mirror of
https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi.git
synced 2026-01-01 10:37:47 -05:00
Compare commits
66 Commits
0.125.0
...
fastapi-to
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
d2753c7382 | ||
|
|
53d2453d1a | ||
|
|
d9b7b65b81 | ||
|
|
9ed5f246ed | ||
|
|
edf7995775 | ||
|
|
47391ea8fb | ||
|
|
3b1b4f034b | ||
|
|
f362fdc234 | ||
|
|
4ce34686d9 | ||
|
|
dbe83f3919 | ||
|
|
13743e115a | ||
|
|
52842fb8d3 | ||
|
|
4d4fb28f9f | ||
|
|
a1735d6d11 | ||
|
|
1b42639296 | ||
|
|
ded035a421 | ||
|
|
44c849c4fc | ||
|
|
8322a4445a | ||
|
|
4b2cfcfd34 | ||
|
|
e300630551 | ||
|
|
1b3bea8b6b | ||
|
|
34e884156f | ||
|
|
cd90c78391 | ||
|
|
93f4dfd88b | ||
|
|
535b5daa31 | ||
|
|
6b53786f62 | ||
|
|
d98f4eb56e | ||
|
|
8cefc4b7cc | ||
|
|
3063ada72f | ||
|
|
5eb8d6ed8a | ||
|
|
7c751a2e1c | ||
|
|
55b556a7d1 | ||
|
|
a4d04c9b7e | ||
|
|
23caa2709b | ||
|
|
c264467efe | ||
|
|
2b212ddd76 | ||
|
|
7203e860b3 | ||
|
|
e55f223b46 | ||
|
|
a329baaa54 | ||
|
|
a7a0aee984 | ||
|
|
6539b80d9f | ||
|
|
e1bd9f3e33 | ||
|
|
b9b2793bda | ||
|
|
c4a1ab5036 | ||
|
|
22c7200ebb | ||
|
|
6e42bcd8ce | ||
|
|
6513d4daa1 | ||
|
|
1d93d531bc | ||
|
|
c2c1cc8aec | ||
|
|
5289259275 | ||
|
|
5783910d0c | ||
|
|
026b43e5d3 | ||
|
|
6b591ddd7e | ||
|
|
10252b1937 | ||
|
|
55ec28b81b | ||
|
|
1cb4e25651 | ||
|
|
eac57f6908 | ||
|
|
e2cd8a4201 | ||
|
|
5c7dceb80f | ||
|
|
d70ed5eceb | ||
|
|
261c11b218 | ||
|
|
75d4f9c098 | ||
|
|
19abc42efe | ||
|
|
09ab90ed35 | ||
|
|
f58d846015 | ||
|
|
caee1d3123 |
2
.github/workflows/build-docs.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/build-docs.yml
vendored
@@ -60,8 +60,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
pyproject.toml
|
||||
- name: Install docs extras
|
||||
run: uv pip install -r requirements-docs.txt
|
||||
- name: Verify Docs
|
||||
run: python ./scripts/docs.py verify-docs
|
||||
- name: Export Language Codes
|
||||
id: show-langs
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
|
||||
27
.github/workflows/pre-commit.yml
vendored
27
.github/workflows/pre-commit.yml
vendored
@@ -7,7 +7,8 @@ on:
|
||||
- synchronize
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
IS_FORK: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.repo.full_name != github.repository }}
|
||||
# Forks and Dependabot don't have access to secrets
|
||||
HAS_SECRETS: ${{ secrets.PRE_COMMIT != '' }}
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
pre-commit:
|
||||
@@ -19,16 +20,23 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: echo "$GITHUB_CONTEXT"
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v5
|
||||
name: Checkout PR for own repo
|
||||
if: env.IS_FORK == 'false'
|
||||
if: env.HAS_SECRETS == 'true'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# To be able to commit it needs more than the last commit
|
||||
# To be able to commit it needs to fetch the head of the branch, not the
|
||||
# merge commit
|
||||
ref: ${{ github.head_ref }}
|
||||
# And it needs the full history to be able to compute diffs
|
||||
fetch-depth: 0
|
||||
# A token other than the default GITHUB_TOKEN is needed to be able to trigger CI
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.PRE_COMMIT }}
|
||||
# pre-commit lite ci needs the default checkout configs to work
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v5
|
||||
name: Checkout PR for fork
|
||||
if: env.IS_FORK == 'true'
|
||||
if: env.HAS_SECRETS == 'false'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# To be able to commit it needs the head branch of the PR, the remote one
|
||||
ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}
|
||||
fetch-depth: 0
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v6
|
||||
with:
|
||||
@@ -44,15 +52,12 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
uv venv
|
||||
uv pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
- name: Run pre-commit
|
||||
- name: Run prek - pre-commit
|
||||
id: precommit
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
# Fetch the base branch for comparison
|
||||
git fetch origin ${{ github.base_ref }}
|
||||
uvx pre-commit run --from-ref origin/${{ github.base_ref }} --to-ref HEAD --show-diff-on-failure
|
||||
run: uvx prek run --from-ref origin/${GITHUB_BASE_REF} --to-ref HEAD --show-diff-on-failure
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
- name: Commit and push changes
|
||||
if: env.IS_FORK == 'false'
|
||||
if: env.HAS_SECRETS == 'true'
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git config user.name "github-actions[bot]"
|
||||
git config user.email "github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
|
||||
@@ -64,7 +69,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
git push
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- uses: pre-commit-ci/lite-action@v1.1.0
|
||||
if: env.IS_FORK == 'true'
|
||||
if: env.HAS_SECRETS == 'false'
|
||||
with:
|
||||
msg: 🎨 Auto format
|
||||
- name: Error out on pre-commit errors
|
||||
|
||||
58
.github/workflows/test.yml
vendored
58
.github/workflows/test.yml
vendored
@@ -16,59 +16,31 @@ env:
|
||||
UV_SYSTEM_PYTHON: 1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
lint:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Dump GitHub context
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GITHUB_CONTEXT: ${{ toJson(github) }}
|
||||
run: echo "$GITHUB_CONTEXT"
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v6
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v6
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.11"
|
||||
- name: Setup uv
|
||||
uses: astral-sh/setup-uv@v7
|
||||
with:
|
||||
cache-dependency-glob: |
|
||||
requirements**.txt
|
||||
pyproject.toml
|
||||
- name: Install Dependencies
|
||||
run: uv pip install -r requirements-tests.txt
|
||||
- name: Lint
|
||||
run: bash scripts/lint.sh
|
||||
|
||||
test:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
os: [ windows-latest, macos-latest ]
|
||||
python-version: [ "3.14" ]
|
||||
pydantic-version: [ "pydantic>=2.0.2,<3.0.0" ]
|
||||
include:
|
||||
- os: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.9"
|
||||
pydantic-version: "pydantic>=1.10.0,<2.0.0"
|
||||
coverage: coverage
|
||||
- os: macos-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.10"
|
||||
pydantic-version: "pydantic>=2.0.2,<3.0.0"
|
||||
coverage: coverage
|
||||
- os: windows-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.11"
|
||||
pydantic-version: "pydantic>=1.10.0,<2.0.0"
|
||||
- os: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.12"
|
||||
pydantic-version: "pydantic>=2.0.2,<3.0.0"
|
||||
- os: macos-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.13"
|
||||
pydantic-version: "pydantic>=1.10.0,<2.0.0"
|
||||
- os: windows-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.13"
|
||||
pydantic-version: "pydantic>=2.0.2,<3.0.0"
|
||||
coverage: coverage
|
||||
- os: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.13"
|
||||
coverage: coverage
|
||||
# Ubuntu with 3.13 needs coverage for CodSpeed benchmarks
|
||||
- os: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.13"
|
||||
coverage: coverage
|
||||
codspeed: codspeed
|
||||
- os: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
python-version: "3.14"
|
||||
pydantic-version: "pydantic>=2.0.2,<3.0.0"
|
||||
coverage: coverage
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
|
||||
@@ -92,14 +64,22 @@ jobs:
|
||||
pyproject.toml
|
||||
- name: Install Dependencies
|
||||
run: uv pip install -r requirements-tests.txt
|
||||
- name: Install Pydantic
|
||||
run: uv pip install "${{ matrix.pydantic-version }}"
|
||||
- run: mkdir coverage
|
||||
- name: Test
|
||||
if: matrix.codspeed != 'codspeed'
|
||||
run: bash scripts/test.sh
|
||||
env:
|
||||
COVERAGE_FILE: coverage/.coverage.${{ runner.os }}-py${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
CONTEXT: ${{ runner.os }}-py${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
- name: CodSpeed benchmarks
|
||||
if: matrix.codspeed == 'codspeed'
|
||||
uses: CodSpeedHQ/action@v4
|
||||
env:
|
||||
COVERAGE_FILE: coverage/.coverage.${{ runner.os }}-py${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
CONTEXT: ${{ runner.os }}-py${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
with:
|
||||
mode: simulation
|
||||
run: coverage run -m pytest tests/ --codspeed
|
||||
# Do not store coverage for all possible combinations to avoid file size max errors in Smokeshow
|
||||
- name: Store coverage files
|
||||
if: matrix.coverage == 'coverage'
|
||||
|
||||
4
.github/workflows/translate.yml
vendored
4
.github/workflows/translate.yml
vendored
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
||||
name: Translate
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 5 15 * *" # Run at 05:00 on the 15 of every month
|
||||
# schedule:
|
||||
# - cron: "0 5 15 * *" # Run at 05:00 on the 15 of every month
|
||||
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
|
||||
2
.gitignore
vendored
2
.gitignore
vendored
@@ -31,3 +31,5 @@ archive.zip
|
||||
|
||||
# Ignore while the setup still depends on requirements.txt files
|
||||
uv.lock
|
||||
|
||||
.codspeed
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -5,25 +5,55 @@ repos:
|
||||
rev: v6.0.0
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: check-added-large-files
|
||||
args: ['--maxkb=750']
|
||||
- id: check-toml
|
||||
- id: check-yaml
|
||||
args:
|
||||
- --unsafe
|
||||
- id: end-of-file-fixer
|
||||
- id: trailing-whitespace
|
||||
- repo: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-pre-commit
|
||||
rev: v0.14.3
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: ruff
|
||||
args:
|
||||
- --fix
|
||||
- id: ruff-format
|
||||
|
||||
- repo: local
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: local-script
|
||||
- id: local-ruff-check
|
||||
name: ruff check
|
||||
entry: uv run ruff check --force-exclude --fix --exit-non-zero-on-fix
|
||||
require_serial: true
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
name: local script
|
||||
types: [python]
|
||||
|
||||
- id: local-ruff-format
|
||||
name: ruff format
|
||||
entry: uv run ruff format --force-exclude --exit-non-zero-on-format
|
||||
require_serial: true
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
types: [python]
|
||||
|
||||
- id: add-permalinks-pages
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
name: add-permalinks-pages
|
||||
entry: uv run ./scripts/docs.py add-permalinks-pages
|
||||
args:
|
||||
- --update-existing
|
||||
files: ^docs/en/docs/.*\.md$
|
||||
|
||||
- id: generate-readme
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
name: generate README.md from index.md
|
||||
entry: uv run ./scripts/docs.py generate-readme
|
||||
files: ^docs/en/docs/index\.md|docs/en/data/sponsors\.yml|scripts/docs\.py$
|
||||
pass_filenames: false
|
||||
|
||||
- id: update-languages
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
name: update languages
|
||||
entry: uv run ./scripts/docs.py update-languages
|
||||
files: ^docs/.*|scripts/docs\.py$
|
||||
pass_filenames: false
|
||||
|
||||
- id: ensure-non-translated
|
||||
language: unsupported
|
||||
name: ensure non-translated files are not modified
|
||||
entry: uv run ./scripts/docs.py ensure-non-translated
|
||||
files: ^docs/(?!en/).*|^scripts/docs\.py$
|
||||
pass_filenames: false
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -120,6 +120,12 @@ The key features are:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## FastAPI mini documentary
|
||||
|
||||
There's a <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI mini documentary</a> released at the end of 2025, you can watch it online:
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" target="_blank"><img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/fastapi-documentary.jpg" alt="FastAPI Mini Documentary"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## **Typer**, the FastAPI of CLIs
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com" target="_blank"><img src="https://typer.tiangolo.com/img/logo-margin/logo-margin-vector.svg" style="width: 20%;"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI basiert auf **Pydantic**, und ich habe Ihnen gezeigt, wie Sie Pydantic-M
|
||||
|
||||
Aber FastAPI unterstützt auf die gleiche Weise auch die Verwendung von <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a>:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Das ist dank **Pydantic** ebenfalls möglich, da es <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses` intern unterstützt</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Wenn Sie jedoch eine Menge Datenklassen herumliegen haben, ist dies ein guter Tr
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können `dataclasses` auch im Parameter `response_model` verwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Die Datenklasse wird automatisch in eine Pydantic-Datenklasse konvertiert.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ In einigen Fällen müssen Sie möglicherweise immer noch Pydantics Version von
|
||||
|
||||
In diesem Fall können Sie einfach die Standard-`dataclasses` durch `pydantic.dataclasses` ersetzen, was einen direkten Ersatz darstellt:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
1. Wir importieren `field` weiterhin von Standard-`dataclasses`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ Sie können die verwendeten Zeilen aus dem Docstring einer *Pfadoperation-Funkti
|
||||
|
||||
Das Hinzufügen eines `\f` (ein maskiertes „Form Feed“-Zeichen) führt dazu, dass **FastAPI** die für OpenAPI verwendete Ausgabe an dieser Stelle abschneidet.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie wird nicht in der Dokumentation angezeigt, aber andere Tools (z. B. Sphinx) können den Rest verwenden.
|
||||
Sie wird nicht in der Dokumentation angezeigt, aber andere Tools (wie z. B. Sphinx) können den Rest verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial004_py310.py hl[17:27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -153,48 +153,16 @@ Und Sie könnten dies auch tun, wenn der Datentyp im Request nicht JSON ist.
|
||||
|
||||
In der folgenden Anwendung verwenden wir beispielsweise weder die integrierte Funktionalität von FastAPI zum Extrahieren des JSON-Schemas aus Pydantic-Modellen noch die automatische Validierung für JSON. Tatsächlich deklarieren wir den Request-Content-Type als YAML und nicht als JSON:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_py39.py hl[15:20, 22] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_pv1_py39.py hl[15:20, 22] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic Version 1 hieß die Methode zum Abrufen des JSON-Schemas für ein Modell `Item.schema()`, in Pydantic Version 2 heißt die Methode `Item.model_json_schema()`.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Obwohl wir nicht die standardmäßig integrierte Funktionalität verwenden, verwenden wir dennoch ein Pydantic-Modell, um das JSON-Schema für die Daten, die wir in YAML empfangen möchten, manuell zu generieren.
|
||||
|
||||
Dann verwenden wir den Request direkt und extrahieren den Body als `bytes`. Das bedeutet, dass FastAPI nicht einmal versucht, den Request-Payload als JSON zu parsen.
|
||||
Dann verwenden wir den Request direkt und extrahieren den Body als `bytes`. Das bedeutet, dass FastAPI nicht einmal versucht, die Request-Payload als JSON zu parsen.
|
||||
|
||||
Und dann parsen wir in unserem Code diesen YAML-Inhalt direkt und verwenden dann wieder dasselbe Pydantic-Modell, um den YAML-Inhalt zu validieren:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_py39.py hl[24:31] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_pv1_py39.py hl[24:31] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic Version 1 war die Methode zum Parsen und Validieren eines Objekts `Item.parse_obj()`, in Pydantic Version 2 heißt die Methode `Item.model_validate()`.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip | Tipp
|
||||
|
||||
Hier verwenden wir dasselbe Pydantic-Modell wieder.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -60,24 +60,8 @@ Auf die gleiche Weise wie bei Pydantic-Modellen deklarieren Sie Klassenattribute
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können dieselben Validierungs-Funktionen und -Tools verwenden, die Sie für Pydantic-Modelle verwenden, z. B. verschiedene Datentypen und zusätzliche Validierungen mit `Field()`.
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/tutorial001_py39.py hl[2,5:8,11] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 würden Sie `BaseSettings` direkt von `pydantic` statt von `pydantic_settings` importieren.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/tutorial001_pv1_py39.py hl[2,5:8,11] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip | Tipp
|
||||
|
||||
Für ein schnelles Copy-and-paste verwenden Sie nicht dieses Beispiel, sondern das letzte unten.
|
||||
@@ -215,8 +199,6 @@ APP_NAME="ChimichangApp"
|
||||
|
||||
Und dann aktualisieren Sie Ihre `config.py` mit:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/app03_an_py39/config.py hl[9] *}
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip | Tipp
|
||||
@@ -225,26 +207,6 @@ Das Attribut `model_config` wird nur für die Pydantic-Konfiguration verwendet.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/app03_an_py39/config_pv1.py hl[9:10] *}
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip | Tipp
|
||||
|
||||
Die Klasse `Config` wird nur für die Pydantic-Konfiguration verwendet. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/1.10/usage/model_config/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic Model Config</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic Version 1 erfolgte die Konfiguration in einer internen Klasse `Config`, in Pydantic Version 2 erfolgt sie in einem Attribut `model_config`. Dieses Attribut akzeptiert ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr>. Um automatische Codevervollständigung und Inline-Fehlerberichte zu erhalten, können Sie `SettingsConfigDict` importieren und verwenden, um dieses `dict` zu definieren.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Hier definieren wir die Konfiguration `env_file` innerhalb Ihrer Pydantic-`Settings`-Klasse und setzen den Wert auf den Dateinamen mit der dotenv-Datei, die wir verwenden möchten.
|
||||
|
||||
### Die `Settings` nur einmal laden mittels `lru_cache` { #creating-the-settings-only-once-with-lru-cache }
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Abhängig von Ihrem Anwendungsfall könnten Sie eine andere Bibliothek vorziehen
|
||||
|
||||
Hier ist eine kleine Vorschau, wie Sie Strawberry mit FastAPI integrieren können:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql_/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen zu Strawberry finden Sie in der <a href="https://strawberry.rocks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Strawberry-Dokumentation</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,21 +2,23 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie eine ältere FastAPI-App haben, nutzen Sie möglicherweise Pydantic Version 1.
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI unterstützt seit Version 0.100.0 sowohl Pydantic v1 als auch v2.
|
||||
FastAPI Version 0.100.0 unterstützte sowohl Pydantic v1 als auch v2. Es verwendete, was auch immer Sie installiert hatten.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie Pydantic v2 installiert hatten, wurde dieses verwendet. Wenn stattdessen Pydantic v1 installiert war, wurde jenes verwendet.
|
||||
FastAPI Version 0.119.0 führte eine teilweise Unterstützung für Pydantic v1 innerhalb von Pydantic v2 (als `pydantic.v1`) ein, um die Migration zu v2 zu erleichtern.
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic v1 ist jetzt deprecatet und die Unterstützung dafür wird in den nächsten Versionen von FastAPI entfernt, Sie sollten also zu **Pydantic v2 migrieren**. Auf diese Weise erhalten Sie die neuesten Features, Verbesserungen und Fixes.
|
||||
FastAPI 0.126.0 entfernte die Unterstützung für Pydantic v1, während `pydantic.v1` noch eine Weile unterstützt wurde.
|
||||
|
||||
/// warning | Achtung
|
||||
|
||||
Außerdem hat das Pydantic-Team die Unterstützung für Pydantic v1 in den neuesten Python-Versionen eingestellt, beginnend mit **Python 3.14**.
|
||||
Das Pydantic-Team hat die Unterstützung für Pydantic v1 in den neuesten Python-Versionen eingestellt, beginnend mit **Python 3.14**.
|
||||
|
||||
Dies schließt `pydantic.v1` ein, das unter Python 3.14 und höher nicht mehr unterstützt wird.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie die neuesten Features von Python nutzen möchten, müssen Sie sicherstellen, dass Sie Pydantic v2 verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie eine ältere FastAPI-App mit Pydantic v1 haben, zeige ich Ihnen hier, wie Sie sie zu Pydantic v2 migrieren, und die **neuen Features in FastAPI 0.119.0**, die Ihnen bei einer schrittweisen Migration helfen.
|
||||
Wenn Sie eine ältere FastAPI-App mit Pydantic v1 haben, zeige ich Ihnen hier, wie Sie sie zu Pydantic v2 migrieren, und die **Features in FastAPI 0.119.0**, die Ihnen bei einer schrittweisen Migration helfen.
|
||||
|
||||
## Offizieller Leitfaden { #official-guide }
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +46,7 @@ Danach können Sie die Tests ausführen und prüfen, ob alles funktioniert. Fall
|
||||
|
||||
## Pydantic v1 in v2 { #pydantic-v1-in-v2 }
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic v2 enthält alles aus Pydantic v1 als Untermodul `pydantic.v1`.
|
||||
Pydantic v2 enthält alles aus Pydantic v1 als Untermodul `pydantic.v1`. Dies wird aber in Versionen oberhalb von Python 3.13 nicht mehr unterstützt.
|
||||
|
||||
Das bedeutet, Sie können die neueste Version von Pydantic v2 installieren und die alten Pydantic‑v1‑Komponenten aus diesem Untermodul importieren und verwenden, als hätten Sie das alte Pydantic v1 installiert.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# Separate OpenAPI-Schemas für Eingabe und Ausgabe oder nicht { #separate-openapi-schemas-for-input-and-output-or-not }
|
||||
|
||||
Bei Verwendung von **Pydantic v2** ist die generierte OpenAPI etwas genauer und **korrekter** als zuvor. 😎
|
||||
Seit der Veröffentlichung von **Pydantic v2** ist die generierte OpenAPI etwas genauer und **korrekter** als zuvor. 😎
|
||||
|
||||
Tatsächlich gibt es in einigen Fällen sogar **zwei JSON-Schemas** in OpenAPI für dasselbe Pydantic-Modell, für Eingabe und Ausgabe, je nachdem, ob sie **Defaultwerte** haben.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -100,5 +100,3 @@ Und jetzt wird es ein einziges Schema für die Eingabe und Ausgabe des Modells g
|
||||
<div class="screenshot">
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/separate-openapi-schemas/image05.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Dies ist das gleiche Verhalten wie in Pydantic v1. 🤓
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -117,6 +117,12 @@ Seine Schlüssel-Merkmale sind:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## FastAPI Mini-Dokumentarfilm { #fastapi-mini-documentary }
|
||||
|
||||
Es gibt einen <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI-Mini-Dokumentarfilm</a>, veröffentlicht Ende 2025, Sie können ihn online ansehen:
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" target="_blank"><img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/fastapi-documentary.jpg" alt="FastAPI Mini-Dokumentarfilm"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## **Typer**, das FastAPI der CLIs { #typer-the-fastapi-of-clis }
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com" target="_blank"><img src="https://typer.tiangolo.com/img/logo-margin/logo-margin-vector.svg" style="width: 20%;"></a>
|
||||
@@ -233,7 +239,7 @@ INFO: Application startup complete.
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<details markdown="1">
|
||||
<summary>Was der Befehl <code>fastapi dev main.py</code> macht ...</summary>
|
||||
<summary>Über den Befehl <code>fastapi dev main.py</code> ...</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
Der Befehl `fastapi dev` liest Ihre `main.py`-Datei, erkennt die **FastAPI**-App darin und startet einen Server mit <a href="https://www.uvicorn.dev" class="external-link" target="_blank">Uvicorn</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -276,7 +282,7 @@ Sie sehen die alternative automatische Dokumentation (bereitgestellt von <a href
|
||||
|
||||
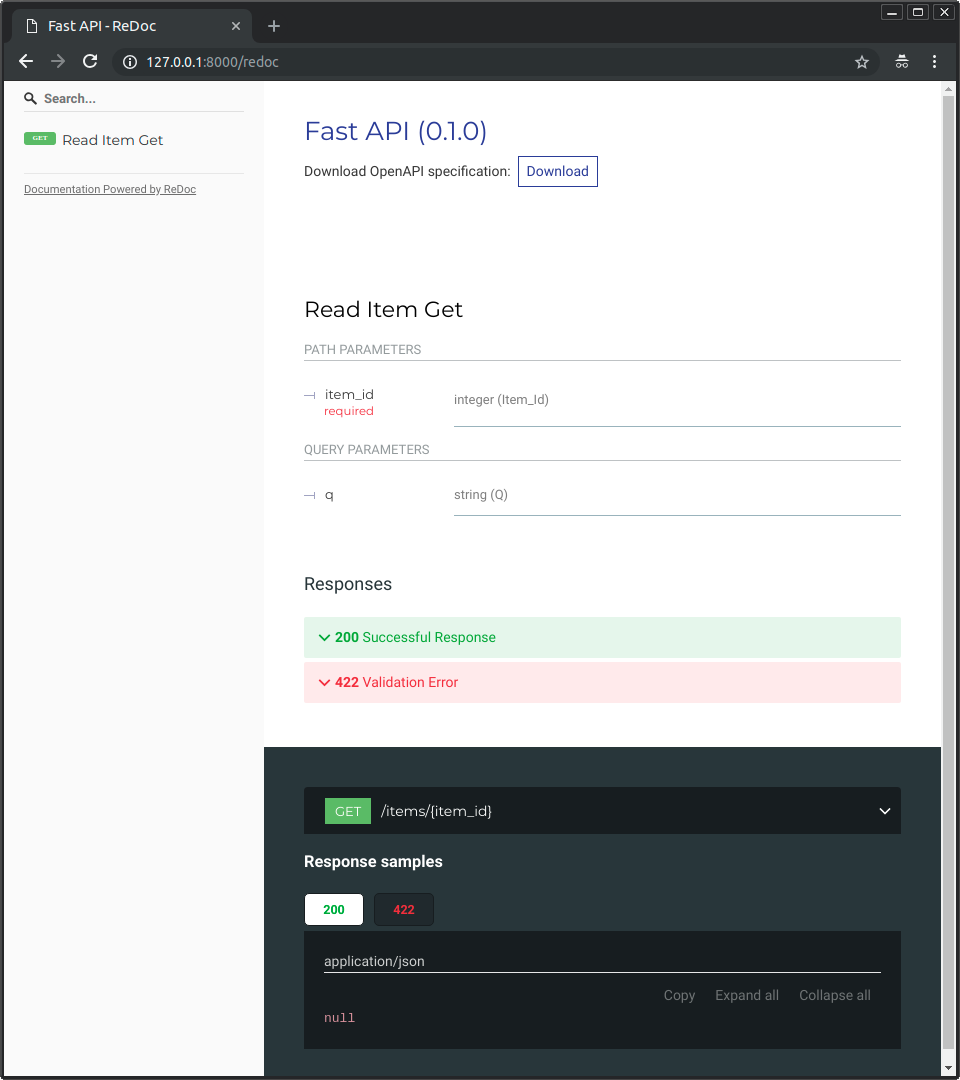
|
||||
|
||||
## Beispiel Aktualisierung { #example-upgrade }
|
||||
## Beispielaktualisierung { #example-upgrade }
|
||||
|
||||
Ändern Sie jetzt die Datei `main.py`, um den <abbr title="Body – Körper, Inhalt: Der eigentliche Inhalt einer Nachricht, nicht die Metadaten">Body</abbr> eines `PUT`-Requests zu empfangen.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -326,7 +332,7 @@ Gehen Sie jetzt auf <a href="http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs" class="external-link" t
|
||||
|
||||
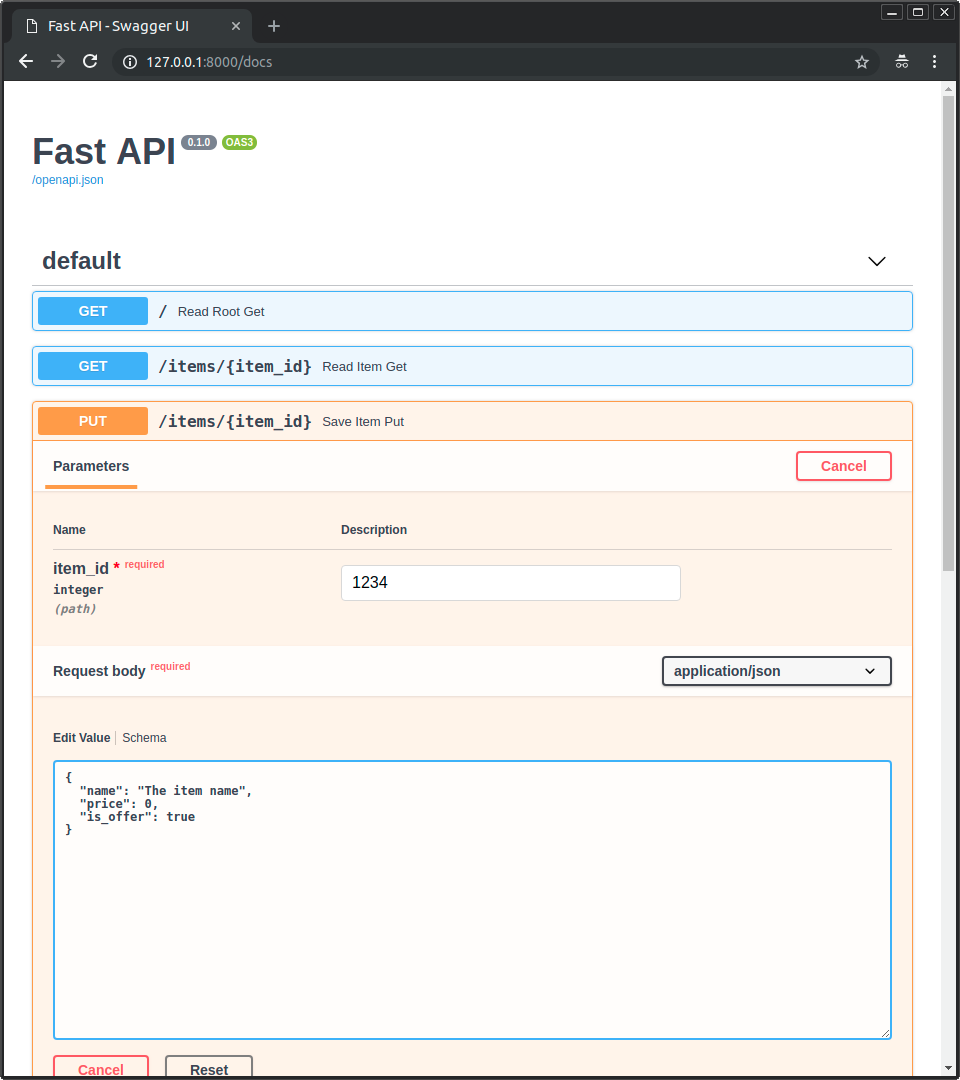
|
||||
|
||||
* Klicken Sie dann auf den Button „Execute“, die Benutzeroberfläche wird mit Ihrer API kommunizieren, sendet die Parameter, holt die Ergebnisse und zeigt sie auf dem Bildschirm an:
|
||||
* Klicken Sie dann auf den Button „Execute“, die Benutzeroberfläche wird mit Ihrer API kommunizieren, die Parameter senden, die Ergebnisse erhalten und sie auf dem Bildschirm anzeigen:
|
||||
|
||||
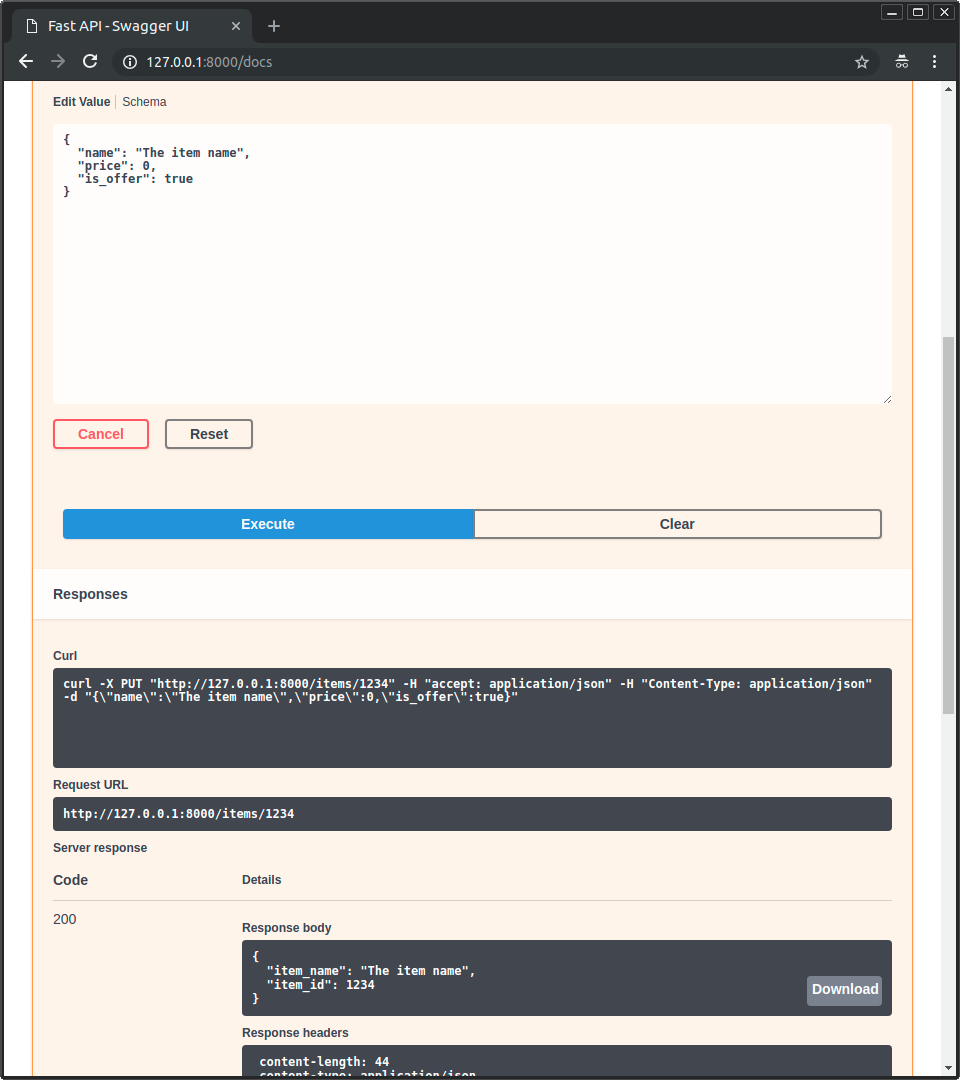
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -439,7 +445,7 @@ Für ein vollständigeres Beispiel, mit weiteren Funktionen, siehe das <a href="
|
||||
|
||||
* Deklaration von **Parametern** von anderen verschiedenen Stellen wie: **Header**, **Cookies**, **Formularfelder** und **Dateien**.
|
||||
* Wie man **Validierungs-Constraints** wie `maximum_length` oder `regex` setzt.
|
||||
* Ein sehr leistungsfähiges und einfach zu bedienendes System für **<abbr title="Dependency Injection – Einbringen von Abhängigkeiten: Auch bekannt als Komponenten, Ressourcen, Provider, Services, Injectables">Dependency Injection</abbr>**.
|
||||
* Ein sehr leistungsfähiges und einfach zu bedienendes System für **<abbr title="auch bekannt als Komponenten, Ressourcen, Provider, Services, Injectables">Dependency Injection</abbr>**.
|
||||
* Sicherheit und Authentifizierung, einschließlich Unterstützung für **OAuth2** mit **JWT-Tokens** und **HTTP Basic** Authentifizierung.
|
||||
* Fortgeschrittenere (aber ebenso einfache) Techniken zur Deklaration **tief verschachtelter JSON-Modelle** (dank Pydantic).
|
||||
* **GraphQL**-Integration mit <a href="https://strawberry.rocks" class="external-link" target="_blank">Strawberry</a> und anderen Bibliotheken.
|
||||
@@ -452,7 +458,7 @@ Für ein vollständigeres Beispiel, mit weiteren Funktionen, siehe das <a href="
|
||||
|
||||
### Ihre App deployen (optional) { #deploy-your-app-optional }
|
||||
|
||||
Optional können Sie Ihre FastAPI-App in die <a href="https://fastapicloud.com" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI Cloud</a> deployen, treten Sie der Warteliste bei, falls noch nicht geschehen. 🚀
|
||||
Optional können Sie Ihre FastAPI-App in die <a href="https://fastapicloud.com" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI Cloud</a> deployen, gehen Sie und treten Sie der Warteliste bei, falls noch nicht geschehen. 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie bereits ein **FastAPI Cloud**-Konto haben (wir haben Sie von der Warteliste eingeladen 😉), können Sie Ihre Anwendung mit einem einzigen Befehl deployen.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -494,7 +500,7 @@ Es vereinfacht den Prozess des **Erstellens**, **Deployens** und **Zugreifens**
|
||||
|
||||
Es bringt die gleiche **Developer-Experience** beim Erstellen von Apps mit FastAPI auch zum **Deployment** in der Cloud. 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI Cloud ist der Hauptsponsor und Finanzierer der „FastAPI and friends“ Open-Source-Projekte. ✨
|
||||
FastAPI Cloud ist der Hauptsponsor und Finanzierer der *FastAPI and friends* Open-Source-Projekte. ✨
|
||||
|
||||
#### Bei anderen Cloudanbietern deployen { #deploy-to-other-cloud-providers }
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -50,14 +50,6 @@ Wenn Sie Teil-Aktualisierungen entgegennehmen, ist der `exclude_unset`-Parameter
|
||||
|
||||
Wie in `item.model_dump(exclude_unset=True)`.
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 hieß diese Methode `.dict()`, in Pydantic v2 wurde sie <abbr title="veraltet, obsolet: Es soll nicht mehr verwendet werden">deprecatet</abbr> (aber immer noch unterstützt) und in `.model_dump()` umbenannt.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Beispiele hier verwenden `.dict()` für die Kompatibilität mit Pydantic v1, Sie sollten jedoch stattdessen `.model_dump()` verwenden, wenn Sie Pydantic v2 verwenden können.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Das wird ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr> erstellen, mit nur den Daten, die gesetzt wurden, als das `item`-Modell erstellt wurde, Defaultwerte ausgeschlossen.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können das verwenden, um ein `dict` zu erstellen, das nur die (im <abbr title="Request – Anfrage: Daten, die der Client zum Server sendet">Request</abbr>) gesendeten Daten enthält, ohne Defaultwerte:
|
||||
@@ -68,14 +60,6 @@ Sie können das verwenden, um ein `dict` zu erstellen, das nur die (im <abbr tit
|
||||
|
||||
Jetzt können Sie eine Kopie des existierenden Modells mittels `.model_copy()` erstellen, wobei Sie dem `update`-Parameter ein `dict` mit den zu ändernden Daten übergeben.
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 hieß diese Methode `.copy()`, in Pydantic v2 wurde sie <abbr title="veraltet, obsolet: Es soll nicht mehr verwendet werden">deprecatet</abbr> (aber immer noch unterstützt) und in `.model_copy()` umbenannt.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Beispiele hier verwenden `.copy()` für die Kompatibilität mit Pydantic v1, Sie sollten jedoch stattdessen `.model_copy()` verwenden, wenn Sie Pydantic v2 verwenden können.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Wie in `stored_item_model.model_copy(update=update_data)`:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/body_updates/tutorial002_py310.py hl[33] *}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -127,14 +127,6 @@ Innerhalb der Funktion können Sie alle Attribute des Modellobjekts direkt verwe
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/body/tutorial002_py310.py *}
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 hieß die Methode `.dict()`, sie wurde in Pydantic v2 deprecatet (aber weiterhin unterstützt) und in `.model_dump()` umbenannt.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Beispiele hier verwenden `.dict()` zur Kompatibilität mit Pydantic v1, aber Sie sollten stattdessen `.model_dump()` verwenden, wenn Sie Pydantic v2 nutzen können.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
## Requestbody- + Pfad-Parameter { #request-body-path-parameters }
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können Pfad-Parameter und den Requestbody gleichzeitig deklarieren.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,21 +22,13 @@ Hier ist eine allgemeine Idee, wie die Modelle mit ihren Passwortfeldern aussehe
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial001_py310.py hl[7,9,14,20,22,27:28,31:33,38:39] *}
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
### Über `**user_in.model_dump()` { #about-user-in-model-dump }
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 hieß die Methode `.dict()`, in Pydantic v2 wurde sie <abbr title="veraltet, obsolet: Es soll nicht mehr verwendet werden">deprecatet</abbr> (aber weiterhin unterstützt) und in `.model_dump()` umbenannt.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Beispiele hier verwenden `.dict()` für die Kompatibilität mit Pydantic v1, aber Sie sollten `.model_dump()` verwenden, wenn Sie Pydantic v2 verwenden können.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
### Über `**user_in.dict()` { #about-user-in-dict }
|
||||
|
||||
#### Die `.dict()`-Methode von Pydantic { #pydantics-dict }
|
||||
#### Pydantics `.model_dump()` { #pydantics-model-dump }
|
||||
|
||||
`user_in` ist ein Pydantic-Modell der Klasse `UserIn`.
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic-Modelle haben eine `.dict()`-Methode, die ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr> mit den Daten des Modells zurückgibt.
|
||||
Pydantic-Modelle haben eine `.model_dump()`-Methode, die ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr> mit den Daten des Modells zurückgibt.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn wir also ein Pydantic-Objekt `user_in` erstellen, etwa so:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -47,7 +39,7 @@ user_in = UserIn(username="john", password="secret", email="john.doe@example.com
|
||||
und dann aufrufen:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.dict()
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.model_dump()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
haben wir jetzt ein `dict` mit den Daten in der Variablen `user_dict` (es ist ein `dict` statt eines Pydantic-Modellobjekts).
|
||||
@@ -103,20 +95,20 @@ UserInDB(
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ein Pydantic-Modell aus dem Inhalt eines anderen { #a-pydantic-model-from-the-contents-of-another }
|
||||
|
||||
Da wir im obigen Beispiel `user_dict` von `user_in.dict()` bekommen haben, wäre dieser Code:
|
||||
Da wir im obigen Beispiel `user_dict` von `user_in.model_dump()` bekommen haben, wäre dieser Code:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.dict()
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.model_dump()
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_dict)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gleichwertig zu:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.dict())
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.model_dump())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
... weil `user_in.dict()` ein `dict` ist, und dann lassen wir Python es „entpacken“, indem wir es an `UserInDB` mit vorangestelltem `**` übergeben.
|
||||
... weil `user_in.model_dump()` ein `dict` ist, und dann lassen wir Python es „entpacken“, indem wir es an `UserInDB` mit vorangestelltem `**` übergeben.
|
||||
|
||||
Auf diese Weise erhalten wir ein Pydantic-Modell aus den Daten eines anderen Pydantic-Modells.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -125,7 +117,7 @@ Auf diese Weise erhalten wir ein Pydantic-Modell aus den Daten eines anderen Pyd
|
||||
Und dann fügen wir das zusätzliche Schlüsselwort-Argument `hashed_password=hashed_password` hinzu, wie in:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.dict(), hashed_password=hashed_password)
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.model_dump(), hashed_password=hashed_password)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
... was so ist wie:
|
||||
@@ -180,7 +172,6 @@ Wenn Sie eine <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/types/#unions"
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,14:15,18:20,33] *}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### `Union` in Python 3.10 { #union-in-python-3-10 }
|
||||
|
||||
In diesem Beispiel übergeben wir `Union[PlaneItem, CarItem]` als Wert des Arguments `response_model`.
|
||||
@@ -203,7 +194,6 @@ Dafür verwenden Sie Pythons Standard-`typing.List` (oder nur `list` in Python 3
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial004_py39.py hl[18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Response mit beliebigem `dict` { #response-with-arbitrary-dict }
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können auch eine Response deklarieren, die ein beliebiges `dict` zurückgibt, indem Sie nur die Typen der Schlüssel und Werte ohne ein Pydantic-Modell deklarieren.
|
||||
@@ -214,7 +204,6 @@ In diesem Fall können Sie `typing.Dict` verwenden (oder nur `dict` in Python 3.
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial005_py39.py hl[6] *}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Zusammenfassung { #recap }
|
||||
|
||||
Verwenden Sie gerne mehrere Pydantic-Modelle und vererben Sie je nach Bedarf.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -205,20 +205,6 @@ Wenn Sie sich mit all diesen **„regulärer Ausdruck“**-Ideen verloren fühle
|
||||
|
||||
Aber nun wissen Sie, dass Sie sie in **FastAPI** immer dann verwenden können, wenn Sie sie brauchen.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pydantic v1 `regex` statt `pattern` { #pydantic-v1-regex-instead-of-pattern }
|
||||
|
||||
Vor Pydantic Version 2 und FastAPI 0.100.0, hieß der Parameter `regex` statt `pattern`, aber das ist jetzt obsolet.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie könnten immer noch Code sehen, der den alten Namen verwendet:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial004_regex_an_py310.py hl[11] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
Beachten Sie aber, dass das obsolet ist und auf den neuen Parameter `pattern` aktualisiert werden sollte. 🤓
|
||||
|
||||
## Defaultwerte { #default-values }
|
||||
|
||||
Natürlich können Sie Defaultwerte verwenden, die nicht `None` sind.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -252,20 +252,6 @@ Wenn Sie also den Artikel mit der ID `foo` bei der *Pfadoperation* anfragen, wir
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 hieß diese Methode `.dict()`, in Pydantic v2 wurde sie <abbr title="veraltet, obsolet: Es soll nicht mehr verwendet werden">deprecatet</abbr> (aber immer noch unterstützt) und in `.model_dump()` umbenannt.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Beispiele hier verwenden `.dict()` für die Kompatibilität mit Pydantic v1, Sie sollten jedoch stattdessen `.model_dump()` verwenden, wenn Sie Pydantic v2 verwenden können.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI verwendet `.dict()` von Pydantic Modellen, <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/1.10/usage/exporting_models/#modeldict" class="external-link" target="_blank">mit dessen `exclude_unset`-Parameter</a>, um das zu erreichen.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
/// info | Info
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können auch:
|
||||
|
||||
* `response_model_exclude_defaults=True`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,36 +8,14 @@ Hier sind mehrere Möglichkeiten, das zu tun.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können `examples` („Beispiele“) für ein Pydantic-Modell deklarieren, welche dem generierten JSON-Schema hinzugefügt werden.
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/schema_extra_example/tutorial001_py310.py hl[13:24] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/schema_extra_example/tutorial001_pv1_py310.py hl[13:23] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
Diese zusätzlichen Informationen werden unverändert zum für dieses Modell ausgegebenen **JSON-Schema** hinzugefügt und in der API-Dokumentation verwendet.
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic Version 2 würden Sie das Attribut `model_config` verwenden, das ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr> akzeptiert, wie beschrieben in <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/api/config/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic-Dokumentation: Configuration</a>.
|
||||
Sie können das Attribut `model_config` verwenden, das ein <abbr title="Dictionary – Zuordnungstabelle: In anderen Sprachen auch Hash, Map, Objekt, Assoziatives Array genannt">`dict`</abbr> akzeptiert, wie beschrieben in <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/api/config/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic-Dokumentation: Configuration</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können `json_schema_extra` setzen, mit einem `dict`, das alle zusätzlichen Daten enthält, die im generierten JSON-Schema angezeigt werden sollen, einschließlich `examples`.
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic Version 1 würden Sie eine interne Klasse `Config` und `schema_extra` verwenden, wie beschrieben in <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/1.10/usage/schema/#schema-customization" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic-Dokumentation: Schema customization</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können `schema_extra` setzen, mit einem `dict`, das alle zusätzlichen Daten enthält, die im generierten JSON-Schema angezeigt werden sollen, einschließlich `examples`.
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip | Tipp
|
||||
|
||||
Mit derselben Technik können Sie das JSON-Schema erweitern und Ihre eigenen benutzerdefinierten Zusatzinformationen hinzufügen.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,213 +4,197 @@ Translate to German (Deutsch).
|
||||
|
||||
Language code: de.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Definitions
|
||||
|
||||
"hyphen"
|
||||
The character «-»
|
||||
Unicode U+002D (HYPHEN-MINUS)
|
||||
Alternative names: hyphen, dash, minus sign
|
||||
|
||||
"dash"
|
||||
The character «–»
|
||||
Unicode U+2013 (EN DASH)
|
||||
German name: Halbgeviertstrich
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Grammar to use when talking to the reader
|
||||
|
||||
Use the formal grammar (use «Sie» instead of «Du»).
|
||||
|
||||
Use the formal grammar (use `Sie` instead of `Du`).
|
||||
|
||||
### Quotes
|
||||
|
||||
1) Convert neutral double quotes («"») and English double typographic quotes («“» and «”») to German double typographic quotes («„» and «“»). Convert neutral single quotes («'») and English single typographic quotes («‘» and «’») to German single typographic quotes («‚» and «‘»). Do NOT convert «`"» to «„», do NOT convert «"`» to «“».
|
||||
1) Convert neutral double quotes (`"`) to German double typographic quotes (`„` and `“`). Convert neutral single quotes (`'`) to German single typographic quotes (`‚` and `‘`).
|
||||
|
||||
Do NOT convert quotes in code snippets and code blocks to their German typographic equivalents.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
"Hello world"
|
||||
“Hello Universe”
|
||||
"He said: 'Hello'"
|
||||
“my name is ‘Nils’”
|
||||
`"__main__"`
|
||||
`"items"`
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
"Hello world"
|
||||
“Hello Universe”
|
||||
"He said: 'Hello'"
|
||||
“my name is ‘Nils’”
|
||||
`"__main__"`
|
||||
`"items"`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Result (German):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
„Hallo Welt“
|
||||
„Hallo Universum“
|
||||
„Er sagte: ‚Hallo‘“
|
||||
„Mein Name ist ‚Nils‘“
|
||||
`"__main__"`
|
||||
`"items"`
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
Result (German):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
„Hallo Welt“
|
||||
„Hallo Universum“
|
||||
„Er sagte: ‚Hallo‘“
|
||||
„Mein Name ist ‚Nils‘“
|
||||
`"__main__"`
|
||||
`"items"`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Ellipsis
|
||||
|
||||
1) Make sure there is a space between an ellipsis and a word following or preceding the ellipsis.
|
||||
- Make sure there is a space between an ellipsis and a word following or preceding the ellipsis.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
...as we intended.
|
||||
...this would work:
|
||||
...etc.
|
||||
others...
|
||||
More to come...
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
...as we intended.
|
||||
...this would work:
|
||||
...etc.
|
||||
others...
|
||||
More to come...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Result (German):
|
||||
Result (German):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
... wie wir es beabsichtigt hatten.
|
||||
... das würde funktionieren:
|
||||
... usw.
|
||||
Andere ...
|
||||
Später mehr ...
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
|
||||
2) This does not apply in URLs, code blocks, and code snippets. Do not remove or add spaces there.
|
||||
```
|
||||
... wie wir es beabsichtigt hatten.
|
||||
... das würde funktionieren:
|
||||
... usw.
|
||||
Andere ...
|
||||
Später mehr ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- This does not apply in URLs, code blocks, and code snippets. Do not remove or add spaces there.
|
||||
|
||||
### Headings
|
||||
|
||||
1) Translate headings using the infinite form.
|
||||
- Translate headings using the infinite form.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
## Create a Project { #create-a-project }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Create a Project { #create-a-project }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Translate with (German):
|
||||
Result (German):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
## Ein Projekt erstellen { #create-a-project }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Ein Projekt erstellen { #create-a-project }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German):
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
## Erstellen Sie ein Projekt { #create-a-project }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Erstellen Sie ein Projekt { #create-a-project }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
# Install Packages { #install-packages }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
# Install Packages { #install-packages }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Translate with (German):
|
||||
Translate with (German):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
# Pakete installieren { #install-packages }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
# Pakete installieren { #install-packages }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German):
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
# Installieren Sie Pakete { #install-packages }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
# Installieren Sie Pakete { #install-packages }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
### Run Your Program { #run-your-program }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Run Your Program { #run-your-program }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Translate with (German):
|
||||
Translate with (German):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
### Ihr Programm ausführen { #run-your-program }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Ihr Programm ausführen { #run-your-program }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German):
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
### Führen Sie Ihr Programm aus { #run-your-program }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
### Führen Sie Ihr Programm aus { #run-your-program }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2) Make sure that the translated part of the heading does not end with a period.
|
||||
- Make sure that the translated part of the heading does not end with a period.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
## Another module with `APIRouter` { #another-module-with-apirouter }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Another module with `APIRouter` { #another-module-with-apirouter }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Translate with (German):
|
||||
Translate with (German):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
## Ein weiteres Modul mit `APIRouter` { #another-module-with-apirouter }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Ein weiteres Modul mit `APIRouter` { #another-module-with-apirouter }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German) – notice the added period:
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German) – notice the added period:
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
## Ein weiteres Modul mit `APIRouter`. { #another-module-with-apirouter }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Ein weiteres Modul mit `APIRouter`. { #another-module-with-apirouter }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3) Replace occurrences of literal « - » (a space followed by a hyphen followed by a space) with « – » (a space followed by a dash followed by a space) in the translated part of the heading.
|
||||
- Replace occurrences of literal ` - ` (a space followed by a hyphen followed by a space) with ` – ` (a space followed by a dash followed by a space) in the translated part of the heading.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
# FastAPI in Containers - Docker { #fastapi-in-containers-docker }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
# FastAPI in Containers - Docker { #fastapi-in-containers-docker }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Translate with (German) – notice the dash:
|
||||
Translate with (German) – notice the dash:
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
# FastAPI in Containern – Docker { #fastapi-in-containers-docker }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
# FastAPI in Containern – Docker { #fastapi-in-containers-docker }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German) – notice the hyphen:
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German) – notice the hyphen:
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
# FastAPI in Containern - Docker { #fastapi-in-containers-docker }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
# FastAPI in Containern - Docker { #fastapi-in-containers-docker }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3.1) Do not apply rule 3 when there is no space before or no space after the hyphen.
|
||||
- Do not apply rule 3 when there is no space before or no space after the hyphen.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
Source (English):
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
## Type hints and annotations { #type-hints-and-annotations }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Type hints and annotations { #type-hints-and-annotations }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Translate with (German) – notice the hyphen:
|
||||
Translate with (German) - notice the hyphen:
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
## Typhinweise und -annotationen { #type-hints-and-annotations }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Typhinweise und -annotationen { #type-hints-and-annotations }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German) – notice the dash:
|
||||
Do NOT translate with (German) - notice the dash:
|
||||
|
||||
«««
|
||||
## Typhinweise und –annotationen { #type-hints-and-annotations }
|
||||
»»»
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Typhinweise und –annotationen { #type-hints-and-annotations }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3.2) Do not apply rule 3 to the untranslated part of the heading inside curly brackets, which you shall not translate.
|
||||
- Do not modify the hyphens in the content in headers inside of curly braces, which you shall not translate.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### German instructions, when to use and when not to use hyphens in words (written in first person, which is you)
|
||||
### German instructions, when to use and when not to use hyphens in words (written in first person, which is you).
|
||||
|
||||
In der Regel versuche ich so weit wie möglich Worte zusammenzuschreiben, also ohne Bindestrich, es sei denn, es ist Konkretesding-Klassevondingen, etwa «Pydantic-Modell» (aber: «Datenbankmodell»), «Python-Modul» (aber: «Standardmodul»). Ich setze auch einen Bindestrich, wenn er die gleichen Buchstaben verbindet, etwa «Enum-Member», «Cloud-Dienst», «Template-Engine». Oder wenn das Wort sonst einfach zu lang wird, etwa, «Performance-Optimierung». Oder um etwas visuell besser zu dokumentieren, etwa «Pfadoperation-Dekorator», «Pfadoperation-Funktion».
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -219,122 +203,122 @@ In der Regel versuche ich so weit wie möglich Worte zusammenzuschreiben, also o
|
||||
|
||||
Ich versuche nicht, alles einzudeutschen. Das bezieht sich besonders auf Begriffe aus dem Bereich der Programmierung. Ich wandele zwar korrekt in Großschreibung um und setze Bindestriche, wo notwendig, aber ansonsten lasse ich solch ein Wort unverändert. Beispielsweise wird aus dem englischen Wort «string» in der deutschen Übersetzung «String», aber nicht «Zeichenkette». Oder aus dem englischen Wort «request body» wird in der deutschen Übersetzung «Requestbody», aber nicht «Anfragekörper». Oder aus dem englischen «response» wird im Deutschen «Response», aber nicht «Antwort».
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### List of English terms and their preferred German translations
|
||||
|
||||
Below is a list of English terms and their preferred German translations, separated by a colon («:»). Use these translations, do not use your own. If an existing translation does not use these terms, update it to use them. In the below list, a term or a translation may be followed by an explanation in brackets, which explains when to translate the term this way. If a translation is preceded by «NOT», then that means: do NOT use this translation for this term. English nouns, starting with the word «the», have the German genus – «der», «die», «das» – prepended to their German translation, to help you to grammatically decline them in the translation. They are given in singular case, unless they have «(plural)» attached, which means they are given in plural case. Verbs are given in the full infinitive – starting with the word «to».
|
||||
Below is a list of English terms and their preferred German translations, separated by a colon (:). Use these translations, do not use your own. If an existing translation does not use these terms, update it to use them. In the below list, a term or a translation may be followed by an explanation in brackets, which explains when to translate the term this way. If a translation is preceded by `NOT`, then that means: do NOT use this translation for this term. English nouns, starting with the word `the`, have the German genus – `der`, `die`, `das` – prepended to their German translation, to help you to grammatically decline them in the translation. They are given in singular case, unless they have `(plural)` attached, which means they are given in plural case. Verbs are given in the full infinitive – starting with the word `to`.
|
||||
|
||||
* «/// check»: «/// check | Testen»
|
||||
* «/// danger»: «/// danger | Gefahr»
|
||||
* «/// info»: «/// info | Info»
|
||||
* «/// note | Technical Details»: «/// note | Technische Details»
|
||||
* «/// note»: «/// note | Hinweis»
|
||||
* «/// tip»: «/// tip | Tipp»
|
||||
* «/// warning»: «/// warning | Achtung»
|
||||
* «you»: «Sie»
|
||||
* «your»: «Ihr»
|
||||
* «e.g»: «z. B.»
|
||||
* «etc.»: «usw.»
|
||||
* «ref»: «Ref.»
|
||||
* «the Tutorial - User guide»: «das Tutorial – Benutzerhandbuch»
|
||||
* «the Advanced User Guide»: «das Handbuch für fortgeschrittene Benutzer»
|
||||
* «the SQLModel docs»: «die SQLModel-Dokumentation»
|
||||
* «the docs»: «die Dokumentation» (use singular case)
|
||||
* «the env var»: «die Umgebungsvariable»
|
||||
* «the `PATH` environment variable»: «die `PATH`-Umgebungsvariable»
|
||||
* «the `PATH`»: «der `PATH`»
|
||||
* «the `requirements.txt`»: «die `requirements.txt`»
|
||||
* «the API Router»: «der API-Router»
|
||||
* «the Authorization-Header»: «der Autorisierungsheader»
|
||||
* «the `Authorization`-Header»: «der `Authorization`-Header»
|
||||
* «the background task»: «der Hintergrundtask»
|
||||
* «the button»: «der Button»
|
||||
* «the cloud provider»: «der Cloudanbieter»
|
||||
* «the CLI»: «Das CLI»
|
||||
* «the command line interface»: «Das Kommandozeileninterface»
|
||||
* «the default value»: «der Defaultwert»
|
||||
* «the default value»: NOT «der Standardwert»
|
||||
* «the default declaration»: «die Default-Deklaration»
|
||||
* «the deployment»: «das Deployment»
|
||||
* «the dict»: «das Dict»
|
||||
* «the dictionary»: «das Dictionary»
|
||||
* «the enumeration»: «die Enumeration»
|
||||
* «the enum»: «das Enum»
|
||||
* «the engine»: «die Engine»
|
||||
* «the error response»: «die Error-Response»
|
||||
* «the event»: «das Event»
|
||||
* «the exception»: «die Exception»
|
||||
* «the exception handler»: «der Exceptionhandler»
|
||||
* «the form model»: «das Formularmodell»
|
||||
* «the form body»: «der Formularbody»
|
||||
* «the header»: «der Header»
|
||||
* «the headers» (plural): «die Header»
|
||||
* «in headers» (plural): «in Headern»
|
||||
* «the forwarded header»: «der Forwarded-Header»
|
||||
* «the lifespan event»: «das Lifespan-Event»
|
||||
* «the lock»: «der Lock»
|
||||
* «the locking»: «das Locking»
|
||||
* «the mobile application»: «die Mobile-Anwendung»
|
||||
* «the model object»: «das Modellobjekt»
|
||||
* «the mounting»: «das Mounten»
|
||||
* «mounted»: «gemountet»
|
||||
* «the origin»: «das Origin»
|
||||
* «the override»: «Die Überschreibung»
|
||||
* «the parameter»: «der Parameter»
|
||||
* «the parameters» (plural): «die Parameter»
|
||||
* «the function parameter»: «der Funktionsparameter»
|
||||
* «the default parameter»: «der Defaultparameter»
|
||||
* «the body parameter»: «der Body-Parameter»
|
||||
* «the request body parameter»: «der Requestbody-Parameter»
|
||||
* «the path parameter»: «der Pfad-Parameter»
|
||||
* «the query parameter»: «der Query-Parameter»
|
||||
* «the cookie parameter»: «der Cookie-Parameter»
|
||||
* «the header parameter»: «der Header-Parameter»
|
||||
* «the form parameter»: «der Formular-Parameter»
|
||||
* «the payload»: «die Payload»
|
||||
* «the performance»: NOT «die Performance»
|
||||
* «the query»: «die Query»
|
||||
* «the recap»: «die Zusammenfassung»
|
||||
* «the request» (what the client sends to the server): «der Request»
|
||||
* «the request body»: «der Requestbody»
|
||||
* «the request bodies» (plural): «die Requestbodys»
|
||||
* «the response» (what the server sends back to the client): «die Response»
|
||||
* «the return type»: «der Rückgabetyp»
|
||||
* «the return value»: «der Rückgabewert»
|
||||
* «the startup» (the event of the app): «der Startup»
|
||||
* «the shutdown» (the event of the app): «der Shutdown»
|
||||
* «the startup event»: «das Startup-Event»
|
||||
* «the shutdown event»: «das Shutdown-Event»
|
||||
* «the startup» (of the server): «das Hochfahren»
|
||||
* «the startup» (the company): «das Startup»
|
||||
* «the SDK»: «das SDK»
|
||||
* «the tag»: «der Tag»
|
||||
* «the type annotation»: «die Typannotation»
|
||||
* «the type hint»: «der Typhinweis»
|
||||
* «the wildcard»: «die Wildcard»
|
||||
* «the worker class»: «die Workerklasse»
|
||||
* «the worker class»: NOT «die Arbeiterklasse»
|
||||
* «the worker process»: «der Workerprozess»
|
||||
* «the worker process»: NOT «der Arbeiterprozess»
|
||||
* «to commit»: «committen»
|
||||
* «to deploy» (in the cloud): «deployen»
|
||||
* «to modify»: «ändern»
|
||||
* «to serve» (an application): «bereitstellen»
|
||||
* «to serve» (a response): «ausliefern»
|
||||
* «to serve»: NOT «bedienen»
|
||||
* «to upgrade»: «aktualisieren»
|
||||
* «to wrap»: «wrappen»
|
||||
* «to wrap»: NOT «hüllen»
|
||||
* «`foo` as a `type`»: «`foo` vom Typ `type`»
|
||||
* «`foo` as a `type`»: «`foo`, ein `type`»
|
||||
* «FastAPI's X»: «FastAPIs X»
|
||||
* «Starlette's Y»: «Starlettes Y»
|
||||
* «X is case-sensitive»: «Groß-/Kleinschreibung ist relevant in X»
|
||||
* «X is case-insensitive»: «Groß-/Kleinschreibung ist nicht relevant in X»
|
||||
* «standard Python»: «Standard-Python»
|
||||
* «deprecated»: «deprecatet»
|
||||
* /// check: /// check | Testen
|
||||
* /// danger: /// danger | Gefahr
|
||||
* /// info: /// info | Info
|
||||
* /// note | Technical Details: /// note | Technische Details
|
||||
* /// note: /// note | Hinweis
|
||||
* /// tip: /// tip | Tipp
|
||||
* /// warning: /// warning | Achtung
|
||||
* you: Sie
|
||||
* your: Ihr
|
||||
* e.g: z. B.
|
||||
* etc.: usw.
|
||||
* ref: Ref.
|
||||
* the Tutorial - User guide: das Tutorial – Benutzerhandbuch
|
||||
* the Advanced User Guide: das Handbuch für fortgeschrittene Benutzer
|
||||
* the SQLModel docs: die SQLModel-Dokumentation
|
||||
* the docs: die Dokumentation (use singular case)
|
||||
* the env var: die Umgebungsvariable
|
||||
* the `PATH` environment variable: die `PATH`-Umgebungsvariable
|
||||
* the `PATH`: der `PATH`
|
||||
* the `requirements.txt`: die `requirements.txt`
|
||||
* the API Router: der API-Router
|
||||
* the Authorization-Header: der Autorisierungsheader
|
||||
* the `Authorization`-Header: der `Authorization`-Header
|
||||
* the background task: der Hintergrundtask
|
||||
* the button: der Button
|
||||
* the cloud provider: der Cloudanbieter
|
||||
* the CLI: Das CLI
|
||||
* the coverage: Die Testabdeckung
|
||||
* the command line interface: Das Kommandozeileninterface
|
||||
* the default value: der Defaultwert
|
||||
* the default value: NOT der Standardwert
|
||||
* the default declaration: die Default-Deklaration
|
||||
* the deployment: das Deployment
|
||||
* the dict: das Dict
|
||||
* the dictionary: das Dictionary
|
||||
* the enumeration: die Enumeration
|
||||
* the enum: das Enum
|
||||
* the engine: die Engine
|
||||
* the error response: die Error-Response
|
||||
* the event: das Event
|
||||
* the exception: die Exception
|
||||
* the exception handler: der Exceptionhandler
|
||||
* the form model: das Formularmodell
|
||||
* the form body: der Formularbody
|
||||
* the header: der Header
|
||||
* the headers (plural): die Header
|
||||
* in headers (plural): in Headern
|
||||
* the forwarded header: der Forwarded-Header
|
||||
* the lifespan event: das Lifespan-Event
|
||||
* the lock: der Lock
|
||||
* the locking: das Locking
|
||||
* the mobile application: die Mobile-Anwendung
|
||||
* the model object: das Modellobjekt
|
||||
* the mounting: das Mounten
|
||||
* mounted: gemountet
|
||||
* the origin: das Origin
|
||||
* the override: Die Überschreibung
|
||||
* the parameter: der Parameter
|
||||
* the parameters (plural): die Parameter
|
||||
* the function parameter: der Funktionsparameter
|
||||
* the default parameter: der Defaultparameter
|
||||
* the body parameter: der Body-Parameter
|
||||
* the request body parameter: der Requestbody-Parameter
|
||||
* the path parameter: der Pfad-Parameter
|
||||
* the query parameter: der Query-Parameter
|
||||
* the cookie parameter: der Cookie-Parameter
|
||||
* the header parameter: der Header-Parameter
|
||||
* the form parameter: der Formular-Parameter
|
||||
* the payload: die Payload
|
||||
* the performance: NOT die Performance
|
||||
* the query: die Query
|
||||
* the recap: die Zusammenfassung
|
||||
* the request (what the client sends to the server): der Request
|
||||
* the request body: der Requestbody
|
||||
* the request bodies (plural): die Requestbodys
|
||||
* the response (what the server sends back to the client): die Response
|
||||
* the return type: der Rückgabetyp
|
||||
* the return value: der Rückgabewert
|
||||
* the startup (the event of the app): der Startup
|
||||
* the shutdown (the event of the app): der Shutdown
|
||||
* the startup event: das Startup-Event
|
||||
* the shutdown event: das Shutdown-Event
|
||||
* the startup (of the server): das Hochfahren
|
||||
* the startup (the company): das Startup
|
||||
* the SDK: das SDK
|
||||
* the tag: der Tag
|
||||
* the type annotation: die Typannotation
|
||||
* the type hint: der Typhinweis
|
||||
* the wildcard: die Wildcard
|
||||
* the worker class: die Workerklasse
|
||||
* the worker class: NOT die Arbeiterklasse
|
||||
* the worker process: der Workerprozess
|
||||
* the worker process: NOT der Arbeiterprozess
|
||||
* to commit: committen
|
||||
* to deploy (in the cloud): deployen
|
||||
* to modify: ändern
|
||||
* to serve (an application): bereitstellen
|
||||
* to serve (a response): ausliefern
|
||||
* to serve: NOT bedienen
|
||||
* to upgrade: aktualisieren
|
||||
* to wrap: wrappen
|
||||
* to wrap: NOT hüllen
|
||||
* `foo` as a `type`: `foo` vom Typ `type`
|
||||
* `foo` as a `type`: `foo`, ein `type`
|
||||
* FastAPI's X: FastAPIs X
|
||||
* Starlette's Y: Starlettes Y
|
||||
* X is case-sensitive: Groß-/Kleinschreibung ist relevant in X
|
||||
* X is case-insensitive: Groß-/Kleinschreibung ist nicht relevant in X
|
||||
* standard Python: Standard-Python
|
||||
* deprecated: deprecatet
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Other rules
|
||||
|
||||
Preserve indentation. Keep emoticons. Encode in utf-8. Use Linux line breaks (LF).
|
||||
Preserve indentation. Keep emojis. Encode in utf-8. Use Linux line breaks (LF).
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,495 +1,495 @@
|
||||
- name: full-stack-fastapi-template
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/fastapi/full-stack-fastapi-template
|
||||
stars: 39475
|
||||
stars: 40334
|
||||
owner_login: fastapi
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/fastapi
|
||||
- name: Hello-Python
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/mouredev/Hello-Python
|
||||
stars: 33090
|
||||
stars: 33628
|
||||
owner_login: mouredev
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/mouredev
|
||||
- name: serve
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/jina-ai/serve
|
||||
stars: 21798
|
||||
stars: 21817
|
||||
owner_login: jina-ai
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/jina-ai
|
||||
- name: HivisionIDPhotos
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Zeyi-Lin/HivisionIDPhotos
|
||||
stars: 20258
|
||||
stars: 20409
|
||||
owner_login: Zeyi-Lin
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Zeyi-Lin
|
||||
- name: sqlmodel
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/fastapi/sqlmodel
|
||||
stars: 17212
|
||||
stars: 17415
|
||||
owner_login: fastapi
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/fastapi
|
||||
- name: Douyin_TikTok_Download_API
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Evil0ctal/Douyin_TikTok_Download_API
|
||||
stars: 15145
|
||||
owner_login: Evil0ctal
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Evil0ctal
|
||||
- name: fastapi-best-practices
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/zhanymkanov/fastapi-best-practices
|
||||
stars: 14644
|
||||
stars: 15776
|
||||
owner_login: zhanymkanov
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/zhanymkanov
|
||||
- name: Douyin_TikTok_Download_API
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Evil0ctal/Douyin_TikTok_Download_API
|
||||
stars: 15588
|
||||
owner_login: Evil0ctal
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Evil0ctal
|
||||
- name: machine-learning-zoomcamp
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/DataTalksClub/machine-learning-zoomcamp
|
||||
stars: 12320
|
||||
stars: 12447
|
||||
owner_login: DataTalksClub
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/DataTalksClub
|
||||
- name: fastapi_mcp
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/tadata-org/fastapi_mcp
|
||||
stars: 11174
|
||||
owner_login: tadata-org
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/tadata-org
|
||||
- name: SurfSense
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/MODSetter/SurfSense
|
||||
stars: 10858
|
||||
stars: 12128
|
||||
owner_login: MODSetter
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/MODSetter
|
||||
- name: fastapi_mcp
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/tadata-org/fastapi_mcp
|
||||
stars: 11326
|
||||
owner_login: tadata-org
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/tadata-org
|
||||
- name: awesome-fastapi
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/mjhea0/awesome-fastapi
|
||||
stars: 10758
|
||||
stars: 10901
|
||||
owner_login: mjhea0
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/mjhea0
|
||||
- name: XHS-Downloader
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/JoeanAmier/XHS-Downloader
|
||||
stars: 9313
|
||||
stars: 9584
|
||||
owner_login: JoeanAmier
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/JoeanAmier
|
||||
- name: FastUI
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/pydantic/FastUI
|
||||
stars: 8915
|
||||
owner_login: pydantic
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/pydantic
|
||||
- name: polar
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/polarsource/polar
|
||||
stars: 8339
|
||||
stars: 8951
|
||||
owner_login: polarsource
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/polarsource
|
||||
- name: FastUI
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/pydantic/FastUI
|
||||
stars: 8934
|
||||
owner_login: pydantic
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/pydantic
|
||||
- name: FileCodeBox
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/vastsa/FileCodeBox
|
||||
stars: 7721
|
||||
stars: 7934
|
||||
owner_login: vastsa
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/vastsa
|
||||
- name: nonebot2
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/nonebot/nonebot2
|
||||
stars: 7170
|
||||
stars: 7248
|
||||
owner_login: nonebot
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/nonebot
|
||||
- name: hatchet
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/hatchet-dev/hatchet
|
||||
stars: 6253
|
||||
stars: 6392
|
||||
owner_login: hatchet-dev
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/hatchet-dev
|
||||
- name: fastapi-users
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/fastapi-users/fastapi-users
|
||||
stars: 5849
|
||||
stars: 5899
|
||||
owner_login: fastapi-users
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/fastapi-users
|
||||
- name: serge
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/serge-chat/serge
|
||||
stars: 5756
|
||||
stars: 5754
|
||||
owner_login: serge-chat
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/serge-chat
|
||||
- name: strawberry
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/strawberry-graphql/strawberry
|
||||
stars: 4569
|
||||
stars: 4577
|
||||
owner_login: strawberry-graphql
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/strawberry-graphql
|
||||
- name: chatgpt-web-share
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/chatpire/chatgpt-web-share
|
||||
stars: 4294
|
||||
owner_login: chatpire
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/chatpire
|
||||
- name: poem
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/poem-web/poem
|
||||
stars: 4276
|
||||
stars: 4303
|
||||
owner_login: poem-web
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/poem-web
|
||||
- name: chatgpt-web-share
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/chatpire/chatgpt-web-share
|
||||
stars: 4287
|
||||
owner_login: chatpire
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/chatpire
|
||||
- name: dynaconf
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/dynaconf/dynaconf
|
||||
stars: 4202
|
||||
stars: 4221
|
||||
owner_login: dynaconf
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/dynaconf
|
||||
- name: atrilabs-engine
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Atri-Labs/atrilabs-engine
|
||||
stars: 4093
|
||||
owner_login: Atri-Labs
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Atri-Labs
|
||||
- name: Kokoro-FastAPI
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/remsky/Kokoro-FastAPI
|
||||
stars: 4019
|
||||
stars: 4181
|
||||
owner_login: remsky
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/remsky
|
||||
- name: atrilabs-engine
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Atri-Labs/atrilabs-engine
|
||||
stars: 4090
|
||||
owner_login: Atri-Labs
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Atri-Labs
|
||||
- name: devpush
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/hunvreus/devpush
|
||||
stars: 4037
|
||||
owner_login: hunvreus
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/hunvreus
|
||||
- name: logfire
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/pydantic/logfire
|
||||
stars: 3805
|
||||
stars: 3896
|
||||
owner_login: pydantic
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/pydantic
|
||||
- name: LitServe
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Lightning-AI/LitServe
|
||||
stars: 3719
|
||||
stars: 3756
|
||||
owner_login: Lightning-AI
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Lightning-AI
|
||||
- name: fastapi-admin
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/fastapi-admin/fastapi-admin
|
||||
stars: 3632
|
||||
owner_login: fastapi-admin
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/fastapi-admin
|
||||
- name: datamodel-code-generator
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/koxudaxi/datamodel-code-generator
|
||||
stars: 3609
|
||||
owner_login: koxudaxi
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/koxudaxi
|
||||
- name: huma
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/danielgtaylor/huma
|
||||
stars: 3603
|
||||
stars: 3702
|
||||
owner_login: danielgtaylor
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/danielgtaylor
|
||||
- name: Yuxi-Know
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/xerrors/Yuxi-Know
|
||||
stars: 3680
|
||||
owner_login: xerrors
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/xerrors
|
||||
- name: datamodel-code-generator
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/koxudaxi/datamodel-code-generator
|
||||
stars: 3675
|
||||
owner_login: koxudaxi
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/koxudaxi
|
||||
- name: fastapi-admin
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/fastapi-admin/fastapi-admin
|
||||
stars: 3659
|
||||
owner_login: fastapi-admin
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/fastapi-admin
|
||||
- name: farfalle
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/rashadphz/farfalle
|
||||
stars: 3490
|
||||
stars: 3497
|
||||
owner_login: rashadphz
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/rashadphz
|
||||
- name: tracecat
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/TracecatHQ/tracecat
|
||||
stars: 3379
|
||||
stars: 3421
|
||||
owner_login: TracecatHQ
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/TracecatHQ
|
||||
- name: opyrator
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/ml-tooling/opyrator
|
||||
stars: 3135
|
||||
stars: 3136
|
||||
owner_login: ml-tooling
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/ml-tooling
|
||||
- name: docarray
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/docarray/docarray
|
||||
stars: 3114
|
||||
stars: 3111
|
||||
owner_login: docarray
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/docarray
|
||||
- name: devpush
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/hunvreus/devpush
|
||||
stars: 3097
|
||||
owner_login: hunvreus
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/hunvreus
|
||||
- name: fastapi-realworld-example-app
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/nsidnev/fastapi-realworld-example-app
|
||||
stars: 3050
|
||||
stars: 3051
|
||||
owner_login: nsidnev
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/nsidnev
|
||||
- name: uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi-docker
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi-docker
|
||||
stars: 2911
|
||||
owner_login: tiangolo
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/tiangolo
|
||||
- name: mcp-context-forge
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/IBM/mcp-context-forge
|
||||
stars: 2899
|
||||
stars: 3034
|
||||
owner_login: IBM
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/IBM
|
||||
- name: best-of-web-python
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/ml-tooling/best-of-web-python
|
||||
stars: 2648
|
||||
owner_login: ml-tooling
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/ml-tooling
|
||||
- name: uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi-docker
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/tiangolo/uvicorn-gunicorn-fastapi-docker
|
||||
stars: 2904
|
||||
owner_login: tiangolo
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/tiangolo
|
||||
- name: FastAPI-template
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/s3rius/FastAPI-template
|
||||
stars: 2637
|
||||
stars: 2680
|
||||
owner_login: s3rius
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/s3rius
|
||||
- name: best-of-web-python
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/ml-tooling/best-of-web-python
|
||||
stars: 2662
|
||||
owner_login: ml-tooling
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/ml-tooling
|
||||
- name: YC-Killer
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/sahibzada-allahyar/YC-Killer
|
||||
stars: 2599
|
||||
stars: 2614
|
||||
owner_login: sahibzada-allahyar
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/sahibzada-allahyar
|
||||
- name: fastapi-react
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Buuntu/fastapi-react
|
||||
stars: 2569
|
||||
owner_login: Buuntu
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Buuntu
|
||||
- name: Yuxi-Know
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/xerrors/Yuxi-Know
|
||||
stars: 2563
|
||||
owner_login: xerrors
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/xerrors
|
||||
- name: sqladmin
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/aminalaee/sqladmin
|
||||
stars: 2558
|
||||
stars: 2587
|
||||
owner_login: aminalaee
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/aminalaee
|
||||
- name: fastapi-react
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Buuntu/fastapi-react
|
||||
stars: 2566
|
||||
owner_login: Buuntu
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Buuntu
|
||||
- name: RasaGPT
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/paulpierre/RasaGPT
|
||||
stars: 2451
|
||||
stars: 2456
|
||||
owner_login: paulpierre
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/paulpierre
|
||||
- name: supabase-py
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/supabase/supabase-py
|
||||
stars: 2344
|
||||
stars: 2394
|
||||
owner_login: supabase
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/supabase
|
||||
- name: nextpy
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/dot-agent/nextpy
|
||||
stars: 2335
|
||||
stars: 2338
|
||||
owner_login: dot-agent
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/dot-agent
|
||||
- name: fastapi-utils
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/fastapiutils/fastapi-utils
|
||||
stars: 2291
|
||||
stars: 2289
|
||||
owner_login: fastapiutils
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/fastapiutils
|
||||
- name: 30-Days-of-Python
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/codingforentrepreneurs/30-Days-of-Python
|
||||
stars: 2220
|
||||
owner_login: codingforentrepreneurs
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/codingforentrepreneurs
|
||||
- name: langserve
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/langchain-ai/langserve
|
||||
stars: 2215
|
||||
stars: 2234
|
||||
owner_login: langchain-ai
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/langchain-ai
|
||||
- name: 30-Days-of-Python
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/codingforentrepreneurs/30-Days-of-Python
|
||||
stars: 2232
|
||||
owner_login: codingforentrepreneurs
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/codingforentrepreneurs
|
||||
- name: solara
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/widgetti/solara
|
||||
stars: 2122
|
||||
stars: 2141
|
||||
owner_login: widgetti
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/widgetti
|
||||
- name: mangum
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Kludex/mangum
|
||||
stars: 2029
|
||||
stars: 2046
|
||||
owner_login: Kludex
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Kludex
|
||||
- name: fastapi_best_architecture
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/fastapi-practices/fastapi_best_architecture
|
||||
stars: 1963
|
||||
owner_login: fastapi-practices
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/fastapi-practices
|
||||
- name: NoteDiscovery
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/gamosoft/NoteDiscovery
|
||||
stars: 1943
|
||||
owner_login: gamosoft
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/gamosoft
|
||||
- name: agentkit
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/BCG-X-Official/agentkit
|
||||
stars: 1912
|
||||
stars: 1936
|
||||
owner_login: BCG-X-Official
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/BCG-X-Official
|
||||
- name: vue-fastapi-admin
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/mizhexiaoxiao/vue-fastapi-admin
|
||||
stars: 1909
|
||||
owner_login: mizhexiaoxiao
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/mizhexiaoxiao
|
||||
- name: manage-fastapi
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/ycd/manage-fastapi
|
||||
stars: 1885
|
||||
stars: 1887
|
||||
owner_login: ycd
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/ycd
|
||||
- name: openapi-python-client
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/openapi-generators/openapi-python-client
|
||||
stars: 1862
|
||||
stars: 1879
|
||||
owner_login: openapi-generators
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/openapi-generators
|
||||
- name: piccolo
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/piccolo-orm/piccolo
|
||||
stars: 1836
|
||||
owner_login: piccolo-orm
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/piccolo-orm
|
||||
- name: vue-fastapi-admin
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/mizhexiaoxiao/vue-fastapi-admin
|
||||
stars: 1831
|
||||
owner_login: mizhexiaoxiao
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/mizhexiaoxiao
|
||||
- name: python-week-2022
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/rochacbruno/python-week-2022
|
||||
stars: 1817
|
||||
owner_login: rochacbruno
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/rochacbruno
|
||||
- name: slowapi
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/laurentS/slowapi
|
||||
stars: 1798
|
||||
stars: 1845
|
||||
owner_login: laurentS
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/laurentS
|
||||
- name: piccolo
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/piccolo-orm/piccolo
|
||||
stars: 1843
|
||||
owner_login: piccolo-orm
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/piccolo-orm
|
||||
- name: python-week-2022
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/rochacbruno/python-week-2022
|
||||
stars: 1813
|
||||
owner_login: rochacbruno
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/rochacbruno
|
||||
- name: fastapi-cache
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/long2ice/fastapi-cache
|
||||
stars: 1789
|
||||
stars: 1805
|
||||
owner_login: long2ice
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/long2ice
|
||||
- name: ormar
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/collerek/ormar
|
||||
stars: 1783
|
||||
stars: 1785
|
||||
owner_login: collerek
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/collerek
|
||||
- name: termpair
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/cs01/termpair
|
||||
stars: 1716
|
||||
owner_login: cs01
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/cs01
|
||||
- name: FastAPI-boilerplate
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/benavlabs/FastAPI-boilerplate
|
||||
stars: 1660
|
||||
owner_login: benavlabs
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/benavlabs
|
||||
- name: fastapi-langgraph-agent-production-ready-template
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/wassim249/fastapi-langgraph-agent-production-ready-template
|
||||
stars: 1638
|
||||
stars: 1780
|
||||
owner_login: wassim249
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/wassim249
|
||||
- name: langchain-serve
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/jina-ai/langchain-serve
|
||||
stars: 1635
|
||||
owner_login: jina-ai
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/jina-ai
|
||||
- name: awesome-fastapi-projects
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Kludex/awesome-fastapi-projects
|
||||
stars: 1589
|
||||
owner_login: Kludex
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Kludex
|
||||
- name: fastapi-pagination
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/uriyyo/fastapi-pagination
|
||||
stars: 1585
|
||||
owner_login: uriyyo
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/uriyyo
|
||||
- name: coronavirus-tracker-api
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/ExpDev07/coronavirus-tracker-api
|
||||
stars: 1574
|
||||
owner_login: ExpDev07
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/ExpDev07
|
||||
- name: FastAPI-boilerplate
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/benavlabs/FastAPI-boilerplate
|
||||
stars: 1734
|
||||
owner_login: benavlabs
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/benavlabs
|
||||
- name: termpair
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/cs01/termpair
|
||||
stars: 1724
|
||||
owner_login: cs01
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/cs01
|
||||
- name: fastapi-crudrouter
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/awtkns/fastapi-crudrouter
|
||||
stars: 1559
|
||||
stars: 1671
|
||||
owner_login: awtkns
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/awtkns
|
||||
- name: langchain-serve
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/jina-ai/langchain-serve
|
||||
stars: 1633
|
||||
owner_login: jina-ai
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/jina-ai
|
||||
- name: fastapi-pagination
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/uriyyo/fastapi-pagination
|
||||
stars: 1588
|
||||
owner_login: uriyyo
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/uriyyo
|
||||
- name: awesome-fastapi-projects
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Kludex/awesome-fastapi-projects
|
||||
stars: 1583
|
||||
owner_login: Kludex
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Kludex
|
||||
- name: coronavirus-tracker-api
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/ExpDev07/coronavirus-tracker-api
|
||||
stars: 1571
|
||||
owner_login: ExpDev07
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/ExpDev07
|
||||
- name: bracket
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/evroon/bracket
|
||||
stars: 1489
|
||||
stars: 1549
|
||||
owner_login: evroon
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/evroon
|
||||
- name: fastapi-amis-admin
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/amisadmin/fastapi-amis-admin
|
||||
stars: 1475
|
||||
stars: 1491
|
||||
owner_login: amisadmin
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/amisadmin
|
||||
- name: fastapi-boilerplate
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/teamhide/fastapi-boilerplate
|
||||
stars: 1436
|
||||
stars: 1452
|
||||
owner_login: teamhide
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/teamhide
|
||||
- name: awesome-python-resources
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/DjangoEx/awesome-python-resources
|
||||
stars: 1426
|
||||
owner_login: DjangoEx
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/DjangoEx
|
||||
- name: fastcrud
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/benavlabs/fastcrud
|
||||
stars: 1414
|
||||
stars: 1452
|
||||
owner_login: benavlabs
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/benavlabs
|
||||
- name: awesome-python-resources
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/DjangoEx/awesome-python-resources
|
||||
stars: 1430
|
||||
owner_login: DjangoEx
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/DjangoEx
|
||||
- name: prometheus-fastapi-instrumentator
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/trallnag/prometheus-fastapi-instrumentator
|
||||
stars: 1388
|
||||
stars: 1399
|
||||
owner_login: trallnag
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/trallnag
|
||||
- name: fastapi_best_architecture
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/fastapi-practices/fastapi_best_architecture
|
||||
stars: 1378
|
||||
owner_login: fastapi-practices
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/fastapi-practices
|
||||
- name: fastapi-code-generator
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/koxudaxi/fastapi-code-generator
|
||||
stars: 1375
|
||||
stars: 1371
|
||||
owner_login: koxudaxi
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/koxudaxi
|
||||
- name: fastapi-tutorial
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/liaogx/fastapi-tutorial
|
||||
stars: 1346
|
||||
owner_login: liaogx
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/liaogx
|
||||
- name: budgetml
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/ebhy/budgetml
|
||||
stars: 1345
|
||||
owner_login: ebhy
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/ebhy
|
||||
- name: fastapi-tutorial
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/liaogx/fastapi-tutorial
|
||||
stars: 1327
|
||||
owner_login: liaogx
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/liaogx
|
||||
- name: fastapi-alembic-sqlmodel-async
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/jonra1993/fastapi-alembic-sqlmodel-async
|
||||
stars: 1259
|
||||
owner_login: jonra1993
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/jonra1993
|
||||
- name: fastapi-scaff
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/atpuxiner/fastapi-scaff
|
||||
stars: 1255
|
||||
stars: 1331
|
||||
owner_login: atpuxiner
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/atpuxiner
|
||||
- name: bedrock-chat
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/aws-samples/bedrock-chat
|
||||
stars: 1254
|
||||
owner_login: aws-samples
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/aws-samples
|
||||
- name: bolt-python
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/slackapi/bolt-python
|
||||
stars: 1253
|
||||
stars: 1266
|
||||
owner_login: slackapi
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/slackapi
|
||||
- name: bedrock-chat
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/aws-samples/bedrock-chat
|
||||
stars: 1266
|
||||
owner_login: aws-samples
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/aws-samples
|
||||
- name: fastapi-alembic-sqlmodel-async
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/jonra1993/fastapi-alembic-sqlmodel-async
|
||||
stars: 1260
|
||||
owner_login: jonra1993
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/jonra1993
|
||||
- name: fastapi_production_template
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/zhanymkanov/fastapi_production_template
|
||||
stars: 1217
|
||||
stars: 1222
|
||||
owner_login: zhanymkanov
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/zhanymkanov
|
||||
- name: langchain-extract
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain-extract
|
||||
stars: 1176
|
||||
stars: 1179
|
||||
owner_login: langchain-ai
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/langchain-ai
|
||||
- name: restish
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/rest-sh/restish
|
||||
stars: 1140
|
||||
stars: 1152
|
||||
owner_login: rest-sh
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/rest-sh
|
||||
- name: odmantic
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/art049/odmantic
|
||||
stars: 1138
|
||||
stars: 1143
|
||||
owner_login: art049
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/art049
|
||||
- name: authx
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/yezz123/authx
|
||||
stars: 1119
|
||||
stars: 1128
|
||||
owner_login: yezz123
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/yezz123
|
||||
- name: NoteDiscovery
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/gamosoft/NoteDiscovery
|
||||
stars: 1107
|
||||
owner_login: gamosoft
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/gamosoft
|
||||
- name: flock
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Onelevenvy/flock
|
||||
stars: 1055
|
||||
owner_login: Onelevenvy
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Onelevenvy
|
||||
- name: fastapi-observability
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/blueswen/fastapi-observability
|
||||
stars: 1038
|
||||
owner_login: blueswen
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/blueswen
|
||||
- name: SAG
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Zleap-AI/SAG
|
||||
stars: 1104
|
||||
owner_login: Zleap-AI
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Zleap-AI
|
||||
- name: aktools
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/akfamily/aktools
|
||||
stars: 1027
|
||||
stars: 1072
|
||||
owner_login: akfamily
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/akfamily
|
||||
- name: RuoYi-Vue3-FastAPI
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/insistence/RuoYi-Vue3-FastAPI
|
||||
stars: 1016
|
||||
stars: 1063
|
||||
owner_login: insistence
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/insistence
|
||||
- name: autollm
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/viddexa/autollm
|
||||
stars: 1002
|
||||
owner_login: viddexa
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/viddexa
|
||||
- name: titiler
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/developmentseed/titiler
|
||||
stars: 999
|
||||
owner_login: developmentseed
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/developmentseed
|
||||
- name: lanarky
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/ajndkr/lanarky
|
||||
stars: 994
|
||||
owner_login: ajndkr
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/ajndkr
|
||||
- name: every-pdf
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/DDULDDUCK/every-pdf
|
||||
stars: 985
|
||||
owner_login: DDULDDUCK
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/DDULDDUCK
|
||||
- name: flock
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/Onelevenvy/flock
|
||||
stars: 1059
|
||||
owner_login: Onelevenvy
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/Onelevenvy
|
||||
- name: fastapi-observability
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/blueswen/fastapi-observability
|
||||
stars: 1046
|
||||
owner_login: blueswen
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/blueswen
|
||||
- name: enterprise-deep-research
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/SalesforceAIResearch/enterprise-deep-research
|
||||
stars: 973
|
||||
stars: 1019
|
||||
owner_login: SalesforceAIResearch
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/SalesforceAIResearch
|
||||
- name: fastapi-mail
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/sabuhish/fastapi-mail
|
||||
stars: 964
|
||||
owner_login: sabuhish
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/sabuhish
|
||||
- name: titiler
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/developmentseed/titiler
|
||||
stars: 1016
|
||||
owner_login: developmentseed
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/developmentseed
|
||||
- name: every-pdf
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/DDULDDUCK/every-pdf
|
||||
stars: 1004
|
||||
owner_login: DDULDDUCK
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/DDULDDUCK
|
||||
- name: autollm
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/viddexa/autollm
|
||||
stars: 1003
|
||||
owner_login: viddexa
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/viddexa
|
||||
- name: lanarky
|
||||
html_url: https://github.com/ajndkr/lanarky
|
||||
stars: 996
|
||||
owner_login: ajndkr
|
||||
owner_html_url: https://github.com/ajndkr
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ Tests added here will be seen by all designers of language specific prompts.
|
||||
|
||||
Use as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
* Have a language specific prompt – `docs/{language code}/llm-prompt.md`.
|
||||
* Have a language specific prompt - `docs/{language code}/llm-prompt.md`.
|
||||
* Do a fresh translation of this document into your desired target language (see e.g. the `translate-page` command of the `translate.py`). This will create the translation under `docs/{language code}/docs/_llm-test.md`.
|
||||
* Check if things are okay in the translation.
|
||||
* If necessary, improve your language specific prompt, the general prompt, or the English document.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI is built on top of **Pydantic**, and I have been showing you how to use
|
||||
|
||||
But FastAPI also supports using <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a> the same way:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
This is still supported thanks to **Pydantic**, as it has <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">internal support for `dataclasses`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ But if you have a bunch of dataclasses laying around, this is a nice trick to us
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use `dataclasses` in the `response_model` parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
The dataclass will be automatically converted to a Pydantic dataclass.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ In some cases, you might still have to use Pydantic's version of `dataclasses`.
|
||||
|
||||
In that case, you can simply swap the standard `dataclasses` with `pydantic.dataclasses`, which is a drop-in replacement:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
1. We still import `field` from standard `dataclasses`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -153,48 +153,16 @@ And you could do this even if the data type in the request is not JSON.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, in this application we don't use FastAPI's integrated functionality to extract the JSON Schema from Pydantic models nor the automatic validation for JSON. In fact, we are declaring the request content type as YAML, not JSON:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_py39.py hl[15:20, 22] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_pv1_py39.py hl[15:20, 22] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic version 1 the method to get the JSON Schema for a model was called `Item.schema()`, in Pydantic version 2, the method is called `Item.model_json_schema()`.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Nevertheless, although we are not using the default integrated functionality, we are still using a Pydantic model to manually generate the JSON Schema for the data that we want to receive in YAML.
|
||||
|
||||
Then we use the request directly, and extract the body as `bytes`. This means that FastAPI won't even try to parse the request payload as JSON.
|
||||
|
||||
And then in our code, we parse that YAML content directly, and then we are again using the same Pydantic model to validate the YAML content:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_py39.py hl[24:31] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/path_operation_advanced_configuration/tutorial007_pv1_py39.py hl[24:31] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic version 1 the method to parse and validate an object was `Item.parse_obj()`, in Pydantic version 2, the method is called `Item.model_validate()`.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip
|
||||
|
||||
Here we reuse the same Pydantic model.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -46,12 +46,6 @@ $ pip install "fastapi[all]"
|
||||
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 it came included with the main package. Now it is distributed as this independent package so that you can choose to install it or not if you don't need that functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
### Create the `Settings` object { #create-the-settings-object }
|
||||
|
||||
Import `BaseSettings` from Pydantic and create a sub-class, very much like with a Pydantic model.
|
||||
@@ -60,24 +54,8 @@ The same way as with Pydantic models, you declare class attributes with type ann
|
||||
|
||||
You can use all the same validation features and tools you use for Pydantic models, like different data types and additional validations with `Field()`.
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/tutorial001_py39.py hl[2,5:8,11] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 you would import `BaseSettings` directly from `pydantic` instead of from `pydantic_settings`.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/tutorial001_pv1_py39.py hl[2,5:8,11] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip
|
||||
|
||||
If you want something quick to copy and paste, don't use this example, use the last one below.
|
||||
@@ -215,8 +193,6 @@ APP_NAME="ChimichangApp"
|
||||
|
||||
And then update your `config.py` with:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/app03_an_py39/config.py hl[9] *}
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip
|
||||
@@ -225,26 +201,6 @@ The `model_config` attribute is used just for Pydantic configuration. You can re
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/settings/app03_an_py39/config_pv1.py hl[9:10] *}
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip
|
||||
|
||||
The `Config` class is used just for Pydantic configuration. You can read more at <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/1.10/usage/model_config/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic Model Config</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic version 1 the configuration was done in an internal class `Config`, in Pydantic version 2 it's done in an attribute `model_config`. This attribute takes a `dict`, and to get autocompletion and inline errors you can import and use `SettingsConfigDict` to define that `dict`.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Here we define the config `env_file` inside of your Pydantic `Settings` class, and set the value to the filename with the dotenv file we want to use.
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating the `Settings` only once with `lru_cache` { #creating-the-settings-only-once-with-lru-cache }
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Depending on your use case, you might prefer to use a different library, but if
|
||||
|
||||
Here's a small preview of how you could integrate Strawberry with FastAPI:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql_/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about Strawberry in the <a href="https://strawberry.rocks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Strawberry documentation</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -2,21 +2,23 @@
|
||||
|
||||
If you have an old FastAPI app, you might be using Pydantic version 1.
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI has had support for either Pydantic v1 or v2 since version 0.100.0.
|
||||
FastAPI version 0.100.0 had support for either Pydantic v1 or v2. It would use whichever you had installed.
|
||||
|
||||
If you had installed Pydantic v2, it would use it. If instead you had Pydantic v1, it would use that.
|
||||
FastAPI version 0.119.0 introduced partial support for Pydantic v1 from inside of Pydantic v2 (as `pydantic.v1`), to facilitate the migration to v2.
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic v1 is now deprecated and support for it will be removed in the next versions of FastAPI, you should **migrate to Pydantic v2**. This way you will get the latest features, improvements, and fixes.
|
||||
FastAPI 0.126.0 dropped support for Pydantic v1, while still supporting `pydantic.v1` for a little while.
|
||||
|
||||
/// warning
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the Pydantic team stopped support for Pydantic v1 for the latest versions of Python, starting with **Python 3.14**.
|
||||
The Pydantic team stopped support for Pydantic v1 for the latest versions of Python, starting with **Python 3.14**.
|
||||
|
||||
This includes `pydantic.v1`, which is no longer supported in Python 3.14 and above.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use the latest features of Python, you will need to make sure you use Pydantic v2.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
If you have an old FastAPI app with Pydantic v1, here I'll show you how to migrate it to Pydantic v2, and the **new features in FastAPI 0.119.0** to help you with a gradual migration.
|
||||
If you have an old FastAPI app with Pydantic v1, here I'll show you how to migrate it to Pydantic v2, and the **features in FastAPI 0.119.0** to help you with a gradual migration.
|
||||
|
||||
## Official Guide { #official-guide }
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -44,7 +46,7 @@ After this, you can run the tests and check if everything works. If it does, you
|
||||
|
||||
## Pydantic v1 in v2 { #pydantic-v1-in-v2 }
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic v2 includes everything from Pydantic v1 as a submodule `pydantic.v1`.
|
||||
Pydantic v2 includes everything from Pydantic v1 as a submodule `pydantic.v1`. But this is no longer supported in versions above Python 3.13.
|
||||
|
||||
This means that you can install the latest version of Pydantic v2 and import and use the old Pydantic v1 components from this submodule, as if you had the old Pydantic v1 installed.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
# Separate OpenAPI Schemas for Input and Output or Not { #separate-openapi-schemas-for-input-and-output-or-not }
|
||||
|
||||
When using **Pydantic v2**, the generated OpenAPI is a bit more exact and **correct** than before. 😎
|
||||
Since **Pydantic v2** was released, the generated OpenAPI is a bit more exact and **correct** than before. 😎
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, in some cases, it will even have **two JSON Schemas** in OpenAPI for the same Pydantic model, for input and output, depending on if they have **default values**.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -100,5 +100,3 @@ And now there will be one single schema for input and output for the model, only
|
||||
<div class="screenshot">
|
||||
<img src="/img/tutorial/separate-openapi-schemas/image05.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
This is the same behavior as in Pydantic v1. 🤓
|
||||
|
||||
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/fastapi-documentary.jpg
Normal file
BIN
docs/en/docs/img/fastapi-documentary.jpg
Normal file
Binary file not shown.
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 187 KiB |
@@ -117,6 +117,12 @@ The key features are:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## FastAPI mini documentary { #fastapi-mini-documentary }
|
||||
|
||||
There's a <a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" class="external-link" target="_blank">FastAPI mini documentary</a> released at the end of 2025, you can watch it online:
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mpR8ngthqiE" target="_blank"><img src="https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/img/fastapi-documentary.jpg" alt="FastAPI Mini Documentary"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## **Typer**, the FastAPI of CLIs { #typer-the-fastapi-of-clis }
|
||||
|
||||
<a href="https://typer.tiangolo.com" target="_blank"><img src="https://typer.tiangolo.com/img/logo-margin/logo-margin-vector.svg" style="width: 20%;"></a>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -7,6 +7,91 @@ hide:
|
||||
|
||||
## Latest Changes
|
||||
|
||||
### Translations
|
||||
|
||||
* 🔧 Add LLM prompt file for Turkish, generated from the existing translations. PR [#14547](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14547) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 🔧 Add LLM prompt file for Traditional Chinese, generated from the existing translations. PR [#14550](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14550) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 🔧 Add LLM prompt file for Simplified Chinese, generated from the existing translations. PR [#14549](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14549) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
### Internal
|
||||
|
||||
* 🌐 Update translation prompts. PR [#14619](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14619) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 🔨 Update LLM translation script to guide reviewers to change the prompt. PR [#14614](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14614) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 👷 Do not run translations on cron while finishing updating existing languages. PR [#14613](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14613) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 🔥 Remove test variants for Pydantic v1 in test_request_params. PR [#14612](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14612) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 🔥 Remove Pydantic v1 specific test variants. PR [#14611](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14611) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.128.0
|
||||
|
||||
### Breaking Changes
|
||||
|
||||
* ➖ Drop support for `pydantic.v1`. PR [#14609](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14609) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
### Internal
|
||||
|
||||
* ✅ Run performance tests only on Pydantic v2. PR [#14608](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14608) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.127.1
|
||||
|
||||
### Refactors
|
||||
|
||||
* 🔊 Add a custom `FastAPIDeprecationWarning`. PR [#14605](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14605) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
### Docs
|
||||
|
||||
* 📝 Add documentary to website. PR [#14600](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14600) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
### Translations
|
||||
|
||||
* 🌐 Update translations for de (update-outdated). PR [#14602](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14602) by [@nilslindemann](https://github.com/nilslindemann).
|
||||
* 🌐 Update translations for de (update-outdated). PR [#14581](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14581) by [@nilslindemann](https://github.com/nilslindemann).
|
||||
|
||||
### Internal
|
||||
|
||||
* 🔧 Update pre-commit to use local Ruff instead of hook. PR [#14604](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14604) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* ✅ Add missing tests for code examples. PR [#14569](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14569) by [@YuriiMotov](https://github.com/YuriiMotov).
|
||||
* 👷 Remove `lint` job from `test` CI workflow. PR [#14593](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14593) by [@YuriiMotov](https://github.com/YuriiMotov).
|
||||
* 👷 Update secrets check. PR [#14592](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14592) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 👷 Run CodSpeed tests in parallel to other tests to speed up CI. PR [#14586](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14586) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 🔨 Update scripts and pre-commit to autofix files. PR [#14585](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14585) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.127.0
|
||||
|
||||
### Breaking Changes
|
||||
|
||||
* 🔊 Add deprecation warnings when using `pydantic.v1`. PR [#14583](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14583) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
### Translations
|
||||
|
||||
* 🔧 Add LLM prompt file for Korean, generated from the existing translations. PR [#14546](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14546) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 🔧 Add LLM prompt file for Japanese, generated from the existing translations. PR [#14545](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14545) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
### Internal
|
||||
|
||||
* ⬆️ Upgrade OpenAI model for translations to gpt-5.2. PR [#14579](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14579) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.126.0
|
||||
|
||||
### Upgrades
|
||||
|
||||
* ➖ Drop support for Pydantic v1, keeping short temporary support for Pydantic v2's `pydantic.v1`. PR [#14575](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14575) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* The minimum version of Pydantic installed is now `pydantic >=2.7.0`.
|
||||
* The `standard` dependencies now include `pydantic-settings >=2.0.0` and `pydantic-extra-types >=2.0.0`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Docs
|
||||
|
||||
* 📝 Fix duplicated variable in `docs_src/python_types/tutorial005_py39.py`. PR [#14565](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14565) by [@paras-verma7454](https://github.com/paras-verma7454).
|
||||
|
||||
### Translations
|
||||
|
||||
* 🔧 Add LLM prompt file for Ukrainian, generated from the existing translations. PR [#14548](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14548) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
### Internal
|
||||
|
||||
* 🔧 Tweak pre-commit to allow committing release-notes. PR [#14577](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14577) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* ⬆️ Use prek as a pre-commit alternative. PR [#14572](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14572) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
* 👷 Add performance tests with CodSpeed. PR [#14558](https://github.com/fastapi/fastapi/pull/14558) by [@tiangolo](https://github.com/tiangolo).
|
||||
|
||||
## 0.125.0
|
||||
|
||||
### Breaking Changes
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -50,14 +50,6 @@ If you want to receive partial updates, it's very useful to use the parameter `e
|
||||
|
||||
Like `item.model_dump(exclude_unset=True)`.
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 the method was called `.dict()`, it was deprecated (but still supported) in Pydantic v2, and renamed to `.model_dump()`.
|
||||
|
||||
The examples here use `.dict()` for compatibility with Pydantic v1, but you should use `.model_dump()` instead if you can use Pydantic v2.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
That would generate a `dict` with only the data that was set when creating the `item` model, excluding default values.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can use this to generate a `dict` with only the data that was set (sent in the request), omitting default values:
|
||||
@@ -68,14 +60,6 @@ Then you can use this to generate a `dict` with only the data that was set (sent
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can create a copy of the existing model using `.model_copy()`, and pass the `update` parameter with a `dict` containing the data to update.
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 the method was called `.copy()`, it was deprecated (but still supported) in Pydantic v2, and renamed to `.model_copy()`.
|
||||
|
||||
The examples here use `.copy()` for compatibility with Pydantic v1, but you should use `.model_copy()` instead if you can use Pydantic v2.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
Like `stored_item_model.model_copy(update=update_data)`:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/body_updates/tutorial002_py310.py hl[33] *}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -128,14 +128,6 @@ Inside of the function, you can access all the attributes of the model object di
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/body/tutorial002_py310.py *}
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 the method was called `.dict()`, it was deprecated (but still supported) in Pydantic v2, and renamed to `.model_dump()`.
|
||||
|
||||
The examples here use `.dict()` for compatibility with Pydantic v1, but you should use `.model_dump()` instead if you can use Pydantic v2.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
## Request body + path parameters { #request-body-path-parameters }
|
||||
|
||||
You can declare path parameters and request body at the same time.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,22 +22,13 @@ Here's a general idea of how the models could look like with their password fiel
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial001_py310.py hl[7,9,14,20,22,27:28,31:33,38:39] *}
|
||||
|
||||
### About `**user_in.model_dump()` { #about-user-in-model-dump }
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 the method was called `.dict()`, it was deprecated (but still supported) in Pydantic v2, and renamed to `.model_dump()`.
|
||||
|
||||
The examples here use `.dict()` for compatibility with Pydantic v1, but you should use `.model_dump()` instead if you can use Pydantic v2.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
### About `**user_in.dict()` { #about-user-in-dict }
|
||||
|
||||
#### Pydantic's `.dict()` { #pydantics-dict }
|
||||
#### Pydantic's `.model_dump()` { #pydantics-model-dump }
|
||||
|
||||
`user_in` is a Pydantic model of class `UserIn`.
|
||||
|
||||
Pydantic models have a `.dict()` method that returns a `dict` with the model's data.
|
||||
Pydantic models have a `.model_dump()` method that returns a `dict` with the model's data.
|
||||
|
||||
So, if we create a Pydantic object `user_in` like:
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +39,7 @@ user_in = UserIn(username="john", password="secret", email="john.doe@example.com
|
||||
and then we call:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.dict()
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.model_dump()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
we now have a `dict` with the data in the variable `user_dict` (it's a `dict` instead of a Pydantic model object).
|
||||
@@ -104,20 +95,20 @@ UserInDB(
|
||||
|
||||
#### A Pydantic model from the contents of another { #a-pydantic-model-from-the-contents-of-another }
|
||||
|
||||
As in the example above we got `user_dict` from `user_in.dict()`, this code:
|
||||
As in the example above we got `user_dict` from `user_in.model_dump()`, this code:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.dict()
|
||||
user_dict = user_in.model_dump()
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_dict)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
would be equivalent to:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.dict())
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.model_dump())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...because `user_in.dict()` is a `dict`, and then we make Python "unpack" it by passing it to `UserInDB` prefixed with `**`.
|
||||
...because `user_in.model_dump()` is a `dict`, and then we make Python "unpack" it by passing it to `UserInDB` prefixed with `**`.
|
||||
|
||||
So, we get a Pydantic model from the data in another Pydantic model.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -126,7 +117,7 @@ So, we get a Pydantic model from the data in another Pydantic model.
|
||||
And then adding the extra keyword argument `hashed_password=hashed_password`, like in:
|
||||
|
||||
```Python
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.dict(), hashed_password=hashed_password)
|
||||
UserInDB(**user_in.model_dump(), hashed_password=hashed_password)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
...ends up being like:
|
||||
@@ -181,7 +172,6 @@ When defining a <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/types/#unions
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,14:15,18:20,33] *}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### `Union` in Python 3.10 { #union-in-python-3-10 }
|
||||
|
||||
In this example we pass `Union[PlaneItem, CarItem]` as the value of the argument `response_model`.
|
||||
@@ -204,7 +194,6 @@ For that, use the standard Python `typing.List` (or just `list` in Python 3.9 an
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial004_py39.py hl[18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Response with arbitrary `dict` { #response-with-arbitrary-dict }
|
||||
|
||||
You can also declare a response using a plain arbitrary `dict`, declaring just the type of the keys and values, without using a Pydantic model.
|
||||
@@ -215,7 +204,6 @@ In this case, you can use `typing.Dict` (or just `dict` in Python 3.9 and above)
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/extra_models/tutorial005_py39.py hl[6] *}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Recap { #recap }
|
||||
|
||||
Use multiple Pydantic models and inherit freely for each case.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -206,20 +206,6 @@ If you feel lost with all these **"regular expression"** ideas, don't worry. The
|
||||
|
||||
Now you know that whenever you need them you can use them in **FastAPI**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Pydantic v1 `regex` instead of `pattern` { #pydantic-v1-regex-instead-of-pattern }
|
||||
|
||||
Before Pydantic version 2 and before FastAPI 0.100.0, the parameter was called `regex` instead of `pattern`, but it's now deprecated.
|
||||
|
||||
You could still see some code using it:
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/query_params_str_validations/tutorial004_regex_an_py310.py hl[11] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
But know that this is deprecated and it should be updated to use the new parameter `pattern`. 🤓
|
||||
|
||||
## Default values { #default-values }
|
||||
|
||||
You can, of course, use default values other than `None`.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -252,20 +252,6 @@ So, if you send a request to that *path operation* for the item with ID `foo`, t
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic v1 the method was called `.dict()`, it was deprecated (but still supported) in Pydantic v2, and renamed to `.model_dump()`.
|
||||
|
||||
The examples here use `.dict()` for compatibility with Pydantic v1, but you should use `.model_dump()` instead if you can use Pydantic v2.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
FastAPI uses Pydantic model's `.dict()` with <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/1.10/usage/exporting_models/#modeldict" class="external-link" target="_blank">its `exclude_unset` parameter</a> to achieve this.
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
/// info
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use:
|
||||
|
||||
* `response_model_exclude_defaults=True`
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -8,36 +8,14 @@ Here are several ways to do it.
|
||||
|
||||
You can declare `examples` for a Pydantic model that will be added to the generated JSON Schema.
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/schema_extra_example/tutorial001_py310.py hl[13:24] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/schema_extra_example/tutorial001_pv1_py310.py hl[13:23] *}
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
That extra info will be added as-is to the output **JSON Schema** for that model, and it will be used in the API docs.
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v2
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic version 2, you would use the attribute `model_config`, that takes a `dict` as described in <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/api/config/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic's docs: Configuration</a>.
|
||||
You can use the attribute `model_config` that takes a `dict` as described in <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/api/config/" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic's docs: Configuration</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You can set `"json_schema_extra"` with a `dict` containing any additional data you would like to show up in the generated JSON Schema, including `examples`.
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
//// tab | Pydantic v1
|
||||
|
||||
In Pydantic version 1, you would use an internal class `Config` and `schema_extra`, as described in <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/1.10/usage/schema/#schema-customization" class="external-link" target="_blank">Pydantic's docs: Schema customization</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
You can set `schema_extra` with a `dict` containing any additional data you would like to show up in the generated JSON Schema, including `examples`.
|
||||
|
||||
////
|
||||
|
||||
/// tip
|
||||
|
||||
You could use the same technique to extend the JSON Schema and add your own custom extra info.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI está construido sobre **Pydantic**, y te he estado mostrando cómo usar
|
||||
|
||||
Pero FastAPI también soporta el uso de <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a> de la misma manera:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Esto sigue siendo soportado gracias a **Pydantic**, ya que tiene <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">soporte interno para `dataclasses`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Pero si tienes un montón de dataclasses por ahí, este es un buen truco para us
|
||||
|
||||
También puedes usar `dataclasses` en el parámetro `response_model`:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
El dataclass será automáticamente convertido a un dataclass de Pydantic.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ En algunos casos, todavía podrías tener que usar la versión de `dataclasses`
|
||||
|
||||
En ese caso, simplemente puedes intercambiar los `dataclasses` estándar con `pydantic.dataclasses`, que es un reemplazo directo:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
1. Todavía importamos `field` de los `dataclasses` estándar.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Dependiendo de tu caso de uso, podrías preferir usar un paquete diferente, pero
|
||||
|
||||
Aquí tienes una pequeña vista previa de cómo podrías integrar Strawberry con FastAPI:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql_/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Puedes aprender más sobre Strawberry en la <a href="https://strawberry.rocks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">documentación de Strawberry</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
47
docs/ja/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
47
docs/ja/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
### Target language
|
||||
|
||||
Translate to Japanese (日本語).
|
||||
|
||||
Language code: ja.
|
||||
|
||||
### Grammar and tone
|
||||
|
||||
- Use polite, instructional Japanese (です/ます調).
|
||||
- Keep the tone concise and technical (match existing Japanese FastAPI docs).
|
||||
|
||||
### Headings
|
||||
|
||||
- Follow the existing Japanese style: short, descriptive headings (often noun phrases), e.g. 「チェック」.
|
||||
- Do not add a trailing period at the end of headings.
|
||||
|
||||
### Quotes
|
||||
|
||||
- Prefer Japanese corner brackets 「」 in normal prose when quoting a term.
|
||||
- Do not change quotes inside inline code, code blocks, URLs, or file paths.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ellipsis
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep ellipsis style consistent with existing Japanese docs (commonly `...`).
|
||||
- Never change `...` in code, URLs, or CLI examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preferred translations / glossary
|
||||
|
||||
Use the following preferred translations when they apply in documentation prose:
|
||||
|
||||
- request (HTTP): リクエスト
|
||||
- response (HTTP): レスポンス
|
||||
- path operation: パスオペレーション
|
||||
- path operation function: パスオペレーション関数
|
||||
|
||||
### `///` admonitions
|
||||
|
||||
1) Keep the admonition keyword in English (do not translate `note`, `tip`, etc.).
|
||||
2) If a title is present, prefer these canonical titles:
|
||||
|
||||
- `/// note | 備考`
|
||||
- `/// note | 技術詳細`
|
||||
- `/// tip | 豆知識`
|
||||
- `/// warning | 注意`
|
||||
- `/// info | 情報`
|
||||
- `/// check | 確認`
|
||||
- `/// danger | 警告`
|
||||
51
docs/ko/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
51
docs/ko/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
### Target language
|
||||
|
||||
Translate to Korean (한국어).
|
||||
|
||||
Language code: ko.
|
||||
|
||||
### Grammar and tone
|
||||
|
||||
- Use polite, instructional Korean (e.g. 합니다/하세요 style).
|
||||
- Keep the tone consistent with the existing Korean FastAPI docs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Headings
|
||||
|
||||
- Follow existing Korean heading style (short, action-oriented headings like “확인하기”).
|
||||
- Do not add trailing punctuation to headings.
|
||||
|
||||
### Quotes
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep quote style consistent with the existing Korean docs.
|
||||
- Never change quotes inside inline code, code blocks, URLs, or file paths.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ellipsis
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep ellipsis style consistent with existing Korean docs (often `...`).
|
||||
- Never change `...` in code, URLs, or CLI examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preferred translations / glossary
|
||||
|
||||
Use the following preferred translations when they apply in documentation prose:
|
||||
|
||||
- request (HTTP): 요청
|
||||
- response (HTTP): 응답
|
||||
- path operation: 경로 처리
|
||||
- path operation function: 경로 처리 함수
|
||||
|
||||
### `///` admonitions
|
||||
|
||||
1) Keep the admonition keyword in English (do not translate `note`, `tip`, etc.).
|
||||
2) If a title is present, prefer these canonical titles:
|
||||
|
||||
- `/// note | 참고`
|
||||
- `/// tip | 팁`
|
||||
- `/// warning | 경고`
|
||||
- `/// info | 정보`
|
||||
- `/// danger | 위험`
|
||||
- `/// note Technical Details | 기술 세부사항`
|
||||
- `/// check | 확인`
|
||||
Notes:
|
||||
|
||||
- `details` blocks exist in Korean docs; keep `/// details` as-is and translate only the title after `|`.
|
||||
- Example canonical title used: `/// details | 상세 설명`
|
||||
@@ -4,6 +4,6 @@ This page hasn’t been translated into your language yet. 🌍
|
||||
|
||||
We’re currently switching to an automated translation system 🤖, which will help keep all translations complete and up to date.
|
||||
|
||||
Learn more: [Contributing – Translations](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/contributing/#translations){.internal-link target=_blank}
|
||||
Learn more: [Contributing - Translations](https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/contributing/#translations){.internal-link target=_blank}
|
||||
|
||||
///
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI é construído em cima do **Pydantic**, e eu tenho mostrado como usar mo
|
||||
|
||||
Mas o FastAPI também suporta o uso de <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a> da mesma forma:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Isso ainda é suportado graças ao **Pydantic**, pois ele tem <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">suporte interno para `dataclasses`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ Mas se você tem um monte de dataclasses por aí, este é um truque legal para u
|
||||
|
||||
Você também pode usar `dataclasses` no parâmetro `response_model`:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
A dataclass será automaticamente convertida para uma dataclass Pydantic.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ Em alguns casos, você ainda pode ter que usar a versão do Pydantic das `datacl
|
||||
|
||||
Nesse caso, você pode simplesmente trocar as `dataclasses` padrão por `pydantic.dataclasses`, que é um substituto direto:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
1. Ainda importamos `field` das `dataclasses` padrão.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Dependendo do seu caso de uso, você pode preferir usar uma biblioteca diferente
|
||||
|
||||
Aqui está uma pequena prévia de como você poderia integrar Strawberry com FastAPI:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql_/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Você pode aprender mais sobre Strawberry na <a href="https://strawberry.rocks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">documentação do Strawberry</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,15 +14,15 @@ When translating documentation into Portuguese, use neutral and widely understan
|
||||
|
||||
For the next terms, use the following translations:
|
||||
|
||||
* «/// check»: «/// check | Verifique»
|
||||
* «/// danger»: «/// danger | Cuidado»
|
||||
* «/// info»: «/// info | Informação»
|
||||
* «/// note | Technical Details»: «/// note | Detalhes Técnicos»
|
||||
* «/// info | Very Technical Details»: «/// note | Detalhes Técnicos Avançados»
|
||||
* «/// note»: «/// note | Nota»
|
||||
* «/// tip»: «/// tip | Dica»
|
||||
* «/// warning»: «/// warning | Atenção»
|
||||
* «(you should)»: «(você deveria)»
|
||||
* /// check: /// check | Verifique
|
||||
* /// danger: /// danger | Cuidado
|
||||
* /// info: /// info | Informação
|
||||
* /// note | Technical Details: /// note | Detalhes Técnicos
|
||||
* /// info | Very Technical Details: /// note | Detalhes Técnicos Avançados
|
||||
* /// note: /// note | Nota
|
||||
* /// tip: /// tip | Dica
|
||||
* /// warning: /// warning | Atenção
|
||||
* (you should): (você deveria)
|
||||
* async context manager: gerenciador de contexto assíncrono
|
||||
* autocomplete: autocompletar
|
||||
* autocompletion: preenchimento automático
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI построен поверх **Pydantic**, и я показывал в
|
||||
|
||||
Но FastAPI также поддерживает использование <a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a> тем же способом:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001_py310.py hl[1,6:11,18:19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Это по-прежнему поддерживается благодаря **Pydantic**, так как в нём есть <a href="https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">встроенная поддержка `dataclasses`</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ FastAPI построен поверх **Pydantic**, и я показывал в
|
||||
|
||||
Вы также можете использовать `dataclasses` в параметре `response_model`:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002_py310.py hl[1,6:12,18] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Этот dataclass будет автоматически преобразован в Pydantic dataclass.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ FastAPI построен поверх **Pydantic**, и я показывал в
|
||||
|
||||
В таком случае вы можете просто заменить стандартные `dataclasses` на `pydantic.dataclasses`, которая является полностью совместимой заменой (drop-in replacement):
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003_py310.py hl[1,4,7:10,13:16,22:24,27] *}
|
||||
|
||||
1. Мы по-прежнему импортируем `field` из стандартных `dataclasses`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -35,7 +35,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Вот небольшой пример того, как можно интегрировать Strawberry с FastAPI:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/graphql_/tutorial001_py39.py hl[3,22,25] *}
|
||||
|
||||
Подробнее о Strawberry можно узнать в <a href="https://strawberry.rocks/" class="external-link" target="_blank">документации Strawberry</a>.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
52
docs/tr/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
52
docs/tr/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
### Target language
|
||||
|
||||
Translate to Turkish (Türkçe).
|
||||
|
||||
Language code: tr.
|
||||
|
||||
### Grammar and tone
|
||||
|
||||
- Use instructional Turkish, consistent with existing Turkish docs.
|
||||
- Use imperative/guide language when appropriate (e.g. “açalım”, “gidin”, “kopyalayalım”).
|
||||
|
||||
### Headings
|
||||
|
||||
- Follow existing Turkish heading style (Title Case where used; no trailing period).
|
||||
|
||||
### Quotes
|
||||
|
||||
- Alıntı stili mevcut Türkçe dokümanlarla tutarlı tutun (genellikle metin içinde ASCII tırnak işaretleri kullanılır).
|
||||
- Satır içi kod, kod blokları, URL'ler veya dosya yolları içindeki tırnak işaretlerini asla değiştirmeyin.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ellipsis
|
||||
|
||||
- Üç nokta (...) stili mevcut Türkçe dokümanlarla tutarlı tutun.
|
||||
- Kod, URL veya CLI örneklerindeki `...` ifadesini asla değiştirmeyin.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preferred translations / glossary
|
||||
|
||||
Do not translate technical terms like path, route, request, response, query, body, cookie, and header, keep them as is.
|
||||
|
||||
- Suffixing is very important, when adding Turkish suffixes to the English words, do that based on the pronunciation of the word and with an apostrophe.
|
||||
|
||||
- Suffixes also changes based on what word comes next in Turkish too, here is an example:
|
||||
|
||||
"Server'a gelen request'leri intercept... " or this could have been "request'e", "request'i" etc.
|
||||
|
||||
- Some words are tricky like "path'e" can't be used like "path'a" but it could have been "path'i" "path'leri" etc.
|
||||
|
||||
- You can use a more instructional style, that is consistent with the document, you can add the Turkish version of the term in parenthesis if it is not something very obvious, or an advanced concept, but do not over do it, do it only the first time it is mentioned, but keep the English term as the primary word.
|
||||
|
||||
### `///` admonitions
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep the admonition keyword in English (do not translate `note`, `tip`, etc.).
|
||||
- If a title is present, prefer these canonical titles:
|
||||
|
||||
- `/// note | Not`
|
||||
- `/// note | Teknik Detaylar`
|
||||
- `/// tip | İpucu`
|
||||
- `/// warning | Uyarı`
|
||||
- `/// info | Bilgi`
|
||||
- `/// check | Ek bilgi`
|
||||
|
||||
Prefer `İpucu` over `Ipucu`.
|
||||
46
docs/uk/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
46
docs/uk/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
### Target language
|
||||
|
||||
Translate to Ukrainian (українська).
|
||||
|
||||
Language code: uk.
|
||||
|
||||
### Grammar and tone
|
||||
|
||||
- Use polite/formal address consistent with existing Ukrainian docs (use “ви/ваш”).
|
||||
- Keep the tone concise and technical.
|
||||
|
||||
### Headings
|
||||
|
||||
- Follow existing Ukrainian heading style; keep headings short and instructional.
|
||||
- Do not add trailing punctuation to headings.
|
||||
|
||||
### Quotes
|
||||
|
||||
- Prefer Ukrainian guillemets «…» for quoted terms in prose, matching existing Ukrainian docs.
|
||||
- Never change quotes inside inline code, code blocks, URLs, or file paths.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ellipsis
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep ellipsis style consistent with existing Ukrainian docs.
|
||||
- Never change `...` in code, URLs, or CLI examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preferred translations / glossary
|
||||
|
||||
Use the following preferred translations when they apply in documentation prose:
|
||||
|
||||
- request (HTTP): запит
|
||||
- response (HTTP): відповідь
|
||||
- path operation: операція шляху
|
||||
- path operation function: функція операції шляху
|
||||
|
||||
### `///` admonitions
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep the admonition keyword in English (do not translate `note`, `tip`, etc.).
|
||||
- If a title is present, prefer these canonical titles (choose one canonical form where variants exist):
|
||||
|
||||
- `/// note | Примітка`
|
||||
- `/// note | Технічні деталі`
|
||||
- `/// tip | Порада`
|
||||
- `/// warning | Попередження`
|
||||
- `/// info | Інформація`
|
||||
- `/// danger | Обережно`
|
||||
60
docs/zh-hant/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
60
docs/zh-hant/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
||||
### Target language
|
||||
|
||||
Translate to Traditional Chinese (繁體中文).
|
||||
|
||||
Language code: zh-hant.
|
||||
|
||||
### Grammar and tone
|
||||
|
||||
- Use clear, concise technical Traditional Chinese consistent with existing docs.
|
||||
- Address the reader naturally (commonly using “你/你的”).
|
||||
|
||||
### Headings
|
||||
|
||||
- Follow existing Traditional Chinese heading style (short and descriptive).
|
||||
- Do not add trailing punctuation to headings.
|
||||
|
||||
### Quotes and punctuation
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep punctuation style consistent with existing Traditional Chinese docs (they often mix English terms like “FastAPI” with Chinese text).
|
||||
- Never change punctuation inside inline code, code blocks, URLs, or file paths.
|
||||
- For more details, please follow the [Chinese Copywriting Guidelines](https://github.com/sparanoid/chinese-copywriting-guidelines).
|
||||
|
||||
### Ellipsis
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep ellipsis style consistent within each document, prefer `...` over `……`.
|
||||
- Never change ellipsis in code, URLs, or CLI examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preferred translations / glossary
|
||||
|
||||
- Should avoid using simplified Chinese characters and terms. Always examine if the translation can be easily comprehended by the Traditional Chinese readers.
|
||||
- For some Python-specific terms like "pickle", "list", "dict" etc, we don't have to translate them.
|
||||
- Use the following preferred translations when they apply in documentation prose:
|
||||
|
||||
- request (HTTP): 請求
|
||||
- response (HTTP): 回應
|
||||
- path operation: 路徑操作
|
||||
- path operation function: 路徑操作函式
|
||||
|
||||
The translation can optionally include the original English text only in the first occurrence of each page (e.g. "路徑操作 (path operation)") if the translation is hard to be comprehended by most of the Chinese readers.
|
||||
|
||||
### `///` admonitions
|
||||
|
||||
1) Keep the admonition keyword in English (do not translate `note`, `tip`, etc.).
|
||||
2) Many Traditional Chinese docs currently omit titles in `///` blocks; that is OK.
|
||||
3) If a generic title is present, prefer these canonical titles:
|
||||
|
||||
- `/// note | 注意`
|
||||
|
||||
Notes:
|
||||
|
||||
- `details` blocks exist; keep `/// details` as-is and translate only the title after `|`.
|
||||
- Example canonical titles used in existing docs:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/// details | 上述指令的含義
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
/// details | 關於 `requirements.txt`
|
||||
```
|
||||
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ FastAPI 基于 **Pydantic** 构建,前文已经介绍过如何使用 Pydantic
|
||||
|
||||
但 FastAPI 还可以使用数据类(<a href="https://docs.python.org/3/library/dataclasses.html" class="external-link" target="_blank">`dataclasses`</a>):
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial001.py hl[1,7:12,19:20] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial001.py hl[1,7:12,19:20] *}
|
||||
|
||||
这还是借助于 **Pydantic** 及其<a href="https://pydantic-docs.helpmanual.io/usage/dataclasses/#use-of-stdlib-dataclasses-with-basemodel" class="external-link" target="_blank">内置的 `dataclasses`</a>。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ FastAPI 基于 **Pydantic** 构建,前文已经介绍过如何使用 Pydantic
|
||||
|
||||
在 `response_model` 参数中使用 `dataclasses`:
|
||||
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial002.py hl[1,7:13,19] *}
|
||||
{* ../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial002.py hl[1,7:13,19] *}
|
||||
|
||||
本例把数据类自动转换为 Pydantic 数据类。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ API 文档中也会显示相关概图:
|
||||
本例把标准的 `dataclasses` 直接替换为 `pydantic.dataclasses`:
|
||||
|
||||
```{ .python .annotate hl_lines="1 5 8-11 14-17 23-25 28" }
|
||||
{!../../docs_src/dataclasses/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
{!../../docs_src/dataclasses_/tutorial003.py!}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. 本例依然要从标准的 `dataclasses` 中导入 `field`;
|
||||
|
||||
46
docs/zh/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
46
docs/zh/llm-prompt.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
### Target language
|
||||
|
||||
Translate to Simplified Chinese (简体中文).
|
||||
|
||||
Language code: zh.
|
||||
|
||||
### Grammar and tone
|
||||
|
||||
- Use clear, concise technical Chinese consistent with existing docs.
|
||||
- Address the reader naturally (commonly using “你/你的”).
|
||||
|
||||
### Headings
|
||||
|
||||
- Follow existing Simplified Chinese heading style (short and descriptive).
|
||||
- Do not add trailing punctuation to headings.
|
||||
- If a heading contains only the name of a FastAPI feature, do not translate it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Quotes and punctuation
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep punctuation style consistent with existing Simplified Chinese docs (they often mix English terms like “FastAPI” with Chinese text).
|
||||
- Never change punctuation inside inline code, code blocks, URLs, or file paths.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ellipsis
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep ellipsis style consistent within each document, prefer `...` over `……`.
|
||||
- Never change ellipsis in code, URLs, or CLI examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preferred translations / glossary
|
||||
|
||||
Use the following preferred translations when they apply in documentation prose:
|
||||
|
||||
- request (HTTP): 请求
|
||||
- response (HTTP): 响应
|
||||
- path operation: 路径操作
|
||||
- path operation function: 路径操作函数
|
||||
|
||||
### `///` admonitions
|
||||
|
||||
- Keep the admonition keyword in English (do not translate `note`, `tip`, etc.).
|
||||
- If a title is present, prefer these canonical titles:
|
||||
|
||||
- `/// tip | 提示`
|
||||
- `/// note | 注意`
|
||||
- `/// warning | 警告`
|
||||
- `/// info | 信息`
|
||||
- `/// danger | 危险`
|
||||
0
docs_src/background_tasks/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/background_tasks/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/behind_a_proxy/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/behind_a_proxy/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body/__init__.py
Normal file
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
@app.post("/items/")
|
||||
async def create_item(item: Item):
|
||||
item_dict = item.dict()
|
||||
item_dict = item.model_dump()
|
||||
if item.tax is not None:
|
||||
price_with_tax = item.price + item.tax
|
||||
item_dict.update({"price_with_tax": price_with_tax})
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
@app.post("/items/")
|
||||
async def create_item(item: Item):
|
||||
item_dict = item.dict()
|
||||
item_dict = item.model_dump()
|
||||
if item.tax is not None:
|
||||
price_with_tax = item.price + item.tax
|
||||
item_dict.update({"price_with_tax": price_with_tax})
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,4 +14,4 @@ app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, **item.model_dump()}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,4 +16,4 @@ app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}
|
||||
return {"item_id": item_id, **item.model_dump()}
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item, q: str | None = None):
|
||||
result = {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}
|
||||
result = {"item_id": item_id, **item.model_dump()}
|
||||
if q:
|
||||
result.update({"q": q})
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
|
||||
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item, q: Union[str, None] = None):
|
||||
result = {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}
|
||||
result = {"item_id": item_id, **item.model_dump()}
|
||||
if q:
|
||||
result.update({"q": q})
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
0
docs_src/body_fields/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_fields/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_multiple_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_multiple_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_nested_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_nested_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_updates/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/body_updates/__init__.py
Normal file
@@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ async def read_item(item_id: str):
|
||||
async def update_item(item_id: str, item: Item):
|
||||
stored_item_data = items[item_id]
|
||||
stored_item_model = Item(**stored_item_data)
|
||||
update_data = item.dict(exclude_unset=True)
|
||||
updated_item = stored_item_model.copy(update=update_data)
|
||||
update_data = item.model_dump(exclude_unset=True)
|
||||
updated_item = stored_item_model.model_copy(update=update_data)
|
||||
items[item_id] = jsonable_encoder(updated_item)
|
||||
return updated_item
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ async def read_item(item_id: str):
|
||||
async def update_item(item_id: str, item: Item):
|
||||
stored_item_data = items[item_id]
|
||||
stored_item_model = Item(**stored_item_data)
|
||||
update_data = item.dict(exclude_unset=True)
|
||||
updated_item = stored_item_model.copy(update=update_data)
|
||||
update_data = item.model_dump(exclude_unset=True)
|
||||
updated_item = stored_item_model.model_copy(update=update_data)
|
||||
items[item_id] = jsonable_encoder(updated_item)
|
||||
return updated_item
|
||||
|
||||
0
docs_src/conditional_openapi/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/conditional_openapi/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/configure_swagger_ui/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/configure_swagger_ui/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/cookie_param_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/cookie_param_models/__init__.py
Normal file
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
||||
from typing import Annotated
|
||||
|
||||
from fastapi import Cookie, FastAPI
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Cookies(BaseModel):
|
||||
class Config:
|
||||
extra = "forbid"
|
||||
|
||||
session_id: str
|
||||
fatebook_tracker: str | None = None
|
||||
googall_tracker: str | None = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/")
|
||||
async def read_items(cookies: Annotated[Cookies, Cookie()]):
|
||||
return cookies
|
||||
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
||||
from typing import Annotated, Union
|
||||
|
||||
from fastapi import Cookie, FastAPI
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Cookies(BaseModel):
|
||||
class Config:
|
||||
extra = "forbid"
|
||||
|
||||
session_id: str
|
||||
fatebook_tracker: Union[str, None] = None
|
||||
googall_tracker: Union[str, None] = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/")
|
||||
async def read_items(cookies: Annotated[Cookies, Cookie()]):
|
||||
return cookies
|
||||
@@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
||||
from fastapi import Cookie, FastAPI
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Cookies(BaseModel):
|
||||
class Config:
|
||||
extra = "forbid"
|
||||
|
||||
session_id: str
|
||||
fatebook_tracker: str | None = None
|
||||
googall_tracker: str | None = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/")
|
||||
async def read_items(cookies: Cookies = Cookie()):
|
||||
return cookies
|
||||
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
|
||||
from typing import Union
|
||||
|
||||
from fastapi import Cookie, FastAPI
|
||||
from pydantic import BaseModel
|
||||
|
||||
app = FastAPI()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Cookies(BaseModel):
|
||||
class Config:
|
||||
extra = "forbid"
|
||||
|
||||
session_id: str
|
||||
fatebook_tracker: Union[str, None] = None
|
||||
googall_tracker: Union[str, None] = None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@app.get("/items/")
|
||||
async def read_items(cookies: Cookies = Cookie()):
|
||||
return cookies
|
||||
0
docs_src/cookie_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/cookie_params/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/cors/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/cors/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_docs_ui/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_docs_ui/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_request_and_route/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_request_and_route/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_response/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/custom_response/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dataclasses_/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dataclasses_/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/debugging/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/debugging/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dependencies/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dependencies/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dependency_testing/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/dependency_testing/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/encoder/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/encoder/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/events/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/events/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extending_openapi/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extending_openapi/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extra_data_types/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extra_data_types/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extra_models/__init__.py
Normal file
0
docs_src/extra_models/__init__.py
Normal file
@@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ def fake_password_hasher(raw_password: str):
|
||||
|
||||
def fake_save_user(user_in: UserIn):
|
||||
hashed_password = fake_password_hasher(user_in.password)
|
||||
user_in_db = UserInDB(**user_in.dict(), hashed_password=hashed_password)
|
||||
user_in_db = UserInDB(**user_in.model_dump(), hashed_password=hashed_password)
|
||||
print("User saved! ..not really")
|
||||
return user_in_db
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user