|
0d73b9ff1c | ||
|
|
43235cf236 | ||
|
|
269a155583 | ||
|
|
12433d51dd | ||
|
|
3699e17212 | ||
|
|
8231fbede4 | ||
|
|
50bc14b835 | ||
|
|
4310c89c83 | ||
|
|
d39dd06a22 | ||
|
|
a0ab47e89e | ||
|
|
5cbcb9a965 | ||
|
|
801ceaec80 | ||
|
|
c7334ae9f8 | ||
|
|
d737599a2c | ||
|
|
d2d72a8e4a | ||
|
|
7895c12fa1 | ||
|
|
5f6a14c413 | ||
|
|
2b4e88fa98 | ||
|
|
11723bca27 | ||
|
|
b49517a64f | ||
|
|
f910e0c96c | ||
|
|
c1ba2a3127 | ||
|
|
28396173c7 | ||
|
|
69974b792e | ||
|
|
352412a3cb | ||
|
|
745ab48d65 | ||
|
|
4a5cda0d77 | ||
|
|
b90bf2da9e | ||
|
|
a552cbdf59 | ||
|
|
2351fb5623 | ||
|
|
807522c616 | ||
|
|
81a529c251 | ||
|
|
7efc15aeef | ||
|
|
d66d8379c0 | ||
|
|
5a00467951 | ||
|
|
434d32b891 | ||
|
|
535247ffc4 | ||
|
|
7e2518350a | ||
|
|
1b2a7546af | ||
|
|
2d9bb64047 | ||
|
|
072c2bc7f9 | ||
|
|
da7826b0eb | ||
|
|
2f478eeca6 | ||
|
|
543ef7753a | ||
|
|
88a887329e | ||
|
|
8cfe254400 | ||
|
|
bfd46e562b | ||
|
|
a0e4d38bea | ||
|
|
b0414b9929 | ||
|
|
3b4413f9f5 | ||
|
|
374cdf29a9 | ||
|
|
8d844bc5cf | ||
|
|
1092261ae1 | ||
|
|
5984233223 | ||
|
|
98bb9f13da | ||
|
|
d375dc6ebe | ||
|
|
ee335bca82 | ||
|
|
601d8eb809 | ||
|
|
b99f350a18 | ||
|
|
c1b0e796c6 | ||
|
|
d9e65147c7 | ||
|
|
6001513c4f | ||
|
|
3fa033d8d5 | ||
|
|
59f7e66ac3 | ||
|
|
08e8dfccbe | ||
|
|
fc70a2f36f | ||
|
|
f5c5dbb739 | ||
|
|
ca939fabf7 | ||
|
|
cc3d795bea | ||
|
|
7fc1bac54b | ||
|
|
27367df90c | ||
|
|
f93861e321 | ||
|
|
30e56ec835 | ||
|
|
48ccef9ad2 | ||
|
|
b79e002635 | ||
|
|
1fa28b7cb6 | ||
|
|
22f7eae3f2 | ||
|
|
ae93773465 | ||
|
|
0f387553d1 | ||
|
|
d53a253c8d | ||
|
|
f8f0a6e462 | ||
|
|
f7eea768f6 | ||
|
|
53d316f706 | ||
|
|
741de7f927 | ||
|
|
16b3669adf | ||
|
|
c5807fdaa4 | ||
|
|
897b7d1b99 | ||
|
|
409264960e | ||
|
|
cfb72eec5a | ||
|
|
778822bd9a | ||
|
|
cfd2c3017f | ||
|
|
caed37a08f | ||
|
|
4c1b54e209 | ||
|
|
e4f0947821 | ||
|
|
22e858f65c | ||
|
|
046d6b7fa0 | ||
|
|
89f36371b9 | ||
|
|
406b3ac805 | ||
|
|
f71ba8885e | ||
|
|
121e87b3e0 | ||
|
|
2d013b8340 | ||
|
|
761e5ff01d | ||
|
|
9812684178 | ||
|
|
f7a87cd6ba | ||
|
|
f67bc3ffe8 | ||
|
|
dff644abe0 | ||
|
|
fc7b4ab880 | ||
|
|
1d0f909ca5 | ||
|
|
a0cdbe449b | ||
|
|
44bd64d797 | ||
|
|
bfa78db458 | ||
|
|
4e77737a3f | ||
|
|
d03c197c80 | ||
|
|
06e42a4e5d | ||
|
|
bd1e85a8d3 | ||
|
|
506d5dce39 | ||
|
|
a7b4c73663 | ||
|
|
d4f3ca1c1b | ||
|
|
471d703611 | ||
|
|
a46bbc54cd | ||
|
|
a4405bbed2 | ||
|
|
e9b189e9f2 | ||
|
|
483bce3ae1 | ||
|
|
7372f6ba11 | ||
|
|
8d92557e53 | ||
|
|
c56342bf79 | ||
|
|
07e094fd50 | ||
|
|
1cc30de32f | ||
|
|
3397d4d69a | ||
|
|
766157bfb4 | ||
|
|
d96223460b | ||
|
|
fd99dfc95b | ||
|
|
10fb7ace04 | ||
|
|
a1a19b103c | ||
|
|
5c111caf40 | ||
|
|
651ee5e4d2 | ||
|
|
c398ac87d9 | ||
|
|
0a77c613b0 | ||
|
|
70bc469373 | ||
|
|
b76334f544 | ||
|
|
14b467db06 | ||
|
|
3a0c22ce7d | ||
|
|
3b7e4e0544 | ||
|
|
d4d5b21b2e |
1
.github/FUNDING.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
github: [tiangolo]
|
||||
62
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug_report.md
vendored
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
name: Bug report
|
||||
about: Create a report to help us improve
|
||||
title: "[BUG]"
|
||||
labels: bug
|
||||
assignees: ''
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Describe the bug
|
||||
|
||||
Write here a clear and concise description of what the bug is.
|
||||
|
||||
### To Reproduce
|
||||
|
||||
Steps to reproduce the behavior with a minimum self-contained file.
|
||||
|
||||
Replace each part with your own scenario:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a file with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/")
|
||||
def read_root():
|
||||
return {"Hello": "World"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Open the browser and call the endpoint `/`.
|
||||
4. It returns a JSON with `{"Hello": "World"}`.
|
||||
5. But I expected it to return `{"Hello": "Sara"}`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Expected behavior
|
||||
|
||||
Add a clear and concise description of what you expected to happen.
|
||||
|
||||
### Screenshots
|
||||
|
||||
If applicable, add screenshots to help explain your problem.
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment
|
||||
|
||||
- OS: [e.g. Linux / Windows / macOS]
|
||||
- FastAPI Version [e.g. 0.3.0], get it with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "import fastapi; print(fastapi.__version__)"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Python version, get it with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python --version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Additional context
|
||||
|
||||
Add any other context about the problem here.
|
||||
92
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature_request.md
vendored
@@ -1,26 +1,104 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
name: Feature request
|
||||
about: Suggest an idea for this project
|
||||
title: "[FEATURE]"
|
||||
title: ""
|
||||
labels: enhancement
|
||||
assignees: ''
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### Is your feature request related to a problem
|
||||
### First check
|
||||
|
||||
Is your feature request related to a problem?
|
||||
* [ ] I added a very descriptive title to this issue.
|
||||
* [ ] I used the GitHub search to find a similar issue and didn't find it.
|
||||
* [ ] I searched the FastAPI documentation, with the integrated search.
|
||||
* [ ] I already searched in Google "How to X in FastAPI" and didn't find any information.
|
||||
* [ ] I already read and followed all the tutorial in the docs and didn't find an answer.
|
||||
* [ ] I already checked if it is not related to FastAPI but to [Pydantic](https://github.com/samuelcolvin/pydantic).
|
||||
* [ ] I already checked if it is not related to FastAPI but to [Swagger UI](https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui).
|
||||
* [ ] I already checked if it is not related to FastAPI but to [ReDoc](https://github.com/Redocly/redoc).
|
||||
* [ ] After submitting this, I commit to:
|
||||
* Read open issues with questions until I find 2 issues where I can help someone and add a comment to help there.
|
||||
* Or, I already hit the "watch" button in this repository to receive notifications and I commit to help at least 2 people that ask questions in the future.
|
||||
* Implement a Pull Request for a confirmed bug.
|
||||
|
||||
Add a clear and concise description of what the problem is. Ex. I want to be able to [...] but I can't because [...]
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
|
||||
I'm asking all this because answering questions and solving problems in GitHub issues consumes a lot of time. I end up not being able to add new features, fix bugs, review Pull Requests, etc. as fast as I wish because I have to spend too much time handling issues.
|
||||
|
||||
All that, on top of all the incredible help provided by a bunch of community members that give a lot of their time to come here and help others.
|
||||
|
||||
That's a lot of work they are doing, but if more FastAPI users came to help others like them just a little bit more, it would be much less effort for them (and you and me 😅).
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
|
||||
Here's a self-contained [minimal, reproducible, example](https://stackoverflow.com/help/minimal-reproducible-example) with my use case:
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- Replace the code below with your own self-contained, minimal, reproducible, example -->
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/")
|
||||
def read_root():
|
||||
return {"Hello": "World"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Description
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- Replace the content below with your own feature request -->
|
||||
|
||||
* Open the browser and call the endpoint `/`.
|
||||
* It returns a JSON with `{"Hello": "World"}`.
|
||||
* I would like it to have an extra parameter to teleport me to the moon and back.
|
||||
|
||||
### The solution you would like
|
||||
|
||||
Add a clear and concise description of what you want to happen.
|
||||
<!-- Replace this with your own content -->
|
||||
|
||||
I would like it to have a `teleport_to_moon` parameter that defaults to `False`, and can be set to `True` to teleport me:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/", teleport_to_moon=True)
|
||||
def read_root():
|
||||
return {"Hello": "World"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Describe alternatives you've considered
|
||||
|
||||
Add a clear and concise description of any alternative solutions or features you've considered.
|
||||
<!-- Replace this with your own ideas -->
|
||||
|
||||
To wait for Space X moon travel plans to drop down long after they release them. But I would rather teleport.
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment
|
||||
|
||||
* OS: [e.g. Linux / Windows / macOS]:
|
||||
* FastAPI Version [e.g. 0.3.0]:
|
||||
|
||||
To know the FastAPI version use:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "import fastapi; print(fastapi.__version__)"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Python version:
|
||||
|
||||
To know the Python version use:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python --version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Additional context
|
||||
|
||||
Add any other context or screenshots about the feature request here.
|
||||
<!-- Add any other context or screenshots about the question here. -->
|
||||
|
||||
71
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/question.md
vendored
@@ -1,24 +1,81 @@
|
||||
---
|
||||
name: Question
|
||||
about: Ask a question
|
||||
title: "[QUESTION]"
|
||||
name: Question or Problem
|
||||
about: Ask a question or ask about a problem
|
||||
title: ""
|
||||
labels: question
|
||||
assignees: ''
|
||||
assignees: ""
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
### First check
|
||||
|
||||
* [ ] I added a very descriptive title to this issue.
|
||||
* [ ] I used the GitHub search to find a similar issue and didn't find it.
|
||||
* [ ] I searched the FastAPI documentation, with the integrated search.
|
||||
* [ ] I already searched in Google "How to X in FastAPI" and didn't find any information.
|
||||
* [ ] I already read and followed all the tutorial in the docs and didn't find an answer.
|
||||
* [ ] I already checked if it is not related to FastAPI but to [Pydantic](https://github.com/samuelcolvin/pydantic).
|
||||
* [ ] I already checked if it is not related to FastAPI but to [Swagger UI](https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui).
|
||||
* [ ] I already checked if it is not related to FastAPI but to [ReDoc](https://github.com/Redocly/redoc).
|
||||
* [ ] After submitting this, I commit to one of:
|
||||
* Read open issues with questions until I find 2 issues where I can help someone and add a comment to help there.
|
||||
* I already hit the "watch" button in this repository to receive notifications and I commit to help at least 2 people that ask questions in the future.
|
||||
* Implement a Pull Request for a confirmed bug.
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
|
||||
I'm asking all this because answering questions and solving problems in GitHub issues consumes a lot of time. I end up not being able to add new features, fix bugs, review Pull Requests, etc. as fast as I wish because I have to spend too much time handling issues.
|
||||
|
||||
All that, on top of all the incredible help provided by a bunch of community members that give a lot of their time to come here and help others.
|
||||
|
||||
That's a lot of work they are doing, but if more FastAPI users came to help others like them just a little bit more, it would be much less effort for them (and you and me 😅).
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
### Example
|
||||
|
||||
Here's a self-contained, [minimal, reproducible, example](https://stackoverflow.com/help/minimal-reproducible-example) with my use case:
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- Replace the code below with your own self-contained, minimal, reproducible, example, if I (or someone) can copy it, run it, and see it right away, there's a much higher chance I (or someone) will be able to help you -->
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/")
|
||||
def read_root():
|
||||
return {"Hello": "World"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Description
|
||||
|
||||
How can I [...]?
|
||||
<!-- Replace the content below with your own problem, question, or error -->
|
||||
|
||||
Is it possible to [...]?
|
||||
* Open the browser and call the endpoint `/`.
|
||||
* It returns a JSON with `{"Hello": "World"}`.
|
||||
* But I expected it to return `{"Hello": "Sara"}`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment
|
||||
|
||||
* OS: [e.g. Linux / Windows / macOS]:
|
||||
* FastAPI Version [e.g. 0.3.0]:
|
||||
|
||||
To know the FastAPI version use:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "import fastapi; print(fastapi.__version__)"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Python version:
|
||||
|
||||
To know the Python version use:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python --version
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Additional context
|
||||
|
||||
Add any other context or screenshots about the feature request here.
|
||||
<!-- Add any other context or screenshots about the question here. -->
|
||||
|
||||
7
.github/actions/get-artifact/Dockerfile
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.7
|
||||
|
||||
RUN pip install httpx "pydantic==1.5.1"
|
||||
|
||||
COPY ./app /app
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["python", "/app/main.py"]
|
||||
16
.github/actions/get-artifact/action.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
name: "Get Artifact"
|
||||
description: "Get artifact, possibly uploaded by a PR, useful to deploy docs previews"
|
||||
author: "Sebastián Ramírez <tiangolo@gmail.com>"
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
token:
|
||||
description: 'Token for the repo. Can be passed in using {{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
name:
|
||||
description: 'Artifact name'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
path:
|
||||
description: 'Where to store the artifact'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
runs:
|
||||
using: 'docker'
|
||||
image: 'Dockerfile'
|
||||
63
.github/actions/get-artifact/app/main.py
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
from datetime import datetime
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from typing import List, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
import httpx
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel, BaseSettings, SecretStr
|
||||
|
||||
github_api = "https://api.github.com"
|
||||
netlify_api = "https://api.netlify.com"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Settings(BaseSettings):
|
||||
input_name: str
|
||||
input_token: SecretStr
|
||||
input_path: str
|
||||
github_repository: str
|
||||
github_event_path: Path
|
||||
github_event_name: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Artifact(BaseModel):
|
||||
id: int
|
||||
node_id: str
|
||||
name: str
|
||||
size_in_bytes: int
|
||||
url: str
|
||||
archive_download_url: str
|
||||
expired: bool
|
||||
created_at: datetime
|
||||
updated_at: datetime
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ArtifactResponse(BaseModel):
|
||||
total_count: int
|
||||
artifacts: List[Artifact]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
|
||||
settings = Settings()
|
||||
logging.info(f"Using config: {settings.json()}")
|
||||
github_headers = {
|
||||
"Authorization": f"token {settings.input_token.get_secret_value()}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
response = httpx.get(
|
||||
f"{github_api}/repos/{settings.github_repository}/actions/artifacts",
|
||||
headers=github_headers,
|
||||
)
|
||||
data = response.json()
|
||||
artifacts_response = ArtifactResponse.parse_obj(data)
|
||||
use_artifact: Optional[Artifact] = None
|
||||
for artifact in artifacts_response.artifacts:
|
||||
if artifact.name == settings.input_name:
|
||||
use_artifact = artifact
|
||||
break
|
||||
assert use_artifact
|
||||
file_response = httpx.get(
|
||||
use_artifact.archive_download_url, headers=github_headers, timeout=30
|
||||
)
|
||||
zip_file = Path(settings.input_path)
|
||||
zip_file.write_bytes(file_response.content)
|
||||
logging.info("Finished")
|
||||
7
.github/actions/watch-previews/Dockerfile
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.7
|
||||
|
||||
RUN pip install httpx PyGithub "pydantic==1.5.1"
|
||||
|
||||
COPY ./app /app
|
||||
|
||||
CMD ["python", "/app/main.py"]
|
||||
10
.github/actions/watch-previews/action.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
name: "Watch docs previews in PRs"
|
||||
description: "Check PRs and trigger new docs deploys"
|
||||
author: "Sebastián Ramírez <tiangolo@gmail.com>"
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
token:
|
||||
description: 'Token for the repo. Can be passed in using {{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
runs:
|
||||
using: 'docker'
|
||||
image: 'Dockerfile'
|
||||
101
.github/actions/watch-previews/app/main.py
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
from datetime import datetime
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from typing import List, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
import httpx
|
||||
from github import Github
|
||||
from github.NamedUser import NamedUser
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel, BaseSettings, SecretStr
|
||||
|
||||
github_api = "https://api.github.com"
|
||||
netlify_api = "https://api.netlify.com"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Settings(BaseSettings):
|
||||
input_token: SecretStr
|
||||
github_repository: str
|
||||
github_event_path: Path
|
||||
github_event_name: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Artifact(BaseModel):
|
||||
id: int
|
||||
node_id: str
|
||||
name: str
|
||||
size_in_bytes: int
|
||||
url: str
|
||||
archive_download_url: str
|
||||
expired: bool
|
||||
created_at: datetime
|
||||
updated_at: datetime
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ArtifactResponse(BaseModel):
|
||||
total_count: int
|
||||
artifacts: List[Artifact]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_message(commit: str) -> str:
|
||||
return f"Docs preview for commit {commit} at"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
|
||||
settings = Settings()
|
||||
logging.info(f"Using config: {settings.json()}")
|
||||
g = Github(settings.input_token.get_secret_value())
|
||||
repo = g.get_repo(settings.github_repository)
|
||||
owner: NamedUser = repo.owner
|
||||
headers = {"Authorization": f"token {settings.input_token.get_secret_value()}"}
|
||||
prs = list(repo.get_pulls(state="open"))
|
||||
response = httpx.get(
|
||||
f"{github_api}/repos/{settings.github_repository}/actions/artifacts",
|
||||
headers=headers,
|
||||
)
|
||||
data = response.json()
|
||||
artifacts_response = ArtifactResponse.parse_obj(data)
|
||||
for pr in prs:
|
||||
logging.info("-----")
|
||||
logging.info(f"Processing PR #{pr.number}: {pr.title}")
|
||||
pr_comments = list(pr.get_issue_comments())
|
||||
pr_commits = list(pr.get_commits())
|
||||
last_commit = pr_commits[0]
|
||||
for pr_commit in pr_commits:
|
||||
if pr_commit.commit.author.date > last_commit.commit.author.date:
|
||||
last_commit = pr_commit
|
||||
commit = last_commit.commit.sha
|
||||
logging.info(f"Last commit: {commit}")
|
||||
message = get_message(commit)
|
||||
notified = False
|
||||
for pr_comment in pr_comments:
|
||||
if message in pr_comment.body:
|
||||
notified = True
|
||||
logging.info(f"Docs preview was notified: {notified}")
|
||||
if not notified:
|
||||
artifact_name = f"docs-zip-{commit}"
|
||||
use_artifact: Optional[Artifact] = None
|
||||
for artifact in artifacts_response.artifacts:
|
||||
if artifact.name == artifact_name:
|
||||
use_artifact = artifact
|
||||
break
|
||||
if not use_artifact:
|
||||
logging.info("Artifact not available")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
logging.info(f"Existing artifact: {use_artifact.name}")
|
||||
response = httpx.post(
|
||||
"https://api.github.com/repos/tiangolo/fastapi/actions/workflows/preview-docs.yml/dispatches",
|
||||
headers=headers,
|
||||
json={
|
||||
"ref": "master",
|
||||
"inputs": {
|
||||
"pr": f"{pr.number}",
|
||||
"name": artifact_name,
|
||||
"commit": commit,
|
||||
},
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
logging.info(
|
||||
f"Trigger sent, response status: {response.status_code} - content: {response.content}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
logging.info("Finished")
|
||||
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
name: Build and Deploy to Netlify
|
||||
name: Build Docs
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
@@ -7,6 +7,10 @@ jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-18.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Dump GitHub context
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GITHUB_CONTEXT: ${{ toJson(github) }}
|
||||
run: echo "$GITHUB_CONTEXT"
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v1
|
||||
@@ -18,8 +22,16 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: python3.7 -m flit install --extras doc
|
||||
- name: Build Docs
|
||||
run: python3.7 ./scripts/docs.py build-all
|
||||
- name: Zip docs
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'pull_request'
|
||||
run: bash ./scripts/zip-docs.sh
|
||||
- uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'pull_request'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: docs-zip-${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}
|
||||
path: ./docs.zip
|
||||
- name: Deploy to Netlify
|
||||
uses: nwtgck/actions-netlify@v1.0.3
|
||||
uses: nwtgck/actions-netlify@v1.1.5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
publish-dir: './site'
|
||||
production-branch: master
|
||||
@@ -1,15 +1,24 @@
|
||||
name: Issue Manager
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 0 * * *"
|
||||
- cron: "0 0 * * *"
|
||||
issue_comment:
|
||||
types:
|
||||
- created
|
||||
- edited
|
||||
issues:
|
||||
types:
|
||||
- labeled
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
issue-manager:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: tiangolo/issue-manager@master
|
||||
with:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
config: >
|
||||
- uses: tiangolo/issue-manager@0.2.0
|
||||
with:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
config: >
|
||||
{
|
||||
"answered": {
|
||||
"users": ["tiangolo", "dmontagu"],
|
||||
14
.github/workflows/pr-approvals.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
name: Label approved pull requests
|
||||
on: pull_request_review
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
labelWhenApproved:
|
||||
name: Label when approved
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Label when approved
|
||||
uses: pullreminders/label-when-approved-action@v1.0.7
|
||||
env:
|
||||
APPROVALS: "2"
|
||||
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
ADD_LABEL: "approved-2"
|
||||
REMOVE_LABEL: "awaiting%20review"
|
||||
43
.github/workflows/preview-docs.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
name: Preview Docs
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
pr:
|
||||
description: Pull Request number
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
name:
|
||||
description: Artifact name for zip file with docs
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
commit:
|
||||
description: Commit SHA hash
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
deploy:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-18.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
- uses: ./.github/actions/get-artifact
|
||||
with:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
name: ${{ github.event.inputs.name }}
|
||||
path: ./archive.zip
|
||||
- name: Unzip docs
|
||||
run: bash ./scripts/unzip-docs.sh
|
||||
- name: Deploy to Netlify
|
||||
id: netlify
|
||||
uses: nwtgck/actions-netlify@v1.1.5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
publish-dir: './site'
|
||||
production-deploy: false
|
||||
github-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
NETLIFY_AUTH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.NETLIFY_AUTH_TOKEN }}
|
||||
NETLIFY_SITE_ID: ${{ secrets.NETLIFY_SITE_ID }}
|
||||
- name: Comment Deploy
|
||||
env:
|
||||
PR: "${{ github.event.inputs.pr }}"
|
||||
DEPLOY_URL: "${{ steps.netlify.outputs.deploy-url }}"
|
||||
GITHUB_TOKEN: "${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}"
|
||||
COMMIT: "${{ github.event.inputs.commit }}"
|
||||
run: bash ./scripts/docs-comment-deploy.sh
|
||||
39
.github/workflows/publish.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
name: Publish
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
release:
|
||||
types:
|
||||
- created
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
publish:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Dump GitHub context
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GITHUB_CONTEXT: ${{ toJson(github) }}
|
||||
run: echo "$GITHUB_CONTEXT"
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.6"
|
||||
- name: Install Flit
|
||||
run: pip install flit
|
||||
- name: Install Dependencies
|
||||
run: flit install --symlink
|
||||
- name: Publish
|
||||
env:
|
||||
FLIT_USERNAME: ${{ secrets.FLIT_USERNAME }}
|
||||
FLIT_PASSWORD: ${{ secrets.FLIT_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
run: bash scripts/publish.sh
|
||||
- name: Dump GitHub context
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GITHUB_CONTEXT: ${{ toJson(github) }}
|
||||
run: echo "$GITHUB_CONTEXT"
|
||||
- name: Notify
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GITTER_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITTER_TOKEN }}
|
||||
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TAG: ${{ github.ref }}
|
||||
run: bash scripts/notify.sh
|
||||
29
.github/workflows/test.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
name: Test
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
types: [opened, synchronize]
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
test:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
python-version: [3.6, 3.7, 3.8]
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
- name: Install Flit
|
||||
run: pip install flit
|
||||
- name: Install Dependencies
|
||||
run: flit install --symlink
|
||||
- name: Test
|
||||
run: bash scripts/test.sh
|
||||
- name: Upload coverage
|
||||
uses: codecov/codecov-action@v1
|
||||
13
.github/workflows/watch-docs-previews.yml
vendored
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
name: Watch Docs Previews
|
||||
on:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 * * * *"
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
deploy:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-18.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
- uses: ./.github/actions/watch-previews
|
||||
with:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.ACTIONS_TOKEN }}
|
||||
8
.gitignore
vendored
@@ -14,4 +14,12 @@ test.db
|
||||
log.txt
|
||||
Pipfile.lock
|
||||
env3.*
|
||||
env
|
||||
docs_build
|
||||
venv
|
||||
docs.zip
|
||||
archive.zip
|
||||
|
||||
# vim temporary files
|
||||
*~
|
||||
.*.sw?
|
||||
|
||||
32
.travis.yml
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
|
||||
dist: xenial
|
||||
|
||||
language: python
|
||||
|
||||
cache: pip
|
||||
|
||||
python:
|
||||
- "3.6"
|
||||
- "3.7"
|
||||
- "3.8"
|
||||
- "nightly"
|
||||
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
allow_failures:
|
||||
- python: "nightly"
|
||||
|
||||
install:
|
||||
- pip install flit
|
||||
- flit install --symlink
|
||||
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- bash scripts/test.sh
|
||||
|
||||
after_script:
|
||||
- bash <(curl -s https://codecov.io/bash)
|
||||
|
||||
deploy:
|
||||
provider: script
|
||||
script: bash scripts/deploy.sh
|
||||
on:
|
||||
tags: true
|
||||
python: "3.6"
|
||||
66
README.md
@@ -5,14 +5,14 @@
|
||||
<em>FastAPI framework, high performance, easy to learn, fast to code, ready for production</em>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://travis-ci.com/tiangolo/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://travis-ci.com/tiangolo/fastapi.svg?branch=master" alt="Build Status">
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/actions?query=workflow%3ATest" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/workflows/Test/badge.svg" alt="Test">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://codecov.io/gh/tiangolo/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://img.shields.io/codecov/c/github/tiangolo/fastapi" alt="Coverage">
|
||||
<img src="https://img.shields.io/codecov/c/github/tiangolo/fastapi?color=%2334D058" alt="Coverage">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pypi.org/project/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://badge.fury.io/py/fastapi.svg" alt="Package version">
|
||||
<img src="https://img.shields.io/pypi/v/fastapi?color=%2334D058&label=pypi%20package" alt="Package version">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://badges.gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi.svg" alt="Join the chat at https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi">
|
||||
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ The key features are:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Fast**: Very high performance, on par with **NodeJS** and **Go** (thanks to Starlette and Pydantic). [One of the fastest Python frameworks available](#performance).
|
||||
|
||||
* **Fast to code**: Increase the speed to develop features by about 200% to 300% *.
|
||||
* **Fast to code**: Increase the speed to develop features by about 200% to 300%. *
|
||||
* **Fewer bugs**: Reduce about 40% of human (developer) induced errors. *
|
||||
* **Intuitive**: Great editor support. <abbr title="also known as auto-complete, autocompletion, IntelliSense">Completion</abbr> everywhere. Less time debugging.
|
||||
* **Easy**: Designed to be easy to use and learn. Less time reading docs.
|
||||
@@ -45,38 +45,44 @@ The key features are:
|
||||
|
||||
## Opinions
|
||||
|
||||
"*[...] I'm using **FastAPI** a ton these days. [...] I'm actually planning to use it for all of my team's **ML services at Microsoft**. Some of them are getting integrated into the core **Windows** product and some **Office** products.*"
|
||||
"_[...] I'm using **FastAPI** a ton these days. [...] I'm actually planning to use it for all of my team's **ML services at Microsoft**. Some of them are getting integrated into the core **Windows** product and some **Office** products._"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Kabir Khan - <strong>Microsoft</strong> <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/26" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*I’m over the moon excited about **FastAPI**. It’s so fun!*"
|
||||
"_We adopted the **FastAPI** library to spawn a **REST** server that can be queried to obtain **predictions**. [for Ludwig]_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Piero Molino, Yaroslav Dudin, and Sai Sumanth Miryala - <strong>Uber</strong> <a href="https://eng.uber.com/ludwig-v0-2/" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"_**Netflix** is pleased to announce the open-source release of our **crisis management** orchestration framework: **Dispatch**! [built with **FastAPI**]_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Kevin Glisson, Marc Vilanova, Forest Monsen - <strong>Netflix</strong> <a href="https://netflixtechblog.com/introducing-dispatch-da4b8a2a8072" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"_I’m over the moon excited about **FastAPI**. It’s so fun!_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Brian Okken - <strong><a href="https://pythonbytes.fm/episodes/show/123/time-to-right-the-py-wrongs?time_in_sec=855" target="_blank">Python Bytes</a> podcast host</strong> <a href="https://twitter.com/brianokken/status/1112220079972728832" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*Honestly, what you've built looks super solid and polished. In many ways, it's what I wanted **Hug** to be - it's really inspiring to see someone build that.*"
|
||||
"_Honestly, what you've built looks super solid and polished. In many ways, it's what I wanted **Hug** to be - it's really inspiring to see someone build that._"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Timothy Crosley - <strong><a href="http://www.hug.rest/" target="_blank">Hug</a> creator</strong> <a href="https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=19455465" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*If you're looking to learn one **modern framework** for building REST APIs, check out **FastAPI** [...] It's fast, easy to use and easy to learn [...]*"
|
||||
"_If you're looking to learn one **modern framework** for building REST APIs, check out **FastAPI** [...] It's fast, easy to use and easy to learn [...]_"
|
||||
|
||||
"*We've switched over to **FastAPI** for our **APIs** [...] I think you'll like it [...]*"
|
||||
"_We've switched over to **FastAPI** for our **APIs** [...] I think you'll like it [...]_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Ines Montani - Matthew Honnibal - <strong><a href="https://explosion.ai" target="_blank">Explosion AI</a> founders - <a href="https://spacy.io" target="_blank">spaCy</a> creators</strong> <a href="https://twitter.com/_inesmontani/status/1144173225322143744" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a> - <a href="https://twitter.com/honnibal/status/1144031421859655680" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*We adopted the **FastAPI** library to spawn a **REST** server that can be queried to obtain **predictions**. [for Ludwig]*"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Piero Molino, Yaroslav Dudin, and Sai Sumanth Miryala - <strong>Uber</strong> <a href="https://eng.uber.com/ludwig-v0-2/" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## **Typer**, the FastAPI of CLIs
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com" target="_blank"><img src="https://typer.tiangolo.com/img/logo-margin/logo-margin-vector.svg" style="width: 20%;"></a>
|
||||
@@ -125,6 +131,8 @@ $ pip install uvicorn
|
||||
* Create a file `main.py` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
@@ -136,7 +144,7 @@ def read_root():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -145,7 +153,9 @@ def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
|
||||
If your code uses `async` / `await`, use `async def`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7 12"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 14"
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
@@ -157,7 +167,7 @@ async def read_root():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
async def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
async def read_item(item_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -176,11 +186,11 @@ Run the server with:
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --reload
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Started reloader process [28720]
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Started server process [28722]
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Waiting for application startup.
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Application startup complete.
|
||||
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
INFO: Started reloader process [28720]
|
||||
INFO: Started server process [28722]
|
||||
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
|
||||
INFO: Application startup complete.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
@@ -235,7 +245,9 @@ Now modify the file `main.py` to receive a body from a `PUT` request.
|
||||
|
||||
Declare the body using standard Python types, thanks to Pydantic.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 7 8 9 10 23 24 25"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 9 10 11 12 25 26 27"
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -245,7 +257,7 @@ app = FastAPI()
|
||||
class Item(BaseModel):
|
||||
name: str
|
||||
price: float
|
||||
is_offer: bool = None
|
||||
is_offer: Optional[bool] = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/")
|
||||
@@ -254,7 +266,7 @@ def read_root():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
222
docs/en/data/external_links.yml
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,222 @@
|
||||
articles:
|
||||
english:
|
||||
- link: https://medium.com/@williamhayes/fastapi-starlette-debug-vs-prod-5f7561db3a59
|
||||
title: FastAPI/Starlette debug vs prod
|
||||
author_link: https://medium.com/@williamhayes
|
||||
author: William Hayes
|
||||
- link: https://medium.com/data-rebels/fastapi-google-as-an-external-authentication-provider-3a527672cf33
|
||||
title: FastAPI — Google as an external authentication provider
|
||||
author_link: https://medium.com/@nilsdebruin
|
||||
author: Nils de Bruin
|
||||
- link: https://medium.com/data-rebels/fastapi-how-to-add-basic-and-cookie-authentication-a45c85ef47d3
|
||||
title: FastAPI — How to add basic and cookie authentication
|
||||
author_link: https://medium.com/@nilsdebruin
|
||||
author: Nils de Bruin
|
||||
- link: https://dev.to/errietta/introduction-to-the-fastapi-python-framework-2n10
|
||||
title: Introduction to the fastapi python framework
|
||||
author_link: https://dev.to/errietta
|
||||
author: Errieta Kostala
|
||||
- link: http://nickc1.github.io/api,/scikit-learn/2019/01/10/scikit-fastapi.html
|
||||
title: "FastAPI and Scikit-Learn: Easily Deploy Models"
|
||||
author_link: http://nickc1.github.io/
|
||||
author: Nick Cortale
|
||||
- link: https://medium.com/data-rebels/fastapi-authentication-revisited-enabling-api-key-authentication-122dc5975680
|
||||
title: "FastAPI authentication revisited: Enabling API key authentication"
|
||||
author_link: https://medium.com/@nilsdebruin
|
||||
author: Nils de Bruin
|
||||
- link: https://medium.com/@nico.axtmann95/deploying-a-scikit-learn-model-with-onnx-und-fastapi-1af398268915
|
||||
title: Deploying a scikit-learn model with ONNX and FastAPI
|
||||
author_link: https://www.linkedin.com/in/nico-axtmann
|
||||
author: Nico Axtmann
|
||||
- link: https://geekflare.com/python-asynchronous-web-frameworks/
|
||||
title: Top 5 Asynchronous Web Frameworks for Python
|
||||
author_link: https://geekflare.com/author/ankush/
|
||||
author: Ankush Thakur
|
||||
- link: https://medium.com/@gntrm/jwt-authentication-with-fastapi-and-aws-cognito-1333f7f2729e
|
||||
title: JWT Authentication with FastAPI and AWS Cognito
|
||||
author_link: https://twitter.com/gntrm
|
||||
author: Johannes Gontrum
|
||||
- link: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-deploy-a-machine-learning-model-dc51200fe8cf
|
||||
title: How to Deploy a Machine Learning Model
|
||||
author_link: https://www.linkedin.com/in/mgrootendorst/
|
||||
author: Maarten Grootendorst
|
||||
- link: https://eng.uber.com/ludwig-v0-2/
|
||||
title: "Uber: Ludwig v0.2 Adds New Features and Other Improvements to its Deep Learning Toolbox [including a FastAPI server]"
|
||||
author_link: https://eng.uber.com
|
||||
author: Uber Engineering
|
||||
- link: https://gitlab.com/euri10/fastapi_cheatsheet
|
||||
title: A FastAPI and Swagger UI visual cheatsheet
|
||||
author_link: https://gitlab.com/euri10
|
||||
author: "@euri10"
|
||||
- link: https://medium.com/@mike.p.moritz/using-docker-compose-to-deploy-a-lightweight-python-rest-api-with-a-job-queue-37e6072a209b
|
||||
title: Using Docker Compose to deploy a lightweight Python REST API with a job queue
|
||||
author_link: https://medium.com/@mike.p.moritz
|
||||
author: Mike Moritz
|
||||
- link: https://robwagner.dev/tortoise-fastapi-setup/
|
||||
title: Setting up Tortoise ORM with FastAPI
|
||||
author_link: https://robwagner.dev/
|
||||
author: Rob Wagner
|
||||
- link: https://dev.to/dbanty/why-i-m-leaving-flask-3ki6
|
||||
title: Why I'm Leaving Flask
|
||||
author_link: https://dev.to/dbanty
|
||||
author: Dylan Anthony
|
||||
- link: https://medium.com/python-data/how-to-deploy-tensorflow-2-0-models-as-an-api-service-with-fastapi-docker-128b177e81f3
|
||||
title: How To Deploy Tensorflow 2.0 Models As An API Service With FastAPI & Docker
|
||||
author_link: https://medium.com/@bbrenyah
|
||||
author: Bernard Brenyah
|
||||
- link: https://testdriven.io/blog/fastapi-crud/
|
||||
title: "TestDriven.io: Developing and Testing an Asynchronous API with FastAPI and Pytest"
|
||||
author_link: https://testdriven.io/authors/herman
|
||||
author: Michael Herman
|
||||
- link: https://towardsdatascience.com/deploying-iris-classifications-with-fastapi-and-docker-7c9b83fdec3a
|
||||
title: "Towards Data Science: Deploying Iris Classifications with FastAPI and Docker"
|
||||
author_link: https://towardsdatascience.com/@mandygu
|
||||
author: Mandy Gu
|
||||
- link: https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/deploy-machine-learning-models-with-keras-fastapi-redis-and-docker-4940df614ece
|
||||
title: Deploy Machine Learning Models with Keras, FastAPI, Redis and Docker
|
||||
author_link: https://medium.com/@shane.soh
|
||||
author: Shane Soh
|
||||
- link: https://medium.com/@arthur393/another-boilerplate-to-fastapi-azure-pipeline-ci-pytest-3c8d9a4be0bb
|
||||
title: "Another Boilerplate to FastAPI: Azure Pipeline CI + Pytest"
|
||||
author_link: https://twitter.com/arthurheinrique
|
||||
author: Arthur Henrique
|
||||
- link: https://iwpnd.pw/articles/2020-01/deploy-fastapi-to-aws-lambda
|
||||
title: How to continuously deploy a FastAPI to AWS Lambda with AWS SAM
|
||||
author_link: https://iwpnd.pw
|
||||
author: Benjamin Ramser
|
||||
- link: https://www.tutlinks.com/create-and-deploy-fastapi-app-to-heroku/
|
||||
title: Create and Deploy FastAPI app to Heroku without using Docker
|
||||
author_link: https://www.linkedin.com/in/navule/
|
||||
author: Navule Pavan Kumar Rao
|
||||
- link: https://iwpnd.pw/articles/2020-03/apache-kafka-fastapi-geostream
|
||||
title: Apache Kafka producer and consumer with FastAPI and aiokafka
|
||||
author_link: https://iwpnd.pw
|
||||
author: Benjamin Ramser
|
||||
- link: https://wuilly.com/2019/10/real-time-notifications-with-python-and-postgres/
|
||||
title: Real-time Notifications with Python and Postgres
|
||||
author_link: https://wuilly.com/
|
||||
author: Guillermo Cruz
|
||||
- link: https://dev.to/paurakhsharma/microservice-in-python-using-fastapi-24cc
|
||||
title: Microservice in Python using FastAPI
|
||||
author_link: https://twitter.com/PaurakhSharma
|
||||
author: Paurakh Sharma Humagain
|
||||
- link: https://dev.to/cuongld2/build-simple-api-service-with-python-fastapi-part-1-581o
|
||||
title: Build simple API service with Python FastAPI — Part 1
|
||||
author_link: https://dev.to/cuongld2
|
||||
author: cuongld2
|
||||
- link: https://paulsec.github.io/posts/fastapi_plus_zeit_serverless_fu/
|
||||
title: FastAPI + Zeit.co = 🚀
|
||||
author_link: https://twitter.com/PaulWebSec
|
||||
author: Paul Sec
|
||||
- link: https://dev.to/tiangolo/build-a-web-api-from-scratch-with-fastapi-the-workshop-2ehe
|
||||
title: Build a web API from scratch with FastAPI - the workshop
|
||||
author_link: https://twitter.com/tiangolo
|
||||
author: Sebastián Ramírez (tiangolo)
|
||||
- link: https://www.twilio.com/blog/build-secure-twilio-webhook-python-fastapi
|
||||
title: Build a Secure Twilio Webhook with Python and FastAPI
|
||||
author_link: https://www.twilio.com
|
||||
author: Twilio
|
||||
- link: https://www.stavros.io/posts/fastapi-with-django/
|
||||
title: Using FastAPI with Django
|
||||
author_link: https://twitter.com/Stavros
|
||||
author: Stavros Korokithakis
|
||||
- link: https://netflixtechblog.com/introducing-dispatch-da4b8a2a8072
|
||||
title: Introducing Dispatch
|
||||
author_link: https://netflixtechblog.com/
|
||||
author: Netflix
|
||||
- link: https://davidefiocco.github.io/2020/06/27/streamlit-fastapi-ml-serving.html
|
||||
title: Machine learning model serving in Python using FastAPI and streamlit
|
||||
author_link: https://github.com/davidefiocco
|
||||
author: Davide Fiocco
|
||||
japanese:
|
||||
- link: https://qiita.com/mtitg/items/47770e9a562dd150631d
|
||||
title: FastAPI|DB接続してCRUDするPython製APIサーバーを構築
|
||||
author_link: https://qiita.com/mtitg
|
||||
author: "@mtitg"
|
||||
- link: https://qiita.com/ryoryomaru/items/59958ed385b3571d50de
|
||||
title: python製の最新APIフレームワーク FastAPI を触ってみた
|
||||
author_link: https://qiita.com/ryoryomaru
|
||||
author: "@ryoryomaru"
|
||||
- link: https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku/items/0e1f5dbbe62efc612a78
|
||||
title: FastAPIでCORSを回避
|
||||
author_link: https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku
|
||||
author: "@angel_katayoku"
|
||||
- link: https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku/items/4fbc1a4e2b33fa2237d2
|
||||
title: FastAPIをMySQLと接続してDockerで管理してみる
|
||||
author_link: https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku
|
||||
author: "@angel_katayoku"
|
||||
- link: https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku/items/8a458a8952f50b73f420
|
||||
title: FastAPIでPOSTされたJSONのレスポンスbodyを受け取る
|
||||
author_link: https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku
|
||||
author: "@angel_katayoku"
|
||||
- link: https://qiita.com/hikarut/items/b178af2e2440c67c6ac4
|
||||
title: フロントエンド開発者向けのDockerによるPython開発環境構築
|
||||
author_link: https://qiita.com/hikarut
|
||||
author: Hikaru Takahashi
|
||||
- link: https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-environment
|
||||
title: "【第1回】FastAPIチュートリアル: ToDoアプリを作ってみよう【環境構築編】"
|
||||
author_link: https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun
|
||||
author: ライトコードメディア編集部
|
||||
- link: https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-model-building
|
||||
title: "【第2回】FastAPIチュートリアル: ToDoアプリを作ってみよう【モデル構築編】"
|
||||
author_link: https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun
|
||||
author: ライトコードメディア編集部
|
||||
- link: https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-authentication-user-registration
|
||||
title: "【第3回】FastAPIチュートリアル: toDoアプリを作ってみよう【認証・ユーザ登録編】"
|
||||
author_link: https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun
|
||||
author: ライトコードメディア編集部
|
||||
- link: https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-admin-page-improvement
|
||||
title: "【第4回】FastAPIチュートリアル: toDoアプリを作ってみよう【管理者ページ改良編】"
|
||||
author_link: https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun
|
||||
author: ライトコードメディア編集部
|
||||
- link: https://qiita.com/bee2/items/0ad260ab9835a2087dae
|
||||
title: PythonのWeb frameworkのパフォーマンス比較 (Django, Flask, responder, FastAPI, japronto)
|
||||
author_link: https://qiita.com/bee2
|
||||
author: "@bee2"
|
||||
- link: https://qiita.com/bee2/items/75d9c0d7ba20e7a4a0e9
|
||||
title: "[FastAPI] Python製のASGI Web フレームワーク FastAPIに入門する"
|
||||
author_link: https://qiita.com/bee2
|
||||
author: "@bee2"
|
||||
vietnamese:
|
||||
- link: https://fullstackstation.com/fastapi-trien-khai-bang-docker/
|
||||
title: "FASTAPI: TRIỂN KHAI BẰNG DOCKER"
|
||||
author_link: https://fullstackstation.com/author/figonking/
|
||||
author: Nguyễn Nhân
|
||||
russian:
|
||||
- link: https://habr.com/ru/post/454440/
|
||||
title: "Мелкая питонячая радость #2: Starlette - Солидная примочка – FastAPI"
|
||||
author_link: https://habr.com/ru/users/57uff3r/
|
||||
author: Andrey Korchak
|
||||
- link: https://habr.com/ru/post/478620/
|
||||
title: Почему Вы должны попробовать FastAPI?
|
||||
author_link: https://github.com/prostomarkeloff
|
||||
author: prostomarkeloff
|
||||
german:
|
||||
- link: https://blog.codecentric.de/2019/08/inbetriebnahme-eines-scikit-learn-modells-mit-onnx-und-fastapi/
|
||||
title: Inbetriebnahme eines scikit-learn-Modells mit ONNX und FastAPI
|
||||
author_link: https://twitter.com/_nicoax
|
||||
author: Nico Axtmann
|
||||
podcasts:
|
||||
english:
|
||||
- link: https://pythonbytes.fm/episodes/show/123/time-to-right-the-py-wrongs?time_in_sec=855
|
||||
title: FastAPI on PythonBytes
|
||||
author_link: https://pythonbytes.fm/
|
||||
author: Python Bytes FM
|
||||
- link: https://www.pythonpodcast.com/fastapi-web-application-framework-episode-259/
|
||||
title: "Build The Next Generation Of Python Web Applications With FastAPI - Episode 259 - interview to Sebastían Ramírez (tiangolo)"
|
||||
author_link: https://www.pythonpodcast.com/
|
||||
author: Podcast.`__init__`
|
||||
talks:
|
||||
english:
|
||||
- link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3DLwPcrE5mA
|
||||
title: "PyCon UK 2019: FastAPI from the ground up"
|
||||
author_link: https://twitter.com/chriswithers13
|
||||
author: Chris Withers
|
||||
- link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z9K5pwb0rt8
|
||||
title: "PyConBY 2020: Serve ML models easily with FastAPI"
|
||||
author_link: https://twitter.com/tiangolo
|
||||
author: "Sebastián Ramírez (tiangolo)"
|
||||
- link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PnpTY1f4k2U
|
||||
title: "[VIRTUAL] Py.Amsterdam's flying Software Circus: Intro to FastAPI"
|
||||
author_link: https://twitter.com/tiangolo
|
||||
author: "Sebastián Ramírez (tiangolo)"
|
||||
@@ -168,7 +168,7 @@ You can use this same `responses` parameter to add different media types for the
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can add an additional media type of `image/png`, declaring that your *path operation* can return a JSON object (with media type `application/json`) or a PNG image:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 28"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="19 20 21 22 23 24 28"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/additional_responses/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -228,7 +228,7 @@ You can use that technique to re-use some predefined responses in your *path ope
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 12 13 14 15 24"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13 14 15 16 17 26"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/additional_responses/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ But you also want it to accept new items. And when the items didn't exist before
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve that, import `JSONResponse`, and return your content there directly, setting the `status_code` that you want:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 19"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 23"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/additional_status_codes/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
346
docs/en/docs/advanced/behind-a-proxy.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,346 @@
|
||||
# Behind a Proxy
|
||||
|
||||
In some situations, you might need to use a **proxy** server like Traefik or Nginx with a configuration that adds an extra path prefix that is not seen by your application.
|
||||
|
||||
In these cases you can use `root_path` to configure your application.
|
||||
|
||||
The `root_path` is a mechanism provided by the ASGI specification (that FastAPI is built on, through Starlette).
|
||||
|
||||
The `root_path` is used to handle these specific cases.
|
||||
|
||||
And it's also used internally when mounting sub-applications.
|
||||
|
||||
## Proxy with a stripped path prefix
|
||||
|
||||
Having a proxy with a stripped path prefix, in this case, means that you could declare a path at `/app` in your code, but then, you add a layer on top (the proxy) that would put your **FastAPI** application under a path like `/api/v1`.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the original path `/app` would actually be served at `/api/v1/app`.
|
||||
|
||||
Even though all your code is written assuming there's just `/app`.
|
||||
|
||||
And the proxy would be **"stripping"** the **path prefix** on the fly before transmitting the request to Uvicorn, keep your application convinced that it is serving at `/app`, so that you don't have to update all your code to include the prefix `/api/v1`.
|
||||
|
||||
Up to here, everything would work as normally.
|
||||
|
||||
But then, when you open the integrated docs UI (the frontend), it would expect to get the OpenAPI schema at `/openapi.json`, instead of `/api/v1/openapi.json`.
|
||||
|
||||
So, the frontend (that runs in the browser) would try to reach `/openapi.json` and wouldn't be able to get the OpenAPI schema.
|
||||
|
||||
Because we have a proxy with a path prefix of `/api/v1` for our app, the frontend needs to fetch the OpenAPI schema at `/api/v1/openapi.json`.
|
||||
|
||||
```mermaid
|
||||
graph LR
|
||||
|
||||
browser("Browser")
|
||||
proxy["Proxy on http://0.0.0.0:9999/api/v1/app"]
|
||||
server["Server on http://127.0.0.1:8000/app"]
|
||||
|
||||
browser --> proxy
|
||||
proxy --> server
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The IP `0.0.0.0` is commonly used to mean that the program listens on all the IPs available in that machine/server.
|
||||
|
||||
The docs UI would also need the OpenAPI schema to declare that this API `server` is located at `/api/v1` (behind the proxy). For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON hl_lines="4 5 6 7 8"
|
||||
{
|
||||
"openapi": "3.0.2",
|
||||
// More stuff here
|
||||
"servers": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"url": "/api/v1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"paths": {
|
||||
// More stuff here
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, the "Proxy" could be something like **Traefik**. And the server would be something like **Uvicorn**, running your FastAPI application.
|
||||
|
||||
### Providing the `root_path`
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve this, you can use the command line option `--root-path` like:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --root-path /api/v1
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
If you use Hypercorn, it also has the option `--root-path`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
The ASGI specification defines a `root_path` for this use case.
|
||||
|
||||
And the `--root-path` command line option provides that `root_path`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Checking the current `root_path`
|
||||
|
||||
You can get the current `root_path` used by your application for each request, it is part of the `scope` dictionary (that's part of the ASGI spec).
|
||||
|
||||
Here we are including it in the message just for demonstration purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/behind_a_proxy/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, if you start Uvicorn with:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --root-path /api/v1
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
The response would be something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{
|
||||
"message": "Hello World",
|
||||
"root_path": "/api/v1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Setting the `root_path` in the FastAPI app
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, if you don't have a way to provide a command line option like `--root-path` or equivalent, you can set the `root_path` parameter when creating your FastAPI app:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/behind_a_proxy/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Passing the `root_path` to `FastAPI` would be the equivalent of passing the `--root-path` command line option to Uvicorn or Hypercorn.
|
||||
|
||||
### About `root_path`
|
||||
|
||||
Have in mind that the server (Uvicorn) won't use that `root_path` for anything else than passing it to the app.
|
||||
|
||||
But if you go with your browser to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/app</a> you will see the normal response:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{
|
||||
"message": "Hello World",
|
||||
"root_path": "/api/v1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
So, it won't expect to be accessed at `http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/app`.
|
||||
|
||||
Uvicorn will expect the proxy to access Uvicorn at `http://127.0.0.1:8000/app`, and then it would be the proxy's responsibility to add the extra `/api/v1` prefix on top.
|
||||
|
||||
## About proxies with a stripped path prefix
|
||||
|
||||
Have in mind that a proxy with stripped path prefix is only one of the ways to configure it.
|
||||
|
||||
Probably in many cases the default will be that the proxy doesn't have a stripped path prefix.
|
||||
|
||||
In a case like that (without a stripped path prefix), the proxy would listen on something like `https://myawesomeapp.com`, and then if the browser goes to `https://myawesomeapp.com/api/v1/app` and your server (e.g. Uvicorn) listens on `http://127.0.0.1:8000` the proxy (without a stripped path prefix) would access Uvicorn at the same path: `http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/v1/app`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Testing locally with Traefik
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily run the experiment locally with a stripped path prefix using <a href="https://docs.traefik.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Traefik</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/containous/traefik/releases" class="external-link" target="_blank">Download Traefik</a>, it's a single binary, you can extract the compressed file and run it directly from the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
Then create a file `traefik.toml` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```TOML hl_lines="3"
|
||||
[entryPoints]
|
||||
[entryPoints.http]
|
||||
address = ":9999"
|
||||
|
||||
[providers]
|
||||
[providers.file]
|
||||
filename = "routes.toml"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This tells Traefik to listen on port 9999 and to use another file `routes.toml`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
We are using port 9999 instead of the standard HTTP port 80 so that you don't have to run it with admin (`sudo`) privileges.
|
||||
|
||||
Now create that other file `routes.toml`:
|
||||
|
||||
```TOML hl_lines="5 12 20"
|
||||
[http]
|
||||
[http.middlewares]
|
||||
|
||||
[http.middlewares.api-stripprefix.stripPrefix]
|
||||
prefixes = ["/api/v1"]
|
||||
|
||||
[http.routers]
|
||||
|
||||
[http.routers.app-http]
|
||||
entryPoints = ["http"]
|
||||
service = "app"
|
||||
rule = "PathPrefix(`/api/v1`)"
|
||||
middlewares = ["api-stripprefix"]
|
||||
|
||||
[http.services]
|
||||
|
||||
[http.services.app]
|
||||
[http.services.app.loadBalancer]
|
||||
[[http.services.app.loadBalancer.servers]]
|
||||
url = "http://127.0.0.1:8000"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This file configures Traefik to use the path prefix `/api/v1`.
|
||||
|
||||
And then it will redirect its requests to your Uvicorn running on `http://127.0.0.1:8000`.
|
||||
|
||||
Now start Traefik:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ ./traefik --configFile=traefik.toml
|
||||
|
||||
INFO[0000] Configuration loaded from file: /home/user/awesomeapi/traefik.toml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
And now start your app with Uvicorn, using the `--root-path` option:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --root-path /api/v1
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
### Check the responses
|
||||
|
||||
Now, if you go to the URL with the port for Uvicorn: <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/app" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/app</a>, you will see the normal response:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{
|
||||
"message": "Hello World",
|
||||
"root_path": "/api/v1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Notice that even though you are accessing it at `http://127.0.0.1:8000/app` it shows the `root_path` of `/api/v1`, taken from the option `--root-path`.
|
||||
|
||||
And now open the URL with the port for Traefik, including the path prefix: <a href="http://127.0.0.1:9999/api/v1/app" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:9999/api/vi/app</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
We get the same response:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{
|
||||
"message": "Hello World",
|
||||
"root_path": "/api/v1"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
but this time at the URL with the prefix path provided by the proxy: `/api/v1`.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, the idea here is that everyone would access the app through the proxy, so the version with the path prefix `/app/v1` is the "correct" one.
|
||||
|
||||
And the version without the path prefix (`http://127.0.0.1:8000/app`), provided by Uvicorn directly, would be exclusively for the _proxy_ (Traefik) to access it.
|
||||
|
||||
That demonstrates how the Proxy (Traefik) uses the path prefix and how the server (Uvicorn) uses the `root_path` from the option `--root-path`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Check the docs UI
|
||||
|
||||
But here's the fun part. ✨
|
||||
|
||||
The "official" way to access the app would be through the proxy with the path prefix that we defined. So, as we would expect, if you try the docs UI served by Uvicorn directly, without the path prefix in the URL, it won't work, because it expects to be accessed through the proxy.
|
||||
|
||||
You can check it at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/behind-a-proxy/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
But if we access the docs UI at the "official" URL using the proxy with port `9999`, at `/api/v1/docs`, it works correctly! 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
You can check it at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:9999/api/v1/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:9999/api/v1/docs</a>:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/behind-a-proxy/image02.png">
|
||||
|
||||
Right as we wanted it. ✔️
|
||||
|
||||
This is because FastAPI uses this `root_path` to create the default `server` in OpenAPI with the URL provided by `root_path`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional servers
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
This is a more advanced use case. Feel free to skip it.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, **FastAPI** will create a `server` in the OpenAPI schema with the URL for the `root_path`.
|
||||
|
||||
But you can also provide other alternative `servers`, for example if you want *the same* docs UI to interact with a staging and production environments.
|
||||
|
||||
If you pass a custom list of `servers` and there's a `root_path` (because your API lives behind a proxy), **FastAPI** will insert a "server" with this `root_path` at the beginning of the list.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 5 6 7"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/behind_a_proxy/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Will generate an OpenAPI schema like:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON hl_lines="5 6 7"
|
||||
{
|
||||
"openapi": "3.0.2",
|
||||
// More stuff here
|
||||
"servers": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"url": "/api/v1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"url": "https://stag.example.com",
|
||||
"description": "Staging environment"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"url": "https://prod.example.com",
|
||||
"description": "Production environment"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"paths": {
|
||||
// More stuff here
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Notice the auto-generated server with a `url` value of `/api/v1`, taken from the `root_path`.
|
||||
|
||||
In the docs UI at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:9999/api/v1/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:9999/api/v1/docs</a> it would look like:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/behind-a-proxy/image03.png">
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The docs UI will interact with the server that you select.
|
||||
|
||||
### Disable automatic server from `root_path`
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't want **FastAPI** to include an automatic server using the `root_path`, you can use the parameter `root_path_in_servers=False`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/behind_a_proxy/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and then it won't include it in the OpenAPI schema.
|
||||
|
||||
## Mounting a sub-application
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to mount a sub-application (as described in [Sub Applications - Mounts](./sub-applications.md){.internal-link target=_blank}) while also using a proxy with `root_path`, you can do it normally, as you would expect.
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI will internally use the `root_path` smartly, so it will just work. ✨
|
||||
58
docs/en/docs/advanced/conditional-openapi.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
# Conditional OpenAPI
|
||||
|
||||
If you needed to, you could use settings and environment variables to configure OpenAPI conditionally depending on the environment, and even disable it entirely.
|
||||
|
||||
## About security, APIs, and docs
|
||||
|
||||
Hiding your documentation user interfaces in production *shouldn't* be the way to protect your API.
|
||||
|
||||
That doesn't add any extra security to your API, the *path operations* will still be available where they are.
|
||||
|
||||
If there's a security flaw in your code, it will still exist.
|
||||
|
||||
Hiding the documentation just makes it more difficult to understand how to interact with your API, and could make it more difficult for you to debug it in production. It could be considered simply a form of <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Security_through_obscurity" class="external-link" target="_blank">Security through obscurity</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to secure your API, there are several better things you can do, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
* Make sure you have well defined Pydantic models for your request bodies and responses.
|
||||
* Configure any required permissions and roles using dependencies.
|
||||
* Never store plaintext passwords, only password hashes.
|
||||
* Implement and use well-known cryptographic tools, like Passlib and JWT tokens, etc.
|
||||
* Add more granular permission controls with OAuth2 scopes where needed.
|
||||
* ...etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Nevertheless, you might have a very specific use case where you really need to disable the API docs for some environment (e.g. for production) or depending on configurations from environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
## Conditional OpenAPI from settings and env vars
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily use the same Pydantic settings to configure your generated OpenAPI and the docs UIs.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6 11"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/conditional_openapi/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here we declare the setting `openapi_url` with the same default of `"/openapi.json"`.
|
||||
|
||||
And then we use it when creating the `FastAPI` app.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you could disable OpenAPI (including the UI docs) by setting the environment variable `OPENAPI_URL` to the empty string, like:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ OPENAPI_URL= uvicorn main:app
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Then if you go to the URLs at `/openapi.json`, `/docs`, or `/redoc` you will just get a `404 Not Found` error like:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{
|
||||
"detail": "Not Found"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -203,6 +203,21 @@ File responses will include appropriate `Content-Length`, `Last-Modified` and `E
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial009.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Default response class
|
||||
|
||||
When creating a **FastAPI** class instance or an `APIRouter` you can specify which response class to use by default.
|
||||
|
||||
The parameter that defines this is `default_response_class`.
|
||||
|
||||
In the example below, **FastAPI** will use `ORJSONResponse` by default, in all *path operations*, instead of `JSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 4"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/custom_response/tutorial010.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
You can still override `response_class` in *path operations* as before.
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional documentation
|
||||
|
||||
You can also declare the media type and many other details in OpenAPI using `responses`: [Additional Responses in OpenAPI](additional-responses.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,6 +4,9 @@ You can define event handlers (functions) that need to be executed before the ap
|
||||
|
||||
These functions can be declared with `async def` or normal `def`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
Only event handlers for the main application will be executed, not for [Sub Applications - Mounts](./sub-applications.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
## `startup` event
|
||||
|
||||
To add a function that should be run before the application starts, declare it with the event `"startup"`:
|
||||
@@ -41,4 +44,4 @@ Here, the `shutdown` event handler function will write a text line `"Application
|
||||
So, we declare the event handler function with standard `def` instead of `async def`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
You can read more about these event handlers in <a href="https://www.starlette.io/events/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette's Events' docs</a>.
|
||||
You can read more about these event handlers in <a href="https://www.starlette.io/events/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette's Events' docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,6 @@ And that function `get_openapi()` receives as parameters:
|
||||
* `openapi_version`: The version of the OpenAPI specification used. By default, the latest: `3.0.2`.
|
||||
* `description`: The description of your API.
|
||||
* `routes`: A list of routes, these are each of the registered *path operations*. They are taken from `app.routes`.
|
||||
* `openapi_prefix`: The URL prefix to be used in your OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overriding the defaults
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -52,7 +51,7 @@ First, write all your **FastAPI** application as normally:
|
||||
|
||||
Then, use the same utility function to generate the OpenAPI schema, inside a `custom_openapi()` function:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 15 16 17 18 19 20"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 15 16 17 18 19 20"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extending_openapi/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -72,7 +71,7 @@ That way, your application won't have to generate the schema every time a user o
|
||||
|
||||
It will be generated only once, and then the same cached schema will be used for the next requests.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13 14 24 25"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13 14 24 25"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extending_openapi/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ You can adapt it to any other NoSQL database like:
|
||||
|
||||
For now, don't pay attention to the rest, only the imports:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6 7 8"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 4 5"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ We will use it later as a fixed field `type` in our documents.
|
||||
|
||||
This is not required by Couchbase, but is a good practice that will help you afterwards.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ This utility function will:
|
||||
* Set defaults for timeouts.
|
||||
* Return it.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -66,7 +66,7 @@ As **Couchbase** "documents" are actually just "JSON objects", we can model them
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's create a `User` model:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="25 26 27 28 29"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="24 25 26 27 28"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ This will have the data that is actually stored in the database.
|
||||
|
||||
We don't create it as a subclass of Pydantic's `BaseModel` but as a subclass of our own `User`, because it will have all the attributes in `User` plus a couple more:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="32 33 34"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="31 32 33"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -100,7 +100,7 @@ Now create a function that will:
|
||||
|
||||
By creating a function that is only dedicated to getting your user from a `username` (or any other parameter) independent of your *path operation function*, you can more easily re-use it in multiple parts and also add <abbr title="Automated test, written in code, that checks if another piece of code is working correctly.">unit tests</abbr> for it:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="37 38 39 40 41 42 43"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="36 37 38 39 40 41 42"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -135,7 +135,7 @@ UserInDB(username="johndoe", hashed_password="some_hash")
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the `FastAPI` app
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="47"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="46"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ As our code is calling Couchbase and we are not using the <a href="https://docs.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, Couchbase recommends not using a single `Bucket` object in multiple "<abbr title="A sequence of code being executed by the program, while at the same time, or at intervals, there can be others being executed too.">thread</abbr>s", so, we can get just get the bucket directly and pass it to our utility functions:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="50 51 52 53 54"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="49 50 51 52 53"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/nosql_databases/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ It will have a *path operation* that will receive an `Invoice` body, and a query
|
||||
|
||||
This part is pretty normal, most of the code is probably already familiar to you:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8 9 10 11 12 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10 11 12 13 14 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/openapi_callbacks/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -92,7 +92,7 @@ Because of that, you need to declare what will be the `default_response_class`,
|
||||
|
||||
But as we are never calling `app.include_router(some_router)`, we need to set the `default_response_class` during creation of the `APIRouter`.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 24"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="5 26"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/openapi_callbacks/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -105,7 +105,7 @@ It should look just like a normal FastAPI *path operation*:
|
||||
* It should probably have a declaration of the body it should receive, e.g. `body: InvoiceEvent`.
|
||||
* And it could also have a declaration of the response it should return, e.g. `response_model=InvoiceEventReceived`.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="15 16 17 20 21 27 28 29 30 31"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="17 18 19 22 23 29 30 31 32 33"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/openapi_callbacks/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -172,7 +172,7 @@ At this point you have the *callback path operation(s)* needed (the one(s) that
|
||||
|
||||
Now use the parameter `callbacks` in *your API's path operation decorator* to pass the attribute `.routes` (that's actually just a `list` of routes/*path operations*) from that callback router:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="34"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="36"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/openapi_callbacks/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ For example, you cannot put a Pydantic model in a `JSONResponse` without first c
|
||||
|
||||
For those cases, you can use the `jsonable_encoder` to convert your data before passing it to a response:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 6 20 21"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6 7 21 22"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_directly/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ They are normally used to declare specific security permissions, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's quickly see the parts that change from the examples in the main **Tutorial - User Guide** for [OAuth2 with Password (and hashing), Bearer with JWT tokens](../../tutorial/security/oauth2-jwt.md){.internal-link target=_blank}. Now using OAuth2 scopes:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 5 9 13 47 65 106 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 122 123 124 125 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 140 154"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 4 8 12 46 64 105 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 121 122 123 124 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 139 153"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -68,7 +68,7 @@ The first change is that now we are declaring the OAuth2 security scheme with tw
|
||||
|
||||
The `scopes` parameter receives a `dict` with each scope as a key and the description as the value:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="63 64 65 66"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="62 63 64 65"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -93,7 +93,7 @@ And we return the scopes as part of the JWT token.
|
||||
|
||||
But in your application, for security, you should make sure you only add the scopes that the user is actually able to have, or the ones you have predefined.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="155"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="153"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ In this case, it requires the scope `me` (it could require more than one scope).
|
||||
|
||||
We are doing it here to demonstrate how **FastAPI** handles scopes declared at different levels.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="5 140 167"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 139 166"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -143,7 +143,7 @@ We also declare a special parameter of type `SecurityScopes`, imported from `fas
|
||||
|
||||
This `SecurityScopes` class is similar to `Request` (`Request` was used to get the request object directly).
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 106"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8 105"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -159,7 +159,7 @@ We create an `HTTPException` that we can re-use (`raise`) later at several point
|
||||
|
||||
In this exception, we include the scopes required (if any) as a string separated by spaces (using `scope_str`). We put that string containing the scopes in in the `WWW-Authenticate` header (this is part of the spec).
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="106 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="105 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -177,7 +177,7 @@ Instead of, for example, a `dict`, or something else, as it could break the appl
|
||||
|
||||
We also verify that we have a user with that username, and if not, we raise that same exception we created before.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="47 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="46 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -187,7 +187,7 @@ We now verify that all the scopes required, by this dependency and all the depen
|
||||
|
||||
For this, we use `security_scopes.scopes`, that contains a `list` with all these scopes as `str`.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="129 130 131 132 133 134 135"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="128 129 130 131 132 133 134"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
382
docs/en/docs/advanced/settings.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,382 @@
|
||||
# Settings and Environment Variables
|
||||
|
||||
In many cases your application could need some external settings or configurations, for example secret keys, database credentials, credentials for email services, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of these settings are variable (can change), like database URLs. And many could be sensitive, like secrets.
|
||||
|
||||
For this reason it's common to provide them in environment variables that are read by the application.
|
||||
|
||||
## Environment Variables
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
If you already know what "environment variables" are and how to use them, feel free to skip to the next section below.
|
||||
|
||||
An <a href="https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Environment_variable" class="external-link" target="_blank">environment variable</a> (also known as "env var") is a variable that lives outside of the Python code, in the operating system, and could be read by your Python code (or by other programs as well).
|
||||
|
||||
You can create and use environment variables in the shell, without needing Python:
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Linux, macOS, Windows Bash"
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
// You could create an env var MY_NAME with
|
||||
$ export MY_NAME="Wade Wilson"
|
||||
|
||||
// Then you could use it with other programs, like
|
||||
$ echo "Hello $MY_NAME"
|
||||
|
||||
Hello Wade Wilson
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Windows PowerShell"
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
// Create an env var MY_NAME
|
||||
$ $Env:MY_NAME = "Wade Wilson"
|
||||
|
||||
// Use it with other programs, like
|
||||
$ echo "Hello $Env:MY_NAME"
|
||||
|
||||
Hello Wade Wilson
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
### Read env vars in Python
|
||||
|
||||
You could also create environment variables outside of Python, in the terminal (or with any other method), and then read them in Python.
|
||||
|
||||
For example you could have a file `main.py` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3"
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
name = os.getenv("MY_NAME", "World")
|
||||
print(f"Hello {name} from Python")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The second argument to <a href="https://docs.python.org/3.8/library/os.html#os.getenv" class="external-link" target="_blank">`os.getenv()`</a> is the default value to return.
|
||||
|
||||
If not provided, it's `None` by default, here we provide `"World"` as the default value to use.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you could call that Python program:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
// Here we don't set the env var yet
|
||||
$ python main.py
|
||||
|
||||
// As we didn't set the env var, we get the default value
|
||||
|
||||
Hello World from Python
|
||||
|
||||
// But if we create an environment variable first
|
||||
$ export MY_NAME="Wade Wilson"
|
||||
|
||||
// And then call the program again
|
||||
$ python main.py
|
||||
|
||||
// Now it can read the environment variable
|
||||
|
||||
Hello Wade Wilson from Python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
As environment variables can be set outside of the code, but can be read by the code, and don't have to be stored (committed to `git`) with the rest of the files, it's common to use them for configurations or settings.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also create an environment variable only for a specific program invocation, that is only available to that program, and only for its duration.
|
||||
|
||||
To do that, create it right before the program itself, on the same line:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
// Create an env var MY_NAME in line for this program call
|
||||
$ MY_NAME="Wade Wilson" python main.py
|
||||
|
||||
// Now it can read the environment variable
|
||||
|
||||
Hello Wade Wilson from Python
|
||||
|
||||
// The env var no longer exists afterwards
|
||||
$ python main.py
|
||||
|
||||
Hello World from Python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
You can read more about it at <a href="https://12factor.net/config" class="external-link" target="_blank">The Twelve-Factor App: Config</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Types and validation
|
||||
|
||||
These environment variables can only handle text strings, as they are external to Python and have to be compatible with other programs and the rest of the system (and even with different operating systems, as Linux, Windows, macOS).
|
||||
|
||||
That means that any value read in Python from an environment variable will be a `str`, and any conversion to a different type or validation has to be done in code.
|
||||
|
||||
## Pydantic `Settings`
|
||||
|
||||
Fortunately, Pydantic provides a great utility to handle these settings coming from environment variables with <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/settings/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic: Settings management</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the `Settings` object
|
||||
|
||||
Import `BaseSettings` from Pydantic and create a sub-class, very much like with a Pydantic model.
|
||||
|
||||
The same way as with Pydantic models, you declare class attributes with type annotations, and possibly default values.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use all the same validation features and tools you use for Pydantic models, like different data types and additional validations with `Field()`.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 5 6 7 8 11"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/settings/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
If you want something quick to copy and paste, don't use this example, use the last one below.
|
||||
|
||||
Then, when you create an instance of that `Settings` class (in this case, in the `settings` object), Pydantic will read the environment variables in a case-insensitive way, so, an upper-case variable `APP_NAME` will still be read for the attribute `app_name`.
|
||||
|
||||
Next it will convert and validate the data. So, when you use that `settings` object, you will have data of the types you declared (e.g. `items_per_user` will be an `int`).
|
||||
|
||||
### Use the `settings`
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can use the new `settings` object in your application:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="18 19 20"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/settings/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Run the server
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you would run the server passing the configurations as environment variables, for example you could set an `ADMIN_EMAIL` and `APP_NAME` with:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ ADMIN_EMAIL="deadpool@example.com" APP_NAME="ChimichangApp" uvicorn main:app
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
To set multiple env vars for a single command just separate them with a space, and put them all before the command.
|
||||
|
||||
And then the `admin_email` setting would be set to `"deadpool@example.com"`.
|
||||
|
||||
The `app_name` would be `"ChimichangApp"`.
|
||||
|
||||
And the `items_per_user` would keep its default value of `50`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Settings in another module
|
||||
|
||||
You could put those settings in another module file as you saw in [Bigger Applications - Multiple Files](../tutorial/bigger-applications.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you could have a file `config.py` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/settings/app01/config.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And then use it in a file `main.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 11 12 13"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/settings/app01/main.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
You would also need a file `__init__.py` as you saw on [Bigger Applications - Multiple Files](../tutorial/bigger-applications.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
## Settings in a dependency
|
||||
|
||||
In some occasions it might be useful to provide the settings from a dependency, instead of having a global object with `settings` that is used everywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
This could be especially useful during testing, as it's very easy to override a dependency with your own custom settings.
|
||||
|
||||
### The config file
|
||||
|
||||
Coming from the previous example, your `config.py` file could look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/settings/app02/config.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that now we don't create a default instance `settings = Settings()`.
|
||||
|
||||
### The main app file
|
||||
|
||||
Now we create a dependency that returns a new `config.Settings()`.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="5 11 12"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/settings/app02/main.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
We'll discuss the `@lru_cache()` in a bit.
|
||||
|
||||
For now you can assume `get_settings()` is a normal function.
|
||||
|
||||
And then we can require it from the *path operation function* as a dependency and use it anywhere we need it.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="16 18 19 20"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/settings/app02/main.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Settings and testing
|
||||
|
||||
Then it would be very easy to provide a different settings object during testing by creating a dependency override for `get_settings`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8 9 12 21"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/settings/app02/test_main.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the dependency override we set a new value for the `admin_email` when creating the new `Settings` object, and then we return that new object.
|
||||
|
||||
Then we can test that it is used.
|
||||
|
||||
## Reading a `.env` file
|
||||
|
||||
If you have many settings that possibly change a lot, maybe in different environments, it might be useful to put them on a file and then read them from it as if they were environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
This practice is common enough that it has a name, these environment variables are commonly placed in a file `.env`, and the file is called a "dotenv".
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
A file starting with a dot (`.`) is a hidden file in Unix-like systems, like Linux and macOS.
|
||||
|
||||
But a dotenv file doesn't really have to have that exact filename.
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic has support for reading from these types of files using an external library. You can read more at <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/settings/#dotenv-env-support" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic Settings: Dotenv (.env) support</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
For this to work, you need to `pip install python-dotenv`.
|
||||
|
||||
### The `.env` file
|
||||
|
||||
You could have a `.env` file with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
ADMIN_EMAIL="deadpool@example.com"
|
||||
APP_NAME="ChimichangApp"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Read settings from `.env`
|
||||
|
||||
And then update your `config.py` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 10"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/settings/app03/config.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here we create a class `Config` inside of your Pydantic `Settings` class, and set the `env_file` to the filename with the dotenv file we want to use.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The `Config` class is used just for Pydantic configuration. You can read more at <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/model_config/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic Model Config</a>
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating the `Settings` only once with `lru_cache`
|
||||
|
||||
Reading a file from disk is normally a costly (slow) operation, so you probably want to do it only once and then re-use the same settings object, instead of reading it for each request.
|
||||
|
||||
But every time we do:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
config.Settings()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
a new `Settings` object would be created, and at creation it would read the `.env` file again.
|
||||
|
||||
If the dependency function was just like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
def get_settings():
|
||||
return config.Settings()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
we would create that object for each request, and we would be reading the `.env` file for each request. ⚠️
|
||||
|
||||
But as we are using the `@lru_cache()` decorator on top, the `Settings` object will be created only once, the first time it's called. ✔️
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 10"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/settings/app03/main.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then for any subsequent calls of `get_settings()` in the dependencies for the next requests, instead of executing the internal code of `get_settings()` and creating a new `Settings` object, it will return the same object that was returned on the first call, again and again.
|
||||
|
||||
#### `lru_cache` Technical Details
|
||||
|
||||
`@lru_cache()` modifies the function it decorates to return the same value that was returned the first time, instead of computing it again, executing the code of the function every time.
|
||||
|
||||
So, the function below it will be executed once for each combination of arguments. And then the values returned by each of those combinations of arguments will be used again and again whenever the function is called with exactly the same combination of arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you have a function:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
@lru_cache()
|
||||
def say_hi(name: str, salutation: str = "Ms."):
|
||||
return f"Hello {salutation} {name}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
your program could execute like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```mermaid
|
||||
sequenceDiagram
|
||||
|
||||
participant code as Code
|
||||
participant function as say_hi()
|
||||
participant execute as Execute function
|
||||
|
||||
rect rgba(0, 255, 0, .1)
|
||||
code ->> function: say_hi(name="Camila")
|
||||
function ->> execute: execute function code
|
||||
execute ->> code: return the result
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
rect rgba(0, 255, 255, .1)
|
||||
code ->> function: say_hi(name="Camila")
|
||||
function ->> code: return stored result
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
rect rgba(0, 255, 0, .1)
|
||||
code ->> function: say_hi(name="Rick")
|
||||
function ->> execute: execute function code
|
||||
execute ->> code: return the result
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
rect rgba(0, 255, 0, .1)
|
||||
code ->> function: say_hi(name="Rick", salutation="Mr.")
|
||||
function ->> execute: execute function code
|
||||
execute ->> code: return the result
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
rect rgba(0, 255, 255, .1)
|
||||
code ->> function: say_hi(name="Rick")
|
||||
function ->> code: return stored result
|
||||
end
|
||||
|
||||
rect rgba(0, 255, 255, .1)
|
||||
code ->> function: say_hi(name="Camila")
|
||||
function ->> code: return stored result
|
||||
end
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the case of our dependency `get_settings()`, the function doesn't even take any arguments, so it always returns the same value.
|
||||
|
||||
That way, it behaves almost as if it was just a global variable. But as it uses a dependency function, then we can override it easily for testing.
|
||||
|
||||
`@lru_cache()` is part of `functools` which is part of Python's standard library, you can read more about it in the <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/functools.html#functools.lru_cache" class="external-link" target="_blank">Python docs for `@lru_cache()`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Recap
|
||||
|
||||
You can use Pydantic Settings to handle the settings or configurations for your application, with all the power of Pydantic models.
|
||||
|
||||
* By using a dependency you can simplify testing.
|
||||
* You can use `.env` files with it.
|
||||
* Using `@lru_cache()` lets you avoid reading the dotenv file again and again for each request, while allowing you to override it during testing.
|
||||
@@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Sub Applications - Behind a Proxy, Mounts
|
||||
|
||||
There are at least two situations where you could need to create your **FastAPI** application using some specific paths.
|
||||
|
||||
But then you need to set them up to be served with a path prefix.
|
||||
|
||||
It could happen if you have a:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Proxy** server.
|
||||
* You are "**mounting**" a FastAPI application inside another FastAPI application (or inside another ASGI application, like Starlette).
|
||||
|
||||
## Proxy
|
||||
|
||||
Having a proxy in this case means that you could declare a path at `/app`, but then, you could need to add a layer on top (the Proxy) that would put your **FastAPI** application under a path like `/api/v1`.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the original path `/app` will actually be served at `/api/v1/app`.
|
||||
|
||||
Even though your application "thinks" it is serving at `/app`.
|
||||
|
||||
And the Proxy could be re-writing the path "on the fly" to keep your application convinced that it is serving at `/app`.
|
||||
|
||||
Up to here, everything would work as normally.
|
||||
|
||||
But then, when you open the integrated docs, they would expect to get the OpenAPI schema at `/openapi.json`, instead of `/api/v1/openapi.json`.
|
||||
|
||||
So, the frontend (that runs in the browser) would try to reach `/openapi.json` and wouldn't be able to get the OpenAPI schema.
|
||||
|
||||
So, it's needed that the frontend looks for the OpenAPI schema at `/api/v1/openapi.json`.
|
||||
|
||||
And it's also needed that the returned JSON OpenAPI schema has the defined path at `/api/v1/app` (behind the proxy) instead of `/app`.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
For these cases, you can declare an `openapi_prefix` parameter in your `FastAPI` application.
|
||||
|
||||
See the section below, about "mounting", for an example.
|
||||
|
||||
## Mounting a **FastAPI** application
|
||||
|
||||
"Mounting" means adding a complete "independent" application in a specific path, that then takes care of handling all the sub-paths.
|
||||
|
||||
You could want to do this if you have several "independent" applications that you want to separate, having their own independent OpenAPI schema and user interfaces.
|
||||
|
||||
### Top-level application
|
||||
|
||||
First, create the main, top-level, **FastAPI** application, and its *path operations*:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 6 7 8"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Sub-application
|
||||
|
||||
Then, create your sub-application, and its *path operations*.
|
||||
|
||||
This sub-application is just another standard FastAPI application, but this is the one that will be "mounted".
|
||||
|
||||
When creating the sub-application, use the parameter `openapi_prefix`. In this case, with a prefix of `/subapi`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 14 15 16"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Mount the sub-application
|
||||
|
||||
In your top-level application, `app`, mount the sub-application, `subapi`.
|
||||
|
||||
Here you need to make sure you use the same path that you used for the `openapi_prefix`, in this case, `/subapi`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 19"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Check the automatic API docs
|
||||
|
||||
Now, run `uvicorn`, if your file is at `main.py`, it would be:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --reload
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
And open the docs at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the automatic API docs for the main app, including only its own paths:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/sub-applications/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
And then, open the docs for the sub-application, at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/subapi/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/subapi/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the automatic API docs for the sub-application, including only its own sub-paths, with their correct prefix:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/sub-applications/image02.png">
|
||||
|
||||
If you try interacting with any of the two user interfaces, they will work, because the browser will be able to talk to the correct path (or sub-path).
|
||||
73
docs/en/docs/advanced/sub-applications.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
# Sub Applications - Mounts
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to have two independent FastAPI applications, with their own independent OpenAPI and their own docs UIs, you can have a main app and "mount" one (or more) sub-application(s).
|
||||
|
||||
## Mounting a **FastAPI** application
|
||||
|
||||
"Mounting" means adding a completely "independent" application in a specific path, that then takes care of handling everything under that path, with the _path operations_ declared in that sub-application.
|
||||
|
||||
### Top-level application
|
||||
|
||||
First, create the main, top-level, **FastAPI** application, and its *path operations*:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 6 7 8"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Sub-application
|
||||
|
||||
Then, create your sub-application, and its *path operations*.
|
||||
|
||||
This sub-application is just another standard FastAPI application, but this is the one that will be "mounted":
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 14 15 16"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Mount the sub-application
|
||||
|
||||
In your top-level application, `app`, mount the sub-application, `subapi`.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, it will be mounted at the path `/subapi`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 19"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sub_applications/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Check the automatic API docs
|
||||
|
||||
Now, run `uvicorn` with the main app, if your file is `main.py`, it would be:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --reload
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
And open the docs at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the automatic API docs for the main app, including only its own _path operations_:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/sub-applications/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
And then, open the docs for the sub-application, at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/subapi/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/subapi/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the automatic API docs for the sub-application, including only its own _path operations_, all under the correct sub-path prefix `/subapi`:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/sub-applications/image02.png">
|
||||
|
||||
If you try interacting with any of the two user interfaces, they will work correctly, because the browser will be able to talk to each specific app or sub-app.
|
||||
|
||||
### Technical Details: `root_path`
|
||||
|
||||
When you mount a sub-application as described above, FastAPI will take care of communicating the mount path for the sub-application using a mechanism from the ASGI specification called a `root_path`.
|
||||
|
||||
That way, the sub-application will know to use that path prefix for the docs UI.
|
||||
|
||||
And the sub-application could also have its own mounted sub-applications and everything would work correctly, because FastAPI handles all these `root_path`s automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
You will learn more about the `root_path` and how to use it explicitly in the section about [Behind a Proxy](./behind-a-proxy.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
95
docs/en/docs/advanced/testing-database.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
# Testing a Database
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the same dependency overrides from [Testing Dependencies with Overrides](testing-dependencies.md){.internal-link target=_blank} to alter a database for testing.
|
||||
|
||||
You could want to set up a different database for testing, rollback the data after the tests, pre-fill it with some testing data, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
The main idea is exactly the same you saw in that previous chapter.
|
||||
|
||||
## Add tests for the SQL app
|
||||
|
||||
Let's update the example from [SQL (Relational) Databases](../tutorial/sql-databases.md){.internal-link target=_blank} to use a testing database.
|
||||
|
||||
All the app code is the same, you can go back to that chapter check how it was.
|
||||
|
||||
The only changes here are in the new testing file.
|
||||
|
||||
Your normal dependency `get_db()` would return a database session.
|
||||
|
||||
In the test, you could use a dependency override to return your *custom* database session instead of the one that would be used normally.
|
||||
|
||||
In this example we'll create a temporary database only for the tests.
|
||||
|
||||
## File structure
|
||||
|
||||
We create a new file at `sql_app/tests/test_sql_app.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
So the new file structure looks like:
|
||||
|
||||
``` hl_lines="9 10 11"
|
||||
.
|
||||
└── sql_app
|
||||
├── __init__.py
|
||||
├── crud.py
|
||||
├── database.py
|
||||
├── main.py
|
||||
├── models.py
|
||||
├── schemas.py
|
||||
└── tests
|
||||
├── __init__.py
|
||||
└── test_sql_app.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Create the new database session
|
||||
|
||||
First, we create a new database session with the new database.
|
||||
|
||||
For the tests we'll use a file `test.db` instead of `sql_app.db`.
|
||||
|
||||
But the rest of the session code is more or less the same, we just copy it.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8 9 10 11 12 13"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases/sql_app/tests/test_sql_app.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
You could reduce duplication in that code by putting it in a function and using it from both `database.py` and `tests/test_sql_app.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
For simplicity and to focus on the specific testing code, we are just copying it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create the database
|
||||
|
||||
Because now we are going to use a new database in a new file, we need to make sure we create the database with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
Base.metadata.create_all(bind=engine)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That is normally called in `main.py`, but the line in `main.py` uses the database file `sql_app.db`, and we need to make sure we create `test.db` for the tests.
|
||||
|
||||
So we add that line here, with the new file.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="16"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases/sql_app/tests/test_sql_app.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Dependency override
|
||||
|
||||
Now we create the dependency override and add it to the overrides for our app.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="19 20 21 22 23 24 27"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases/sql_app/tests/test_sql_app.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
The code for `override_get_db()` is almost exactly the same as for `get_db()`, but in `override_get_db()` we use the `TestingSessionLocal` for the testing database instead.
|
||||
|
||||
## Test the app
|
||||
|
||||
Then we can just test the app as normally.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/sql_databases/sql_app/tests/test_sql_app.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And all the modifications we made in the database during the tests will be in the `test.db` database instead of the main `sql_app.db`.
|
||||
@@ -20,18 +20,6 @@ You probably want to test the external provider once, but not necessarily call i
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, you can override the dependency that calls that provider, and use a custom dependency that returns a mock user, only for your tests.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use case: testing database
|
||||
|
||||
Other example could be that you are using a specific database only for testing.
|
||||
|
||||
Your normal dependency would return a database session.
|
||||
|
||||
But then, after each test, you could want to rollback all the operations or remove data.
|
||||
|
||||
Or you could want to alter the data before the tests run, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, you could use a dependency override to return your *custom* database session instead of the one that would be used normally.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use the `app.dependency_overrides` attribute
|
||||
|
||||
For these cases, your **FastAPI** application has an attribute `app.dependency_overrides`, it is a simple `dict`.
|
||||
@@ -40,7 +28,7 @@ To override a dependency for testing, you put as a key the original dependency (
|
||||
|
||||
And then **FastAPI** will call that override instead of the original dependency.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="24 25 28"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="26 27 30"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependency_testing/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -51,38 +51,7 @@ In your WebSocket route you can `await` for messages and send messages.
|
||||
|
||||
You can receive and send binary, text, and JSON data.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using `Depends` and others
|
||||
|
||||
In WebSocket endpoints you can import from `fastapi` and use:
|
||||
|
||||
* `Depends`
|
||||
* `Security`
|
||||
* `Cookie`
|
||||
* `Header`
|
||||
* `Path`
|
||||
* `Query`
|
||||
|
||||
They work the same way as for other FastAPI endpoints/*path operations*:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="53 54 55 56 57 58 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/websockets/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
In a WebSocket it doesn't really make sense to raise an `HTTPException`. So it's better to close the WebSocket connection directly.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use a closing code from the <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6455#section-7.4.1" class="external-link" target="_blank">valid codes defined in the specification</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
In the future, there will be a `WebSocketException` that you will be able to `raise` from anywhere, and add exception handlers for it. It depends on the <a href="https://github.com/encode/starlette/pull/527" class="external-link" target="_blank">PR #527</a> in Starlette.
|
||||
|
||||
## More info
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about the options, check Starlette's documentation for:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.starlette.io/websockets/" class="external-link" target="_blank">The `WebSocket` class</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.starlette.io/endpoints/#websocketendpoint" class="external-link" target="_blank">Class-based WebSocket handling</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Test it
|
||||
## Try it
|
||||
|
||||
If your file is named `main.py`, run your application with:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -115,3 +84,62 @@ You can send (and receive) many messages:
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/websockets/image04.png">
|
||||
|
||||
And all of them will use the same WebSocket connection.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using `Depends` and others
|
||||
|
||||
In WebSocket endpoints you can import from `fastapi` and use:
|
||||
|
||||
* `Depends`
|
||||
* `Security`
|
||||
* `Cookie`
|
||||
* `Header`
|
||||
* `Path`
|
||||
* `Query`
|
||||
|
||||
They work the same way as for other FastAPI endpoints/*path operations*:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/websockets/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
In a WebSocket it doesn't really make sense to raise an `HTTPException`. So it's better to close the WebSocket connection directly.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use a closing code from the <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6455#section-7.4.1" class="external-link" target="_blank">valid codes defined in the specification</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
In the future, there will be a `WebSocketException` that you will be able to `raise` from anywhere, and add exception handlers for it. It depends on the <a href="https://github.com/encode/starlette/pull/527" class="external-link" target="_blank">PR #527</a> in Starlette.
|
||||
|
||||
### Try the WebSockets with dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
If your file is named `main.py`, run your application with:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --reload
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Open your browser at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
There you can set:
|
||||
|
||||
* The "Item ID", used in the path.
|
||||
* The "Token" used as a query parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Notice that the query `token` will be handled by a dependency.
|
||||
|
||||
With that you can connect the WebSocket and then send and receive messages:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/websockets/image05.png">
|
||||
|
||||
## More info
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about the options, check Starlette's documentation for:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.starlette.io/websockets/" class="external-link" target="_blank">The `WebSocket` class</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.starlette.io/endpoints/#websocketendpoint" class="external-link" target="_blank">Class-based WebSocket handling</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# Including WSGI - Flask, Django, others
|
||||
|
||||
You can mount WSGI applications as you saw with [Sub Applications - Behind a Proxy, Mounts](./sub-applications-proxy.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
You can mount WSGI applications as you saw with [Sub Applications - Mounts](./sub-applications.md){.internal-link target=_blank}, [Behind a Proxy](./behind-a-proxy.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
For that, you can use the `WSGIMiddleware` and use it to wrap your WSGI application, for example, Flask, Django, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ But by following the steps above, it will be able to do some performance optimiz
|
||||
|
||||
Modern versions of Python have support for **"asynchronous code"** using something called **"coroutines"**, with **`async` and `await`** syntax.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's see that phrase by parts in the sections below, below:
|
||||
Let's see that phrase by parts in the sections below:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Asynchronous Code**
|
||||
* **`async` and `await`**
|
||||
@@ -63,13 +63,13 @@ Let's see that phrase by parts in the sections below, below:
|
||||
|
||||
## Asynchronous Code
|
||||
|
||||
Asynchronous code just means that the language has a way to tell the computer / program that at some point in the code, he will have to wait for *something else* to finish somewhere else. Let's say that *something else* is called "slow-file".
|
||||
Asynchronous code just means that the language 💬 has a way to tell the computer / program 🤖 that at some point in the code, it 🤖 will have to wait for *something else* to finish somewhere else. Let's say that *something else* is called "slow-file" 📝.
|
||||
|
||||
So, during that time, the computer can go and do some other work, while "slow-file" finishes.
|
||||
So, during that time, the computer can go and do some other work, while "slow-file" 📝 finishes.
|
||||
|
||||
Then the computer / program will come back every time it has a chance because it's waiting again, or whenever he finished all the work he had at that point. And it will see if any of the tasks he was waiting for has already finished doing whatever it had to do.
|
||||
Then the computer / program 🤖 will come back every time it has a chance because it's waiting again, or whenever it 🤖 finished all the work it had at that point. And it 🤖 will see if any of the tasks it was waiting for have already finished, doing whatever it had to do.
|
||||
|
||||
And then it takes the first task to finish (let's say, our "slow-file") and continues whatever it had to do with it.
|
||||
Next, it 🤖 takes the first task to finish (let's say, our "slow-file" 📝) and continues whatever it had to do with it.
|
||||
|
||||
That "wait for something else" normally refers to <abbr title="Input and Output">I/O</abbr> operations that are relatively "slow" (compared to the speed of the processor and the RAM memory), like waiting for:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -82,7 +82,7 @@ That "wait for something else" normally refers to <abbr title="Input and Output"
|
||||
* a database query to return the results
|
||||
* etc.
|
||||
|
||||
As the execution time is consumed mostly by waiting for <abbr title="Input and Output">I/O</abbr> operations, so they call them "I/O bound".
|
||||
As the execution time is consumed mostly by waiting for <abbr title="Input and Output">I/O</abbr> operations, they call them "I/O bound" operations.
|
||||
|
||||
It's called "asynchronous" because the computer / program doesn't have to be "synchronized" with the slow task, waiting for the exact moment that the task finishes, while doing nothing, to be able to take the task result and continue the work.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -94,7 +94,7 @@ For "synchronous" (contrary to "asynchronous") they commonly also use the term "
|
||||
|
||||
This idea of **asynchronous** code described above is also sometimes called **"concurrency"**. It is different from **"parallelism"**.
|
||||
|
||||
**Concurrency** and **parallelism** both relate to "different things happening more or less at the same time".
|
||||
**Concurrency** and **parallelism** both relate to "different things happening more or less at the same time".
|
||||
|
||||
But the details between *concurrency* and *parallelism* are quite different.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -102,107 +102,109 @@ To see the difference, imagine the following story about burgers:
|
||||
|
||||
### Concurrent Burgers
|
||||
|
||||
You go with your crush to get fast food, you stand in line while the cashier takes the orders from the people in front of you.
|
||||
You go with your crush 😍 to get fast food 🍔, you stand in line while the cashier 💁 takes the orders from the people in front of you.
|
||||
|
||||
Then it's your turn, you place your order of 2 very fancy burgers for your crush and you.
|
||||
Then it's your turn, you place your order of 2 very fancy burgers 🍔 for your crush 😍 and you.
|
||||
|
||||
You pay.
|
||||
You pay 💸.
|
||||
|
||||
The cashier says something to the guy in the kitchen so he knows he has to prepare your burgers (even though he is currently preparing the ones for the previous clients).
|
||||
The cashier 💁 says something to the guy in the kitchen 👨🍳 so he knows he has to prepare your burgers 🍔 (even though he is currently preparing the ones for the previous clients).
|
||||
|
||||
The cashier gives you the number of your turn.
|
||||
The cashier 💁 gives you the number of your turn.
|
||||
|
||||
While you are waiting, you go with your crush and pick a table, you sit and talk with your crush for a long time (as your burgers are very fancy and take some time to prepare).
|
||||
While you are waiting, you go with your crush 😍 and pick a table, you sit and talk with your crush 😍 for a long time (as your burgers are very fancy and take some time to prepare ✨🍔✨).
|
||||
|
||||
As you are seating on the table with your crush, while you wait for the burgers, you can spend that time admiring how awesome, cute and smart your crush is.
|
||||
As you are sitting on the table with your crush 😍, while you wait for the burgers 🍔, you can spend that time admiring how awesome, cute and smart your crush is ✨😍✨.
|
||||
|
||||
While waiting and talking to your crush, from time to time, you check the number displayed on the counter to see if it's your turn already.
|
||||
While waiting and talking to your crush 😍, from time to time, you check the number displayed on the counter to see if it's your turn already.
|
||||
|
||||
Then at some point, it finally is your turn. You go to the counter, get your burgers and come back to the table.
|
||||
Then at some point, it finally is your turn. You go to the counter, get your burgers 🍔 and come back to the table.
|
||||
|
||||
You and your crush eat the burgers and have a nice time.
|
||||
You and your crush 😍 eat the burgers 🍔 and have a nice time ✨.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Imagine you are the computer / program in that story.
|
||||
Imagine you are the computer / program 🤖 in that story.
|
||||
|
||||
While you are at the line, you are just idle, waiting for your turn, not doing anything very "productive". But the line is fast because the cashier is only taking the orders, so that's fine.
|
||||
While you are at the line, you are just idle 😴, waiting for your turn, not doing anything very "productive". But the line is fast because the cashier 💁 is only taking the orders (not preparing them), so that's fine.
|
||||
|
||||
Then, when it's your turn, you do actual "productive" work, you process the menu, decide what you want, get your crush's choice, pay, check that you give the correct bill or card, check that you are charged correctly, check that the order has the correct items, etc.
|
||||
Then, when it's your turn, you do actual "productive" work 🤓, you process the menu, decide what you want, get your crush's 😍 choice, pay 💸, check that you give the correct bill or card, check that you are charged correctly, check that the order has the correct items, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
But then, even though you still don't have your burgers, your work with the cashier is "on pause", because you have to wait for your burgers to be ready.
|
||||
But then, even though you still don't have your burgers 🍔, your work with the cashier 💁 is "on pause" ⏸, because you have to wait 🕙 for your burgers to be ready.
|
||||
|
||||
But as you go away from the counter and seat on the table with a number for your turn, you can switch your attention to your crush, and "work" on that. Then you are again doing something very "productive", as is flirting with your crush.
|
||||
But as you go away from the counter and sit on the table with a number for your turn, you can switch 🔀 your attention to your crush 😍, and "work" ⏯ 🤓 on that. Then you are again doing something very "productive" 🤓, as is flirting with your crush 😍.
|
||||
|
||||
Then the cashier says "I'm finished with doing the burgers" by putting your number on the counter display, but you don't jump like crazy immediately when the displayed number changes to your turn number. You know no one will steal your burgers because you have the number of your turn, and they have theirs.
|
||||
Then the cashier 💁 says "I'm finished with doing the burgers" 🍔 by putting your number on the counter's display, but you don't jump like crazy immediately when the displayed number changes to your turn number. You know no one will steal your burgers 🍔 because you have the number of your turn, and they have theirs.
|
||||
|
||||
So you wait for your crush to finish the story (finish the current work / task being processed), smile gently and say that you are going for the burgers.
|
||||
So you wait for your crush 😍 to finish the story (finish the current work ⏯ / task being processed 🤓), smile gently and say that you are going for the burgers ⏸.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you go to the counter, to the initial task that is now finished, pick the burgers, say thanks and take them to the table. That finishes that step / task of interaction with the counter. That in turn, creates a new task, of "eating burgers", but the previous one of "getting burgers" is finished.
|
||||
Then you go to the counter 🔀, to the initial task that is now finished ⏯, pick the burgers 🍔, say thanks and take them to the table. That finishes that step / task of interaction with the counter ⏹. That in turn, creates a new task, of "eating burgers" 🔀 ⏯, but the previous one of "getting burgers" is finished ⏹.
|
||||
|
||||
### Parallel Burgers
|
||||
|
||||
You go with your crush to get parallel fast food.
|
||||
Now let's imagine these aren't "Concurrent Burgers", but "Parallel Burgers".
|
||||
|
||||
You stand in line while several (let's say 8) cashiers take the orders from the people in front of you.
|
||||
You go with your crush 😍 to get parallel fast food 🍔.
|
||||
|
||||
Everyone before you is waiting for their burgers to be ready before leaving the counter because each of the 8 cashiers goes himself and prepares the burger right away before getting the next order.
|
||||
You stand in line while several (let's say 8) cashiers that at the same time are cooks 👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳 take the orders from the people in front of you.
|
||||
|
||||
Then it's finally your turn, you place your order of 2 very fancy burgers for your crush and you.
|
||||
Everyone before you is waiting 🕙 for their burgers 🍔 to be ready before leaving the counter because each of the 8 cashiers goes himself and prepares the burger right away before getting the next order.
|
||||
|
||||
You pay.
|
||||
Then it's finally your turn, you place your order of 2 very fancy burgers 🍔 for your crush 😍 and you.
|
||||
|
||||
The cashier goes to the kitchen.
|
||||
You pay 💸.
|
||||
|
||||
You wait, standing in front of the counter, so that no one else takes your burgers before you, as there are no numbers for turns.
|
||||
The cashier goes to the kitchen 👨🍳.
|
||||
|
||||
As you and your crush are busy not letting anyone get in front of you and take your burgers whenever they arrive, you cannot pay attention to your crush.
|
||||
You wait, standing in front of the counter 🕙, so that no one else takes your burgers 🍔 before you do, as there are no numbers for turns.
|
||||
|
||||
This is "synchronous" work, you are "synchronized" with the cashier/cook. You have to wait and be there at the exact moment that the cashier/cook finishes the burgers and gives them to you, or otherwise, someone else might take them.
|
||||
As you and your crush 😍 are busy not letting anyone get in front of you and take your burgers whenever they arrive 🕙, you cannot pay attention to your crush 😞.
|
||||
|
||||
Then your cashier/cook finally comes back with your burgers, after a long time waiting there in front of the counter.
|
||||
This is "synchronous" work, you are "synchronized" with the cashier/cook 👨🍳. You have to wait 🕙 and be there at the exact moment that the cashier/cook 👨🍳 finishes the burgers 🍔 and gives them to you, or otherwise, someone else might take them.
|
||||
|
||||
You take your burgers and go to the table with your crush.
|
||||
Then your cashier/cook 👨🍳 finally comes back with your burgers 🍔, after a long time waiting 🕙 there in front of the counter.
|
||||
|
||||
You just eat them, and you are done.
|
||||
You take your burgers 🍔 and go to the table with your crush 😍.
|
||||
|
||||
There was not much talk or flirting as most of the time was spent waiting in front of the counter.
|
||||
You just eat them, and you are done 🍔 ⏹.
|
||||
|
||||
There was not much talk or flirting as most of the time was spent waiting 🕙 in front of the counter 😞.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
In this scenario of the parallel burgers, you are a computer / program with two processors (you and your crush), both waiting and dedicating their attention to be "waiting on the counter" for a long time.
|
||||
In this scenario of the parallel burgers, you are a computer / program 🤖 with two processors (you and your crush 😍), both waiting 🕙 and dedicating their attention ⏯ to be "waiting on the counter" 🕙 for a long time.
|
||||
|
||||
The fast food store has 8 processors (cashiers/cooks). While the concurrent burgers store might have had only 2 (one cashier and one cook).
|
||||
The fast food store has 8 processors (cashiers/cooks) 👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳. While the concurrent burgers store might have had only 2 (one cashier and one cook) 💁 👨🍳.
|
||||
|
||||
But still, the final experience is not the best.
|
||||
But still, the final experience is not the best 😞.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
This would be the parallel equivalent story for burgers.
|
||||
This would be the parallel equivalent story for burgers 🍔.
|
||||
|
||||
For a more "real life" example of this, imagine a bank.
|
||||
|
||||
Up to recently, most of the banks had multiple cashiers and a big line.
|
||||
Up to recently, most of the banks had multiple cashiers 👨💼👨💼👨💼👨💼 and a big line 🕙🕙🕙🕙🕙🕙🕙🕙.
|
||||
|
||||
All of the cashiers doing all the work with one client after the other.
|
||||
All of the cashiers doing all the work with one client after the other 👨💼⏯.
|
||||
|
||||
And you have to wait in the line for a long time or you lose your turn.
|
||||
And you have to wait 🕙 in the line for a long time or you lose your turn.
|
||||
|
||||
You probably wouldn't want to take your crush with you to do errands at the bank.
|
||||
You probably wouldn't want to take your crush 😍 with you to do errands at the bank 🏦.
|
||||
|
||||
### Burger Conclusion
|
||||
|
||||
In this scenario of "fast food burgers with your crush", as there is a lot of waiting, it makes a lot more sense to have a concurrent system.
|
||||
In this scenario of "fast food burgers with your crush", as there is a lot of waiting 🕙, it makes a lot more sense to have a concurrent system ⏸🔀⏯.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the case for most of the web applications.
|
||||
|
||||
Many, many users, but your server is waiting for their not-so-good connection to send their requests.
|
||||
Many, many users, but your server is waiting 🕙 for their not-so-good connection to send their requests.
|
||||
|
||||
And then waiting again for the responses to come back.
|
||||
And then waiting 🕙 again for the responses to come back.
|
||||
|
||||
This "waiting" is measured in microseconds, but still, summing it all, it's a lot of waiting in the end.
|
||||
This "waiting" 🕙 is measured in microseconds, but still, summing it all, it's a lot of waiting in the end.
|
||||
|
||||
That's why it makes a lot of sense to use asynchronous code for web APIs.
|
||||
That's why it makes a lot of sense to use asynchronous ⏸🔀⏯ code for web APIs.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the existing popular Python frameworks (including Flask and Django) were created before the new asynchronous features in Python existed. So, the ways they can be deployed support parallel execution and an older form of asynchronous execution that is not as powerful as the new capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -210,7 +212,7 @@ Even though the main specification for asynchronous web Python (ASGI) was develo
|
||||
|
||||
That kind of asynchronicity is what made NodeJS popular (even though NodeJS is not parallel) and that's the strength of Go as a programing language.
|
||||
|
||||
And that's the same level of performance</a> you get with **FastAPI**.
|
||||
And that's the same level of performance you get with **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
And as you can have parallelism and asynchronicity at the same time, you get higher performance than most of the tested NodeJS frameworks and on par with Go, which is a compiled language closer to C <a href="https://www.techempower.com/benchmarks/#section=data-r17&hw=ph&test=query&l=zijmkf-1" class="external-link" target="_blank">(all thanks to Starlette)</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -228,15 +230,15 @@ So, to balance that out, imagine the following short story:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
There's no waiting anywhere, just a lot of work to be done, on multiple places of the house.
|
||||
There's no waiting 🕙 anywhere, just a lot of work to be done, on multiple places of the house.
|
||||
|
||||
You could have turns as in the burgers example, first the living room, then the kitchen, but as you are not waiting for anything, just cleaning and cleaning, the turns wouldn't affect anything.
|
||||
You could have turns as in the burgers example, first the living room, then the kitchen, but as you are not waiting 🕙 for anything, just cleaning and cleaning, the turns wouldn't affect anything.
|
||||
|
||||
It would take the same amount of time to finish with or without turns (concurrency) and you would have done the same amount of work.
|
||||
|
||||
But in this case, if you could bring the 8 ex-cashier/cooks/now-cleaners, and each one of them (plus you) could take a zone of the house to clean it, you could do all the work in **parallel**, with the extra help, and finish much sooner.
|
||||
But in this case, if you could bring the 8 ex-cashier/cooks/now-cleaners 👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳, and each one of them (plus you) could take a zone of the house to clean it, you could do all the work in **parallel**, with the extra help, and finish much sooner.
|
||||
|
||||
In this scenario, each one of the cleaners (including you) would be a processor, doing their part of the job.
|
||||
In this scenario, each one of the cleaners (including you) would be a processor, doing their part of the job.
|
||||
|
||||
And as most of the execution time is taken by actual work (instead of waiting), and the work in a computer is done by a <abbr title="Central Processing Unit">CPU</abbr>, they call these problems "CPU bound".
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -246,8 +248,8 @@ Common examples of CPU bound operations are things that require complex math pro
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Audio** or **image processing**
|
||||
* **Computer vision**: an image is composed of millions of pixels, each pixel has 3 values / colors, processing that normally requires computing something on those pixels, all at the same time)
|
||||
* **Audio** or **image processing**.
|
||||
* **Computer vision**: an image is composed of millions of pixels, each pixel has 3 values / colors, processing that normally requires computing something on those pixels, all at the same time.
|
||||
* **Machine Learning**: it normally requires lots of "matrix" and "vector" multiplications. Think of a huge spreadsheet with numbers and multiplying all of them together at the same time.
|
||||
* **Deep Learning**: this is a sub-field of Machine Learning, so, the same applies. It's just that there is not a single spreadsheet of numbers to multiply, but a huge set of them, and in many cases, you use a special processor to build and / or use those models.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -263,7 +265,7 @@ To see how to achieve this parallelism in production see the section about [Depl
|
||||
|
||||
## `async` and `await`
|
||||
|
||||
Modern versions of python have a very intuitive way to define asynchronous code. This makes it look just like normal "sequential" code and do the "awaiting" for you at the right moments.
|
||||
Modern versions of Python have a very intuitive way to define asynchronous code. This makes it look just like normal "sequential" code and do the "awaiting" for you at the right moments.
|
||||
|
||||
When there is an operation that will require waiting before giving the results and has support for these new Python features, you can code it like:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -271,7 +273,7 @@ When there is an operation that will require waiting before giving the results a
|
||||
burgers = await get_burgers(2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The key here is the `await`. It tells Python that it has to wait for `get_burgers(2)` to finish doing its thing before storing the results in `burgers`. With that, Python will know that it can go and do something else in the meanwhile (like receiving another request).
|
||||
The key here is the `await`. It tells Python that it has to wait ⏸ for `get_burgers(2)` to finish doing its thing 🕙 before storing the results in `burgers`. With that, Python will know that it can go and do something else 🔀 ⏯ in the meanwhile (like receiving another request).
|
||||
|
||||
For `await` to work, it has to be inside a function that supports this asynchronicity. To do that, you just declare it with `async def`:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -290,7 +292,7 @@ def get_sequential_burgers(number: int):
|
||||
return burgers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With `async def`, Python knows that, inside that function, it has to be aware of `await` expressions, and that it can "pause" the execution of that function and go do something else before coming back.
|
||||
With `async def`, Python knows that, inside that function, it has to be aware of `await` expressions, and that it can "pause" ⏸ the execution of that function and go do something else 🔀 before coming back.
|
||||
|
||||
When you want to call an `async def` function, you have to "await" it. So, this won't work:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -334,11 +336,11 @@ But before that, handling asynchronous code was quite more complex and difficult
|
||||
|
||||
In previous versions of Python, you could have used threads or <a href="http://www.gevent.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Gevent</a>. But the code is way more complex to understand, debug, and think about.
|
||||
|
||||
In previous versions of NodeJS / Browser JavaScript, you would have used "callbacks". Which lead to <a href="http://callbackhell.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">callback hell</a>.
|
||||
In previous versions of NodeJS / Browser JavaScript, you would have used "callbacks". Which leads to <a href="http://callbackhell.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">callback hell</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Coroutines
|
||||
|
||||
**Coroutine** is just the very fancy term for the thing returned by an `async def` function. Python knows that it is something like a function that it can start and that it will end at some point, but that it might be paused internally too, whenever there is an `await` inside of it.
|
||||
**Coroutine** is just the very fancy term for the thing returned by an `async def` function. Python knows that it is something like a function that it can start and that it will end at some point, but that it might be paused ⏸ internally too, whenever there is an `await` inside of it.
|
||||
|
||||
But all this functionality of using asynchronous code with `async` and `await` is many times summarized as using "coroutines". It is comparable to the main key feature of Go, the "Goroutines".
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -348,7 +350,7 @@ Let's see the same phrase from above:
|
||||
|
||||
> Modern versions of Python have support for **"asynchronous code"** using something called **"coroutines"**, with **`async` and `await`** syntax.
|
||||
|
||||
That should make more sense now.
|
||||
That should make more sense now. ✨
|
||||
|
||||
All that is what powers FastAPI (through Starlette) and what makes it have such an impressive performance.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -356,16 +358,16 @@ All that is what powers FastAPI (through Starlette) and what makes it have such
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
You can probably skip this.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
These are very technical details of how **FastAPI** works underneath.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If you have quite some technical knowledge (co-routines, threads, blocking, etc) and are curious about how FastAPI handles `async def` vs normal `def`, go ahead.
|
||||
|
||||
### Path operation functions
|
||||
|
||||
When you declare a *path operation function* with normal `def` instead of `async def`, it is run in an external threadpool that is then awaited, instead of being called directly (as it would block the server).
|
||||
|
||||
If you are coming from another async framework that does not work in the way described above and you are used to define trivial compute-only *path operation functions* with plain `def` for a tiny performance gain (about 100 nanoseconds), please note that in **FastAPI** the effect would be quite opposite. In these cases, it's better to use `async def` unless your *path operation functions* use code that performs blocking <abbr title="Input/Output: disk reading or writing, network communications.">IO</abbr>.
|
||||
If you are coming from another async framework that does not work in the way described above and you are used to define trivial compute-only *path operation functions* with plain `def` for a tiny performance gain (about 100 nanoseconds), please note that in **FastAPI** the effect would be quite opposite. In these cases, it's better to use `async def` unless your *path operation functions* use code that performs blocking <abbr title="Input/Output: disk reading or writing, network communications.">I/O</abbr>.
|
||||
|
||||
Still, in both situations, chances are that **FastAPI** will [still be faster](/#performance){.internal-link target=_blank} than (or at least comparable to) your previous framework.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -375,7 +377,7 @@ The same applies for dependencies. If a dependency is a standard `def` function
|
||||
|
||||
### Sub-dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
You can have multiple dependencies and sub-dependencies requiring each other (as parameters of the function definitions), some of them might be created with `async def` and some with normal `def`. It would still work, and the ones created with normal `def` would be called on an external thread instead of being "awaited".
|
||||
You can have multiple dependencies and sub-dependencies requiring each other (as parameters of the function definitions), some of them might be created with `async def` and some with normal `def`. It would still work, and the ones created with normal `def` would be called on an external thread (from the threadpool) instead of being "awaited".
|
||||
|
||||
### Other utility functions
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -383,7 +385,7 @@ Any other utility function that you call directly can be created with normal `de
|
||||
|
||||
This is in contrast to the functions that FastAPI calls for you: *path operation functions* and dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
If your utility function is a normal function with `def`, it will be called directly (as you write it in your code), not in a threadpool, if the function is created with `async def` then you should await for that function when you call it in your code.
|
||||
If your utility function is a normal function with `def`, it will be called directly (as you write it in your code), not in a threadpool, if the function is created with `async def` then you should `await` for that function when you call it in your code.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,59 +24,67 @@ That will create a directory `./env/` with the Python binaries and then you will
|
||||
|
||||
Activate the new environment with:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
=== "Linux, macOS"
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ source ./env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ source ./env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or in Windows' PowerShell:
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
=== "Windows PowerShell"
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ .\env\Scripts\Activate.ps1
|
||||
```
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ .\env\Scripts\Activate.ps1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or if you use Bash for Windows (e.g. <a href="https://gitforwindows.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Git Bash</a>):
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
=== "Windows Bash"
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ source ./env/Scripts/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
Or if you use Bash for Windows (e.g. <a href="https://gitforwindows.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Git Bash</a>):
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ source ./env/Scripts/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
To check it worked, use:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
=== "Linux, macOS, Windows Bash"
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ which pip
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
some/directory/fastapi/env/bin/pip
|
||||
```
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ which pip
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
some/directory/fastapi/env/bin/pip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
=== "Windows PowerShell"
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ Get-Command pip
|
||||
|
||||
some/directory/fastapi/env/bin/pip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
If it shows the `pip` binary at `env/bin/pip` then it worked. 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
Or in Windows PowerShell:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ Get-Command pip
|
||||
|
||||
some/directory/fastapi/env/bin/pip
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Every time you install a new package with `pip` under that environment, activate the environment again.
|
||||
@@ -103,27 +111,31 @@ Now re-activate the environment to make sure you are using the `flit` you just i
|
||||
|
||||
And now use `flit` to install the development dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
=== "Linux, macOS"
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ flit install --deps develop --symlink
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ flit install --deps develop --symlink
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you are on Windows, use `--pth-file` instead of `--symlink`:
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
=== "Windows"
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ flit install --deps develop --pth-file
|
||||
If you are on Windows, use `--pth-file` instead of `--symlink`:
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ flit install --deps develop --pth-file
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
It will install all the dependencies and your local FastAPI in your local environment.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -257,7 +269,16 @@ Here are the steps to help with translations.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tips and guidelines
|
||||
|
||||
* Add a single Pull Request per page translated. That will make it much easier for others to review it.
|
||||
* Check the currently <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pulls" class="external-link" target="_blank">existing pull requests</a> for your language and add reviews requesting changes or approving them.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
You can <a href="https://help.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/commenting-on-a-pull-request" class="external-link" target="_blank">add comments with change suggestions</a> to existing pull requests.
|
||||
|
||||
Check the docs about <a href="https://help.github.com/en/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/about-pull-request-reviews" class="external-link" target="_blank">adding a pull request review</a> to approve it or request changes.
|
||||
|
||||
* Check in the <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/issues" class="external-link" target="_blank">issues</a> to see if there's one coordinating translations for your language.
|
||||
|
||||
* Add a single pull request per page translated. That will make it much easier for others to review it.
|
||||
|
||||
For the languages I don't speak, I'll wait for several others to review the translation before merging.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -385,6 +406,11 @@ Updating en
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can check in your code editor the newly created directory `docs/ht/`.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Create a first pull request with just this, to set up the configuration for the new language, before adding translations.
|
||||
|
||||
That way others can help with other pages while you work on the first one. 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
Start by translating the main page, `docs/ht/index.md`.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can continue with the previous instructions, for an "Existing Language".
|
||||
@@ -473,13 +499,3 @@ $ bash scripts/test-cov-html.sh
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
This command generates a directory `./htmlcov/`, if you open the file `./htmlcov/index.html` in your browser, you can explore interactively the regions of code that are covered by the tests, and notice if there is any region missing.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tests in your editor
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use the integrated tests in your editor add `./docs_src` to your `PYTHONPATH` variable.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, in VS Code you can create a file `.env` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```env
|
||||
PYTHONPATH=./docs_src
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -11,3 +11,8 @@ a.internal-link::after {
|
||||
*/
|
||||
content: "\00A0↪";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Give space to lower icons so Gitter chat doesn't get on top of them */
|
||||
.md-footer-meta {
|
||||
padding-bottom: 2em;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -161,6 +161,8 @@ CMD ["uvicorn", "app.main:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "80"]
|
||||
* Create a `main.py` file with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
@@ -172,7 +174,7 @@ def read_root():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -329,55 +331,61 @@ You can deploy **FastAPI** directly without Docker too.
|
||||
|
||||
You just need to install an ASGI compatible server like:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.uvicorn.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uvicorn</a>, a lightning-fast ASGI server, built on uvloop and httptools.
|
||||
=== "Uvicorn"
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.uvicorn.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uvicorn</a>, a lightning-fast ASGI server, built on uvloop and httptools.
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install uvicorn
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install uvicorn
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://gitlab.com/pgjones/hypercorn" class="external-link" target="_blank">Hypercorn</a>, an ASGI server also compatible with HTTP/2.
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
=== "Hypercorn"
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install hypercorn
|
||||
* <a href="https://gitlab.com/pgjones/hypercorn" class="external-link" target="_blank">Hypercorn</a>, an ASGI server also compatible with HTTP/2.
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install hypercorn
|
||||
|
||||
...or any other ASGI server.
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
...or any other ASGI server.
|
||||
|
||||
And run your application the same way you have done in the tutorials, but without the `--reload` option, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
=== "Uvicorn"
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 80
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:80 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --host 0.0.0.0 --port 80
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:80 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or with Hypercorn:
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
=== "Hypercorn"
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ hypercorn main:app --bind 0.0.0.0:80
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
Running on 0.0.0.0:8080 over http (CTRL + C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ hypercorn main:app --bind 0.0.0.0:80
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
Running on 0.0.0.0:8080 over http (CTRL + C to quit)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
You might want to set up some tooling to make sure it is restarted automatically if it stops.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,113 +7,72 @@ There are many posts, articles, tools, and projects, related to **FastAPI**.
|
||||
Here's an incomplete list of some of them.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
If you have an article, project, tool, or anything related to **FastAPI** that is not yet listed here, create a <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/edit/master/docs/external-links.md" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pull Request adding it</a>.
|
||||
If you have an article, project, tool, or anything related to **FastAPI** that is not yet listed here, create a <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/edit/master/docs/en/data/external_links.yml" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pull Request adding it</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Articles
|
||||
|
||||
### English
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@williamhayes/fastapi-starlette-debug-vs-prod-5f7561db3a59" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI/Starlette debug vs prod</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@williamhayes" class="external-link" target="_blank">William Hayes</a>.
|
||||
{% if external_links %}
|
||||
{% for article in external_links.articles.english %}
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/data-rebels/fastapi-google-as-an-external-authentication-provider-3a527672cf33" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI — Google as an external authentication provider</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@nils_29588" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nils de Bruin</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/data-rebels/fastapi-how-to-add-basic-and-cookie-authentication-a45c85ef47d3" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI — How to add basic and cookie authentication</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@nils_29588" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nils de Bruin</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://dev.to/errietta/introduction-to-the-fastapi-python-framework-2n10" class="external-link" target="_blank">Introduction to the fastapi python framework</a> by <a href="https://dev.to/errietta" class="external-link" target="_blank">Errieta Kostala</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="http://nickc1.github.io/api,/scikit-learn/2019/01/10/scikit-fastapi.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI and Scikit-Learn: Easily Deploy Models</a> by <a href="http://nickc1.github.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nick Cortale</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/data-rebels/fastapi-authentication-revisited-enabling-api-key-authentication-122dc5975680" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI authentication revisited: Enabling API key authentication</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@nils_29588" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nils de Bruin</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://blog.bartab.fr/fastapi-logging-on-the-fly/" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI, a simple use case on logging</a> by <a href="https://blog.bartab.fr/" class="external-link" target="_blank">@euri10</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@nico.axtmann95/deploying-a-scikit-learn-model-with-onnx-und-fastapi-1af398268915" class="external-link" target="_blank">Deploying a scikit-learn model with ONNX and FastAPI</a> by <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/nico-axtmann" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nico Axtmann</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://geekflare.com/python-asynchronous-web-frameworks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Top 5 Asynchronous Web Frameworks for Python</a> by <a href="https://geekflare.com/author/ankush/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Ankush Thakur</a> on <a href="https://geekflare.com" class="external-link" target="_blank">GeekFlare</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@gntrm/jwt-authentication-with-fastapi-and-aws-cognito-1333f7f2729e" class="external-link" target="_blank">JWT Authentication with FastAPI and AWS Cognito</a> by <a href="https://twitter.com/gntrm" class="external-link" target="_blank">Johannes Gontrum</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-deploy-a-machine-learning-model-dc51200fe8cf" class="external-link" target="_blank">How to Deploy a Machine Learning Model</a> by <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/mgrootendorst/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Maarten Grootendorst</a> on <a href="https://towardsdatascience.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Towards Data Science</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* [Uber: Ludwig v0.2 Adds New Features and Other Improvements to its Deep Learning Toolbox [including a FastAPI server]](https://eng.uber.com/ludwig-v0-2/){.external-link target=_blank} on <a href="https://eng.uber.com" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uber Engineering</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://gitlab.com/euri10/fastapi_cheatsheet" class="external-link" target="_blank">A FastAPI and Swagger UI visual cheatsheet</a> by <a href="https://gitlab.com/euri10" class="external-link" target="_blank">@euri10</a>
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@mike.p.moritz/using-docker-compose-to-deploy-a-lightweight-python-rest-api-with-a-job-queue-37e6072a209b" class="external-link" target="_blank">Using Docker Compose to deploy a lightweight Python REST API with a job queue</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@mike.p.moritz" class="external-link" target="_blank">Mike Moritz</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://robwagner.dev/tortoise-fastapi-setup/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Setting up Tortoise ORM with FastAPI</a> by <a href="https://robwagner.dev/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Rob Wagner</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://dev.to/dbanty/why-i-m-leaving-flask-3ki6" class="external-link" target="_blank">Why I'm Leaving Flask</a> by <a href="https://dev.to/dbanty" class="external-link" target="_blank">Dylan Anthony</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/python-data/how-to-deploy-tensorflow-2-0-models-as-an-api-service-with-fastapi-docker-128b177e81f3" class="external-link" target="_blank">How To Deploy Tensorflow 2.0 Models As An API Service With FastAPI & Docker</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@bbrenyah" class="external-link" target="_blank">Bernard Brenyah</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://testdriven.io/blog/fastapi-crud/" class="external-link" target="_blank">TestDriven.io: Developing and Testing an Asynchronous API with FastAPI and Pytest</a> by <a href="https://testdriven.io/authors/herman/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Michael Herman</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://towardsdatascience.com/deploying-iris-classifications-with-fastapi-and-docker-7c9b83fdec3a" class="external-link" target="_blank">Towards Data Science: Deploying Iris Classifications with FastAPI and Docker</a> by <a href="https://towardsdatascience.com/@mandygu" class="external-link" target="_blank">Mandy Gu</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/analytics-vidhya/deploy-machine-learning-models-with-keras-fastapi-redis-and-docker-4940df614ece" class="external-link" target="_blank">Deploy Machine Learning Models with Keras, FastAPI, Redis and Docker</a> by <a href="https://medium.com/@shane.soh" class="external-link" target="_blank">Shane Soh</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@arthur393/another-boilerplate-to-fastapi-azure-pipeline-ci-pytest-3c8d9a4be0bb" class="external-link" target="_blank">Another Boilerplate to FastAPI: Azure Pipeline CI + Pytest</a> by <a href="https://twitter.com/arthurheinrique" class="external-link" target="_blank">Arthur Henrique</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://iwpnd.pw/articles/2020-01/deploy-fastapi-to-aws-lambda" class="external-link" target="_blank">How to continuously deploy a FastAPI to AWS Lambda with AWS SAM</a> by <a href="https://iwpnd.pw" class="external-link" target="_blank">Benjamin Ramser</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.tutlinks.com/create-and-deploy-fastapi-app-to-heroku/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Create and Deploy FastAPI app to Heroku without using Docker</a> by <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/navule/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Navule Pavan Kumar Rao</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://iwpnd.pw/articles/2020-03/apache-kafka-fastapi-geostream" class="external-link" target="_blank">Apache Kafka producer and consumer with FastAPI and aiokafka</a> by <a href="https://iwpnd.pw" class="external-link" target="_blank">Benjamin Ramser</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="{{ article.link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.title }}</a> by <a href="{{ article.author_link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.author }}</a>.
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Japanese
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/mtitg/items/47770e9a562dd150631d" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI|DB接続してCRUDするPython製APIサーバーを構築</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/mtitg" class="external-link" target="_blank">@mtitg</a>.
|
||||
{% if external_links %}
|
||||
{% for article in external_links.articles.japanese %}
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/ryoryomaru/items/59958ed385b3571d50de" class="external-link" target="_blank">python製の最新APIフレームワーク FastAPI を触ってみた</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/ryoryomaru" class="external-link" target="_blank">@ryoryomaru</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku/items/0e1f5dbbe62efc612a78" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPIでCORSを回避</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku" class="external-link" target="_blank">@angel_katayoku</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku/items/4fbc1a4e2b33fa2237d2" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPIをMySQLと接続してDockerで管理してみる</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku" class="external-link" target="_blank">@angel_katayoku</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku/items/8a458a8952f50b73f420" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPIでPOSTされたJSONのレスポンスbodyを受け取る</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/angel_katayoku" class="external-link" target="_blank">@angel_katayoku</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/hikarut/items/b178af2e2440c67c6ac4" class="external-link" target="_blank">フロントエンド開発者向けのDockerによるPython開発環境構築</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/hikarut" class="external-link" target="_blank">Hikaru Takahashi</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-environment" class="external-link" target="_blank">【第1回】FastAPIチュートリアル: ToDoアプリを作ってみよう【環境構築編】</a> by <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun" class="external-link" target="_blank">ライトコードメディア編集部</a>
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-model-building" class="external-link" target="_blank">【第2回】FastAPIチュートリアル: ToDoアプリを作ってみよう【モデル構築編】</a> by <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun" class="external-link" target="_blank">ライトコードメディア編集部</a>
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-authentication-user-registration" class="external-link" target="_blank">【第3回】FastAPIチュートリアル: toDoアプリを作ってみよう【認証・ユーザ登録編】</a> by <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun" class="external-link" target="_blank">ライトコードメディア編集部</a>
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/blog/information-technology/fastapi-tutorial-todo-apps-admin-page-improvement" class="external-link" target="_blank">【第4回】FastAPIチュートリアル: toDoアプリを作ってみよう【管理者ページ改良編】</a> by <a href="https://rightcode.co.jp/author/jun" class="external-link" target="_blank">ライトコードメディア編集部</a>
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/bee2/items/0ad260ab9835a2087dae" class="external-link" target="_blank">PythonのWeb frameworkのパフォーマンス比較 (Django, Flask, responder, FastAPI, japronto)</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/bee2" class="external-link" target="_blank">@bee2</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://qiita.com/bee2/items/75d9c0d7ba20e7a4a0e9" class="external-link" target="_blank">[FastAPI] Python製のASGI Web フレームワーク FastAPIに入門する</a> by <a href="https://qiita.com/bee2" class="external-link" target="_blank">@bee2</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Chinese
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1431448" class="external-link" target="_blank">使用FastAPI框架快速构建高性能的api服务</a> by <a href="https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/user/5471722" class="external-link" target="_blank">逍遥散人</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://wxq0309.github.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI框架中文文档</a> by <a href="https://wxq0309.github.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">何大仙</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="{{ article.link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.title }}</a> by <a href="{{ article.author_link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.author }}</a>.
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Vietnamese
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://fullstackstation.com/fastapi-trien-khai-bang-docker/" class="external-link" target="_blank">FASTAPI: TRIỂN KHAI BẰNG DOCKER</a> by <a href="https://fullstackstation.com/author/figonking/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nguyễn Nhân</a>.
|
||||
{% if external_links %}
|
||||
{% for article in external_links.articles.vietnamese %}
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="{{ article.link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.title }}</a> by <a href="{{ article.author_link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.author }}</a>.
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### Russian
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://habr.com/ru/post/454440/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Мелкая питонячая радость #2: Starlette - Солидная примочка – FastAPI</a> by <a href="https://habr.com/ru/users/57uff3r/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Andrey Korchak</a>.
|
||||
{% if external_links %}
|
||||
{% for article in external_links.articles.russian %}
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://habr.com/ru/post/478620/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Почему Вы должны попробовать FastAPI?</a> by <a href="https://github.com/prostomarkeloff" class="external-link" target="_blank">prostomarkeloff</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="{{ article.link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.title }}</a> by <a href="{{ article.author_link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.author }}</a>.
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
### German
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://blog.codecentric.de/2019/08/inbetriebnahme-eines-scikit-learn-modells-mit-onnx-und-fastapi/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Inbetriebnahme eines scikit-learn-Modells mit ONNX und FastAPI</a> by <a href="https://twitter.com/_nicoax" class="external-link" target="_blank">Nico Axtmann</a>.
|
||||
{% if external_links %}
|
||||
{% for article in external_links.articles.german %}
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="{{ article.link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.title }}</a> by <a href="{{ article.author_link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.author }}</a>.
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
## Podcasts
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://pythonbytes.fm/episodes/show/123/time-to-right-the-py-wrongs?time_in_sec=855" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI on PythonBytes</a> by <a href="https://pythonbytes.fm/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Python Bytes FM</a>.
|
||||
{% if external_links %}
|
||||
{% for article in external_links.podcasts.english %}
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="{{ article.link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.title }}</a> by <a href="{{ article.author_link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.author }}</a>.
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
## Talks
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3DLwPcrE5mA" class="external-link" target="_blank">PyCon UK 2019: FastAPI from the ground up</a> by <a href="https://twitter.com/chriswithers13" class="external-link" target="_blank">Chris Withers</a>.
|
||||
{% if external_links %}
|
||||
{% for article in external_links.talks.english %}
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="{{ article.link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.title }}</a> by <a href="{{ article.author_link }}" class="external-link" target="_blank">{{ article.author }}</a>.
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
|
||||
## Projects
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ my_second_user: User = User(**second_user_data)
|
||||
|
||||
### Editor support
|
||||
|
||||
All the framework was designed to be easy and intuitive to use, all the decisions where tested on multiple editors even before starting development, to ensure the best development experience.
|
||||
All the framework was designed to be easy and intuitive to use, all the decisions were tested on multiple editors even before starting development, to ensure the best development experience.
|
||||
|
||||
In the last Python developer survey it was clear <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/research/python-developers-survey-2017/#tools-and-features" class="external-link" target="_blank">that the most used feature is "autocompletion"</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,28 +12,18 @@ And there are several ways to get help too.
|
||||
|
||||
## Star **FastAPI** in GitHub
|
||||
|
||||
You can "star" FastAPI in GitHub (clicking the star button at the top right): <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi</a>.
|
||||
You can "star" FastAPI in GitHub (clicking the star button at the top right): <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi</a>. ⭐️
|
||||
|
||||
By adding a star, other users will be able to find it more easily and see that it has been already useful for others.
|
||||
|
||||
## Watch the GitHub repository for releases
|
||||
|
||||
You can "watch" FastAPI in GitHub (clicking the "watch" button at the top right): <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi</a>.
|
||||
You can "watch" FastAPI in GitHub (clicking the "watch" button at the top right): <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi</a>. 👀
|
||||
|
||||
There you can select "Releases only".
|
||||
|
||||
Doing it, you will receive notifications (in your email) whenever there's a new release (a new version) of **FastAPI** with bug fixes and new features.
|
||||
|
||||
## Join the chat
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://badges.gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi.svg" alt="Join the chat at https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Join the chat on Gitter: <a href="https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
There you can ask quick questions, help others, share ideas, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
## Connect with the author
|
||||
|
||||
You can connect with <a href="https://tiangolo.com" class="external-link" target="_blank">me (Sebastián Ramírez / `tiangolo`)</a>, the author.
|
||||
@@ -45,40 +35,32 @@ You can:
|
||||
* Follow me to see when I create a new Open Source project.
|
||||
* <a href="https://twitter.com/tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">Follow me on **Twitter**</a>.
|
||||
* Tell me how you use FastAPI (I love to hear that).
|
||||
* Ask questions.
|
||||
* Hear when I make announcements or release new tools.
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/tiangolo/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Connect with me on **Linkedin**</a>.
|
||||
* Talk to me.
|
||||
* Endorse me or recommend me :)
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">Read what I write (or follow me) on **Medium**</a>.
|
||||
* Read other ideas, articles and tools I have created.
|
||||
* Follow me to see when I publish something new.
|
||||
* Hear when I make announcements or release new tools (although I use Twitter more often 🤷♂).
|
||||
* Read what I write (or follow me) on <a href="https://dev.to/tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">**Dev.to**</a> or <a href="https://medium.com/@tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">**Medium**</a>.
|
||||
* Read other ideas, articles, and about tools I have created.
|
||||
* Follow me to read when I publish something new.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tweet about **FastAPI**
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://twitter.com/compose/tweet?text=I'm loving FastAPI because... https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi cc @tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">Tweet about **FastAPI**</a> and let me and others know why you like it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Let me know how are you using **FastAPI**
|
||||
<a href="https://twitter.com/compose/tweet?text=I'm loving FastAPI because... https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi cc @tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">Tweet about **FastAPI**</a> and let me and others know why you like it. 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
I love to hear about how **FastAPI** is being used, what have you liked in it, in which project/company are you using it, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
You can let me know:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://twitter.com/compose/tweet?text=Hey @tiangolo, I'm using FastAPI at..." class="external-link" target="_blank">On **Twitter**</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.linkedin.com/in/tiangolo/" class="external-link" target="_blank">On **Linkedin**</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://medium.com/@tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">On **Medium**</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Vote for FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/vinta/awesome-python/pull/1209" class="external-link" target="_blank">Vote to include **FastAPI** in `awesome-python`</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.slant.co/options/34241/~fastapi-review" class="external-link" target="_blank">Vote for **FastAPI** in Slant</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://alternativeto.net/software/fastapi/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Vote for **FastAPI** in AlternativeTo</a>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/marmelab/awesome-rest/pull/93" class="external-link" target="_blank">Vote for **FastAPI** on awesome-rest</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Help others with issues in GitHub
|
||||
|
||||
You can see <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/issues" class="external-link" target="_blank">existing issues</a> and try and help others.
|
||||
You can see <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/issues" class="external-link" target="_blank">existing issues</a> and try and help others, most of the times they are questions that you might already know the answer for. 🤓
|
||||
|
||||
## Watch the GitHub repository
|
||||
|
||||
You can "watch" FastAPI in GitHub (clicking the "watch" button at the top right): <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi</a>.
|
||||
You can "watch" FastAPI in GitHub (clicking the "watch" button at the top right): <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi</a>. 👀
|
||||
|
||||
If you select "Watching" instead of "Releases only", you will receive notifications when someone creates a new issue.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -88,9 +70,10 @@ Then you can try and help them solving those issues.
|
||||
|
||||
You can <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/issues/new/choose" class="external-link" target="_blank">create a new issue</a> in the GitHub repository, for example to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Report a bug/issue.
|
||||
* Ask a question or ask about a problem.
|
||||
* Suggest a new feature.
|
||||
* Ask a question.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: if you create an issue then I'm going to ask you to also help others. 😉
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a Pull Request
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -101,6 +84,39 @@ You can <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" targ
|
||||
* To fix an existing issue/bug.
|
||||
* To add a new feature.
|
||||
|
||||
## Join the chat
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://badges.gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi.svg" alt="Join the chat at https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Join the chat on Gitter: <a href="https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
There you can have quick conversations with others, help others, share ideas, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
But have in mind that as it allows more "free conversation", it's easy to ask questions that are too general and more difficult to answer, so, you might not receive answers.
|
||||
|
||||
In GitHub issues the template will guide to to write the right question so that you can more easily get a good answer, or even solve the problem yourself even before asking. And in GitHub I can make sure I always answer everything, even if it takes some time. I can't personally do that with the Gitter chat. 😅
|
||||
|
||||
Conversations in Gitter are also not as easily searchable as in GitHub, so questions and answers might get lost in the conversation.
|
||||
|
||||
On the other side, there's more than 1000 people in the chat, so there's a high chance you'll find someone to talk to there, almost all the time. 😄
|
||||
|
||||
## Sponsor the author
|
||||
|
||||
You can also financially support the author (me) through <a href="https://github.com/sponsors/tiangolo" class="external-link" target="_blank">GitHub sponsors</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
There you could buy me a coffee ☕️ to say thanks 😄.
|
||||
|
||||
## Sponsor the tools that power FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
As you have seen in the documentation, FastAPI stands on the shoulders of giants, Starlette and Pydantic.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also sponsor:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/sponsors/samuelcolvin" class="external-link" target="_blank">Samuel Colvin (Pydantic)</a>
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/sponsors/encode" class="external-link" target="_blank">Encode (Starlette, Uvicorn)</a>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks!
|
||||
Thanks! 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 80 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 71 KiB |
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/tutorial/behind-a-proxy/image01.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 28 KiB |
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/tutorial/behind-a-proxy/image02.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 61 KiB |
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/tutorial/behind-a-proxy/image03.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 72 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 37 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 37 KiB |
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/tutorial/metadata/image02.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 47 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 79 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 88 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 82 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 82 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 79 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 80 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 86 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 87 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 79 KiB After Width: | Height: | Size: 76 KiB |
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/tutorial/websockets/image05.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 52 KiB |
@@ -5,14 +5,14 @@
|
||||
<em>FastAPI framework, high performance, easy to learn, fast to code, ready for production</em>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://travis-ci.com/tiangolo/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://travis-ci.com/tiangolo/fastapi.svg?branch=master" alt="Build Status">
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/actions?query=workflow%3ATest" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/workflows/Test/badge.svg" alt="Test">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://codecov.io/gh/tiangolo/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://img.shields.io/codecov/c/github/tiangolo/fastapi" alt="Coverage">
|
||||
<img src="https://img.shields.io/codecov/c/github/tiangolo/fastapi?color=%2334D058" alt="Coverage">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pypi.org/project/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://badge.fury.io/py/fastapi.svg" alt="Package version">
|
||||
<img src="https://img.shields.io/pypi/v/fastapi?color=%2334D058&label=pypi%20package" alt="Package version">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://badges.gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi.svg" alt="Join the chat at https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi">
|
||||
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ The key features are:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Fast**: Very high performance, on par with **NodeJS** and **Go** (thanks to Starlette and Pydantic). [One of the fastest Python frameworks available](#performance).
|
||||
|
||||
* **Fast to code**: Increase the speed to develop features by about 200% to 300% *.
|
||||
* **Fast to code**: Increase the speed to develop features by about 200% to 300%. *
|
||||
* **Fewer bugs**: Reduce about 40% of human (developer) induced errors. *
|
||||
* **Intuitive**: Great editor support. <abbr title="also known as auto-complete, autocompletion, IntelliSense">Completion</abbr> everywhere. Less time debugging.
|
||||
* **Easy**: Designed to be easy to use and learn. Less time reading docs.
|
||||
@@ -45,38 +45,44 @@ The key features are:
|
||||
|
||||
## Opinions
|
||||
|
||||
"*[...] I'm using **FastAPI** a ton these days. [...] I'm actually planning to use it for all of my team's **ML services at Microsoft**. Some of them are getting integrated into the core **Windows** product and some **Office** products.*"
|
||||
"_[...] I'm using **FastAPI** a ton these days. [...] I'm actually planning to use it for all of my team's **ML services at Microsoft**. Some of them are getting integrated into the core **Windows** product and some **Office** products._"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Kabir Khan - <strong>Microsoft</strong> <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/26" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*I’m over the moon excited about **FastAPI**. It’s so fun!*"
|
||||
"_We adopted the **FastAPI** library to spawn a **REST** server that can be queried to obtain **predictions**. [for Ludwig]_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Piero Molino, Yaroslav Dudin, and Sai Sumanth Miryala - <strong>Uber</strong> <a href="https://eng.uber.com/ludwig-v0-2/" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"_**Netflix** is pleased to announce the open-source release of our **crisis management** orchestration framework: **Dispatch**! [built with **FastAPI**]_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Kevin Glisson, Marc Vilanova, Forest Monsen - <strong>Netflix</strong> <a href="https://netflixtechblog.com/introducing-dispatch-da4b8a2a8072" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"_I’m over the moon excited about **FastAPI**. It’s so fun!_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Brian Okken - <strong><a href="https://pythonbytes.fm/episodes/show/123/time-to-right-the-py-wrongs?time_in_sec=855" target="_blank">Python Bytes</a> podcast host</strong> <a href="https://twitter.com/brianokken/status/1112220079972728832" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*Honestly, what you've built looks super solid and polished. In many ways, it's what I wanted **Hug** to be - it's really inspiring to see someone build that.*"
|
||||
"_Honestly, what you've built looks super solid and polished. In many ways, it's what I wanted **Hug** to be - it's really inspiring to see someone build that._"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Timothy Crosley - <strong><a href="http://www.hug.rest/" target="_blank">Hug</a> creator</strong> <a href="https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=19455465" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*If you're looking to learn one **modern framework** for building REST APIs, check out **FastAPI** [...] It's fast, easy to use and easy to learn [...]*"
|
||||
"_If you're looking to learn one **modern framework** for building REST APIs, check out **FastAPI** [...] It's fast, easy to use and easy to learn [...]_"
|
||||
|
||||
"*We've switched over to **FastAPI** for our **APIs** [...] I think you'll like it [...]*"
|
||||
"_We've switched over to **FastAPI** for our **APIs** [...] I think you'll like it [...]_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Ines Montani - Matthew Honnibal - <strong><a href="https://explosion.ai" target="_blank">Explosion AI</a> founders - <a href="https://spacy.io" target="_blank">spaCy</a> creators</strong> <a href="https://twitter.com/_inesmontani/status/1144173225322143744" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a> - <a href="https://twitter.com/honnibal/status/1144031421859655680" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*We adopted the **FastAPI** library to spawn a **REST** server that can be queried to obtain **predictions**. [for Ludwig]*"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Piero Molino, Yaroslav Dudin, and Sai Sumanth Miryala - <strong>Uber</strong> <a href="https://eng.uber.com/ludwig-v0-2/" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## **Typer**, the FastAPI of CLIs
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com" target="_blank"><img src="https://typer.tiangolo.com/img/logo-margin/logo-margin-vector.svg" style="width: 20%;"></a>
|
||||
@@ -125,6 +131,8 @@ $ pip install uvicorn
|
||||
* Create a file `main.py` with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
@@ -136,7 +144,7 @@ def read_root():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -145,7 +153,9 @@ def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
|
||||
If your code uses `async` / `await`, use `async def`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7 12"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 14"
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
@@ -157,7 +167,7 @@ async def read_root():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
async def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
async def read_item(item_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -176,11 +186,11 @@ Run the server with:
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --reload
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Started reloader process [28720]
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Started server process [28722]
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Waiting for application startup.
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Application startup complete.
|
||||
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
INFO: Started reloader process [28720]
|
||||
INFO: Started server process [28722]
|
||||
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
|
||||
INFO: Application startup complete.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
@@ -235,7 +245,9 @@ Now modify the file `main.py` to receive a body from a `PUT` request.
|
||||
|
||||
Declare the body using standard Python types, thanks to Pydantic.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 7 8 9 10 23 24 25"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 9 10 11 12 25 26 27"
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -245,7 +257,7 @@ app = FastAPI()
|
||||
class Item(BaseModel):
|
||||
name: str
|
||||
price: float
|
||||
is_offer: bool = None
|
||||
is_offer: Optional[bool] = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/")
|
||||
@@ -254,7 +266,7 @@ def read_root():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ function setupTermynal() {
|
||||
|
||||
function createTermynals() {
|
||||
document
|
||||
.querySelectorAll(`.${termynalActivateClass} .codehilite`)
|
||||
.querySelectorAll(`.${termynalActivateClass} .highlight`)
|
||||
.forEach(node => {
|
||||
const text = node.textContent;
|
||||
const lines = text.split("\n");
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,16 +1,18 @@
|
||||
# Project Generation - Template
|
||||
|
||||
There is a project generator that you can use to get started, with a lot of the initial set up, security, database and first API endpoints already done for you.
|
||||
You can use a project generator to get started, as it includes a lot of the initial set up, security, database and first API endpoints already done for you.
|
||||
|
||||
## Full-Stack-FastAPI-PostgreSQL
|
||||
A project generator will always have a very opinionated setup that you should update and adapt for your own needs, but it might be a good starting point for your project.
|
||||
|
||||
## Full Stack FastAPI PostgreSQL
|
||||
|
||||
GitHub: <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-postgresql" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-postgresql</a>
|
||||
|
||||
### Full-Stack-FastAPI-PostgreSQL Features
|
||||
### Full Stack FastAPI PostgreSQL - Features
|
||||
|
||||
* Full **Docker** integration (Docker based).
|
||||
* Docker Swarm Mode deployment.
|
||||
* **Docker Compose** integration and optimization for local development
|
||||
* **Docker Compose** integration and optimization for local development.
|
||||
* **Production ready** Python web server using Uvicorn and Gunicorn.
|
||||
* Python <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">**FastAPI**</a> backend:
|
||||
* **Fast**: Very high performance, on par with **NodeJS** and **Go** (thanks to Starlette and Pydantic).
|
||||
@@ -19,14 +21,14 @@ GitHub: <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-postgresql" clas
|
||||
* **Short**: Minimize code duplication. Multiple features from each parameter declaration.
|
||||
* **Robust**: Get production-ready code. With automatic interactive documentation.
|
||||
* **Standards-based**: Based on (and fully compatible with) the open standards for APIs: <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI</a> and <a href="http://json-schema.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">JSON Schema</a>.
|
||||
* Many other features including automatic validation, serialization, interactive documentation, authentication with OAuth2 JWT tokens, etc.
|
||||
* <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/features/" class="external-link" target="_blank">**Many other features**</a> including automatic validation, serialization, interactive documentation, authentication with OAuth2 JWT tokens, etc.
|
||||
* **Secure password** hashing by default.
|
||||
* **JWT token** authentication.
|
||||
* **SQLAlchemy** models (independent of Flask extensions, so they can be used with Celery workers directly).
|
||||
* Basic starting models for users (modify and remove as you need).
|
||||
* **Alembic** migrations.
|
||||
* **CORS** (Cross Origin Resource Sharing).
|
||||
* **Celery** worker that can import and use models and code from the rest of the backend selectively (you don't have to install the complete app in each worker).
|
||||
* **Celery** worker that can import and use models and code from the rest of the backend selectively.
|
||||
* REST backend tests based on **Pytest**, integrated with Docker, so you can test the full API interaction, independent on the database. As it runs in Docker, it can build a new data store from scratch each time (so you can use ElasticSearch, MongoDB, CouchDB, or whatever you want, and just test that the API works).
|
||||
* Easy Python integration with **Jupyter Kernels** for remote or in-Docker development with extensions like Atom Hydrogen or Visual Studio Code Jupyter.
|
||||
* **Vue** frontend:
|
||||
@@ -50,53 +52,33 @@ GitHub: <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-postgresql" clas
|
||||
* Traefik integration, including Let's Encrypt **HTTPS** certificates automatic generation.
|
||||
* GitLab **CI** (continuous integration), including frontend and backend testing.
|
||||
|
||||
## Full-Stack-FastAPI-Couchbase
|
||||
## Full Stack FastAPI Couchbase
|
||||
|
||||
GitHub: <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-couchbase" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-couchbase</a>
|
||||
|
||||
### Full-Stack-FastAPI-Couchbase Features
|
||||
⚠️ **WARNING** ⚠️
|
||||
|
||||
* Full **Docker** integration (Docker based).
|
||||
* Docker Swarm Mode deployment.
|
||||
* **Docker Compose** integration and optimization for local development.
|
||||
If you are starting a new project from scratch, check the alternatives here.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, the project generator <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-postgresql" class="external-link" target="_blank">Full Stack FastAPI PostgreSQL</a> might be a better alternative, as it is actively maintained and used. And it includes all the new features and improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
You are still free to use the Couchbase-based generator if you want to, it should probably still work fine, and if you already have a project generated with it that's fine as well (and you probably already updated it to suit your needs).
|
||||
|
||||
You can read more about it in the docs for the repo.
|
||||
|
||||
## Full Stack FastAPI MongoDB
|
||||
|
||||
...might come later, depending on my time availability and other factors. 😅 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
## Machine Learning models with spaCy and FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
GitHub: <a href="https://github.com/microsoft/cookiecutter-spacy-fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://github.com/microsoft/cookiecutter-spacy-fastapi</a>
|
||||
|
||||
### Machine Learning models with spaCy and FastAPI - Features
|
||||
|
||||
* **spaCy** NER model integration.
|
||||
* **Azure Cognitive Search** request format built in.
|
||||
* **Production ready** Python web server using Uvicorn and Gunicorn.
|
||||
* Python <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" class="external-link" target="_blank">**FastAPI**</a> backend:
|
||||
* **Fast**: Very high performance, on par with **NodeJS** and **Go** (thanks to Starlette and Pydantic).
|
||||
* **Intuitive**: Great editor support. <abbr title="also known as auto-complete, autocompletion, IntelliSense">Completion</abbr> everywhere. Less time debugging.
|
||||
* **Easy**: Designed to be easy to use and learn. Less time reading docs.
|
||||
* **Short**: Minimize code duplication. Multiple features from each parameter declaration.
|
||||
* **Robust**: Get production-ready code. With automatic interactive documentation.
|
||||
* **Standards-based**: <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI</a> and <a href="http://json-schema.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">JSON Schema</a>.
|
||||
* Many other features including automatic validation, serialization, interactive documentation, authentication with OAuth2 JWT tokens, etc.
|
||||
* **Secure password** hashing by default.
|
||||
* **JWT token** authentication.
|
||||
* **CORS** (Cross Origin Resource Sharing).
|
||||
* **Celery** worker that can import and use code from the rest of the backend selectively (you don't have to install the complete app in each worker).
|
||||
* **NoSQL Couchbase** database that supports direct synchronization via Couchbase Sync Gateway for offline-first applications.
|
||||
* **Full Text Search** integrated, using Couchbase.
|
||||
* REST backend tests based on Pytest, integrated with Docker, so you can test the full API interaction, independent on the database. As it runs in Docker, it can build a new data store from scratch each time (so you can use ElasticSearch, MongoDB, or whatever you want, and just test that the API works).
|
||||
* Easy Python integration with **Jupyter** Kernels for remote or in-Docker development with extensions like Atom Hydrogen or Visual Studio Code Jupyter.
|
||||
* **Email notifications** for account creation and password recovery, compatible with:
|
||||
* Mailgun
|
||||
* SparkPost
|
||||
* SendGrid
|
||||
* ...any other provider that can generate standard SMTP credentials.
|
||||
* **Vue** frontend:
|
||||
* Generated with Vue CLI.
|
||||
* **JWT Authentication** handling.
|
||||
* Login view.
|
||||
* After login, main dashboard view.
|
||||
* Main dashboard with user creation and edition.
|
||||
* Self user edition.
|
||||
* **Vuex**.
|
||||
* **Vue-router**.
|
||||
* **Vuetify** for beautiful material design components.
|
||||
* **TypeScript**.
|
||||
* Docker server based on **Nginx** (configured to play nicely with Vue-router).
|
||||
* Docker multi-stage building, so you don't need to save or commit compiled code.
|
||||
* Frontend tests ran at build time (can be disabled too).
|
||||
* Made as modular as possible, so it works out of the box, but you can re-generate with Vue CLI or create it as you need, and re-use what you want.
|
||||
* **Flower** for Celery jobs monitoring.
|
||||
* Load balancing between frontend and backend with **Traefik**, so you can have both under the same domain, separated by path, but served by different containers.
|
||||
* Traefik integration, including Let's Encrypt **HTTPS** certificates automatic generation.
|
||||
* GitLab **CI** (continuous integration), including frontend and backend testing.
|
||||
* **Azure DevOps** Kubernetes (AKS) CI/CD deployment built in.
|
||||
* **Multilingual** Easily choose one of spaCy's built in languages during project setup.
|
||||
* **Easily extensible** to other model frameworks (Pytorch, Tensorflow), not just spaCy.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -144,15 +144,15 @@ You can use, for example:
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Types with subtypes
|
||||
### Generic types with type parameters
|
||||
|
||||
There are some data structures that can contain other values, like `dict`, `list`, `set` and `tuple`. And the internal values can have their own type too.
|
||||
|
||||
To declare those types and the subtypes, you can use the standard Python module `typing`.
|
||||
To declare those types and the internal types, you can use the standard Python module `typing`.
|
||||
|
||||
It exists specifically to support these type hints.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Lists
|
||||
#### `List`
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let's define a variable to be a `list` of `str`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -166,25 +166,30 @@ Declare the variable, with the same colon (`:`) syntax.
|
||||
|
||||
As the type, put the `List`.
|
||||
|
||||
As the list is a type that takes a "subtype", you put the subtype in square brackets:
|
||||
As the list is a type that contains some internal types, you put them in square brackets:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial006.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Those internal types in the square brackets are called "type parameters".
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, `str` is the type parameter passed to `List`.
|
||||
|
||||
That means: "the variable `items` is a `list`, and each of the items in this list is a `str`".
|
||||
|
||||
By doing that, your editor can provide support even while processing items from the list.
|
||||
|
||||
Without types, that's almost impossible to achieve:
|
||||
By doing that, your editor can provide support even while processing items from the list:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/python-types/image05.png">
|
||||
|
||||
Without types, that's almost impossible to achieve.
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that the variable `item` is one of the elements in the list `items`.
|
||||
|
||||
And still, the editor knows it is a `str`, and provides support for that.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tuples and Sets
|
||||
#### `Tuple` and `Set`
|
||||
|
||||
You would do the same to declare `tuple`s and `set`s:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -194,16 +199,16 @@ You would do the same to declare `tuple`s and `set`s:
|
||||
|
||||
This means:
|
||||
|
||||
* The variable `items_t` is a `tuple`, and each of its items is an `int`.
|
||||
* The variable `items_t` is a `tuple` with 3 items, an `int`, another `int`, and a `str`.
|
||||
* The variable `items_s` is a `set`, and each of its items is of type `bytes`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Dicts
|
||||
#### `Dict`
|
||||
|
||||
To define a `dict`, you pass 2 subtypes, separated by commas.
|
||||
To define a `dict`, you pass 2 type parameters, separated by commas.
|
||||
|
||||
The first subtype is for the keys of the `dict`.
|
||||
The first type parameter is for the keys of the `dict`.
|
||||
|
||||
The second subtype is for the values of the `dict`:
|
||||
The second type parameter is for the values of the `dict`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 4"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial008.py!}
|
||||
@@ -215,6 +220,29 @@ This means:
|
||||
* The keys of this `dict` are of type `str` (let's say, the name of each item).
|
||||
* The values of this `dict` are of type `float` (let's say, the price of each item).
|
||||
|
||||
#### `Optional`
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use `Optional` to declare that a variable has a type, like `str`, but that it is "optional", which means that it could also be `None`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 4"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial009.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Using `Optional[str]` instead of just `str` will let the editor help you detecting errors where you could be assuming that a value is always a `str`, when it could actually be `None` too.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Generic types
|
||||
|
||||
These types that take type parameters in square brackets, like:
|
||||
|
||||
* `List`
|
||||
* `Tuple`
|
||||
* `Set`
|
||||
* `Dict`
|
||||
* `Optional`
|
||||
* ...and others.
|
||||
|
||||
are called **Generic types** or **Generics**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Classes as types
|
||||
|
||||
You can also declare a class as the type of a variable.
|
||||
@@ -222,13 +250,13 @@ You can also declare a class as the type of a variable.
|
||||
Let's say you have a class `Person`, with a name:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 2 3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial009.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial010.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can declare a variable to be of type `Person`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial009.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial010.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And then, again, you get all the editor support:
|
||||
@@ -250,7 +278,7 @@ And you get all the editor support with that resulting object.
|
||||
Taken from the official Pydantic docs:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial010.py!}
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial011.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,6 +2,199 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## Latest changes
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.60.1
|
||||
|
||||
* Add debugging logs for GitHub actions to introspect GitHub hidden context. PR [#1764](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1764).
|
||||
* Use OS preference theme for online docs. PR [#1760](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1760) by [@https://github.com/adriencaccia](https://github.com/adriencaccia).
|
||||
* Upgrade Starlette to version `0.13.6` to handle a vulnerability when using static files in Windows. PR [#1759](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1759) by [@jamesag26](https://github.com/jamesag26).
|
||||
* Pin Swagger UI temporarily, waiting for a fix for [swagger-api/swagger-ui#6249](https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui/issues/6249). PR [#1763](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1763).
|
||||
* Update GitHub Actions, use commit from PR for docs preview, not commit from pre-merge. PR [#1761](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1761).
|
||||
* Update GitHub Actions, refactor Gitter bot. PR [#1746](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1746).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.60.0
|
||||
|
||||
* Add GitHub Action to watch for missing preview docs and trigger a preview deploy. PR [#1740](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1740).
|
||||
* Add custom GitHub Action to get artifact with docs preview. PR [#1739](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1739).
|
||||
* Add new GitHub Actions to preview docs from PRs. PR [#1738](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1738).
|
||||
* Add XML test coverage to support GitHub Actions. PR [#1737](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1737).
|
||||
* Update badges and remove Travis now that GitHub Actions is the main CI. PR [#1736](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1736).
|
||||
* Add GitHub Actions for CI, move from Travis. PR [#1735](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1735).
|
||||
* Add support for adding OpenAPI schema for GET requests with a body. PR [#1626](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1626) by [@victorphoenix3](https://github.com/victorphoenix3).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.59.0
|
||||
|
||||
* Fix typo in docstring for OAuth2 utils. PR [#1621](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1621) by [@tomarv2](https://github.com/tomarv2).
|
||||
* Update JWT docs to use Python-jose instead of PyJWT. Initial PR [#1610](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1610) by [@asheux](https://github.com/asheux).
|
||||
* Fix/re-enable search bar in docs. PR [#1703](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1703).
|
||||
* Auto-generate a "server" in OpenAPI `servers` when there's a `root_path` instead of prefixing all the `paths`:
|
||||
* Add a new parameter for `FastAPI` classes: `root_path_in_servers` to disable the auto-generation of `servers`.
|
||||
* New docs about `root_path` and `servers` in [Additional Servers](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/advanced/behind-a-proxy/#additional-servers).
|
||||
* Update OAuth2 examples to use a relative URL for `tokenUrl="token"` to make sure those examples keep working as-is even when behind a reverse proxy.
|
||||
* Initial PR [#1596](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1596) by [@rkbeatss](https://github.com/rkbeatss).
|
||||
* Fix typo/link in External Links. PR [#1702](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1702).
|
||||
* Update handling of [External Links](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/external-links/) to use a data file and allow translating the headers without becoming obsolete quickly when new links are added. PR [#https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1701](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1701).
|
||||
* Add external link [Machine learning model serving in Python using FastAPI and Streamlit](https://davidefiocco.github.io/2020/06/27/streamlit-fastapi-ml-serving.html) to docs. PR [#1669](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1669) by [@davidefiocco](https://github.com/davidefiocco).
|
||||
* Add note in docs on order in Pydantic Unions. PR [#1591](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1591) by [@kbanc](https://github.com/kbanc).
|
||||
* Improve support for tests in editor. PR [#1699](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1699).
|
||||
* Pin dependencies. PR [#1697](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1697).
|
||||
* Update isort to version 5.x.x. PR [#1670](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1670) by [@asheux](https://github.com/asheux).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.58.1
|
||||
|
||||
* Add link in docs to Pydantic data types. PR [#1612](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1612) by [@tayoogunbiyi](https://github.com/tayoogunbiyi).
|
||||
* Fix link in warning logs for `openapi_prefix`. PR [#1611](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1611) by [@bavaria95](https://github.com/bavaria95).
|
||||
* Fix bad link in docs. PR [#1603](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1603) by [@molto0504](https://github.com/molto0504).
|
||||
* Add Vim temporary files to `.gitignore` for contributors using Vim. PR [#1590](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1590) by [@asheux](https://github.com/asheux).
|
||||
* Fix typo in docs for sub-applications. PR [#1578](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1578) by [@schlpbch](https://github.com/schlpbch).
|
||||
* Use `Optional` in all the examples in the docs. Original PR [#1574](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1574) by [@chrisngyn](https://github.com/chrisngyn), [@kx-chen](https://github.com/kx-chen), [@YKo20010](https://github.com/YKo20010). Updated and merged PR [#1644](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1644).
|
||||
* Update tests and handling of `response_model_by_alias`. PR [#1642](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1642).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Body - Fields - 请求体 - 字段](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/tutorial/body-fields/). PR [#1569](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1569) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Update Chinese translation of main page. PR [#1564](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1564) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Body - Multiple Parameters - 请求体 - 多个参数](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/tutorial/body-multiple-params/). PR [#1532](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1532) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Path Parameters and Numeric Validations - 路径参数和数值校验](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/tutorial/path-params-numeric-validations/). PR [#1506](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1506) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Add GitHub action to auto-label approved PRs (mainly for translations). PR [#1638](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1638).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.58.0
|
||||
|
||||
* Deep merge OpenAPI responses to preserve all the additional metadata. PR [#1577](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1577).
|
||||
* Mention in docs that only main app events are run (not sub-apps). PR [#1554](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1554) by [@amacfie](https://github.com/amacfie).
|
||||
* Fix body validation error response, do not include body variable when it is not embedded. PR [#1553](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1553) by [@amacfie](https://github.com/amacfie).
|
||||
* Fix testing OAuth2 security scopes when using dependency overrides. PR [#1549](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1549) by [@amacfie](https://github.com/amacfie).
|
||||
* Fix Model for JSON Schema keyword `not` as a JSON Schema instead of a list. PR [#1548](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1548) by [@v-do](https://github.com/v-do).
|
||||
* Add support for OpenAPI `servers`. PR [#1547](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1547) by [@mikaello](https://github.com/mikaello).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.57.0
|
||||
|
||||
* Remove broken link from "External Links". PR [#1565](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1565) by [@victorphoenix3](https://github.com/victorphoenix3).
|
||||
* Update/fix docs for [WebSockets with dependencies](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/advanced/websockets/#using-depends-and-others). Original PR [#1540](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1540) by [@ChihSeanHsu](https://github.com/ChihSeanHsu).
|
||||
* Add support for Python's `http.HTTPStatus` in `status_code` parameters. PR [#1534](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1534) by [@retnikt](https://github.com/retnikt).
|
||||
* When using Pydantic models with `__root__`, use the internal value in `jsonable_encoder`. PR [#1524](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1524) by [@patrickkwang](https://github.com/patrickkwang).
|
||||
* Update docs for path parameters. PR [#1521](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1521) by [@yankeexe](https://github.com/yankeexe).
|
||||
* Update docs for first steps, links and rewording. PR [#1518](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1518) by [@yankeexe](https://github.com/yankeexe).
|
||||
* Enable `showCommonExtensions` in Swagger UI to show additional validations like `maxLength`, etc. PR [#1466](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1466) by [@TiewKH](https://github.com/TiewKH).
|
||||
* Make `OAuth2PasswordRequestFormStrict` importable directly from `fastapi.security`. PR [#1462](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1462) by [@RichardHoekstra](https://github.com/RichardHoekstra).
|
||||
* Add docs about [Default response class](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/advanced/custom-response/#default-response-class). PR [#1455](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1455) by [@TezRomacH](https://github.com/TezRomacH).
|
||||
* Add note in docs about additional parameters `response_model_exclude_defaults` and `response_model_exclude_none` in [Response Model](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/response-model/#use-the-response_model_exclude_unset-parameter). PR [#1427](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1427) by [@wshayes](https://github.com/wshayes).
|
||||
* Add note about [PyCharm Pydantic plugin](https://github.com/koxudaxi/pydantic-pycharm-plugin) to docs. PR [#1420](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1420) by [@koxudaxi](https://github.com/koxudaxi).
|
||||
* Update and clarify testing function name. PR [#1395](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1395) by [@chenl](https://github.com/chenl).
|
||||
* Fix duplicated headers created by indirect dependencies that use the request directly. PR [#1386](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1386) by [@obataku](https://github.com/obataku) from tests by [@scottsmith2gmail](https://github.com/scottsmith2gmail).
|
||||
* Upgrade Starlette version to `0.13.4`. PR [#1361](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1361) by [@rushton](https://github.com/rushton).
|
||||
* Improve error handling and feedback for requests with invalid JSON. PR [#1354](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1354) by [@aviramha](https://github.com/aviramha).
|
||||
* Add support for declaring metadata for tags in OpenAPI. New docs at [Tutorial - Metadata and Docs URLs - Metadata for tags](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/metadata/#metadata-for-tags). PR [#1348](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1348) by [@thomas-maschler](https://github.com/thomas-maschler).
|
||||
* Add basic setup for Russian translations. PR [#1566](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1566).
|
||||
* Remove obsolete Chinese articles after adding official community translations. PR [#1510](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1510) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Add `__repr__` for *path operation function* parameter helpers (like `Query`, `Depends`, etc) to simplify debugging. PR [#1560](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1560) by [@rkbeatss](https://github.com/rkbeatss) and [@victorphoenix3](https://github.com/victorphoenix3).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.56.1
|
||||
|
||||
* Add link to advanced docs from tutorial. PR [#1512](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1512) by [@kx-chen](https://github.com/kx-chen).
|
||||
* Remove internal unnecessary f-strings. PR [#1526](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1526) by [@kotamatsuoka](https://github.com/kotamatsuoka).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Query Parameters and String Validations - 查询参数和字符串校验](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/tutorial/query-params-str-validations/). PR [#1500](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1500) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Request Body - 请求体](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/tutorial/body/). PR [#1492](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1492) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Help FastAPI - Get Help - 帮助 FastAPI - 获取帮助](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/help-fastapi/). PR [#1465](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1465) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Query Parameters - 查询参数](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/tutorial/query-params/). PR [#1454](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1454) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Contributing - 开发 - 贡献](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/contributing/). PR [#1460](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1460) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Path Parameters - 路径参数](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/tutorial/path-params/). PR [#1453](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1453) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Add official Microsoft project generator for [serving spaCy with FastAPI and Azure Cognitive Skills](https://github.com/microsoft/cookiecutter-spacy-fastapi) to [Project Generators](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/project-generation/). PR [#1390](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1390) by [@kabirkhan](https://github.com/kabirkhan).
|
||||
* Update docs in [Python Types Intro](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/python-types/) to include info about `Optional`. Original PR [#1377](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1377) by [@yaegassy](https://github.com/yaegassy).
|
||||
* Fix support for callable class dependencies with `yield`. PR [#1365](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1365) by [@mrosales](https://github.com/mrosales).
|
||||
* Fix/remove incorrect error logging when a client sends invalid payloads. PR [#1351](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1351) by [@dbanty](https://github.com/dbanty).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [First Steps - 第一步](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/tutorial/first-steps/). PR [#1323](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1323) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Fix generating OpenAPI for apps using callbacks with routers including Pydantic models. PR [#1322](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1322) by [@nsidnev](https://github.com/nsidnev).
|
||||
* Optimize internal regex performance in `get_path_param_names()`. PR [#1243](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1243) by [@heckad](https://github.com/heckad).
|
||||
* Remove `*,` from functions in docs where it's not needed. PR [#1239](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1239) by [@pankaj-giri](https://github.com/pankaj-giri).
|
||||
* Start translations for Italian. PR [#1557](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1557) by [@csr](https://github.com/csr).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.56.0
|
||||
|
||||
* Add support for ASGI `root_path`:
|
||||
* Use `root_path` internally for mounted applications, so that OpenAPI and the docs UI works automatically without extra configurations and parameters.
|
||||
* Add new `root_path` parameter for `FastAPI` applications to provide it in cases where it can be set with the command line (e.g. for Uvicorn and Hypercorn, with the parameter `--root-path`).
|
||||
* Deprecate `openapi_prefix` parameter in favor of the new `root_path` parameter.
|
||||
* Add new/updated docs for [Sub Applications - Mounts](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/advanced/sub-applications/), without `openapi_prefix` (as it is now handled automatically).
|
||||
* Add new/updated docs for [Behind a Proxy](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/advanced/behind-a-proxy/), including how to setup a local testing proxy with Traefik and using `root_path`.
|
||||
* Update docs for [Extending OpenAPI](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/advanced/extending-openapi/) with the new `openapi_prefix` parameter passed (internally generated from `root_path`).
|
||||
* Original PR [#1199](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1199) by [@iksteen](https://github.com/iksteen).
|
||||
* Update new issue templates and docs: [Help FastAPI - Get Help](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/help-fastapi/). PR [#1531](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1531).
|
||||
* Update GitHub action issue-manager. PR [#1520](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1520).
|
||||
* Add new links:
|
||||
* **English articles**:
|
||||
* [Real-time Notifications with Python and Postgres](https://wuilly.com/2019/10/real-time-notifications-with-python-and-postgres/) by [Guillermo Cruz](https://wuilly.com/).
|
||||
* [Microservice in Python using FastAPI](https://dev.to/paurakhsharma/microservice-in-python-using-fastapi-24cc) by [Paurakh Sharma Humagain](https://twitter.com/PaurakhSharma).
|
||||
* [Build simple API service with Python FastAPI — Part 1](https://dev.to/cuongld2/build-simple-api-service-with-python-fastapi-part-1-581o) by [cuongld2](https://dev.to/cuongld2).
|
||||
* [FastAPI + Zeit.co = 🚀](https://paulsec.github.io/posts/fastapi_plus_zeit_serverless_fu/) by [Paul Sec](https://twitter.com/PaulWebSec).
|
||||
* [Build a web API from scratch with FastAPI - the workshop](https://dev.to/tiangolo/build-a-web-api-from-scratch-with-fastapi-the-workshop-2ehe) by [Sebastián Ramírez (tiangolo)](https://twitter.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* [Build a Secure Twilio Webhook with Python and FastAPI](https://www.twilio.com/blog/build-secure-twilio-webhook-python-fastapi) by [Twilio](https://www.twilio.com).
|
||||
* [Using FastAPI with Django](https://www.stavros.io/posts/fastapi-with-django/) by [Stavros Korokithakis](https://twitter.com/Stavros).
|
||||
* [Introducing Dispatch](https://netflixtechblog.com/introducing-dispatch-da4b8a2a8072) by [Netflix](https://netflixtechblog.com/).
|
||||
* **Podcasts**:
|
||||
* [Build The Next Generation Of Python Web Applications With FastAPI - Episode 259 - interview to Sebastían Ramírez (tiangolo)](https://www.pythonpodcast.com/fastapi-web-application-framework-episode-259/) by [Podcast.`__init__`](https://www.pythonpodcast.com/).
|
||||
* **Talks**:
|
||||
* [PyConBY 2020: Serve ML models easily with FastAPI](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=z9K5pwb0rt8) by [Sebastián Ramírez (tiangolo)](https://twitter.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* [[VIRTUAL] Py.Amsterdam's flying Software Circus: Intro to FastAPI](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PnpTY1f4k2U) by [Sebastián Ramírez (tiangolo)](https://twitter.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* PR [#1467](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1467).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Python Types Intro - Python 类型提示简介](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/python-types/). PR [#1197](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1197) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.55.1
|
||||
|
||||
* Fix handling of enums with their own schema in path parameters. To support [samuelcolvin/pydantic#1432](https://github.com/samuelcolvin/pydantic/pull/1432) in FastAPI. PR [#1463](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1463).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.55.0
|
||||
|
||||
* Allow enums to allow them to have their own schemas in OpenAPI. To support [samuelcolvin/pydantic#1432](https://github.com/samuelcolvin/pydantic/pull/1432) in FastAPI. PR [#1461](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1461).
|
||||
* Add links for funding through [GitHub sponsors](https://github.com/sponsors/tiangolo). PR [#1425](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1425).
|
||||
* Update issue template for for questions. PR [#1344](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1344) by [@retnikt](https://github.com/retnikt).
|
||||
* Update warning about storing passwords in docs. PR [#1336](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1336) by [@skorokithakis](https://github.com/skorokithakis).
|
||||
* Fix typo. PR [#1326](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1326) by [@chenl](https://github.com/chenl).
|
||||
* Add translation to Portuguese for [Alternatives, Inspiration and Comparisons - Alternativas, Inspiração e Comparações](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/pt/alternatives/). PR [#1325](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1325) by [@Serrones](https://github.com/Serrones).
|
||||
* Fix 2 typos in docs. PR [#1324](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1324) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Update CORS docs, fix correct default of `max_age=600`. PR [#1301](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1301) by [@derekbekoe](https://github.com/derekbekoe).
|
||||
* Add translation of [main page to Portuguese](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/pt/). PR [#1300](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1300) by [@Serrones](https://github.com/Serrones).
|
||||
* Re-word and clarify docs for extra info in fields. PR [#1299](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1299) by [@chris-allnutt](https://github.com/chris-allnutt).
|
||||
* Make sure the `*` in short features in the docs is consistent (after `.`) in all languages. PR [#1424](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1424).
|
||||
* Update order of execution for `get_db` in SQLAlchemy tutorial. PR [#1293](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1293) by [@bcb](https://github.com/bcb).
|
||||
* Fix typos in Async docs. PR [#1423](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1423).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.54.2
|
||||
|
||||
* Add translation to Spanish for [Concurrency and async / await - Concurrencia y async / await](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/es/async/). PR [#1290](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1290) by [@alvaropernas](https://github.com/alvaropernas).
|
||||
* Remove obsolete vote link. PR [#1289](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1289) by [@donhui](https://github.com/donhui).
|
||||
* Allow disabling docs UIs by just disabling OpenAPI with `openapi_url=None`. New example in docs: [Advanced: Conditional OpenAPI](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/advanced/conditional-openapi/). PR [#1421](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1421).
|
||||
* Add translation to Portuguese for [Benchmarks - Comparações](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/pt/benchmarks/). PR [#1274](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1274) by [@Serrones](https://github.com/Serrones).
|
||||
* Add translation to Portuguese for [Tutorial - User Guide - Intro - Tutorial - Guia de Usuário - Introdução](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/pt/tutorial/). PR [#1259](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1259) by [@marcosmmb](https://github.com/marcosmmb).
|
||||
* Allow using Unicode in MkDocs for translations. PR [#1419](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1419).
|
||||
* Add translation to Spanish for [Advanced User Guide - Intro - Guía de Usuario Avanzada - Introducción](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/es/advanced/). PR [#1250](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1250) by [@jfunez](https://github.com/jfunez).
|
||||
* Add translation to Portuguese for [History, Design and Future - História, Design e Futuro](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/pt/history-design-future/). PR [#1249](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1249) by [@marcosmmb](https://github.com/marcosmmb).
|
||||
* Add translation to Portuguese for [Features - Recursos](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/pt/features/). PR [#1248](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1248) by [@marcosmmb](https://github.com/marcosmmb).
|
||||
* Add translation to Spanish for [Tutorial - User Guide - Intro - Tutorial - Guía de Usuario - Introducción](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/es/tutorial/). PR [#1244](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1244) by [@MartinEliasQ](https://github.com/MartinEliasQ).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Deployment - 部署](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/deployment/). PR [#1203](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1203) by [@RunningIkkyu](https://github.com/RunningIkkyu).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Tutorial - User Guide - Intro - 教程 - 用户指南 - 简介](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/tutorial/). PR [#1202](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1202) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Add translation to Chinese for [Features - 特性](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/features/). PR [#1192](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1192) by [@Dustyposa](https://github.com/Dustyposa).
|
||||
* Add translation for [main page to Chinese](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/) PR [#1191](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1191) by [@waynerv](https://github.com/waynerv).
|
||||
* Update docs for project generation. PR [#1287](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1287).
|
||||
* Add Spanish translation for [Introducción a los Tipos de Python (Python Types Intro)](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/es/python-types/). PR [#1237](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1237) by [@mariacamilagl](https://github.com/mariacamilagl).
|
||||
* Add Spanish translation for [Características (Features)](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/es/features/). PR [#1220](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1220) by [@mariacamilagl](https://github.com/mariacamilagl).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.54.1
|
||||
|
||||
* Update database test setup. PR [#1226](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1226).
|
||||
* Improve test debugging by showing response text in failing tests. PR [#1222](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1222) by [@samuelcolvin](https://github.com/samuelcolvin).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.54.0
|
||||
|
||||
* Fix grammatical mistakes in async docs. PR [#1188](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1188) by [@mickeypash](https://github.com/mickeypash).
|
||||
* Add support for `response_model_exclude_defaults` and `response_model_exclude_none`:
|
||||
* Deprecate the parameter `include_none` in `jsonable_encoder` and add the inverted `exclude_none`, to keep in sync with Pydantic.
|
||||
* PR [#1166](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1166) by [@voegtlel](https://github.com/voegtlel).
|
||||
* Add example about [Testing a Database](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/advanced/testing-database/). Initial PR [#1144](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1144) by [@duganchen](https://github.com/duganchen).
|
||||
* Update docs for [Development - Contributing: Translations](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/contributing/#translations) including note about reviewing translation PRs. [#1215](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1215).
|
||||
* Update log style in README.md for GitHub Markdown compatibility. PR [#1200](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1200) by [#geekgao](https://github.com/geekgao).
|
||||
* Add Python venv `env` to `.gitignore`. PR [#1212](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1212) by [@cassiobotaro](https://github.com/cassiobotaro).
|
||||
* Start Portuguese translations. PR [#1210](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1210) by [@cassiobotaro](https://github.com/cassiobotaro).
|
||||
* Update docs for Pydantic's `Settings` using a dependency with `@lru_cache()`. PR [#1214](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1214).
|
||||
* Add first translation to Spanish [FastAPI](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/es/). PR [#1201](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1201) by [@mariacamilagl](https://github.com/mariacamilagl).
|
||||
* Add docs about [Settings and Environment Variables](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/advanced/settings/). Initial PR [1118](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1118) by [@alexmitelman](https://github.com/alexmitelman).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.53.2
|
||||
|
||||
* Fix automatic embedding of body fields for dependencies and sub-dependencies. Original PR [#1079](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/1079) by [@Toad2186](https://github.com/Toad2186).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Application Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
There are several things that you can configure in your FastAPI application.
|
||||
|
||||
## Title, description, and version
|
||||
|
||||
You can set the:
|
||||
|
||||
* Title: used as your API's title/name, in OpenAPI and the automatic API docs UIs.
|
||||
* Description: the description of your API, in OpenAPI and the automatic API docs UIs.
|
||||
* Version: the version of your API, e.g. `v2` or `2.5.0`.
|
||||
* Useful for example if you had a previous version of the application, also using OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
To set them, use the parameters `title`, `description`, and `version`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 5 6"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/application_configuration/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With this configuration, the automatic API docs would look like:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/application-configuration/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
## OpenAPI URL
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the OpenAPI schema is served at `/openapi.json`.
|
||||
|
||||
But you can configure it with the parameter `openapi_url`.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to set it to be served at `/api/v1/openapi.json`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/application_configuration/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to disable the OpenAPI schema completely you can set `openapi_url=None`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Docs URLs
|
||||
|
||||
You can configure the two documentation user interfaces included:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Swagger UI**: served at `/docs`.
|
||||
* You can set its URL with the parameter `docs_url`.
|
||||
* You can disable it by setting `docs_url=None`.
|
||||
* ReDoc: served at `/redoc`.
|
||||
* You can set its URL with the parameter `redoc_url`.
|
||||
* You can disable it by setting `redoc_url=None`.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to set Swagger UI to be served at `/documentation` and disable ReDoc:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/application_configuration/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ Using `BackgroundTasks` also works with the dependency injection system, you can
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** knows what to do in each case and how to re-use the same object, so that all the background tasks are merged together and are run in the background afterwards:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 14 20 23"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13 15 22 25"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/background_tasks/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ The same way you can declare additional validation and metadata in *path operati
|
||||
|
||||
First, you have to import it:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body_fields/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ First, you have to import it:
|
||||
|
||||
You can then use `Field` with model attributes:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 10"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 12 13 14"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body_fields/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ You can then use `Field` with model attributes:
|
||||
|
||||
You can declare extra information in `Field`, `Query`, `Body`, etc. And it will be included in the generated JSON Schema.
|
||||
|
||||
You will learn more about it later to declare examples examples.
|
||||
You will learn more about adding extra information later in the docs, when learning to declare examples.
|
||||
|
||||
## Recap
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ First, of course, you can mix `Path`, `Query` and request body parameter declara
|
||||
|
||||
And you can also declare body parameters as optional, by setting the default to `None`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="17 18 19"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="19 20 21"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body_multiple_params/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ In the previous example, the *path operations* would expect a JSON body with the
|
||||
|
||||
But you can also declare multiple body parameters, e.g. `item` and `user`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="20"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="22"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body_multiple_params/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ If you declare it as is, because it is a singular value, **FastAPI** will assume
|
||||
But you can instruct **FastAPI** to treat it as another body key using `Body`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="21"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="23"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body_multiple_params/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -104,12 +104,12 @@ Of course, you can also declare additional query parameters whenever you need, a
|
||||
As, by default, singular values are interpreted as query parameters, you don't have to explicitly add a `Query`, you can just do:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
q: str = None
|
||||
q: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
as in:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="25"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="27"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body_multiple_params/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -131,7 +131,7 @@ item: Item = Body(..., embed=True)
|
||||
|
||||
as in:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="15"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="17"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body_multiple_params/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,15 +6,15 @@ With **FastAPI**, you can define, validate, document, and use arbitrarily deeply
|
||||
|
||||
You can define an attribute to be a subtype. For example, a Python `list`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="12"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="14"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body_nested_models/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will make `tags` be a list of items. Although it doesn't declare the type of each of the items.
|
||||
|
||||
## List fields with subtype
|
||||
## List fields with type parameter
|
||||
|
||||
But Python has a specific way to declare lists with subtypes:
|
||||
But Python has a specific way to declare lists with internal types, or "type parameters":
|
||||
|
||||
### Import typing's `List`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -24,12 +24,12 @@ First, import `List` from standard Python's `typing` module:
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body_nested_models/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Declare a `List` with a subtype
|
||||
### Declare a `List` with a type parameter
|
||||
|
||||
To declare types that have subtypes, like `list`, `dict`, `tuple`:
|
||||
To declare types that have type parameters (internal types), like `list`, `dict`, `tuple`:
|
||||
|
||||
* Import them from the `typing` module
|
||||
* Pass the subtype(s) as "type arguments" using square brackets: `[` and `]`
|
||||
* Pass the internal type(s) as "type parameters" using square brackets: `[` and `]`
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from typing import List
|
||||
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ my_list: List[str]
|
||||
|
||||
That's all standard Python syntax for type declarations.
|
||||
|
||||
Use that same standard syntax for model attributes with subtypes.
|
||||
Use that same standard syntax for model attributes with internal types.
|
||||
|
||||
So, in our example, we can make `tags` be specifically a "list of strings":
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ Each attribute of a Pydantic model has a type.
|
||||
|
||||
But that type can itself be another Pydantic model.
|
||||
|
||||
So, you can declare deeply nested JSON `object`s with specific attribute names, types and validations.
|
||||
So, you can declare deeply nested JSON "objects" with specific attribute names, types and validations.
|
||||
|
||||
All that, arbitrarily nested.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -174,7 +174,7 @@ You can define arbitrarily deeply nested models:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Notice how `Offer` as a list of `Item`s, which in turn have an optional list of `Image`s
|
||||
Notice how `Offer` has a list of `Item`s, which in turn have an optional list of `Image`s
|
||||
|
||||
## Bodies of pure lists
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -9,15 +9,17 @@ Your API almost always has to send a **response** body. But clients don't necess
|
||||
To declare a **request** body, you use <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic</a> models with all their power and benefits.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
You cannot send a request body using a `GET` operation (HTTP method).
|
||||
To send data, you should use one of: `POST` (the more common), `PUT`, `DELETE` or `PATCH`.
|
||||
|
||||
To send data, you have to use one of: `POST` (the more common), `PUT`, `DELETE` or `PATCH`.
|
||||
Sending a body with a `GET` request has an undefined behavior in the specifications, nevertheless, it is supported by FastAPI, only for very complex/extreme use cases.
|
||||
|
||||
As it is discouraged, the interactive docs with Swagger UI won't show the documentation for the body when using `GET`, and proxies in the middle might not support it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Import Pydantic's `BaseModel`
|
||||
|
||||
First, you need to import `BaseModel` from `pydantic`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -27,7 +29,7 @@ Then you declare your data model as a class that inherits from `BaseModel`.
|
||||
|
||||
Use standard Python types for all the attributes:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="5 6 7 8 9"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7 8 9 10 11"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -57,7 +59,7 @@ For example, this model above declares a JSON "`object`" (or Python `dict`) like
|
||||
|
||||
To add it to your *path operation*, declare it the same way you declared path and query parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="16"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="18"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -108,11 +110,22 @@ But you would get the same editor support with <a href="https://www.jetbrains.co
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/body/image05.png">
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
If you use <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/" class="external-link" target="_blank">PyCharm</a> as your editor, you can use the <a href="https://github.com/koxudaxi/pydantic-pycharm-plugin/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic PyCharm Plugin</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
It improves editor support for Pydantic models, with:
|
||||
|
||||
* auto-completion
|
||||
* type checks
|
||||
* refactoring
|
||||
* searching
|
||||
* inspections
|
||||
|
||||
## Use the model
|
||||
|
||||
Inside of the function, you can access all the attributes of the model object directly:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="19"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="21"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -122,7 +135,7 @@ You can declare path parameters and body requests at the same time.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** will recognize that the function parameters that match path parameters should be **taken from the path**, and that function parameters that are declared to be Pydantic models should be **taken from the request body**.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="15 16"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="17 18"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -132,7 +145,7 @@ You can also declare **body**, **path** and **query** parameters, all at the sam
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** will recognize each of them and take the data from the correct place.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="16"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="18"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/body/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -142,6 +155,11 @@ The function parameters will be recognized as follows:
|
||||
* If the parameter is of a **singular type** (like `int`, `float`, `str`, `bool`, etc) it will be interpreted as a **query** parameter.
|
||||
* If the parameter is declared to be of the type of a **Pydantic model**, it will be interpreted as a request **body**.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
FastAPI will know that the value of `q` is not required because of the default value `= None`.
|
||||
|
||||
The `Optional` in `Optional[str]` is not used by FastAPI, but will allow your editor to give you better support and detect errors.
|
||||
|
||||
## Without Pydantic
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't want to use Pydantic models, you can also use **Body** parameters. See the docs for [Body - Multiple Parameters: Singular values in body](body-multiple-params.md#singular-values-in-body){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ You can define Cookie parameters the same way you define `Query` and `Path` para
|
||||
|
||||
First import `Cookie`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/cookie_params/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Then declare the cookie parameters using the same structure as with `Path` and `
|
||||
|
||||
The first value is the default value, you can pass all the extra validation or annotation parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/cookie_params/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ The following arguments are supported:
|
||||
* `allow_headers` - A list of HTTP request headers that should be supported for cross-origin requests. Defaults to `[]`. You can use `['*']` to allow all headers. The `Accept`, `Accept-Language`, `Content-Language` and `Content-Type` headers are always allowed for CORS requests.
|
||||
* `allow_credentials` - Indicate that cookies should be supported for cross-origin requests. Defaults to `False`.
|
||||
* `expose_headers` - Indicate any response headers that should be made accessible to the browser. Defaults to `[]`.
|
||||
* `max_age` - Sets a maximum time in seconds for browsers to cache CORS responses. Defaults to `60`.
|
||||
* `max_age` - Sets a maximum time in seconds for browsers to cache CORS responses. Defaults to `600`.
|
||||
|
||||
The middleware responds to two particular types of HTTP request...
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ Before diving deeper into the **Dependency Injection** system, let's upgrade the
|
||||
|
||||
In the previous example, we were returning a `dict` from our dependency ("dependable"):
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,19 +71,19 @@ That also applies to callables with no parameters at all. The same as it would b
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we can change the dependency "dependable" `common_parameters` from above to the class `CommonQueryParameters`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 10 11 12 13"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 12 13 14 15"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pay attention to the `__init__` method used to create the instance of the class:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="12"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...it has the same parameters as our previous `common_parameters`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -103,7 +103,7 @@ Now you can declare your dependency using this class.
|
||||
|
||||
And as when **FastAPI** calls that class the value that will be passed as `commons` to your function will be an "instance" of the class, you can declare that parameter `commons` to be of type of the class, `CommonQueryParams`.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="17"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="19"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -143,7 +143,7 @@ commons = Depends(CommonQueryParams)
|
||||
|
||||
..as in:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="17"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="19"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -179,7 +179,7 @@ So, you can declare the dependency as the type of the variable, and use `Depends
|
||||
|
||||
So, the same example would look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="17"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="19"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ Let's first focus on the dependency.
|
||||
|
||||
It is just a function that can take all the same parameters that a *path operation function* can take:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6 7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8 9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ And then it just returns a `dict` containing those values.
|
||||
|
||||
### Import `Depends`
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ And then it just returns a `dict` containing those values.
|
||||
|
||||
The same way you use `Body`, `Query`, etc. with your *path operation function* parameters, use `Depends` with a new parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11 16"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13 18"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ They can be as **deep** as you need them to be.
|
||||
|
||||
You could create a first dependency ("dependable") like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6 7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8 9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ This is quite simple (not very useful), but will help us focus on how the sub-de
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can create another dependency function (a "dependable") that at the same time declares a dependency of its own (so it is a "dependant" too):
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ Let's focus on the parameters declared:
|
||||
|
||||
Then we can use the dependency with:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="19"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="21"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/dependencies/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ You can use `jsonable_encoder` for that.
|
||||
|
||||
It receives an object, like a Pydantic model, and returns a JSON compatible version:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 21"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="5 22"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/encoder/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -49,17 +49,18 @@ Here are some of the additional data types you can use:
|
||||
* `Decimal`:
|
||||
* Standard Python `Decimal`.
|
||||
* In requests and responses, handled the same as a `float`.
|
||||
* You can check all the valid pydantic data types here: <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/types" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic data types</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example *path operation* with parameters using some of the above types.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 2 11 12 13 14 15"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 3 12 13 14 15 16"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extra_data_types/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the parameters inside the function have their natural data type, and you can, for example, perform normal date manipulations, like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="17 18"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="18 19"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extra_data_types/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ This is especially the case for user models, because:
|
||||
|
||||
Here's a general idea of how the models could look like with their password fields and the places where they are used:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7 9 14 20 22 27 28 31 32 33 38 39"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 11 16 22 24 29 30 33 34 35 40 41"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -150,7 +150,7 @@ All the data conversion, validation, documentation, etc. will still work as norm
|
||||
|
||||
That way, we can declare just the differences between the models (with plaintext `password`, with `hashed_password` and without password):
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7 13 14 17 18 21 22"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 15 16 19 20 23 24"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -162,6 +162,9 @@ It will be defined in OpenAPI with `anyOf`.
|
||||
|
||||
To do that, use the standard Python type hint <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/typing.html#typing.Union" class="external-link" target="_blank">`typing.Union`</a>:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
When defining a <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/types/#unions" class="external-link" target="_blank">`Union`</a>, include the most specific type first, followed by the less specific type. In the example below, the more specific `PlaneItem` comes before `CarItem` in `Union[PlaneItem, CarItem]`.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 14 15 18 19 20 33"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -71,13 +71,13 @@ You will see the alternative automatic documentation (provided by <a href="https
|
||||
|
||||
#### "Schema"
|
||||
|
||||
A "schema" is a definition or description of something. Not the code that implements it, but just the abstract description.
|
||||
A "schema" is a definition or description of something. Not the code that implements it, but just an abstract description.
|
||||
|
||||
#### API "schema"
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, OpenAPI is a specification that dictates how to define a schema of your API.
|
||||
In this case, <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI</a> is a specification that dictates how to define a schema of your API.
|
||||
|
||||
This OpenAPI schema would include your API paths, the possible parameters they take, etc.
|
||||
This schema definition includes your API paths, the possible parameters they take, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Data "schema"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ OpenAPI defines an API schema for your API. And that schema includes definitions
|
||||
|
||||
#### Check the `openapi.json`
|
||||
|
||||
If you are curious about how the raw OpenAPI schema looks like, it is just an automatically generated JSON with the descriptions of all your API.
|
||||
If you are curious about how the raw OpenAPI schema looks like, FastAPI automatically generates a JSON (schema) with the descriptions of all your API.
|
||||
|
||||
You can see it directly at: <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/openapi.json" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/openapi.json</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ It will show a JSON starting with something like:
|
||||
|
||||
#### What is OpenAPI for
|
||||
|
||||
This OpenAPI schema is what powers the 2 interactive documentation systems included.
|
||||
The OpenAPI schema is what powers the two interactive documentation systems included.
|
||||
|
||||
And there are dozens of alternatives, all based on OpenAPI. You could easily add any of those alternatives to your application built with **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -139,7 +139,7 @@ You could also use it to generate code automatically, for clients that communica
|
||||
!!! note "Technical Details"
|
||||
`FastAPI` is a class that inherits directly from `Starlette`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use all the Starlette functionality with `FastAPI` too.
|
||||
You can use all the <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette</a> functionality with `FastAPI` too.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: create a `FastAPI` "instance"
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -202,7 +202,7 @@ https://example.com/items/foo
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
A "path" is also commonly called an "endpoint" or a "route".
|
||||
|
||||
Building an API, the "path" is the main way to separate "concerns" and "resources".
|
||||
While building an API, the "path" is the main way to separate "concerns" and "resources".
|
||||
|
||||
#### Operation
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -239,7 +239,7 @@ So, in OpenAPI, each of the HTTP methods is called an "operation".
|
||||
|
||||
We are going to call them "**operations**" too.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Define a *path operation function*
|
||||
#### Define a *path operation decorator*
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/first_steps/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
@@ -281,7 +281,7 @@ And the more exotic ones:
|
||||
|
||||
The information here is presented as a guideline, not a requirement.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, when using GraphQL you normally perform all the actions using only `post`.
|
||||
For example, when using GraphQL you normally perform all the actions using only `POST` operations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: define the **path operation function**
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -297,7 +297,7 @@ This is our "**path operation function**":
|
||||
|
||||
This is a Python function.
|
||||
|
||||
It will be called by **FastAPI** whenever it receives a request to the URL "`/`" using `GET`.
|
||||
It will be called by **FastAPI** whenever it receives a request to the URL "`/`" using a `GET` operation.
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, it is an `async` function.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ So, you will receive a clean error, with an HTTP status code of `418` and a JSON
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** has some default exception handlers.
|
||||
|
||||
These handlers are in charge or returning the default JSON responses when you `raise` an `HTTPException` and when the request has invalid data.
|
||||
These handlers are in charge of returning the default JSON responses when you `raise` an `HTTPException` and when the request has invalid data.
|
||||
|
||||
You can override these exception handlers with your own.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -209,13 +209,12 @@ Now try sending an invalid item like:
|
||||
|
||||
You will receive a response telling you that the data is invalid containing the received body:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON hl_lines="13 14 15 16"
|
||||
```JSON hl_lines="12 13 14 15"
|
||||
{
|
||||
"detail": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"loc": [
|
||||
"body",
|
||||
"item",
|
||||
"size"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"msg": "value is not a valid integer",
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ You can define Header parameters the same way you define `Query`, `Path` and `Co
|
||||
|
||||
First import `Header`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/header_params/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Then declare the header parameters using the same structure as with `Path`, `Que
|
||||
|
||||
The first value is the default value, you can pass all the extra validation or annotation parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/header_params/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ So, you can use `user_agent` as you normally would in Python code, instead of ne
|
||||
|
||||
If for some reason you need to disable automatic conversion of underscores to hyphens, set the parameter `convert_underscores` of `Header` to `False`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/header_params/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -75,6 +75,6 @@ There is also an **Advanced User Guide** that you can read later after this **Tu
|
||||
|
||||
The **Advanced User Guide**, builds on this, uses the same concepts, and teaches you some extra features.
|
||||
|
||||
But you should first read the **Tutorial - User guide** (what you are reading right now).
|
||||
But you should first read the **Tutorial - User Guide** (what you are reading right now).
|
||||
|
||||
It's designed so that you can build a complete application with just the **Tutorial - User guide**, and then extend it in different ways, depending on your needs, using some of the additional ideas from the **Advanced User Guide**.
|
||||
It's designed so that you can build a complete application with just the **Tutorial - User Guide**, and then extend it in different ways, depending on your needs, using some of the additional ideas from the **Advanced User Guide**.
|
||||
|
||||
105
docs/en/docs/tutorial/metadata.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
# Metadata and Docs URLs
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize several metadata configurations in your **FastAPI** application.
|
||||
|
||||
## Title, description, and version
|
||||
|
||||
You can set the:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Title**: used as your API's title/name, in OpenAPI and the automatic API docs UIs.
|
||||
* **Description**: the description of your API, in OpenAPI and the automatic API docs UIs.
|
||||
* **Version**: the version of your API, e.g. `v2` or `2.5.0`.
|
||||
* Useful for example if you had a previous version of the application, also using OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
To set them, use the parameters `title`, `description`, and `version`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 5 6"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/metadata/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With this configuration, the automatic API docs would look like:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/metadata/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
## Metadata for tags
|
||||
|
||||
You can also add additional metadata for the different tags used to group your path operations with the parameter `openapi_tags`.
|
||||
|
||||
It takes a list containing one dictionary for each tag.
|
||||
|
||||
Each dictionary can contain:
|
||||
|
||||
* `name` (**required**): a `str` with the same tag name you use in the `tags` parameter in your *path operations* and `APIRouter`s.
|
||||
* `description`: a `str` with a short description for the tag. It can have Markdown and will be shown in the docs UI.
|
||||
* `externalDocs`: a `dict` describing external documentation with:
|
||||
* `description`: a `str` with a short description for the external docs.
|
||||
* `url` (**required**): a `str` with the URL for the external documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create metadata for tags
|
||||
|
||||
Let's try that in an example with tags for `users` and `items`.
|
||||
|
||||
Create metadata for your tags and pass it to the `openapi_tags` parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 18"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/metadata/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that you can use Markdown inside of the descriptions, for example "login" will be shown in bold (**login**) and "fancy" will be shown in italics (_fancy_).
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
You don't have to add metadata for all the tags that you use.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use your tags
|
||||
|
||||
Use the `tags` parameter with your *path operations* (and `APIRouter`s) to assign them to different tags:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="21 26"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/metadata/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Read more about tags in [Path Operation Configuration](../path-operation-configuration/#tags){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
### Check the docs
|
||||
|
||||
Now, if you check the docs, they will show all the additional metadata:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/metadata/image02.png">
|
||||
|
||||
### Order of tags
|
||||
|
||||
The order of each tag metadata dictionary also defines the order shown in the docs UI.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, even though `users` would go after `items` in alphabetical order, it is shown before them, because we added their metadata as the first dictionary in the list.
|
||||
|
||||
## OpenAPI URL
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the OpenAPI schema is served at `/openapi.json`.
|
||||
|
||||
But you can configure it with the parameter `openapi_url`.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to set it to be served at `/api/v1/openapi.json`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/metadata/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to disable the OpenAPI schema completely you can set `openapi_url=None`, that will also disable the documentation user interfaces that use it.
|
||||
|
||||
## Docs URLs
|
||||
|
||||
You can configure the two documentation user interfaces included:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Swagger UI**: served at `/docs`.
|
||||
* You can set its URL with the parameter `docs_url`.
|
||||
* You can disable it by setting `docs_url=None`.
|
||||
* ReDoc: served at `/redoc`.
|
||||
* You can set its URL with the parameter `redoc_url`.
|
||||
* You can disable it by setting `redoc_url=None`.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to set Swagger UI to be served at `/documentation` and disable ReDoc:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/metadata/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ The same way you can declare more validations and metadata for query parameters
|
||||
|
||||
First, import `Path` from `fastapi`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/path_params_numeric_validations/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ You can declare all the same parameters as for `Query`.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to declare a `title` metadata value for the path parameter `item_id` you can type:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/path_params_numeric_validations/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ And when you open your browser at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="ex
|
||||
|
||||
And because the generated schema is from the <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification/blob/master/versions/3.0.2.md" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI</a> standard, there are many compatible tools.
|
||||
|
||||
Because of this, **FastAPI** itself provides an alternative API documentation (using ReDoc):
|
||||
Because of this, **FastAPI** itself provides an alternative API documentation (using ReDoc), which you can access at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc</a>:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/path-params/image02.png">
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -125,7 +125,7 @@ Import `Enum` and create a sub-class that inherits from `str` and from `Enum`.
|
||||
|
||||
By inheriting from `str` the API docs will be able to know that the values must be of type `string` and will be able to render correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
And create class attributes with fixed values, those fixed values will be the available valid values:
|
||||
Then create class attributes with fixed values, which will be the available valid values:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 6 7 8 9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/path_params/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
@@ -147,7 +147,7 @@ Then create a *path parameter* with a type annotation using the enum class you c
|
||||
|
||||
### Check the docs
|
||||
|
||||
Because the available values for the *path parameter* are specified, the interactive docs can show them nicely:
|
||||
Because the available values for the *path parameter* are predefined, the interactive docs can show them nicely:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/path-params/image03.png">
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -167,7 +167,7 @@ You can compare it with the *enumeration member* in your created enum `ModelName
|
||||
|
||||
You can get the actual value (a `str` in this case) using `model_name.value`, or in general, `your_enum_member.value`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="19"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="20"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/path_params/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -178,12 +178,21 @@ You can get the actual value (a `str` in this case) using `model_name.value`, or
|
||||
|
||||
You can return *enum members* from your *path operation*, even nested in a JSON body (e.g. a `dict`).
|
||||
|
||||
They will be converted to their corresponding values before returning them to the client:
|
||||
They will be converted to their corresponding values (strings in this case) before returning them to the client:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="18 20 21"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="18 21 23"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/path_params/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In your client you will get a JSON response like:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{
|
||||
"model_name": "alexnet",
|
||||
"message": "Deep Learning FTW!"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Path parameters containing paths
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say you have a *path operation* with a path `/files/{file_path}`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,11 +4,16 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take this application as example:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The query parameter `q` is of type `str`, and by default is `None`, so it is optional.
|
||||
The query parameter `q` is of type `Optional[str]`, that means that it's of type `str` but could also be `None`, and indeed, the default value is `None`, so FastAPI will know it's not required.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
FastAPI will know that the value of `q` is not required because of the default value `= None`.
|
||||
|
||||
The `Optional` in `Optional[str]` is not used by FastAPI, but will allow your editor to give you better support and detect errors.
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional validation
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -18,7 +23,7 @@ We are going to enforce that even though `q` is optional, whenever it is provide
|
||||
|
||||
To achieve that, first import `Query` from `fastapi`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,7 +31,7 @@ To achieve that, first import `Query` from `fastapi`:
|
||||
|
||||
And now use it as the default value of your parameter, setting the parameter `max_length` to 50:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,18 +40,35 @@ As we have to replace the default value `None` with `Query(None)`, the first par
|
||||
So:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
q: str = Query(None)
|
||||
q: Optional[str] = Query(None)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...makes the parameter optional, the same as:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
q: str = None
|
||||
q: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
But it declares it explicitly as being a query parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
And then, we can pass more parameters to `Query`. In this case, the `max_length` parameter that applies to strings:
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
Have in mind that FastAPI cares about the part:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
= None
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or the:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
= Query(None)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and will use that `None` to detect that the query parameter is not required.
|
||||
|
||||
The `Optional` part is only to allow your editor to provide better support.
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we can pass more parameters to `Query`. In this case, the `max_length` parameter that applies to strings:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
q: str = Query(None, max_length=50)
|
||||
@@ -58,7 +80,7 @@ This will validate the data, show a clear error when the data is not valid, and
|
||||
|
||||
You can also add a parameter `min_length`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -66,7 +88,7 @@ You can also add a parameter `min_length`:
|
||||
|
||||
You can define a <abbr title="A regular expression, regex or regexp is a sequence of characters that define a search pattern for strings.">regular expression</abbr> that the parameter should match:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -104,13 +126,13 @@ q: str
|
||||
instead of:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
q: str = None
|
||||
q: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
But we are now declaring it with `Query`, for example like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
q: str = Query(None, min_length=3)
|
||||
q: Optional[str] = Query(None, min_length=3)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
So, when you need to declare a value as required while using `Query`, you can use `...` as the first argument:
|
||||
@@ -211,13 +233,13 @@ That information will be included in the generated OpenAPI and used by the docum
|
||||
|
||||
You can add a `title`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial007.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And a `description`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="11"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial008.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -239,7 +261,7 @@ But you still need it to be exactly `item-query`...
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can declare an `alias`, and that alias is what will be used to find the parameter value:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial009.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -251,7 +273,7 @@ You have to leave it there a while because there are clients using it, but you w
|
||||
|
||||
Then pass the parameter `deprecated=True` to `Query`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="16"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="18"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial010.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ The parameter values in your function will be:
|
||||
|
||||
The same way, you can declare optional query parameters, by setting their default to `None`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -72,11 +72,16 @@ In this case, the function parameter `q` will be optional, and will be `None` by
|
||||
!!! check
|
||||
Also notice that **FastAPI** is smart enough to notice that the path parameter `item_id` is a path parameter and `q` is not, so, it's a query parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note
|
||||
FastAPI will know that `q` is optional because of the `= None`.
|
||||
|
||||
The `Optional` in `Optional[str]` is not used by FastAPI (FastAPI will only use the `str` part), but the `Optional[str]` will let your editor help you finding errors in your code.
|
||||
|
||||
## Query parameter type conversion
|
||||
|
||||
You can also declare `bool` types, and they will be converted:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -121,7 +126,7 @@ And you don't have to declare them in any specific order.
|
||||
|
||||
They will be detected by name:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6 8"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="8 10"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -179,7 +184,7 @@ http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/foo-item?needy=sooooneedy
|
||||
|
||||
And of course, you can define some parameters as required, some as having a default value, and some entirely optional:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="10"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params/tutorial006.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -191,36 +196,3 @@ In this case, there are 3 query parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
You could also use `Enum`s the same way as with [Path Parameters](path-params.md#predefined-values){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
## Optional type declarations
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning
|
||||
This might be an advanced use case.
|
||||
|
||||
You might want to skip it.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using `mypy` it could complain with type declarations like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
limit: int = None
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With an error like:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Incompatible types in assignment (expression has type "None", variable has type "int")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In those cases you can use `Optional` to tell `mypy` that the value could be `None`, like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
limit: Optional[int] = None
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In a *path operation* that could look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/query_params/tutorial007.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,13 +35,13 @@ But most importantly:
|
||||
|
||||
Here we are declaring a `UserIn` model, it will contain a plaintext password:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7 9"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 11"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_model/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And we are using this model to declare our input and the same model to declare our output:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="15 16"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="17 18"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_model/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -52,25 +52,25 @@ In this case, it might not be a problem, because the user himself is sending the
|
||||
But if we use the same model for another *path operation*, we could be sending our user's passwords to every client.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! danger
|
||||
Never send the plain password of a user in a response.
|
||||
Never store the plain password of a user or send it in a response.
|
||||
|
||||
## Add an output model
|
||||
|
||||
We can instead create an input model with the plaintext password and an output model without it:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7 9 14"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="9 11 16"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_model/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, even though our *path operation function* is returning the same input user that contains the password:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="22"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="24"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_model/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...we declared the `response_model` to be our model `UserOut`, that doesn't include the password:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="20"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="22"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_model/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -94,9 +94,9 @@ Your response model could have default values, like:
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_model/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* `description: str = None` has a default of `None`.
|
||||
* `description: Optional[str] = None` has a default of `None`.
|
||||
* `tax: float = 10.5` has a default of `10.5`.
|
||||
* `tags: List[str] = []` has a default of an empty list: `[]`.
|
||||
* `tags: List[str] = []` as a default of an empty list: `[]`.
|
||||
|
||||
but you might want to omit them from the result if they were not actually stored.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -124,6 +124,14 @@ So, if you send a request to that *path operation* for the item with ID `foo`, t
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
FastAPI uses Pydantic model's `.dict()` with <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/exporting_models/#modeldict" class="external-link" target="_blank">its `exclude_unset` parameter</a> to achieve this.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
You can also use:
|
||||
|
||||
* `response_model_exclude_defaults=True`
|
||||
* `response_model_exclude_none=True`
|
||||
|
||||
as described in <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/exporting_models/#modeldict" class="external-link" target="_blank">the Pydantic docs</a> for `exclude_defaults` and `exclude_none`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Data with values for fields with defaults
|
||||
|
||||
But if your data has values for the model's fields with default values, like the item with ID `bar`:
|
||||
@@ -175,7 +183,9 @@ This can be used as a quick shortcut if you have only one Pydantic model and wan
|
||||
|
||||
This is because the JSON Schema generated in your app's OpenAPI (and the docs) will still be the one for the complete model, even if you use `response_model_include` or `response_model_exclude` to omit some attributes.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="29 35"
|
||||
This also applies to `response_model_by_alias` that works similarly.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="31 37"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_model/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -188,7 +198,7 @@ This can be used as a quick shortcut if you have only one Pydantic model and wan
|
||||
|
||||
If you forget to use a `set` and use a `list` or `tuple` instead, FastAPI will still convert it to a `set` and it will work correctly:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="29 35"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="31 37"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/response_model/tutorial006.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -17,6 +17,9 @@ The same way you can specify a response model, you can also declare the HTTP sta
|
||||
|
||||
The `status_code` parameter receives a number with the HTTP status code.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
`status_code` can alternatively also receive an `IntEnum`, such as Python's <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/http.html#http.HTTPStatus" class="external-link" target="_blank">`http.HTTPStatus`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
It will:
|
||||
|
||||
* Return that status code in the response.
|
||||
@@ -83,4 +86,4 @@ They are just a convenience, they hold the same number, but that way you can use
|
||||
|
||||
## Changing the default
|
||||
|
||||
Later, in the **Advanced User Guide**, you will see how to return a different status code than the default you are declaring here.
|
||||
Later, in the [Advanced User Guide](../advanced/response-change-status-code.md){.internal-link target=_blank}, you will see how to return a different status code than the default you are declaring here.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ There are several ways you can declare extra JSON Schema information.
|
||||
|
||||
You can declare an example for a Pydantic model using `Config` and `schema_extra`, as described in <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/schema/#schema-customization" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic's docs: Schema customization</a>:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/schema_extra_example/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ That extra info will be added as-is to the output JSON Schema.
|
||||
|
||||
In `Field`, `Path`, `Query`, `Body` and others you'll see later, you can also declare extra info for the JSON Schema by passing any other arbitrary arguments to the function, for example, to add an `example`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 8 9 10 11"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 10 11 12 13"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/schema_extra_example/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ The same way you can pass extra info to `Field`, you can do the same with `Path`
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can pass an `example` for a body request to `Body`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="20 21 22 23 24 25"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="21 22 23 24 25 26"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/schema_extra_example/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -86,8 +86,8 @@ But in this case, the same **FastAPI** application will handle the API and the a
|
||||
So, let's review it from that simplified point of view:
|
||||
|
||||
* The user types his `username` and `password` in the frontend, and hits `Enter`.
|
||||
* The frontend (running in the user's browser) sends that `username` and `password` to a specific URL in our API.
|
||||
* The API checks that `username` and `password`, and responds with a "token".
|
||||
* The frontend (running in the user's browser) sends that `username` and `password` to a specific URL in our API (declared with `tokenUrl="token"`).
|
||||
* The API checks that `username` and `password`, and responds with a "token" (we haven't implemented any of this yet).
|
||||
* A "token" is just a string with some content that we can use later to verify this user.
|
||||
* Normally, a token is set to expire after some time.
|
||||
* So, the user will have to login again at some point later.
|
||||
@@ -114,13 +114,20 @@ In this example we are going to use **OAuth2**, with the **Password** flow, usin
|
||||
|
||||
In that case, **FastAPI** also provides you with the tools to build it.
|
||||
|
||||
`OAuth2PasswordBearer` is a class that we create passing a parameter of the URL in where the client (the frontend running in the user's browser) can use to send the `username` and `password` and get a token.
|
||||
`OAuth2PasswordBearer` is a class that we create passing a parameter with the URL the client (the frontend running in the user's browser) can use to send the `username` and `password` and get a token.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It doesn't create that endpoint / *path operation*, but declares that that URL is the one that the client should use to get the token. That information is used in OpenAPI, and then in the interactive API documentation systems.
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
here `tokenUrl="token"` refers to a relative URL `token` that we haven't created yet. As it's a relative URL, it's equivalent to `./token`.
|
||||
|
||||
Because we are using a relative URL, if your API was located at `https://example.com/`, then it would refer to `https://example.com/token`. But if your API was located at `https://example.com/api/v1/`, then it would refer to `https://example.com/api/v1/token`.
|
||||
|
||||
Using a relative URL is important to make sure your application keeps working even in an advanced use case like [Behind a Proxy](../../advanced/behind-a-proxy.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
It doesn't create that endpoint / *path operation* for `./token`, but declares that that URL `./token` is the one that the client should use to get the token. That information is used in OpenAPI, and then in the interactive API documentation systems.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
If you are a very strict "Pythonista" you might dislike the style of the parameter name `tokenUrl` instead of `token_url`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -26,20 +26,29 @@ And after a week, the token will be expired and the user will not be authorized
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to play with JWT tokens and see how they work, check <a href="https://jwt.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">https://jwt.io</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install `PyJWT`
|
||||
## Install `python-jose`
|
||||
|
||||
We need to install `PyJWT` to generate and verify the JWT tokens in Python:
|
||||
We need to install `python-jose` to generate and verify the JWT tokens in Python:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ pip install pyjwt
|
||||
$ pip install python-jose[cryptography]
|
||||
|
||||
---> 100%
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/mpdavis/python-jose" class="external-link" target="_blank">Python-jose</a> requires a cryptographic backend as an extra.
|
||||
|
||||
Here we are using the recommended one: <a href="http://cryptography.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">pyca/cryptography</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
This tutorial previously used <a href="https://pyjwt.readthedocs.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">PyJWT</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
But it was updated to use Python-jose instead as it provides all the features from PyJWT plus some extras that you might need later when building integrations with other tools.
|
||||
|
||||
## Password hashing
|
||||
|
||||
"Hashing" means converting some content (a password in this case) into a sequence of bytes (just a string) that looks like gibberish.
|
||||
@@ -135,7 +144,7 @@ Define a Pydantic Model that will be used in the token endpoint for the response
|
||||
|
||||
Create a utility function to generate a new access token.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 6 12 13 14 28 29 30 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6 12 13 14 28 29 30 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -167,13 +176,13 @@ The JWT specification says that there's a key `sub`, with the subject of the tok
|
||||
|
||||
It's optional to use it, but that's where you would put the user's identification, so we are using it here.
|
||||
|
||||
JWT might be used for other things apart from identifying a user and allowing him to perform operations directly on your API.
|
||||
JWT might be used for other things apart from identifying a user and allowing them to perform operations directly on your API.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you could identify a "car" or a "blog post".
|
||||
|
||||
Then you could add permissions about that entity, like "drive" (for the car) or "edit" (for the blog).
|
||||
|
||||
And then, you could give that JWT token to a user (or bot), and he could use it to perform those actions (drive the car, or edit the blog post) without even needing to have an account, just with the JWT token your API generated for that.
|
||||
And then, you could give that JWT token to a user (or bot), and they could use it to perform those actions (drive the car, or edit the blog post) without even needing to have an account, just with the JWT token your API generated for that.
|
||||
|
||||
Using these ideas, JWT can be used for way more sophisticated scenarios.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -247,7 +256,7 @@ Many packages that simplify it a lot have to make many compromises with the data
|
||||
|
||||
It gives you all the flexibility to choose the ones that fit your project the best.
|
||||
|
||||
And you can use directly many well maintained and widely used packages like `passlib` and `pyjwt`, because **FastAPI** doesn't require any complex mechanisms to integrate external packages.
|
||||
And you can use directly many well maintained and widely used packages like `passlib` and `python-jose`, because **FastAPI** doesn't require any complex mechanisms to integrate external packages.
|
||||
|
||||
But it provides you the tools to simplify the process as much as possible without compromising flexibility, robustness, or security.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,9 +47,9 @@ Now let's use the utilities provided by **FastAPI** to handle this.
|
||||
|
||||
### `OAuth2PasswordRequestForm`
|
||||
|
||||
First, import `OAuth2PasswordRequestForm`, and use it as a dependency with `Depends` for the path `/token`:
|
||||
First, import `OAuth2PasswordRequestForm`, and use it as a dependency with `Depends` in the *path operation* for `/token`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 74"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4 76"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ If there is no such user, we return an error saying "incorrect username or passw
|
||||
|
||||
For the error, we use the exception `HTTPException`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 75 76 77"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="3 77 78 79"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ If your database is stolen, the thief won't have your users' plaintext passwords
|
||||
|
||||
So, the thief won't be able to try to use those same passwords in another system (as many users use the same password everywhere, this would be dangerous).
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="78 79 80 81"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="80 81 82 83"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -156,7 +156,7 @@ For this simple example, we are going to just be completely insecure and return
|
||||
|
||||
But for now, let's focus on the specific details we need.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="83"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="85"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -181,7 +181,7 @@ Both of these dependencies will just return an HTTP error if the user doesn't ex
|
||||
|
||||
So, in our endpoint, we will only get a user if the user exists, was correctly authenticated, and is active:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 67 68 69 70 88"
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 69 70 71 72 90"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/security/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -98,9 +98,9 @@ Let's refer to the file `sql_app/database.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, we are "connecting" to a SQLite database (opening a file with the SQLite database).
|
||||
|
||||
The file will be located at the same directory in the file `test.db`.
|
||||
The file will be located at the same directory in the file `sql_app.db`.
|
||||
|
||||
That's why the last part is `./test.db`.
|
||||
That's why the last part is `./sql_app.db`.
|
||||
|
||||
If you were using a **PostgreSQL** database instead, you would just have to uncomment the line:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -437,6 +437,8 @@ And you would also use Alembic for "migrations" (that's its main job).
|
||||
|
||||
A "migration" is the set of steps needed whenever you change the structure of your SQLAlchemy models, add a new attribute, etc. to replicate those changes in the database, add a new column, a new table, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
You can find an example of Alembic in a FastAPI project in the templates from [Project Generation - Template](../project-generation.md){.internal-link target=_blank}. Specifically in <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/full-stack-fastapi-postgresql/tree/master/%7B%7Bcookiecutter.project_slug%7D%7D/backend/app/alembic/" class="external-link" target="_blank">the `alembic` directory in the source code</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a dependency
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,8 +4,11 @@ site_url: https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/
|
||||
theme:
|
||||
name: material
|
||||
palette:
|
||||
scheme: preference
|
||||
primary: teal
|
||||
accent: amber
|
||||
icon:
|
||||
repo: fontawesome/brands/github-alt
|
||||
logo: img/icon-white.svg
|
||||
favicon: img/favicon.png
|
||||
language: en
|
||||
@@ -15,11 +18,18 @@ edit_uri: ''
|
||||
google_analytics:
|
||||
- UA-133183413-1
|
||||
- auto
|
||||
plugins:
|
||||
- search
|
||||
- markdownextradata:
|
||||
data: data
|
||||
nav:
|
||||
- FastAPI: index.md
|
||||
- Languages:
|
||||
- en: /
|
||||
- es: /es/
|
||||
- it: /it/
|
||||
- pt: /pt/
|
||||
- ru: /ru/
|
||||
- zh: /zh/
|
||||
- features.md
|
||||
- python-types.md
|
||||
@@ -65,7 +75,7 @@ nav:
|
||||
- tutorial/sql-databases.md
|
||||
- tutorial/bigger-applications.md
|
||||
- tutorial/background-tasks.md
|
||||
- tutorial/application-configuration.md
|
||||
- tutorial/metadata.md
|
||||
- tutorial/static-files.md
|
||||
- tutorial/testing.md
|
||||
- tutorial/debugging.md
|
||||
@@ -89,7 +99,8 @@ nav:
|
||||
- advanced/sql-databases-peewee.md
|
||||
- advanced/async-sql-databases.md
|
||||
- advanced/nosql-databases.md
|
||||
- advanced/sub-applications-proxy.md
|
||||
- advanced/sub-applications.md
|
||||
- advanced/behind-a-proxy.md
|
||||
- advanced/templates.md
|
||||
- advanced/graphql.md
|
||||
- advanced/websockets.md
|
||||
@@ -98,6 +109,9 @@ nav:
|
||||
- advanced/testing-websockets.md
|
||||
- advanced/testing-events.md
|
||||
- advanced/testing-dependencies.md
|
||||
- advanced/testing-database.md
|
||||
- advanced/settings.md
|
||||
- advanced/conditional-openapi.md
|
||||
- advanced/extending-openapi.md
|
||||
- advanced/openapi-callbacks.md
|
||||
- advanced/wsgi.md
|
||||
@@ -126,19 +140,20 @@ markdown_extensions:
|
||||
- name: mermaid
|
||||
class: mermaid
|
||||
format: !!python/name:pymdownx.superfences.fence_div_format ''
|
||||
- pymdownx.tabbed
|
||||
extra:
|
||||
social:
|
||||
- type: github
|
||||
- icon: fontawesome/brands/github-alt
|
||||
link: https://github.com/tiangolo/typer
|
||||
- type: twitter
|
||||
- icon: fontawesome/brands/twitter
|
||||
link: https://twitter.com/tiangolo
|
||||
- type: linkedin
|
||||
- icon: fontawesome/brands/linkedin
|
||||
link: https://www.linkedin.com/in/tiangolo
|
||||
- type: rss
|
||||
- icon: fontawesome/brands/dev
|
||||
link: https://dev.to/tiangolo
|
||||
- type: medium
|
||||
- icon: fontawesome/brands/medium
|
||||
link: https://medium.com/@tiangolo
|
||||
- type: globe
|
||||
- icon: fontawesome/solid/globe
|
||||
link: https://tiangolo.com
|
||||
extra_css:
|
||||
- css/termynal.css
|
||||
|
||||
18
docs/es/docs/advanced/index.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
# Guía de Usuario Avanzada - Introducción
|
||||
|
||||
## Características Adicionales
|
||||
|
||||
El [Tutorial - Guía de Usuario](../tutorial/){.internal-link target=_blank} principal debe ser suficiente para darte un paseo por todas las características principales de **FastAPI**
|
||||
|
||||
En las secciones siguientes verás otras opciones, configuraciones, y características adicionales.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! tip
|
||||
Las próximas secciones **no son necesariamente "avanzadas"**.
|
||||
|
||||
Y es posible que para tu caso, la solución se encuentre en una de estas.
|
||||
|
||||
## Lee primero el Tutorial
|
||||
|
||||
Puedes continuar usando la mayoría de las características de **FastAPI** con el conocimiento del [Tutorial - Guía de Usuario](../tutorial/){.internal-link target=_blank} principal.
|
||||
|
||||
En las siguientes secciones se asume que lo has leído y conoces esas ideas principales.
|
||||
394
docs/es/docs/async.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,394 @@
|
||||
# Concurrencia y async / await
|
||||
|
||||
Detalles sobre la sintaxis `async def` para *path operation functions* y un poco de información sobre código asíncrono, concurrencia y paralelismo.
|
||||
|
||||
## ¿Tienes prisa?
|
||||
|
||||
<abbr title="too long; didn't read"><strong>TL;DR:</strong></abbr>
|
||||
|
||||
Si estás utilizando libraries de terceros que te dicen que las llames con `await`, del tipo:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
results = await some_library()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Entonces declara tus *path operation functions* con `async def` de la siguiente manera:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2"
|
||||
@app.get('/')
|
||||
async def read_results():
|
||||
results = await some_library()
|
||||
return results
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Nota"
|
||||
Solo puedes usar `await` dentro de funciones creadas con `async def`.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Si estás utilizando libraries de terceros que se comunican con algo (una base de datos, una API, el sistema de archivos, etc.) y no tienes soporte para `await` (este es el caso para la mayoría de las libraries de bases de datos), declara tus *path operation functions* de forma habitual, con solo `def`, de la siguiente manera:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2"
|
||||
@app.get('/')
|
||||
def results():
|
||||
results = some_library()
|
||||
return results
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Si tu aplicación (de alguna manera) no tiene que comunicarse con nada más y en consecuencia esperar a que responda, usa `async def`.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Si simplemente no lo sabes, usa `def` normal.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**Nota**: puedes mezclar `def` y `async def` en tus *path operation functions* tanto como lo necesites y definir cada una utilizando la mejor opción para ti. FastAPI hará lo correcto con ellos.
|
||||
|
||||
De todos modos, en cualquiera de los casos anteriores, FastAPI seguirá funcionando de forma asíncrona y será extremadamente rápido.
|
||||
|
||||
Pero siguiendo los pasos anteriores, FastAPI podrá hacer algunas optimizaciones de rendimiento.
|
||||
|
||||
## Detalles Técnicos
|
||||
|
||||
Las versiones modernas de Python tienen soporte para **"código asíncrono"** usando algo llamado **"coroutines"**, usando la sintaxis **`async` y `await`**.
|
||||
|
||||
Veamos esa frase por partes en las secciones siguientes:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Código Asíncrono**
|
||||
* **`async` y `await`**
|
||||
* **Coroutines**
|
||||
|
||||
## Código Asíncrono
|
||||
|
||||
El código asíncrono sólo significa que el lenguaje 💬 tiene una manera de decirle al sistema / programa 🤖 que, en algún momento del código, 🤖 tendrá que esperar a que *algo más* termine en otro sitio. Digamos que ese *algo más* se llama, por ejemplo, "archivo lento" 📝.
|
||||
|
||||
Durante ese tiempo, el sistema puede hacer otras cosas, mientras "archivo lento" 📝 termina.
|
||||
|
||||
Entonces el sistema / programa 🤖 volverá cada vez que pueda, sea porque está esperando otra vez, porque 🤖 ha terminado todo el trabajo que tenía en ese momento. Y 🤖 verá si alguna de las tareas por las que estaba esperando ha terminado, haciendo lo que tenía que hacer.
|
||||
|
||||
Luego, 🤖 cogerá la primera tarea finalizada (digamos, nuestro "archivo lento" 📝) y continuará con lo que tenía que hacer con esa tarea.
|
||||
|
||||
Esa "espera de otra cosa" normalmente se refiere a operaciones <abbr title = "Input and Output, en español: Entrada y Salida.">I/O</abbr> que son relativamente "lentas" (en relación a la velocidad del procesador y memoria RAM), como por ejemplo esperar por:
|
||||
|
||||
* los datos de cliente que se envían a través de la red
|
||||
* los datos enviados por tu programa para ser recibidos por el cliente a través de la red
|
||||
* el contenido de un archivo en disco para ser leído por el sistema y entregado al programa
|
||||
* los contenidos que tu programa da al sistema para ser escritos en disco
|
||||
* una operación relacionada con una API remota
|
||||
* una operación de base de datos
|
||||
* el retorno de resultados de una consulta de base de datos
|
||||
* etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Como el tiempo de ejecución se consume principalmente al esperar a operaciones de <abbr title = "Input and Output">I/O</abbr>, las llaman operaciones "<abbr title="atadas a Entrada y Salida">I/O bound</abbr>".
|
||||
|
||||
Se llama "asíncrono" porque el sistema / programa no tiene que estar "sincronizado" con la tarea lenta, esperando el momento exacto en que finaliza la tarea, sin hacer nada, para poder recoger el resultado de la tarea y continuar el trabajo.
|
||||
|
||||
En lugar de eso, al ser un sistema "asíncrono", una vez finalizada, la tarea puede esperar un poco en la cola (algunos microsegundos) para que la computadora / programa termine lo que estaba haciendo, y luego vuelva para recoger los resultados y seguir trabajando con ellos.
|
||||
|
||||
Por "síncrono" (contrario a "asíncrono") también se usa habitualmente el término "secuencial", porque el sistema / programa sigue todos los pasos secuencialmente antes de cambiar a una tarea diferente, incluso si esos pasos implican esperas.
|
||||
|
||||
### Concurrencia y Hamburguesas
|
||||
|
||||
El concepto de código **asíncrono** descrito anteriormente a veces también se llama **"concurrencia"**. Es diferente del **"paralelismo"**.
|
||||
|
||||
**Concurrencia** y **paralelismo** ambos se relacionan con "cosas diferentes que suceden más o menos al mismo tiempo".
|
||||
|
||||
Pero los detalles entre *concurrencia* y *paralelismo* son bastante diferentes.
|
||||
|
||||
Para entender las diferencias, imagina la siguiente historia sobre hamburguesas:
|
||||
|
||||
### Hamburguesas Concurrentes
|
||||
|
||||
Vas con la persona que te gusta 😍 a pedir comida rápida 🍔, haces cola mientras el cajero 💁 recoge los pedidos de las personas de delante tuyo.
|
||||
|
||||
Llega tu turno, haces tu pedido de 2 hamburguesas impresionantes para esa persona 😍 y para ti.
|
||||
|
||||
Pagas 💸.
|
||||
|
||||
El cajero 💁 le dice algo al chico de la cocina 👨🍳 para que sepa que tiene que preparar tus hamburguesas 🍔 (a pesar de que actualmente está preparando las de los clientes anteriores).
|
||||
|
||||
El cajero 💁 te da el número de tu turno.
|
||||
|
||||
Mientras esperas, vas con esa persona 😍 y eliges una mesa, se sientan y hablan durante un rato largo (ya que las hamburguesas son muy impresionantes y necesitan un rato para prepararse ✨🍔✨).
|
||||
|
||||
Mientras te sientas en la mesa con esa persona 😍, esperando las hamburguesas 🍔, puedes disfrutar ese tiempo admirando lo increíble, inteligente, y bien que se ve ✨😍✨.
|
||||
|
||||
Mientras esperas y hablas con esa persona 😍, de vez en cuando, verificas el número del mostrador para ver si ya es tu turno.
|
||||
|
||||
Al final, en algún momento, llega tu turno. Vas al mostrador, coges tus hamburguesas 🍔 y vuelves a la mesa.
|
||||
|
||||
Tú y esa persona 😍 se comen las hamburguesas 🍔 y la pasan genial ✨.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Imagina que eres el sistema / programa 🤖 en esa historia.
|
||||
|
||||
Mientras estás en la cola, estás quieto 😴, esperando tu turno, sin hacer nada muy "productivo". Pero la línea va rápida porque el cajero 💁 solo recibe los pedidos (no los prepara), así que está bien.
|
||||
|
||||
Luego, cuando llega tu turno, haces un trabajo "productivo" real 🤓, procesas el menú, decides lo que quieres, lo que quiere esa persona 😍, pagas 💸, verificas que das el billete o tarjeta correctos, verificas que te cobren correctamente, que el pedido tiene los artículos correctos, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Pero entonces, aunque aún no tienes tus hamburguesas 🍔, el trabajo hecho con el cajero 💁 está "en pausa" ⏸, porque debes esperar 🕙 a que tus hamburguesas estén listas.
|
||||
|
||||
Pero como te alejas del mostrador y te sientas en la mesa con un número para tu turno, puedes cambiar tu atención 🔀 a esa persona 😍 y "trabajar" ⏯ 🤓 en eso. Entonces nuevamente estás haciendo algo muy "productivo" 🤓, como coquetear con esa persona 😍.
|
||||
|
||||
Después, el 💁 cajero dice "he terminado de hacer las hamburguesas" 🍔 poniendo tu número en la pantalla del mostrador, pero no saltas al momento que el número que se muestra es el tuyo. Sabes que nadie robará tus hamburguesas 🍔 porque tienes el número de tu turno y ellos tienen el suyo.
|
||||
|
||||
Así que esperas a que esa persona 😍 termine la historia (terminas el trabajo actual ⏯ / tarea actual que se está procesando 🤓), sonríes gentilmente y le dices que vas por las hamburguesas ⏸.
|
||||
|
||||
Luego vas al mostrador 🔀, a la tarea inicial que ya está terminada ⏯, recoges las hamburguesas 🍔, les dices gracias y las llevas a la mesa. Eso termina esa fase / tarea de interacción con el mostrador ⏹. Eso a su vez, crea una nueva tarea, "comer hamburguesas" 🔀 ⏯, pero la anterior de "conseguir hamburguesas" está terminada ⏹.
|
||||
|
||||
### Hamburguesas Paralelas
|
||||
|
||||
Ahora imagina que estas no son "Hamburguesas Concurrentes" sino "Hamburguesas Paralelas".
|
||||
|
||||
Vas con la persona que te gusta 😍 por comida rápida paralela 🍔.
|
||||
|
||||
Haces la cola mientras varios cajeros (digamos 8) que a la vez son cocineros 👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳 toman los pedidos de las personas que están delante de ti.
|
||||
|
||||
Todos los que están antes de ti están esperando 🕙 que sus hamburguesas 🍔 estén listas antes de dejar el mostrador porque cada uno de los 8 cajeros prepara la hamburguesa de inmediato antes de recibir el siguiente pedido.
|
||||
|
||||
Entonces finalmente es tu turno, haces tu pedido de 2 hamburguesas 🍔 impresionantes para esa persona 😍 y para ti.
|
||||
|
||||
Pagas 💸.
|
||||
|
||||
El cajero va a la cocina 👨🍳.
|
||||
|
||||
Esperas, de pie frente al mostrador 🕙, para que nadie más recoja tus hamburguesas 🍔, ya que no hay números para los turnos.
|
||||
|
||||
Como tu y esa persona 😍 están ocupados en impedir que alguien se ponga delante y recoja tus hamburguesas apenas llegan 🕙, tampoco puedes prestarle atención a esa persona 😞.
|
||||
|
||||
Este es un trabajo "síncrono", estás "sincronizado" con el cajero / cocinero 👨🍳. Tienes que esperar y estar allí en el momento exacto en que el cajero / cocinero 👨🍳 termina las hamburguesas 🍔 y te las da, o de lo contrario, alguien más podría cogerlas.
|
||||
|
||||
Luego, el cajero / cocinero 👨🍳 finalmente regresa con tus hamburguesas 🍔, después de mucho tiempo esperando 🕙 frente al mostrador.
|
||||
|
||||
Cojes tus hamburguesas 🍔 y vas a la mesa con esa persona 😍.
|
||||
|
||||
Sólo las comes y listo 🍔 ⏹.
|
||||
|
||||
No has hablado ni coqueteado mucho, ya que has pasado la mayor parte del tiempo esperando 🕙 frente al mostrador 😞.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
En este escenario de las hamburguesas paralelas, tú eres un sistema / programa 🤖 con dos procesadores (tú y la persona que te gusta 😍), ambos esperando 🕙 y dedicando su atención ⏯ a estar "esperando en el mostrador" 🕙 durante mucho tiempo.
|
||||
|
||||
La tienda de comida rápida tiene 8 procesadores (cajeros / cocineros) 👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳. Mientras que la tienda de hamburguesas concurrentes podría haber tenido solo 2 (un cajero y un cocinero) 💁 👨🍳.
|
||||
|
||||
Pero aún así, la experiencia final no es la mejor 😞.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Esta sería la historia paralela equivalente de las hamburguesas 🍔.
|
||||
|
||||
Para un ejemplo más "real" de ésto, imagina un banco.
|
||||
|
||||
Hasta hace poco, la mayoría de los bancos tenían varios cajeros 👨💼👨💼👨💼👨💼 y una gran línea 🕙🕙🕙🕙🕙🕙🕙🕙.
|
||||
|
||||
Todos los cajeros haciendo todo el trabajo con un cliente tras otro 👨💼⏯.
|
||||
|
||||
Y tienes que esperar 🕙 en la fila durante mucho tiempo o perderás tu turno.
|
||||
|
||||
Probablemente no querrás llevar contigo a la persona que te gusta 😍 a hacer encargos al banco 🏦.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusión de las Hamburguesa
|
||||
|
||||
En este escenario de "hamburguesas de comida rápida con tu pareja", debido a que hay mucha espera 🕙, tiene mucho más sentido tener un sistema con concurrencia ⏸🔀⏯.
|
||||
|
||||
Este es el caso de la mayoría de las aplicaciones web.
|
||||
|
||||
Muchos, muchos usuarios, pero el servidor está esperando 🕙 el envío de las peticiones ya que su conexión no es buena.
|
||||
|
||||
Y luego esperando 🕙 nuevamente a que las respuestas retornen.
|
||||
|
||||
Esta "espera" 🕙 se mide en microsegundos, pero aun así, sumando todo, al final es mucha espera.
|
||||
|
||||
Es por eso que tiene mucho sentido usar código asíncrono ⏸🔀⏯ para las API web.
|
||||
|
||||
La mayoría de los framework populares de Python existentes (incluidos Flask y Django) se crearon antes de que existieran las nuevas funciones asíncronas en Python. Por lo tanto, las formas en que pueden implementarse admiten la ejecución paralela y una forma más antigua de ejecución asíncrona que no es tan potente como la actual.
|
||||
|
||||
A pesar de que la especificación principal para Python web asíncrono (ASGI) se desarrolló en Django, para agregar soporte para WebSockets.
|
||||
|
||||
Ese tipo de asincronía es lo que hizo popular a NodeJS (aunque NodeJS no es paralelo) y esa es la fortaleza de Go como lenguaje de programación.
|
||||
|
||||
Y ese es el mismo nivel de rendimiento que obtienes con **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
Y como puede tener paralelismo y asincronía al mismo tiempo, obtienes un mayor rendimiento que la mayoría de los frameworks de NodeJS probados y a la par con Go, que es un lenguaje compilado más cercano a C <a href="https://www.techempower.com/benchmarks/#section=data-r17&hw=ph&test=query&l=zijmkf-1" class="external-link" target="_blank">(todo gracias Starlette)</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### ¿Es la concurrencia mejor que el paralelismo?
|
||||
|
||||
¡No! Esa no es la moraleja de la historia.
|
||||
|
||||
La concurrencia es diferente al paralelismo. Y es mejor en escenarios **específicos** que implican mucha espera. Debido a eso, generalmente es mucho mejor que el paralelismo para el desarrollo de aplicaciones web. Pero no para todo.
|
||||
|
||||
Entonces, para explicar eso, imagina la siguiente historia corta:
|
||||
|
||||
> Tienes que limpiar una casa grande y sucia.
|
||||
|
||||
*Sí, esa es toda la historia*.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
No hay esperas 🕙, solo hay mucho trabajo por hacer, en varios lugares de la casa.
|
||||
|
||||
Podrías tener turnos como en el ejemplo de las hamburguesas, primero la sala de estar, luego la cocina, pero como no estás esperando nada, solo limpiando y limpiando, los turnos no afectarían nada.
|
||||
|
||||
Tomaría la misma cantidad de tiempo terminar con o sin turnos (concurrencia) y habrías hecho la misma cantidad de trabajo.
|
||||
|
||||
Pero en este caso, si pudieras traer a los 8 ex cajeros / cocineros / ahora limpiadores 👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳👨🍳, y cada uno de ellos (y tú) podría tomar una zona de la casa para limpiarla, podría hacer todo el trabajo en **paralelo**, con la ayuda adicional y terminar mucho antes.
|
||||
|
||||
En este escenario, cada uno de los limpiadores (incluido tú) sería un procesador, haciendo su parte del trabajo.
|
||||
|
||||
Y como la mayor parte del tiempo de ejecución lo coge el trabajo real (en lugar de esperar), y el trabajo en un sistema lo realiza una <abbr title = "Central Processing Unit. En español: Unidad Central de Procesamiento."> CPU </abbr>, a estos problemas se les llama "<abbr title="En español: atado a CPU.">CPU bond</abbr>".
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Ejemplos típicos de operaciones dependientes de CPU son cosas que requieren un procesamiento matemático complejo.
|
||||
|
||||
Por ejemplo:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Audio** o **procesamiento de imágenes**.
|
||||
* **Visión por computadora**: una imagen está compuesta de millones de píxeles, cada píxel tiene 3 valores / colores, procesamiento que normalmente requiere calcular algo en esos píxeles, todo al mismo tiempo.
|
||||
* **Machine Learning**: normalmente requiere muchas multiplicaciones de "matrices" y "vectores". Imagina en una enorme hoja de cálculo con números y tener que multiplicarlos todos al mismo tiempo.
|
||||
* **Deep Learning**: este es un subcampo de Machine Learning, por lo tanto, aplica lo mismo. Es solo que no hay una sola hoja de cálculo de números para multiplicar, sino un gran conjunto de ellas, y en muchos casos, usa un procesador especial para construir y / o usar esos modelos.
|
||||
|
||||
### Concurrencia + Paralelismo: Web + Machine Learning
|
||||
|
||||
Con **FastAPI** puedes aprovechar la concurrencia que es muy común para el desarrollo web (atractivo principal de NodeJS).
|
||||
|
||||
Pero también puedes aprovechar los beneficios del paralelismo y el multiprocesamiento (tener múltiples procesos ejecutándose en paralelo) para cargas de trabajo **CPU bond** como las de los sistemas de Machine Learning.
|
||||
|
||||
Eso, más el simple hecho de que Python es el lenguaje principal para **Data Science**, Machine Learning y especialmente Deep Learning, hacen de FastAPI una muy buena combinación para las API y aplicaciones web de Data Science / Machine Learning (entre muchas otras).
|
||||
|
||||
Para ver cómo lograr este paralelismo en producción, consulta la sección sobre [Despliegue](deployment.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
## `async` y `await`
|
||||
|
||||
Las versiones modernas de Python tienen una forma muy intuitiva de definir código asíncrono. Esto hace que se vea como un código "secuencial" normal y que haga la "espera" por ti en los momentos correctos.
|
||||
|
||||
Cuando hay una operación que requerirá esperar antes de dar los resultados y tiene soporte para estas nuevas características de Python, puedes programarlo como:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
burgers = await get_burgers(2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
La clave aquí es `await`. Eso le dice a Python que tiene que esperar ⏸ a que `get_burgers (2)` termine de hacer lo suyo 🕙 antes de almacenar los resultados en `hamburguesas`. Con eso, Python sabrá que puede ir y hacer otra cosa 🔀 ⏯ mientras tanto (como recibir otra solicitud).
|
||||
|
||||
Para que `await` funcione, tiene que estar dentro de una función que admita esta asincronía. Para hacer eso, simplemente lo declaras con `async def`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1"
|
||||
async def get_burgers(number: int):
|
||||
# Do some asynchronous stuff to create the burgers
|
||||
return burgers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...en vez de `def`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2"
|
||||
# This is not asynchronous
|
||||
def get_sequential_burgers(number: int):
|
||||
# Do some sequential stuff to create the burgers
|
||||
return burgers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Con `async def`, Python sabe que, dentro de esa función, debe tener en cuenta las expresiones `wait` y que puede "pausar" ⏸ la ejecución de esa función e ir a hacer otra cosa 🔀 antes de regresar.
|
||||
|
||||
Cuando desees llamar a una función `async def`, debes "esperarla". Entonces, esto no funcionará:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
# Esto no funcionará, porque get_burgers se definió con: async def
|
||||
hamburguesas = get_burgers (2)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Por lo tanto, si estás utilizando una library que te dice que puedes llamarla con `await`, debes crear las *path operation functions* que la usan con `async def`, como en:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 3"
|
||||
@app.get('/burgers')
|
||||
async def read_burgers():
|
||||
burgers = await get_burgers(2)
|
||||
return burgers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Más detalles técnicos
|
||||
|
||||
Es posible que hayas notado que `await` solo se puede usar dentro de las funciones definidas con `async def`.
|
||||
|
||||
Pero al mismo tiempo, las funciones definidas con `async def` deben ser "esperadas". Por lo tanto, las funciones con `async def` solo se pueden invocar dentro de las funciones definidas con `async def` también.
|
||||
|
||||
Entonces, relacionado con la paradoja del huevo y la gallina, ¿cómo se llama a la primera función `async`?
|
||||
|
||||
Si estás trabajando con **FastAPI** no tienes que preocuparte por eso, porque esa "primera" función será tu *path operation function*, y FastAPI sabrá cómo hacer lo pertinente.
|
||||
|
||||
En el caso de que desees usar `async` / `await` sin FastAPI, <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/asyncio-task.html#coroutine" class="external-link" target="_blank">revisa la documentación oficial de Python</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
### Otras formas de código asíncrono
|
||||
|
||||
Este estilo de usar `async` y `await` es relativamente nuevo en el lenguaje.
|
||||
|
||||
Pero hace que trabajar con código asíncrono sea mucho más fácil.
|
||||
|
||||
Esta misma sintaxis (o casi idéntica) también se incluyó recientemente en las versiones modernas de JavaScript (en Browser y NodeJS).
|
||||
|
||||
Pero antes de eso, manejar código asíncrono era bastante más complejo y difícil.
|
||||
|
||||
En versiones anteriores de Python, podrías haber utilizado <abbr title="En español: hilos.">threads</abbr> o <a href="http://www.gevent.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Gevent</a>. Pero el código es mucho más complejo de entender, depurar y desarrollar.
|
||||
|
||||
En versiones anteriores de NodeJS / Browser JavaScript, habrías utilizado "callbacks". Lo que conduce a <a href="http://callbackhell.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">callback hell</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Coroutines
|
||||
|
||||
**Coroutine** es un término sofisticado para referirse a la cosa devuelta por una función `async def`. Python sabe que es algo así como una función que puede iniciar y que terminará en algún momento, pero que también podría pausarse ⏸ internamente, siempre que haya un `await` dentro de ella.
|
||||
|
||||
Pero toda esta funcionalidad de usar código asincrónico con `async` y `await` se resume muchas veces como usar "coroutines". Es comparable a la característica principal de Go, las "Goroutines".
|
||||
|
||||
## Conclusión
|
||||
|
||||
Veamos la misma frase de arriba:
|
||||
|
||||
> Las versiones modernas de Python tienen soporte para **"código asíncrono"** usando algo llamado **"coroutines"**, con la sintaxis **`async` y `await`**.
|
||||
|
||||
Eso ya debería tener más sentido ahora. ✨
|
||||
|
||||
Todo eso es lo que impulsa FastAPI (a través de Starlette) y lo que hace que tenga un rendimiento tan impresionante.
|
||||
|
||||
## Detalles muy técnicos
|
||||
|
||||
!!! warning "Advertencia"
|
||||
Probablemente puedas saltarte esto.
|
||||
|
||||
Estos son detalles muy técnicos de cómo **FastAPI** funciona a muy bajo nivel.
|
||||
|
||||
Si tienes bastante conocimiento técnico (coroutines, threads, bloqueos, etc.) y tienes curiosidad acerca de cómo FastAPI gestiona `async def` vs `def` normal, continúa.
|
||||
|
||||
### Path operation functions
|
||||
|
||||
Cuando declaras una *path operation function* con `def` normal en lugar de `async def`, se ejecuta en un threadpool externo que luego es "<abbr title="En español: esperado. Usando await.">awaited</abbr>", en lugar de ser llamado directamente (ya que bloquearía el servidor).
|
||||
|
||||
Si vienes de otro framework asíncrono que no funciona de la manera descrita anteriormente y estás acostumbrado a definir *path operation functions* del tipo sólo cálculo con `def` simple para una pequeña ganancia de rendimiento (aproximadamente 100 nanosegundos), ten en cuenta que en **FastAPI** el efecto sería bastante opuesto. En estos casos, es mejor usar `async def` a menos que tus *path operation functions* usen un código que realice el bloqueo <abbr title="Input/Output: disk reading or writing, network communications.">I/O</abbr>.
|
||||
|
||||
Aún así, en ambas situaciones, es probable que **FastAPI** sea [aún más rápido](/#rendimiento){.Internal-link target=_blank} que (o al menos comparable) a tu framework anterior.
|
||||
|
||||
### Dependencias
|
||||
|
||||
Lo mismo se aplica para las dependencias. Si una dependencia es una función estándar `def` en lugar de `async def`, se ejecuta en el threadpool externo.
|
||||
|
||||
### Subdependencias
|
||||
|
||||
Puedes tener múltiples dependencias y subdependencias que se requieren unas a otras (como parámetros de las definiciones de cada función), algunas de ellas pueden crearse con `async def` y otras con `def` normal. Igual todo seguiría funcionando correctamente, y las creadas con `def` normal se llamarían en un thread externo (del threadpool) en lugar de ser "awaited".
|
||||
|
||||
### Otras funciones de utilidades
|
||||
|
||||
Cualquier otra función de utilidad que llames directamente se puede crear con `def` o `async def` normales y FastAPI no afectará la manera en que la llames.
|
||||
|
||||
Esto contrasta con las funciones que FastAPI llama por ti: las *path operation functions* y dependencias.
|
||||
|
||||
Si tu función de utilidad es creada con `def` normal, se llamará directamente (tal cual la escribes en tu código), no en un threadpool, si la función se crea con `async def`, entonces debes usar `await` con esa función cuando la llamas en tu código.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Nuevamente, estos son detalles muy técnicos que probablemente sólo son útiles si los viniste a buscar expresamente.
|
||||
|
||||
De lo contrario, la guía de la sección anterior debería ser suficiente: <a href="#in-a-hurry">¿Tienes prisa?</a>.
|
||||
202
docs/es/docs/features.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,202 @@
|
||||
# Características
|
||||
|
||||
## Características de FastAPI
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** te provee lo siguiente:
|
||||
|
||||
### Basado en estándares abiertos
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>OpenAPI</strong></a> para la creación de APIs, incluyendo declaraciones de <abbr title="en español: ruta. En inglés también conocido cómo: endpoints, routes">path</abbr> <abbr title="también conocido como HTTP methods, cómo POST, GET, PUT, DELETE">operations</abbr>, parámetros, <abbr title="cuerpo del mensaje HTTP">body</abbr> requests, seguridad, etc.
|
||||
* Documentación automática del modelo de datos con <a href="http://json-schema.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>JSON Schema</strong></a> (dado que OpenAPI mismo está basado en JSON Schema).
|
||||
* Diseñado alrededor de estos estándares después de un estudio meticuloso. En vez de ser una capa añadida a último momento.
|
||||
* Esto también permite la **generación automática de código de cliente** para muchos lenguajes.
|
||||
|
||||
### Documentación automática
|
||||
|
||||
Documentación interactiva de la API e interfaces web de exploración. Hay múltiples opciones, dos incluídas por defecto, porque el framework está basado en OpenAPI.
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>Swagger UI</strong></a>, con exploración interactiva, llama y prueba tu API directamente desde tu navegador.
|
||||
|
||||
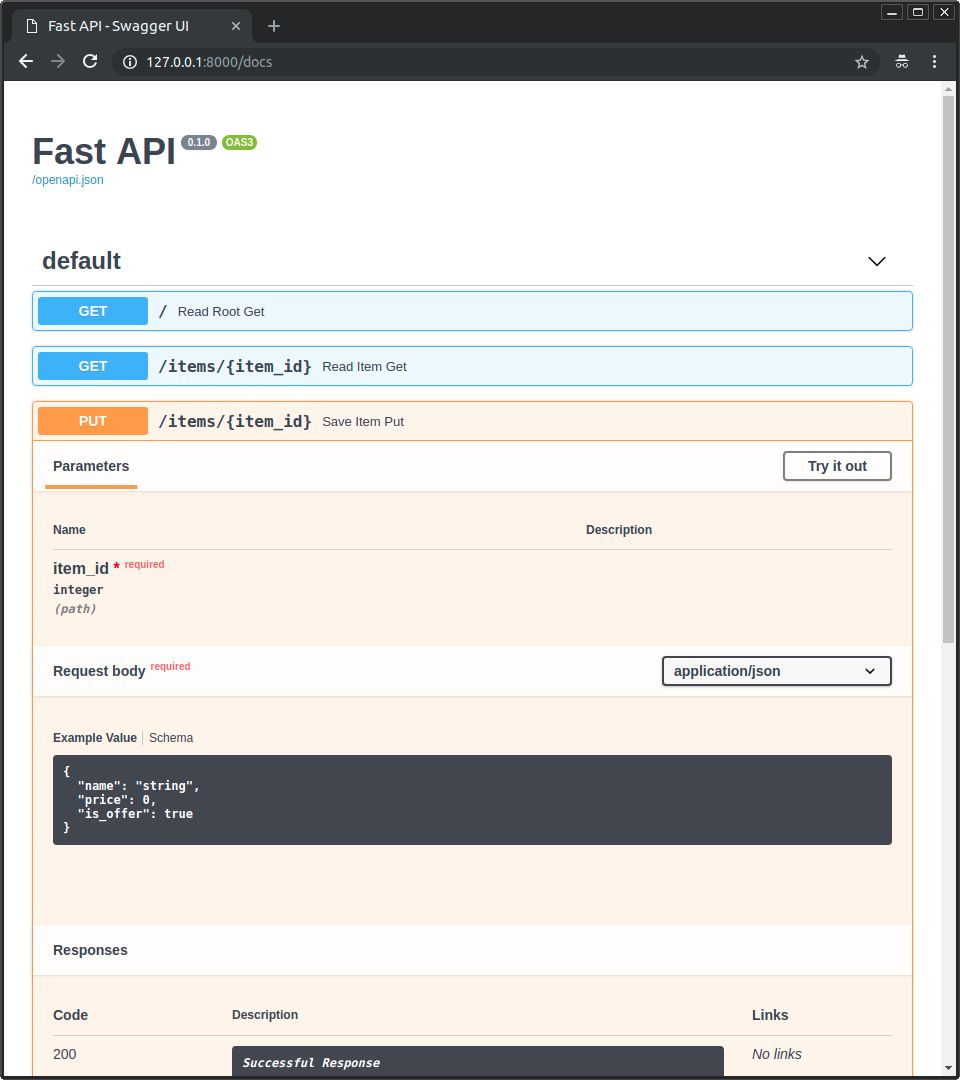
|
||||
|
||||
* Documentación alternativa de la API con <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>ReDoc</strong></a>.
|
||||
|
||||
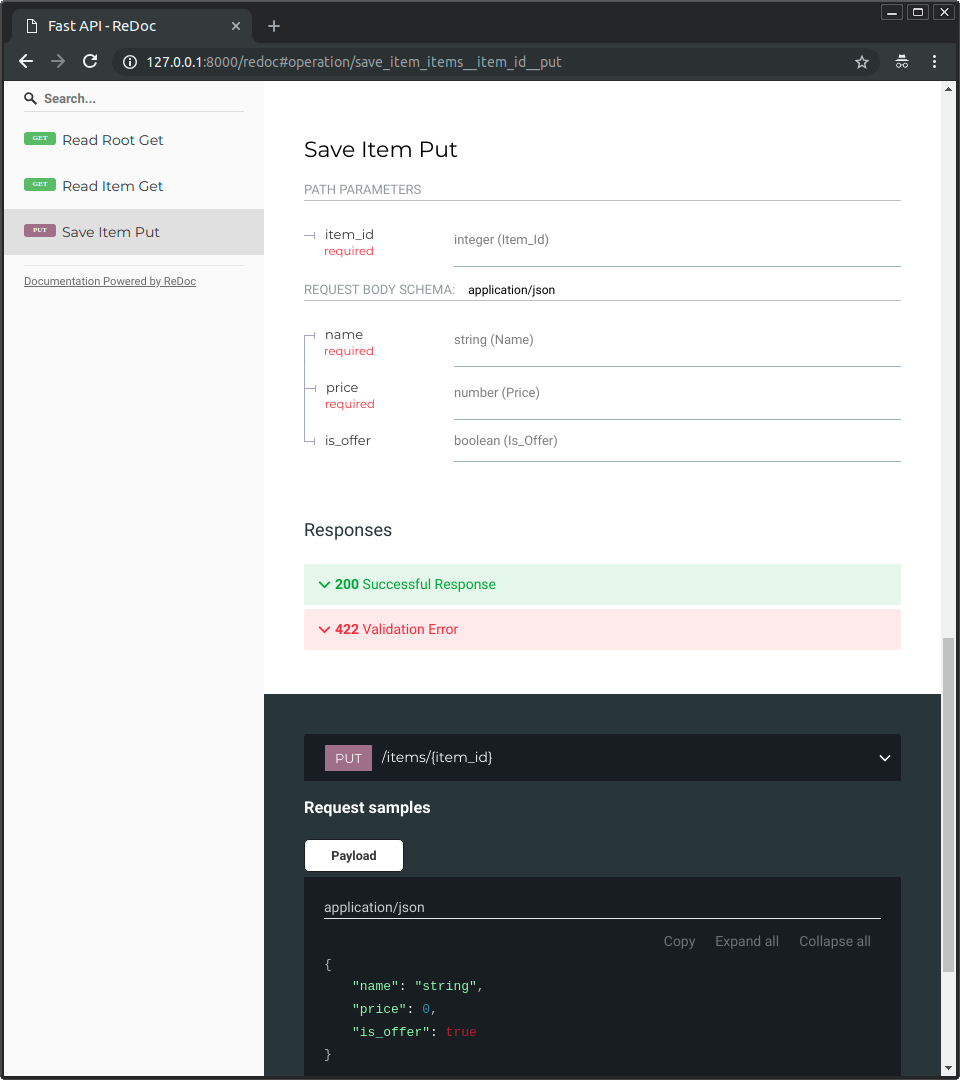
|
||||
|
||||
### Simplemente Python moderno
|
||||
|
||||
Todo está basado en las declaraciones de tipo de **Python 3.6** estándar (gracias a Pydantic). No necesitas aprender una sintáxis nueva, solo Python moderno.
|
||||
|
||||
Si necesitas un repaso de 2 minutos de cómo usar los tipos de Python (así no uses FastAPI) prueba el tutorial corto: [Python Types](python-types.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
Escribes Python estándar con tipos así:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from typing import List, Dict
|
||||
from datetime import date
|
||||
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
# Declaras la variable como un str
|
||||
# y obtienes soporte del editor dentro de la función
|
||||
def main(user_id: str):
|
||||
return user_id
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Un modelo de Pydantic
|
||||
class User(BaseModel):
|
||||
id: int
|
||||
name: str
|
||||
joined: date
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Este puede ser usado como:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
my_user: User = User(id=3, name="John Doe", joined="2018-07-19")
|
||||
|
||||
second_user_data = {
|
||||
"id": 4,
|
||||
"name": "Mary",
|
||||
"joined": "2018-11-30",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
my_second_user: User = User(**second_user_data)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info
|
||||
`**second_user_data` significa:
|
||||
|
||||
Pasa las <abbr title="en español key se refiere a la guía de un diccionario">keys</abbr> y los valores del dict `second_user_data` directamente como argumentos de key-value, equivalente a: `User(id=4, name="Mary", joined="2018-11-30")`
|
||||
|
||||
### Soporte del editor
|
||||
|
||||
El framework fue diseñado en su totalidad para ser fácil e intuitivo de usar. Todas las decisiones fueron probadas en múltiples editores antes de comenzar el desarrollo para asegurar la mejor experiencia de desarrollo.
|
||||
|
||||
En la última encuesta a desarrolladores de Python fue claro que <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/research/python-developers-survey-2017/#tools-and-features" class="external-link" target="_blank">la característica más usada es el "autocompletado"</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
El framework **FastAPI** está creado para satisfacer eso. El autocompletado funciona en todas partes.
|
||||
|
||||
No vas a tener que volver a la documentación seguido.
|
||||
|
||||
Así es como tu editor te puede ayudar:
|
||||
|
||||
* en <a href="https://code.visualstudio.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Visual Studio Code</a>:
|
||||
|
||||
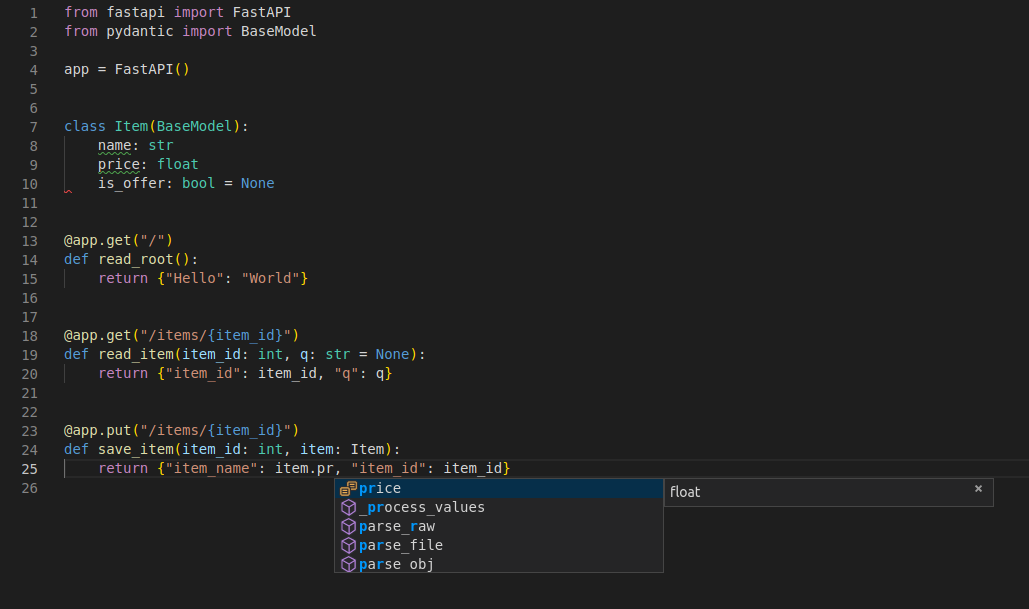
|
||||
|
||||
* en <a href="https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/" class="external-link" target="_blank">PyCharm</a>:
|
||||
|
||||
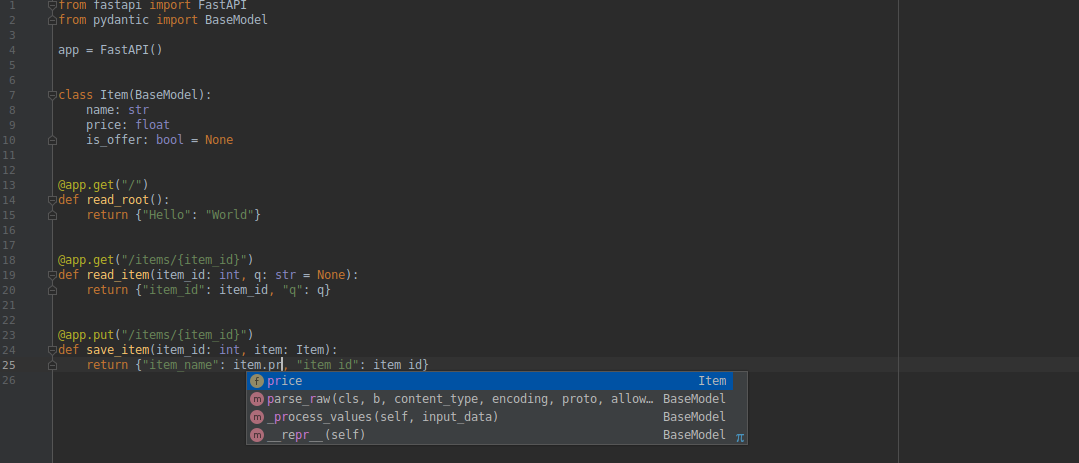
|
||||
|
||||
Obtendrás completado para tu código que podrías haber considerado imposible antes. Por ejemplo, el key `price` dentro del JSON body (que podría haber estado anidado) que viene de un request.
|
||||
|
||||
Ya no pasará que escribas los nombres de key equivocados, o que tengas que revisar constantemente la documentación o desplazarte arriba y abajo para saber si usaste `username` o `user_name`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Corto
|
||||
|
||||
Tiene **configuraciones por defecto** razonables para todo, con configuraciones opcionales en todas partes. Todos los parámetros pueden ser ajustados para tus necesidades y las de tu API.
|
||||
|
||||
Pero, todo **simplemente funciona** por defecto.
|
||||
|
||||
### Validación
|
||||
|
||||
* Validación para la mayoría (¿o todos?) los **tipos de datos** de Python incluyendo:
|
||||
* Objetos JSON (`dict`).
|
||||
* JSON array (`list`) definiendo tipos de ítem.
|
||||
* Campos de texto (`str`) definiendo longitudes mínimas y máximas.
|
||||
* Números (`int`, `float`) con valores mínimos y máximos, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
* Validación para tipos más exóticos como:
|
||||
* URL.
|
||||
* Email.
|
||||
* UUID.
|
||||
* ...y otros.
|
||||
|
||||
Toda la validación es manejada por **Pydantic**, que es robusto y sólidamente establecido.
|
||||
|
||||
### Seguridad y autenticación
|
||||
|
||||
La seguridad y la autenticación están integradas. Sin ningún compromiso con bases de datos ni modelos de datos.
|
||||
|
||||
Todos los schemes de seguridad están definidos en OpenAPI incluyendo:
|
||||
|
||||
* HTTP Basic.
|
||||
* **OAuth2** (también con **JWT tokens**). Prueba el tutorial en [OAuth2 with JWT](tutorial/security/oauth2-jwt.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
* API keys en:
|
||||
* Headers.
|
||||
* Parámetros de Query.
|
||||
* Cookies, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Más todas las características de seguridad de Starlette (incluyendo **session cookies**).
|
||||
|
||||
Todo ha sido construido como herramientas y componentes reutilizables que son fácilmente integrados con tus sistemas, almacenamiento de datos, bases de datos relacionales y no relacionales, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
### Dependency Injection
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI incluye un sistema de <abbr title='En español: Inyección de Dependencias. También conocido en inglés cómo: "components", "resources", "services", "providers"'><strong>Dependency Injection</strong></abbr> extremadamente poderoso y fácil de usar.
|
||||
|
||||
* Inclusive las dependencias pueden tener dependencias creando una jerarquía o un **"grafo" de dependencias**.
|
||||
* Todas son **manejadas automáticamente** por el framework.
|
||||
* Todas las dependencias pueden requerir datos de los requests y aumentar las restricciones del *path operation* y la documentación automática.
|
||||
* **Validación automática** inclusive para parámetros del *path operation* definidos en las dependencias.
|
||||
* Soporte para sistemas complejos de autenticación de usuarios, **conexiones con bases de datos**, etc.
|
||||
* **Sin comprometerse** con bases de datos, frontends, etc. Pero permitiendo integración fácil con todos ellos.
|
||||
|
||||
### "Plug-ins" ilimitados
|
||||
|
||||
O dicho de otra manera, no hay necesidad para "plug-ins". Importa y usa el código que necesites.
|
||||
|
||||
Cualquier integración está diseñada para que sea tan sencilla de usar (con dependencias) que puedas crear un "plug-in" para tu aplicación en dos líneas de código usando la misma estructura y sintáxis que usaste para tus *path operations*.
|
||||
|
||||
### Probado
|
||||
|
||||
* <abbr title="La cantidad de código que es probado automáticamente">Cobertura de pruebas</abbr> al 100%.
|
||||
* Base de código 100% <abbr title="Type annotations de Python, con esto tu editor y otras herramientas externas pueden darte mejor soporte">anotada con tipos</abbr>.
|
||||
* Usado en aplicaciones en producción.
|
||||
|
||||
## Características de Starlette
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** está basado y es completamente compatible con <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>Starlette</strong></a>. Tanto así, que cualquier código de Starlette que tengas también funcionará.
|
||||
|
||||
`FastAPI` es realmente una sub-clase de `Starlette`. Así que, si ya conoces o usas Starlette, muchas de las características funcionarán de la misma manera.
|
||||
|
||||
Con **FastAPI** obtienes todas las características de **Starlette** (porque FastAPI es simplemente Starlette en esteroides):
|
||||
|
||||
* Desempeño realmente impresionante. Es uno <a href="https://github.com/encode/starlette#performance" class="external-link" target="_blank"> de los frameworks de Python más rápidos, a la par con **NodeJS** y **Go**</a>.
|
||||
* Soporte para **WebSocket**.
|
||||
* Soporte para **GraphQL**.
|
||||
* <abbr title="En español: tareas que se ejecutan en el fondo, sin frenar requests, en el mismo proceso. En ingles: In-process background tasks">Tareas en background</abbr>.
|
||||
* Eventos de startup y shutdown.
|
||||
* Cliente de pruebas construido con `requests`.
|
||||
* **CORS**, GZip, Static Files, Streaming responses.
|
||||
* Soporte para **Session and Cookie**.
|
||||
* Cobertura de pruebas al 100%.
|
||||
* Base de código 100% anotada con tipos.
|
||||
|
||||
## Características de Pydantic
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** está basado y es completamente compatible con <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io" class="external-link" target="_blank"><strong>Pydantic</strong></a>. Tanto así, que cualquier código de Pydantic que tengas también funcionará.
|
||||
|
||||
Esto incluye a librerías externas basadas en Pydantic como <abbr title="Object-Relational Mapper">ORM</abbr>s y <abbr title="Object-Document Mapper">ODM</abbr>s para bases de datos.
|
||||
|
||||
Esto también significa que en muchos casos puedes pasar el mismo objeto que obtuviste de un request **directamente a la base de datos**, dado que todo es validado automáticamente.
|
||||
|
||||
Lo mismo aplica para el sentido contrario. En muchos casos puedes pasarle el objeto que obtienes de la base de datos **directamente al cliente**.
|
||||
|
||||
Con **FastAPI** obtienes todas las características de **Pydantic** (dado que FastAPI está basado en Pydantic para todo el manejo de datos):
|
||||
|
||||
* **Sin dificultades para entender**:
|
||||
* No necesitas aprender un nuevo micro-lenguaje de definición de schemas.
|
||||
* Si sabes tipos de Python, sabes cómo usar Pydantic.
|
||||
* Interactúa bien con tu **<abbr title="en inglés: Integrated Development Environment, similar a editor de código">IDE</abbr>/<abbr title="Un programa que chequea errores en el código">linter</abbr>/cerebro**:
|
||||
* Porque las estructuras de datos de Pydantic son solo <abbr title='En español: ejemplares. Aunque a veces los llaman incorrectamente "instancias"'>instances</abbr> de clases que tu defines, el auto-completado, el linting, mypy y tu intuición deberían funcionar bien con tus datos validados.
|
||||
* **Rápido**:
|
||||
* En <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/#benchmarks-tag" class="external-link" target="_blank">benchmarks</a> Pydantic es más rápido que todas las otras <abbr title='Herramienta, paquete. A veces llamado "librería"'>libraries</abbr> probadas.
|
||||
* Valida **estructuras complejas**:
|
||||
* Usa modelos jerárquicos de modelos de Pydantic, `typing` de Python, `List` y `Dict`, etc.
|
||||
* Los validadores también permiten que se definan fácil y claramente schemas complejos de datos. Estos son chequeados y documentados como JSON Schema.
|
||||
* Puedes tener objetos de **JSON profundamente anidados** y que todos sean validados y anotados.
|
||||
* **Extensible**:
|
||||
* Pydantic permite que se definan tipos de datos a la medida o puedes extender la validación con métodos en un modelo decorado con el <abbr title="en inglés: validator decorator"> decorador de validación</abbr>.
|
||||
* Cobertura de pruebas al 100%.
|
||||
@@ -2,17 +2,17 @@
|
||||
<a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com"><img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/logo-margin/logo-teal.png" alt="FastAPI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<em>FastAPI framework, high performance, easy to learn, fast to code, ready for production</em>
|
||||
<em>FastAPI framework, alto desempeño, fácil de aprender, rápido de programar, listo para producción</em>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://travis-ci.com/tiangolo/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://travis-ci.com/tiangolo/fastapi.svg?branch=master" alt="Build Status">
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/actions?query=workflow%3ATest" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/workflows/Test/badge.svg" alt="Test">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://codecov.io/gh/tiangolo/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://img.shields.io/codecov/c/github/tiangolo/fastapi" alt="Coverage">
|
||||
<img src="https://img.shields.io/codecov/c/github/tiangolo/fastapi?color=%2334D058" alt="Coverage">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://pypi.org/project/fastapi" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://badge.fury.io/py/fastapi.svg" alt="Package version">
|
||||
<img src="https://img.shields.io/pypi/v/fastapi?color=%2334D058&label=pypi%20package" alt="Package version">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge" target="_blank">
|
||||
<img src="https://badges.gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi.svg" alt="Join the chat at https://gitter.im/tiangolo/fastapi">
|
||||
@@ -21,80 +21,85 @@
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
**Documentation**: <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com" target="_blank">https://fastapi.tiangolo.com</a>
|
||||
**Documentación**: <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com" target="_blank">https://fastapi.tiangolo.com</a>
|
||||
|
||||
**Source Code**: <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi</a>
|
||||
**Código Fuente**: <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi" target="_blank">https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi</a>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
FastAPI es un web framework moderno y rápido (de alto rendimiento) para construir APIs con Python 3.6+ basado en las anotaciones de tipos estándar de Python.
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI is a modern, fast (high-performance), web framework for building APIs with Python 3.6+ based on standard Python type hints.
|
||||
Sus características principales son:
|
||||
|
||||
The key features are:
|
||||
* **Rapidez**: Alto rendimiento, a la par con **NodeJS** y **Go** (gracias a Starlette y Pydantic). [Uno de los frameworks de Python más rápidos](#rendimiento).
|
||||
|
||||
* **Fast**: Very high performance, on par with **NodeJS** and **Go** (thanks to Starlette and Pydantic). [One of the fastest Python frameworks available](#performance).
|
||||
* **Rápido de programar**: Incrementa la velocidad de desarrollo entre 200% y 300%. *
|
||||
* **Menos errores**: Reduce los errores humanos (de programador) aproximadamente un 40%. *
|
||||
* **Intuitivo**: Gran soporte en los editores con <abbr title="conocido en inglés como auto-complete, autocompletion, IntelliSense, completion">auto completado</abbr> en todas partes. Gasta menos tiempo <abbr title="buscando y corrigiendo errores">debugging</abbr>.
|
||||
* **Fácil**: Está diseñado para ser fácil de usar y aprender. Gastando menos tiempo leyendo documentación.
|
||||
* **Corto**: Minimiza la duplicación de código. Múltiples funcionalidades con cada declaración de parámetros. Menos errores.
|
||||
* **Robusto**: Crea código listo para producción con documentación automática interactiva.
|
||||
* **Basado en estándares**: Basado y totalmente compatible con los estándares abiertos para APIs: <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI</a> (conocido previamente como Swagger) y <a href="http://json-schema.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">JSON Schema</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* **Fast to code**: Increase the speed to develop features by about 200% to 300% *.
|
||||
* **Fewer bugs**: Reduce about 40% of human (developer) induced errors. *
|
||||
* **Intuitive**: Great editor support. <abbr title="also known as auto-complete, autocompletion, IntelliSense">Completion</abbr> everywhere. Less time debugging.
|
||||
* **Easy**: Designed to be easy to use and learn. Less time reading docs.
|
||||
* **Short**: Minimize code duplication. Multiple features from each parameter declaration. Fewer bugs.
|
||||
* **Robust**: Get production-ready code. With automatic interactive documentation.
|
||||
* **Standards-based**: Based on (and fully compatible with) the open standards for APIs: <a href="https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification" class="external-link" target="_blank">OpenAPI</a> (previously known as Swagger) and <a href="http://json-schema.org/" class="external-link" target="_blank">JSON Schema</a>.
|
||||
<small>* Esta estimación está basada en pruebas con un equipo de desarrollo interno contruyendo aplicaciones listas para producción.</small>
|
||||
|
||||
<small>* estimation based on tests on an internal development team, building production applications.</small>
|
||||
## Opiniones
|
||||
|
||||
## Opinions
|
||||
|
||||
"*[...] I'm using **FastAPI** a ton these days. [...] I'm actually planning to use it for all of my team's **ML services at Microsoft**. Some of them are getting integrated into the core **Windows** product and some **Office** products.*"
|
||||
"_[...] I'm using **FastAPI** a ton these days. [...] I'm actually planning to use it for all of my team's **ML services at Microsoft**. Some of them are getting integrated into the core **Windows** product and some **Office** products._"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Kabir Khan - <strong>Microsoft</strong> <a href="https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi/pull/26" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*I’m over the moon excited about **FastAPI**. It’s so fun!*"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Brian Okken - <strong><a href="https://pythonbytes.fm/episodes/show/123/time-to-right-the-py-wrongs?time_in_sec=855" target="_blank">Python Bytes</a> podcast host</strong> <a href="https://twitter.com/brianokken/status/1112220079972728832" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*Honestly, what you've built looks super solid and polished. In many ways, it's what I wanted **Hug** to be - it's really inspiring to see someone build that.*"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Timothy Crosley - <strong><a href="http://www.hug.rest/" target="_blank">Hug</a> creator</strong> <a href="https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=19455465" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*If you're looking to learn one **modern framework** for building REST APIs, check out **FastAPI** [...] It's fast, easy to use and easy to learn [...]*"
|
||||
|
||||
"*We've switched over to **FastAPI** for our **APIs** [...] I think you'll like it [...]*"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Ines Montani - Matthew Honnibal - <strong><a href="https://explosion.ai" target="_blank">Explosion AI</a> founders - <a href="https://spacy.io" target="_blank">spaCy</a> creators</strong> <a href="https://twitter.com/_inesmontani/status/1144173225322143744" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a> - <a href="https://twitter.com/honnibal/status/1144031421859655680" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"*We adopted the **FastAPI** library to spawn a **REST** server that can be queried to obtain **predictions**. [for Ludwig]*"
|
||||
"_We adopted the **FastAPI** library to spawn a **REST** server that can be queried to obtain **predictions**. [for Ludwig]_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Piero Molino, Yaroslav Dudin, and Sai Sumanth Miryala - <strong>Uber</strong> <a href="https://eng.uber.com/ludwig-v0-2/" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## **Typer**, the FastAPI of CLIs
|
||||
"_**Netflix** is pleased to announce the open-source release of our **crisis management** orchestration framework: **Dispatch**! [built with **FastAPI**]_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Kevin Glisson, Marc Vilanova, Forest Monsen - <strong>Netflix</strong> <a href="https://netflixtechblog.com/introducing-dispatch-da4b8a2a8072" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"_I’m over the moon excited about **FastAPI**. It’s so fun!_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Brian Okken - <strong><a href="https://pythonbytes.fm/episodes/show/123/time-to-right-the-py-wrongs?time_in_sec=855" target="_blank">Python Bytes</a> podcast host</strong> <a href="https://twitter.com/brianokken/status/1112220079972728832" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"_Honestly, what you've built looks super solid and polished. In many ways, it's what I wanted **Hug** to be - it's really inspiring to see someone build that._"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Timothy Crosley - <strong><a href="http://www.hug.rest/" target="_blank">Hug</a> creator</strong> <a href="https://news.ycombinator.com/item?id=19455465" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
"_If you're looking to learn one **modern framework** for building REST APIs, check out **FastAPI** [...] It's fast, easy to use and easy to learn [...]_"
|
||||
|
||||
"_We've switched over to **FastAPI** for our **APIs** [...] I think you'll like it [...]_"
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: right; margin-right: 10%;">Ines Montani - Matthew Honnibal - <strong><a href="https://explosion.ai" target="_blank">Explosion AI</a> founders - <a href="https://spacy.io" target="_blank">spaCy</a> creators</strong> <a href="https://twitter.com/_inesmontani/status/1144173225322143744" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a> - <a href="https://twitter.com/honnibal/status/1144031421859655680" target="_blank"><small>(ref)</small></a></div>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## **Typer**, el FastAPI de las CLIs
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com" target="_blank"><img src="https://typer.tiangolo.com/img/logo-margin/logo-margin-vector.svg" style="width: 20%;"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
If you are building a <abbr title="Command Line Interface">CLI</abbr> app to be used in the terminal instead of a web API, check out <a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">**Typer**</a>.
|
||||
Si estás construyendo un app de <abbr title="Interfaz de línea de comandos en español">CLI</abbr> para ser usada en la terminal en vez de una API web, fíjate en <a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com/" class="external-link" target="_blank">**Typer**</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
**Typer** is FastAPI's little sibling. And it's intended to be the **FastAPI of CLIs**. ⌨️ 🚀
|
||||
**Typer** es el hermano menor de FastAPI. La intención es que sea el **FastAPI de las CLIs**. ⌨️ 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
## Requisitos
|
||||
|
||||
Python 3.6+
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI stands on the shoulders of giants:
|
||||
FastAPI está sobre los hombros de gigantes:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette</a> for the web parts.
|
||||
* <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic</a> for the data parts.
|
||||
* <a href="https://www.starlette.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Starlette</a> para las partes web.
|
||||
* <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic</a> para las partes de datos.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
## Instalación
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -106,7 +111,7 @@ $ pip install fastapi
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
You will also need an ASGI server, for production such as <a href="http://www.uvicorn.org" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uvicorn</a> or <a href="https://gitlab.com/pgjones/hypercorn" class="external-link" target="_blank">Hypercorn</a>.
|
||||
También vas a necesitar un servidor ASGI para producción cómo <a href="http://www.uvicorn.org" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uvicorn</a> o <a href="https://gitlab.com/pgjones/hypercorn" class="external-link" target="_blank">Hypercorn</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -118,14 +123,15 @@ $ pip install uvicorn
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Example
|
||||
## Ejemplo
|
||||
|
||||
### Create it
|
||||
### Créalo
|
||||
|
||||
* Create a file `main.py` with:
|
||||
* Crea un archivo `main.py` con:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -136,17 +142,18 @@ def read_root():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown="1">
|
||||
<summary>Or use <code>async def</code>...</summary>
|
||||
<summary>O usa <code>async def</code>...</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
If your code uses `async` / `await`, use `async def`:
|
||||
Si tu código usa `async` / `await`, usa `async def`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="7 12"
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -157,87 +164,88 @@ async def read_root():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
async def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
async def read_item(item_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**:
|
||||
**Nota**:
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't know, check the _"In a hurry?"_ section about <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/async/#in-a-hurry" target="_blank">`async` and `await` in the docs</a>.
|
||||
Si no lo sabes, revisa la sección _"¿Con prisa?"_ sobre <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/es/async/#con-prisa" target="_blank">`async` y `await` en la documentación</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### Run it
|
||||
### Córrelo
|
||||
|
||||
Run the server with:
|
||||
Corre el servidor con:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="termy">
|
||||
|
||||
```console
|
||||
$ uvicorn main:app --reload
|
||||
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Started reloader process [28720]
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Started server process [28722]
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Waiting for application startup.
|
||||
<span style="color: green;">INFO</span>: Application startup complete.
|
||||
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://127.0.0.1:8000 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
|
||||
INFO: Started reloader process [28720]
|
||||
INFO: Started server process [28722]
|
||||
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
|
||||
INFO: Application startup complete.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown="1">
|
||||
<summary>About the command <code>uvicorn main:app --reload</code>...</summary>
|
||||
<summary>Sobre el comando <code>uvicorn main:app --reload</code>...</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
The command `uvicorn main:app` refers to:
|
||||
El comando `uvicorn main:app` se refiere a:
|
||||
|
||||
* `main`: the file `main.py` (the Python "module").
|
||||
* `app`: the object created inside of `main.py` with the line `app = FastAPI()`.
|
||||
* `--reload`: make the server restart after code changes. Only do this for development.
|
||||
* `main`: el archivo `main.py` (el"modulo" de Python).
|
||||
* `app`: el objeto creado dentro de `main.py` con la línea `app = FastAPI()`.
|
||||
* `--reload`: hace que el servidor se reinicie después de cambios en el código. Esta opción solo debe ser usada en desarrollo.
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
### Check it
|
||||
### Revísalo
|
||||
|
||||
Open your browser at <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/5?q=somequery" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/5?q=somequery</a>.
|
||||
Abre tu navegador en <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/5?q=somequery" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/5?q=somequery</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the JSON response as:
|
||||
Verás la respuesta de JSON cómo:
|
||||
|
||||
```JSON
|
||||
{"item_id": 5, "q": "somequery"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You already created an API that:
|
||||
Ya creaste una API que:
|
||||
|
||||
* Receives HTTP requests in the _paths_ `/` and `/items/{item_id}`.
|
||||
* Both _paths_ take `GET` <em>operations</em> (also known as HTTP _methods_).
|
||||
* The _path_ `/items/{item_id}` has a _path parameter_ `item_id` that should be an `int`.
|
||||
* The _path_ `/items/{item_id}` has an optional `str` _query parameter_ `q`.
|
||||
* Recibe HTTP requests en los _paths_ `/` y `/items/{item_id}`.
|
||||
* Ambos _paths_ toman <em>operaciones</em> `GET` (también conocido como HTTP _methods_).
|
||||
* El _path_ `/items/{item_id}` tiene un _path parameter_ `item_id` que debería ser un `int`.
|
||||
* El _path_ `/items/{item_id}` tiene un `str` _query parameter_ `q` opcional.
|
||||
|
||||
### Interactive API docs
|
||||
### Documentación interactiva de APIs
|
||||
|
||||
Now go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
Ahora ve a <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the automatic interactive API documentation (provided by <a href="https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui" class="external-link" target="_blank">Swagger UI</a>):
|
||||
Verás la documentación automática e interactiva de la API (proveída por <a href="https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui" class="external-link" target="_blank">Swagger UI</a>):
|
||||
|
||||
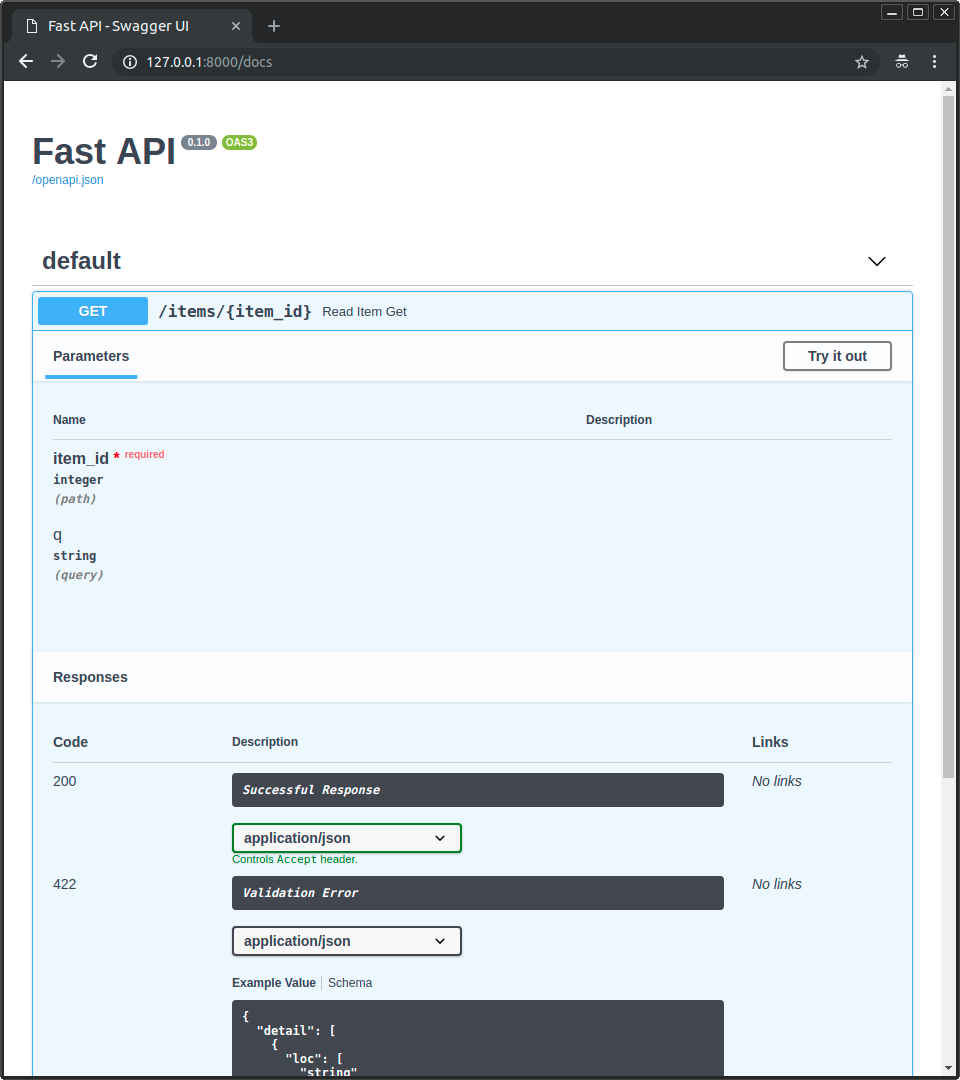
|
||||
|
||||
### Alternative API docs
|
||||
### Documentación alternativa de la API
|
||||
|
||||
And now, go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc</a>.
|
||||
Ahora, ve a <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the alternative automatic documentation (provided by <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">ReDoc</a>):
|
||||
Ahora verás la documentación automática alternativa (proveída por <a href="https://github.com/Rebilly/ReDoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">ReDoc</a>):
|
||||
|
||||
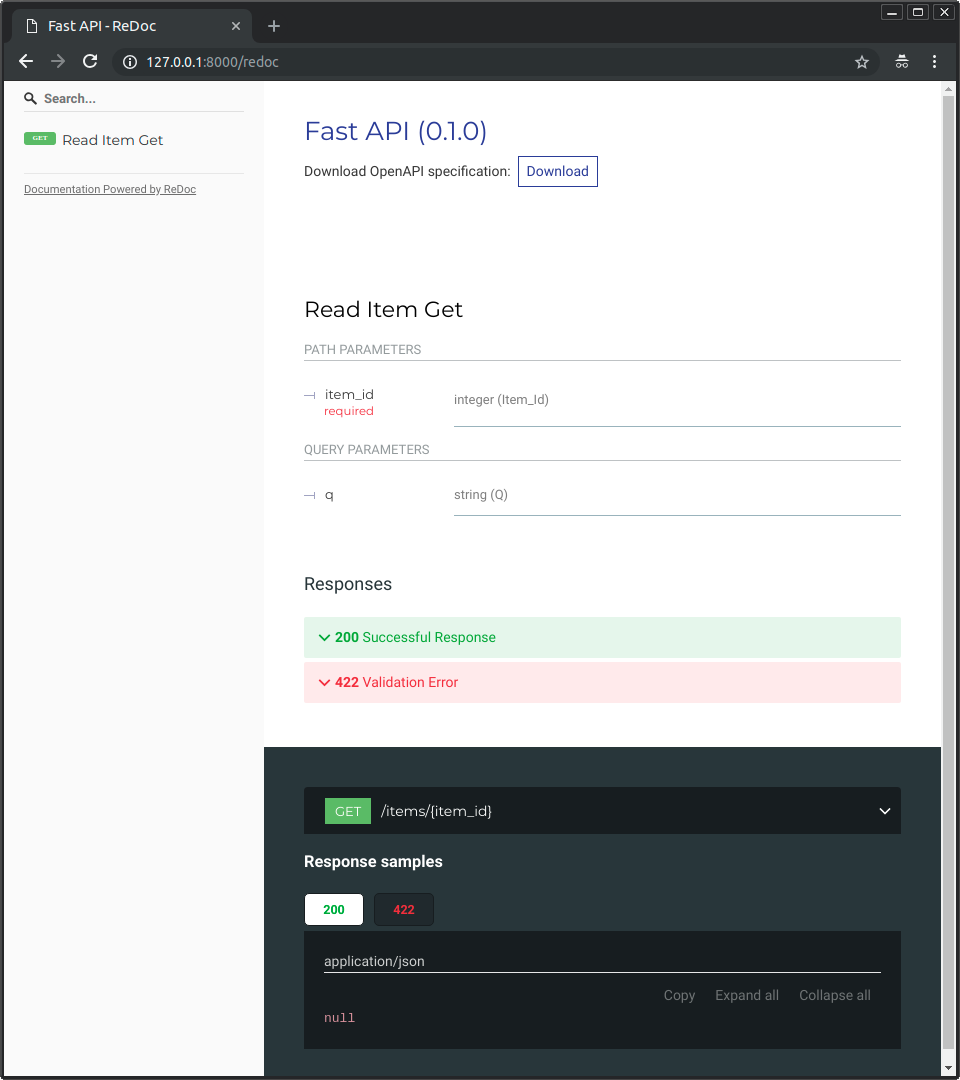
|
||||
|
||||
## Example upgrade
|
||||
## Mejora al ejemplo
|
||||
|
||||
Now modify the file `main.py` to receive a body from a `PUT` request.
|
||||
Ahora modifica el archivo `main.py` para recibir un <abbr title="cuerpo del mensaje HTTP">body</abbr> del `PUT` request.
|
||||
|
||||
Declare the body using standard Python types, thanks to Pydantic.
|
||||
Declara el body usando las declaraciones de tipo estándares de Python gracias a Pydantic.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2 7 8 9 10 23 24 25"
|
||||
from fastapi import FastAPI
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -245,7 +253,7 @@ app = FastAPI()
|
||||
class Item(BaseModel):
|
||||
name: str
|
||||
price: float
|
||||
is_offer: bool = None
|
||||
is_offer: Optional[bool] = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/")
|
||||
@@ -254,7 +262,7 @@ def read_root():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
|
||||
def read_item(item_id: int, q: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -263,175 +271,175 @@ def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):
|
||||
return {"item_name": item.name, "item_id": item_id}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The server should reload automatically (because you added `--reload` to the `uvicorn` command above).
|
||||
El servidor debería recargar automáticamente (porque añadiste `--reload` al comando `uvicorn` que está más arriba).
|
||||
|
||||
### Interactive API docs upgrade
|
||||
### Mejora a la documentación interactiva de APIs
|
||||
|
||||
Now go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
Ahora ve a <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* The interactive API documentation will be automatically updated, including the new body:
|
||||
* La documentación interactiva de la API se actualizará automáticamente, incluyendo el nuevo body:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Click on the button "Try it out", it allows you to fill the parameters and directly interact with the API:
|
||||
* Haz clíck en el botón de "Try it out" que te permite llenar los parámetros e interactuar directamente con la API:
|
||||
|
||||
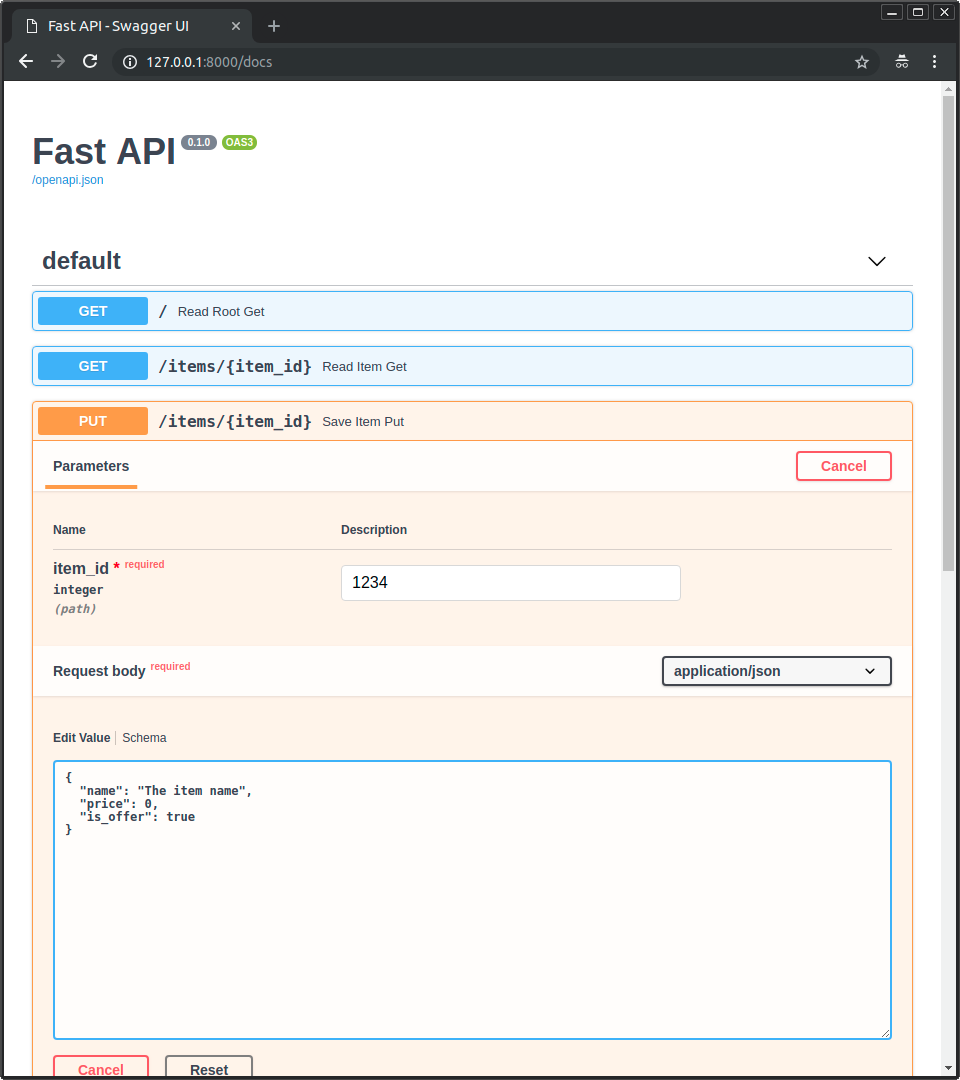
|
||||
|
||||
* Then click on the "Execute" button, the user interface will communicate with your API, send the parameters, get the results and show them on the screen:
|
||||
* Luego haz clíck en el botón de "Execute". La interfaz de usuario se comunicará con tu API, enviará los parámetros y recibirá los resultados para mostrarlos en pantalla:
|
||||
|
||||
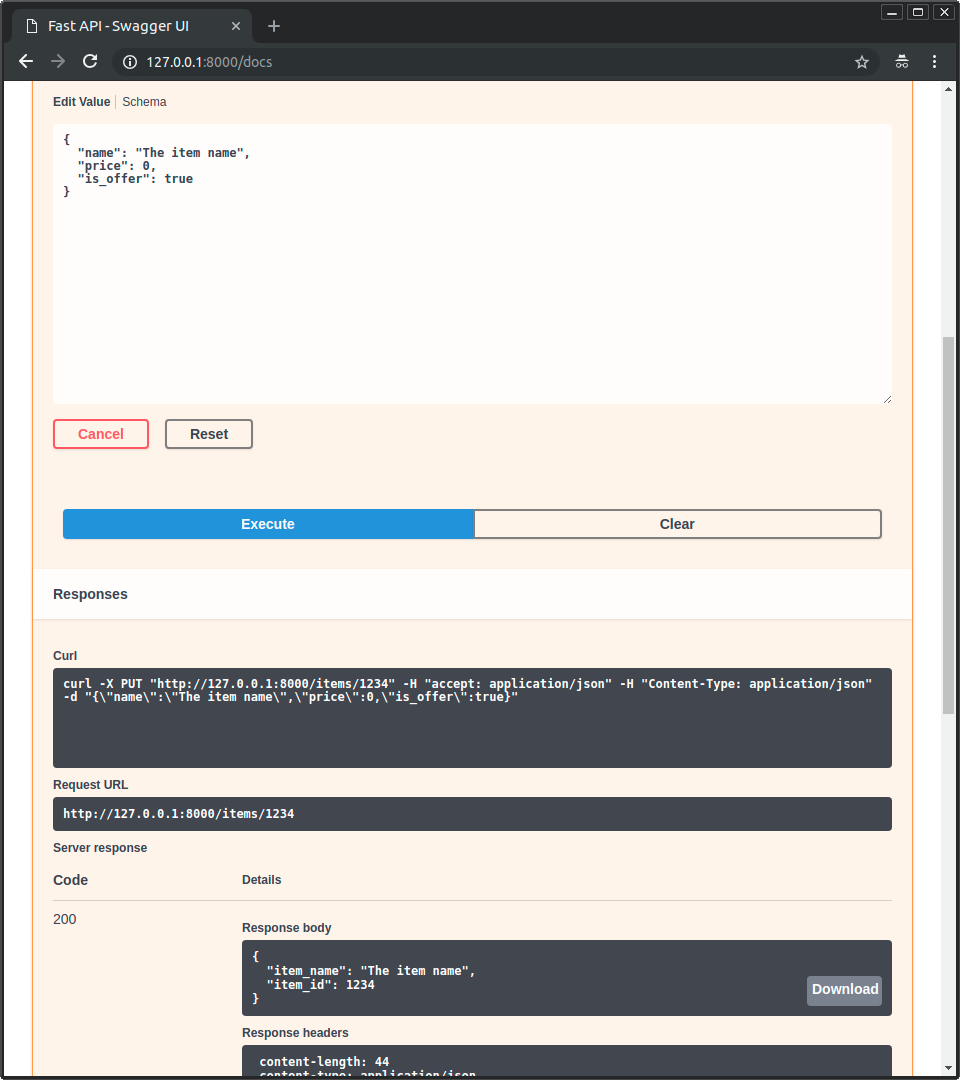
|
||||
|
||||
### Alternative API docs upgrade
|
||||
### Mejora a la documentación alternativa de la API
|
||||
|
||||
And now, go to <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc</a>.
|
||||
Ahora, ve a <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc" class="external-link" target="_blank">http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
* The alternative documentation will also reflect the new query parameter and body:
|
||||
* La documentación alternativa también reflejará el nuevo parámetro de query y el body:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Recap
|
||||
### Resumen
|
||||
|
||||
In summary, you declare **once** the types of parameters, body, etc. as function parameters.
|
||||
En resumen, declaras los tipos de parámetros, body, etc. **una vez** como parámetros de la función.
|
||||
|
||||
You do that with standard modern Python types.
|
||||
Lo haces con tipos modernos estándar de Python.
|
||||
|
||||
You don't have to learn a new syntax, the methods or classes of a specific library, etc.
|
||||
No tienes que aprender una sintáxis nueva, los métodos o clases de una library específica, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Just standard **Python 3.6+**.
|
||||
Solo **Python 3.6+** estándar.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, for an `int`:
|
||||
Por ejemplo, para un `int`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
item_id: int
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or for a more complex `Item` model:
|
||||
o para un modelo más complejo de `Item`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
item: Item
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...and with that single declaration you get:
|
||||
...y con esa única declaración obtienes:
|
||||
|
||||
* Editor support, including:
|
||||
* Completion.
|
||||
* Type checks.
|
||||
* Validation of data:
|
||||
* Automatic and clear errors when the data is invalid.
|
||||
* Validation even for deeply nested JSON objects.
|
||||
* <abbr title="also known as: serialization, parsing, marshalling">Conversion</abbr> of input data: coming from the network to Python data and types. Reading from:
|
||||
* Soporte del editor incluyendo:
|
||||
* Auto completado.
|
||||
* Anotaciones de tipos.
|
||||
* Validación de datos:
|
||||
* Errores automáticos y claros cuándo los datos son inválidos.
|
||||
* Validación, incluso para objetos JSON profundamente anidados.
|
||||
* <abbr title="en inglés: serialization, parsing, marshalling">Conversión</abbr> de datos de input: viniendo de la red a datos y tipos de Python. Leyendo desde:
|
||||
* JSON.
|
||||
* Path parameters.
|
||||
* Query parameters.
|
||||
* Cookies.
|
||||
* Headers.
|
||||
* Forms.
|
||||
* Files.
|
||||
* <abbr title="also known as: serialization, parsing, marshalling">Conversion</abbr> of output data: converting from Python data and types to network data (as JSON):
|
||||
* Convert Python types (`str`, `int`, `float`, `bool`, `list`, etc).
|
||||
* `datetime` objects.
|
||||
* `UUID` objects.
|
||||
* Database models.
|
||||
* ...and many more.
|
||||
* Automatic interactive API documentation, including 2 alternative user interfaces:
|
||||
* Formularios.
|
||||
* Archivos.
|
||||
* <abbr title="en inglés: serialization, parsing, marshalling">Conversión</abbr> de datos de output: convirtiendo de datos y tipos de Python a datos para la red (como JSON):
|
||||
* Convertir tipos de Python (`str`, `int`, `float`, `bool`, `list`, etc).
|
||||
* Objetos `datetime`.
|
||||
* Objetos `UUID`.
|
||||
* Modelos de bases de datos.
|
||||
* ...y muchos más.
|
||||
* Documentación automática e interactiva incluyendo 2 interfaces de usuario alternativas:
|
||||
* Swagger UI.
|
||||
* ReDoc.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Coming back to the previous code example, **FastAPI** will:
|
||||
Volviendo al ejemplo de código anterior, **FastAPI** va a:
|
||||
|
||||
* Validate that there is an `item_id` in the path for `GET` and `PUT` requests.
|
||||
* Validate that the `item_id` is of type `int` for `GET` and `PUT` requests.
|
||||
* If it is not, the client will see a useful, clear error.
|
||||
* Check if there is an optional query parameter named `q` (as in `http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/foo?q=somequery`) for `GET` requests.
|
||||
* As the `q` parameter is declared with `= None`, it is optional.
|
||||
* Without the `None` it would be required (as is the body in the case with `PUT`).
|
||||
* For `PUT` requests to `/items/{item_id}`, Read the body as JSON:
|
||||
* Check that it has a required attribute `name` that should be a `str`.
|
||||
* Check that it has a required attribute `price` that has to be a `float`.
|
||||
* Check that it has an optional attribute `is_offer`, that should be a `bool`, if present.
|
||||
* All this would also work for deeply nested JSON objects.
|
||||
* Convert from and to JSON automatically.
|
||||
* Document everything with OpenAPI, that can be used by:
|
||||
* Interactive documentation systems.
|
||||
* Automatic client code generation systems, for many languages.
|
||||
* Provide 2 interactive documentation web interfaces directly.
|
||||
* Validar que existe un `item_id` en el path para requests usando `GET` y `PUT`.
|
||||
* Validar que el `item_id` es del tipo `int` para requests de tipo `GET` y `PUT`.
|
||||
* Si no lo es, el cliente verá un mensaje de error útil y claro.
|
||||
* Revisar si existe un query parameter opcional llamado `q` (cómo en `http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/foo?q=somequery`) para requests de tipo `GET`.
|
||||
* Como el parámetro `q` fue declarado con `= None` es opcional.
|
||||
* Sin el `None` sería obligatorio (cómo lo es el body en el caso con `PUT`).
|
||||
* Para requests de tipo `PUT` a `/items/{item_id}` leer el body como JSON:
|
||||
* Revisar si tiene un atributo requerido `name` que debe ser un `str`.
|
||||
* Revisar si tiene un atributo requerido `price` que debe ser un `float`.
|
||||
* Revisar si tiene un atributo opcional `is_offer`, que debe ser un `bool`si está presente.
|
||||
* Todo esto funcionaría para objetos JSON profundamente anidados.
|
||||
* Convertir de y a JSON automáticamente.
|
||||
* Documentar todo con OpenAPI que puede ser usado por:
|
||||
* Sistemas de documentación interactiva.
|
||||
* Sistemas de generación automática de código de cliente para muchos lenguajes.
|
||||
* Proveer directamente 2 interfaces de documentación web interactivas.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
We just scratched the surface, but you already get the idea of how it all works.
|
||||
Hasta ahora, escasamente vimos lo básico pero ya tienes una idea de cómo funciona.
|
||||
|
||||
Try changing the line with:
|
||||
Intenta cambiando la línea a:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
return {"item_name": item.name, "item_id": item_id}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...from:
|
||||
...de:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
... "item_name": item.name ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...to:
|
||||
...a:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
... "item_price": item.price ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...and see how your editor will auto-complete the attributes and know their types:
|
||||
... y mira como el editor va a auto-completar los atributos y sabrá sus tipos:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For a more complete example including more features, see the <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/">Tutorial - User Guide</a>.
|
||||
Para un ejemplo más completo que incluye más características ve el <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/tutorial/">Tutorial - Guía de Usuario</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
**Spoiler alert**: the tutorial - user guide includes:
|
||||
**Spoiler alert**: el Tutorial - Guía de Usuario incluye:
|
||||
|
||||
* Declaration of **parameters** from other different places as: **headers**, **cookies**, **form fields** and **files**.
|
||||
* How to set **validation constraints** as `maximum_length` or `regex`.
|
||||
* A very powerful and easy to use **<abbr title="also known as components, resources, providers, services, injectables">Dependency Injection</abbr>** system.
|
||||
* Security and authentication, including support for **OAuth2** with **JWT tokens** and **HTTP Basic** auth.
|
||||
* More advanced (but equally easy) techniques for declaring **deeply nested JSON models** (thanks to Pydantic).
|
||||
* Many extra features (thanks to Starlette) as:
|
||||
* Declaración de **parámetros** en otros lugares diferentes cómo los: **headers**, **cookies**, **formularios** y **archivos**.
|
||||
* Cómo agregar **requisitos de validación** cómo `maximum_length` o `regex`.
|
||||
* Un sistema de **<abbr title="también conocido en inglés cómo: components, resources, providers, services, injectables">Dependency Injection</abbr>** poderoso y fácil de usar.
|
||||
* Seguridad y autenticación incluyendo soporte para **OAuth2** con **JWT tokens** y **HTTP Basic** auth.
|
||||
* Técnicas más avanzadas, pero igual de fáciles, para declarar **modelos de JSON profundamente anidados** (gracias a Pydantic).
|
||||
* Muchas características extra (gracias a Starlette) como:
|
||||
* **WebSockets**
|
||||
* **GraphQL**
|
||||
* extremely easy tests based on `requests` and `pytest`
|
||||
* pruebas extremadamente fáciles con `requests` y `pytest`
|
||||
* **CORS**
|
||||
* **Cookie Sessions**
|
||||
* ...and more.
|
||||
* ...y mucho más.
|
||||
|
||||
## Performance
|
||||
## Rendimiento
|
||||
|
||||
Independent TechEmpower benchmarks show **FastAPI** applications running under Uvicorn as <a href="https://www.techempower.com/benchmarks/#section=test&runid=7464e520-0dc2-473d-bd34-dbdfd7e85911&hw=ph&test=query&l=zijzen-7" class="external-link" target="_blank">one of the fastest Python frameworks available</a>, only below Starlette and Uvicorn themselves (used internally by FastAPI). (*)
|
||||
Benchmarks independientes de TechEmpower muestran que aplicaciones de **FastAPI** corriendo con Uvicorn cómo <a href="https://www.techempower.com/benchmarks/#section=test&runid=7464e520-0dc2-473d-bd34-dbdfd7e85911&hw=ph&test=query&l=zijzen-7" class="external-link" target="_blank">uno de los frameworks de Python más rápidos</a>, únicamente debajo de Starlette y Uvicorn (usados internamente por FastAPI). (*)
|
||||
|
||||
To understand more about it, see the section <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/benchmarks/" class="internal-link" target="_blank">Benchmarks</a>.
|
||||
Para entender más al respecto revisa la sección <a href="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/benchmarks/" class="internal-link" target="_blank">Benchmarks</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
## Optional Dependencies
|
||||
## Dependencias Opcionales
|
||||
|
||||
Used by Pydantic:
|
||||
Usadas por Pydantic:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/esnme/ultrajson" target="_blank"><code>ujson</code></a> - for faster JSON <abbr title="converting the string that comes from an HTTP request into Python data">"parsing"</abbr>.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/JoshData/python-email-validator" target="_blank"><code>email_validator</code></a> - for email validation.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/esnme/ultrajson" target="_blank"><code>ujson</code></a> - para <abbr title="convertir el string que viene de un HTTP request a datos de Python">"parsing"</abbr> de JSON más rápido.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/JoshData/python-email-validator" target="_blank"><code>email_validator</code></a> - para validación de emails.
|
||||
|
||||
Used by Starlette:
|
||||
Usados por Starlette:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="http://docs.python-requests.org" target="_blank"><code>requests</code></a> - Required if you want to use the `TestClient`.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/Tinche/aiofiles" target="_blank"><code>aiofiles</code></a> - Required if you want to use `FileResponse` or `StaticFiles`.
|
||||
* <a href="http://jinja.pocoo.org" target="_blank"><code>jinja2</code></a> - Required if you want to use the default template configuration.
|
||||
* <a href="https://andrew-d.github.io/python-multipart/" target="_blank"><code>python-multipart</code></a> - Required if you want to support form <abbr title="converting the string that comes from an HTTP request into Python data">"parsing"</abbr>, with `request.form()`.
|
||||
* <a href="https://pythonhosted.org/itsdangerous/" target="_blank"><code>itsdangerous</code></a> - Required for `SessionMiddleware` support.
|
||||
* <a href="https://pyyaml.org/wiki/PyYAMLDocumentation" target="_blank"><code>pyyaml</code></a> - Required for Starlette's `SchemaGenerator` support (you probably don't need it with FastAPI).
|
||||
* <a href="https://graphene-python.org/" target="_blank"><code>graphene</code></a> - Required for `GraphQLApp` support.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/esnme/ultrajson" target="_blank"><code>ujson</code></a> - Required if you want to use `UJSONResponse`.
|
||||
* <a href="http://docs.python-requests.org" target="_blank"><code>requests</code></a> - Requerido si quieres usar el `TestClient`.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/Tinche/aiofiles" target="_blank"><code>aiofiles</code></a> - Requerido si quieres usar `FileResponse` o `StaticFiles`.
|
||||
* <a href="http://jinja.pocoo.org" target="_blank"><code>jinja2</code></a> - Requerido si quieres usar la configuración por defecto de templates.
|
||||
* <a href="https://andrew-d.github.io/python-multipart/" target="_blank"><code>python-multipart</code></a> - Requerido si quieres dar soporte a <abbr title="convertir el string que viene de un HTTP request a datos de Python">"parsing"</abbr> de formularios, con `request.form()`.
|
||||
* <a href="https://pythonhosted.org/itsdangerous/" target="_blank"><code>itsdangerous</code></a> - Requerido para dar soporte a `SessionMiddleware`.
|
||||
* <a href="https://pyyaml.org/wiki/PyYAMLDocumentation" target="_blank"><code>pyyaml</code></a> - Requerido para dar soporte al `SchemaGenerator` de Starlette (probablemente no lo necesites con FastAPI).
|
||||
* <a href="https://graphene-python.org/" target="_blank"><code>graphene</code></a> - Requerido para dar soporte a `GraphQLApp`.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/esnme/ultrajson" target="_blank"><code>ujson</code></a> - Requerido si quieres usar `UJSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
Used by FastAPI / Starlette:
|
||||
Usado por FastAPI / Starlette:
|
||||
|
||||
* <a href="http://www.uvicorn.org" target="_blank"><code>uvicorn</code></a> - for the server that loads and serves your application.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/ijl/orjson" target="_blank"><code>orjson</code></a> - Required if you want to use `ORJSONResponse`.
|
||||
* <a href="http://www.uvicorn.org" target="_blank"><code>uvicorn</code></a> - para el servidor que carga y sirve tu aplicación.
|
||||
* <a href="https://github.com/ijl/orjson" target="_blank"><code>orjson</code></a> - Requerido si quieres usar `ORJSONResponse`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can install all of these with `pip install fastapi[all]`.
|
||||
Puedes instalarlos con `pip install fastapi[all]`.
|
||||
|
||||
## License
|
||||
## Licencia
|
||||
|
||||
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.
|
||||
Este proyecto está licenciado bajo los términos de la licencia del MIT.
|
||||
|
||||
286
docs/es/docs/python-types.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,286 @@
|
||||
# Introducción a los Tipos de Python
|
||||
|
||||
**Python 3.6+** tiene soporte para <abbr title="en español, anotaciones de tipo. En inglés también se conocen como: type annotations">"type hints"</abbr> opcionales.
|
||||
|
||||
Estos **type hints** son una nueva sintáxis, desde Python 3.6+, que permite declarar el <abbr title="por ejemplo: str, int, float, bool">tipo</abbr> de una variable.
|
||||
|
||||
Usando las declaraciones de tipos para tus variables, los editores y otras herramientas pueden proveerte un soporte mejor.
|
||||
|
||||
Este es solo un **tutorial corto** sobre los Python type hints. Solo cubre lo mínimo necesario para usarlos con **FastAPI**... realmente es muy poco lo que necesitas.
|
||||
|
||||
Todo **FastAPI** está basado en estos type hints, lo que le da muchas ventajas y beneficios.
|
||||
|
||||
Pero, así nunca uses **FastAPI** te beneficiarás de aprender un poco sobre los type hints.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! note "Nota"
|
||||
Si eres un experto en Python y ya lo sabes todo sobre los type hints, salta al siguiente capítulo.
|
||||
|
||||
## Motivación
|
||||
|
||||
Comencemos con un ejemplo simple:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Llamar este programa nos muestra el siguiente <abbr title="en español: salida">output</abbr>:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
John Doe
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
La función hace lo siguiente:
|
||||
|
||||
* Toma un `first_name` y un `last_name`.
|
||||
* Convierte la primera letra de cada uno en una letra mayúscula con `title()`.
|
||||
* Las <abbr title="las junta como si fuesen una. Con el contenido de una después de la otra. En inlgés: concatenate.">concatena</abbr> con un espacio en la mitad.
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial001.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Edítalo
|
||||
|
||||
Es un programa muy simple.
|
||||
|
||||
Ahora, imagina que lo estás escribiendo desde ceros.
|
||||
|
||||
En algún punto habrías comenzado con la definición de la función, tenías los parámetros listos...
|
||||
|
||||
Pero, luego tienes que llamar "ese método que convierte la primera letra en una mayúscula".
|
||||
|
||||
Era `upper`? O era `uppercase`? `first_uppercase`? `capitalize`?
|
||||
|
||||
Luego lo intentas con el viejo amigo de los programadores, el autocompletado del editor.
|
||||
|
||||
Escribes el primer parámetro de la función `first_name`, luego un punto (`.`) y luego presionas `Ctrl+Space` para iniciar el autocompletado.
|
||||
|
||||
Tristemente, no obtienes nada útil:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/python-types/image01.png">
|
||||
|
||||
### Añade tipos
|
||||
|
||||
Vamos a modificar una única línea de la versión previa.
|
||||
|
||||
Vamos a cambiar exactamente este fragmento, los parámetros de la función, de:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
first_name, last_name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
a:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
first_name: str, last_name: str
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Eso es todo.
|
||||
|
||||
Esos son los "type hints":
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial002.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
No es lo mismo a declarar valores por defecto, como sería con:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
first_name="john", last_name="doe"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Es algo diferente.
|
||||
|
||||
Estamos usando los dos puntos (`:`), no un símbolo de igual (`=`).
|
||||
|
||||
Añadir los type hints normalmente no cambia lo que sucedería si ellos no estuviesen presentes.
|
||||
|
||||
Pero ahora imagina que nuevamente estás creando la función, pero con los type hints.
|
||||
|
||||
En el mismo punto intentas iniciar el autocompletado con `Ctrl+Space` y ves:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/python-types/image02.png">
|
||||
|
||||
Con esto puedes moverte hacia abajo viendo las opciones hasta que encuentras una que te suene:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/python-types/image03.png">
|
||||
|
||||
## Más motivación
|
||||
|
||||
Mira esta función que ya tiene type hints:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Como el editor conoce el tipo de las variables no solo obtienes autocompletado, si no que también obtienes chequeo de errores:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/python-types/image04.png">
|
||||
|
||||
Ahora que sabes que tienes que arreglarlo convierte `age` a un string con `str(age)`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="2"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial004.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Declarando tipos
|
||||
|
||||
Acabas de ver el lugar principal para declarar los type hints. Como parámetros de las funciones.
|
||||
|
||||
Este es también el lugar principal en que los usarías con **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tipos simples
|
||||
|
||||
Puedes declarar todos los tipos estándar de Python, no solamente `str`.
|
||||
|
||||
Por ejemplo, puedes usar:
|
||||
|
||||
* `int`
|
||||
* `float`
|
||||
* `bool`
|
||||
* `bytes`
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial005.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Tipos con sub-tipos
|
||||
|
||||
Existen algunas estructuras de datos que pueden contener otros valores, como `dict`, `list`, `set` y `tuple`. Los valores internos pueden tener su propio tipo también.
|
||||
|
||||
Para declarar esos tipos y sub-tipos puedes usar el módulo estándar de Python `typing`.
|
||||
|
||||
Él existe específicamente para dar soporte a este tipo de type hints.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Listas
|
||||
|
||||
Por ejemplo, vamos a definir una variable para que sea una `list` compuesta de `str`.
|
||||
|
||||
De `typing`, importa `List` (con una `L` mayúscula):
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial006.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Declara la variable con la misma sintáxis de los dos puntos (`:`).
|
||||
|
||||
Pon `List` como el tipo.
|
||||
|
||||
Como la lista es un tipo que permite tener un "sub-tipo" pones el sub-tipo en corchetes `[]`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="4"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial006.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Esto significa: la variable `items` es una `list` y cada uno de los ítems en esta lista es un `str`.
|
||||
|
||||
Con esta declaración tu editor puede proveerte soporte inclusive mientras está procesando ítems de la lista.
|
||||
|
||||
Sin tipos el autocompletado en este tipo de estructura es casi imposible de lograr:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/python-types/image05.png">
|
||||
|
||||
Observa que la variable `item` es unos de los elementos en la lista `items`.
|
||||
|
||||
El editor aún sabe que es un `str` y provee soporte para ello.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tuples y Sets
|
||||
|
||||
Harías lo mismo para declarar `tuple`s y `set`s:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 4"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial007.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Esto significa:
|
||||
|
||||
* La variable `items_t` es un `tuple` con 3 ítems, un `int`, otro `int`, y un `str`.
|
||||
* La variable `items_s` es un `set` y cada uno de sus ítems es de tipo `bytes`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Diccionarios (Dicts)
|
||||
|
||||
Para definir un `dict` le pasas 2 sub-tipos separados por comas.
|
||||
|
||||
El primer sub-tipo es para los keys del `dict`.
|
||||
|
||||
El segundo sub-tipo es para los valores del `dict`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 4"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial008.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Esto significa:
|
||||
|
||||
* La variable `prices` es un `dict`:
|
||||
* Los keys de este `dict` son de tipo `str` (Digamos que son el nombre de cada ítem).
|
||||
* Los valores de este `dict` son de tipo `float` (Digamos que son el precio de cada ítem).
|
||||
|
||||
### Clases como tipos
|
||||
|
||||
También puedes declarar una clase como el tipo de una variable.
|
||||
|
||||
Digamos que tienes una clase `Person`con un nombre:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="1 2 3"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial009.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Entonces puedes declarar una variable que sea de tipo `Person`:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python hl_lines="6"
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial009.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Una vez más tendrás todo el soporte del editor:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/python-types/image06.png">
|
||||
|
||||
## Modelos de Pydantic
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic</a> es una library de Python para llevar a cabo validación de datos.
|
||||
|
||||
Tú declaras la "forma" de los datos mediante clases con atributos.
|
||||
|
||||
Cada atributo tiene un tipo.
|
||||
|
||||
Luego creas un instance de esa clase con algunos valores y Pydantic validará los valores, los convertirá al tipo apropiado (si ese es el caso) y te dará un objeto con todos los datos.
|
||||
|
||||
Y obtienes todo el soporte del editor con el objeto resultante.
|
||||
|
||||
Tomado de la documentación oficial de Pydantic:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
{!../../../docs_src/python_types/tutorial010.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info "Información"
|
||||
Para aprender más sobre <a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic mira su documentación</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** está todo basado en Pydantic.
|
||||
|
||||
Vas a ver mucho más de esto en práctica en el [Tutorial - User Guide](tutorial/index.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
## Type hints en **FastAPI**
|
||||
|
||||
**FastAPI** aprovecha estos type hints para hacer varias cosas.
|
||||
|
||||
Con **FastAPI** declaras los parámetros con type hints y obtienes:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Soporte en el editor**.
|
||||
* **Type checks**.
|
||||
|
||||
...y **FastAPI** usa las mismas declaraciones para:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Definir requerimientos**: desde request path parameters, query parameters, headers, bodies, dependencies, etc.
|
||||
* **Convertir datos**: desde el request al tipo requerido.
|
||||
* **Validar datos**: viniendo de cada request:
|
||||
* Generando **errores automáticos** devueltos al cliente cuando los datos son inválidos.
|
||||
* **Documentar** la API usando OpenAPI:
|
||||
* que en su caso es usada por las interfaces de usuario de la documentación automática e interactiva.
|
||||
|
||||
Puede que todo esto suene abstracto. Pero no te preocupes que todo lo verás en acción en el [Tutorial - User Guide](tutorial/index.md){.internal-link target=_blank}.
|
||||
|
||||
Lo importante es que usando los tipos de Python estándar en un único lugar (en vez de añadir más clases, decorator, etc.) **FastAPI** hará mucho del trabajo por ti.
|
||||
|
||||
!!! info "Información"
|
||||
Si ya pasaste por todo el tutorial y volviste a la sección de los tipos, una buena referencia es <a href="https://mypy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/cheat_sheet_py3.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">la "cheat sheet" de `mypy`</a>.
|
||||